Overview
The article titled "10 Green Land Zoning Techniques for Sustainable Development" addresses the pressing challenge of sustainability in land use and urban planning. It outlines various strategies, including:
- Mixed-use zoning
- Green infrastructure
- Performance-based zoning
These techniques are not merely theoretical; they have been shown to enhance community engagement, promote environmental protection, and support economic viability. By implementing these approaches, urban areas can effectively address the urgent need for sustainable development.
Introduction
In an era where sustainable development is paramount, the intersection of land use and environmental stewardship has never been more critical. This comprehensive exploration delves into the multifaceted approaches shaping land services, from the innovative techniques employed by companies like Harbinger Land to the pivotal role of BREEAM certification in enhancing project marketability.
As communities strive for resilience, value capture techniques and smart growth principles emerge as essential strategies for fostering vibrant urban environments. The integration of green infrastructure and mixed-use zoning not only promotes ecological balance but also enriches community life.
Through effective stakeholder engagement and adaptive reuse, municipalities are reimagining their landscapes, ensuring that development aligns with both sustainability goals and the needs of their residents. This article unveils the dynamic landscape of zoning practices that prioritize environmental protection while paving the way for future growth.
Harbinger Land | Comprehensive Solutions for Land Services in Energy and Infrastructure
Harbinger Land stands out in providing specialized land services for energy and infrastructure projects across the United States. The complexities of land acquisition, including legal and regulatory challenges, can be daunting. However, Harbinger Land's extensive offerings—spanning site and right-of-way acquisition, advanced title research, GIS mapping, and document imaging solutions—address these challenges head-on.
By leveraging cutting-edge technology, such as AI-powered title research software and integrated GIS modeling services, Harbinger Land significantly enhances operational efficiency and elevates client satisfaction. Have you considered how technology could streamline your land acquisition process? The company's experienced team is adept at swiftly mobilizing large groups to meet diverse project requirements, ensuring timely and precise services tailored to the needs of clients, including natural gas companies, solar developers, and municipalities.
As the demand for sustainable land use continues to grow, Harbinger Land remains at the forefront of green land zoning techniques in the industry. They adeptly adapt to emerging trends and ensure compliance with evolving regulations in land disposal practices. The time to act is now—partner with Harbinger Land to navigate the complexities of land acquisition and secure the success of your projects.
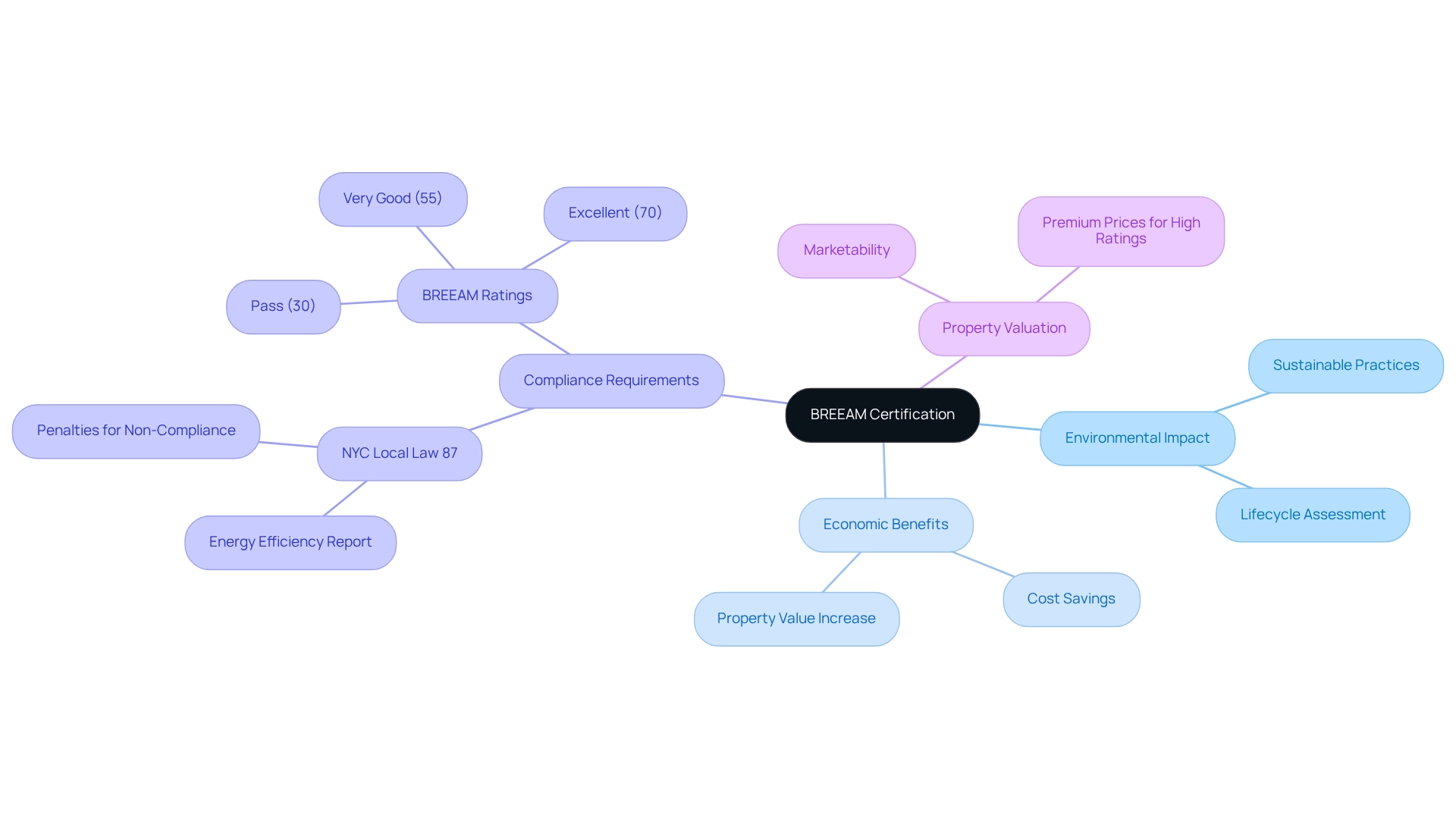
BREEAM Certification: Setting Standards for Sustainable Land Development
BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method) is a leading sustainability assessment framework for master planning, infrastructure, and buildings. It plays a pivotal role in recognizing and enhancing the value of high-performing assets throughout their lifecycle, from new construction to refurbishment and ongoing use. By promoting sustainable practices, BREEAM certification not only aids developers in minimizing environmental impacts but also maximizes social and economic benefits. This certification is increasingly vital for developers looking to enhance project marketability and meet the growing regulatory demands for sustainability.
As we approach 2025, the number of BREEAM-certified projects in the U.S. continues to rise, reflecting a broader commitment to sustainable progress. Compliance with BREEAM standards mitigates the risk of fines and leads to long-term savings, making it an attractive option for property owners. For example, under NYC Local Law 87, buildings exceeding 50,000 square feet must submit an Energy Efficiency Report every decade, which includes an Energy Audit and Retro-Commissioning Report. Non-compliance can result in escalating penalties, prompting proactive measures from building owners to align with sustainability standards. This underscores the importance of BREEAM compliance in avoiding penalties while achieving cost savings.
Moreover, BREEAM certification positively influences property values, with studies indicating that properties with higher BREEAM ratings command premium prices. As Matt Morley, a BREEAM Associate, states, "The primary objective of BREEAM In-Use is to identify areas for sustainability improvements during the operational phase of existing buildings." This focus on continuous enhancement highlights BREEAM's role in elevating project marketability and ensuring compliance with evolving sustainability regulations. Notably, BREEAM ratings are categorized as Pass, Very Good, and Excellent, providing developers with clear benchmarks for sustainability performance. Additionally, BREEAM and LEED share common goals of promoting sustainability in the built environment, further emphasizing the relevance of BREEAM within the broader sustainability framework.
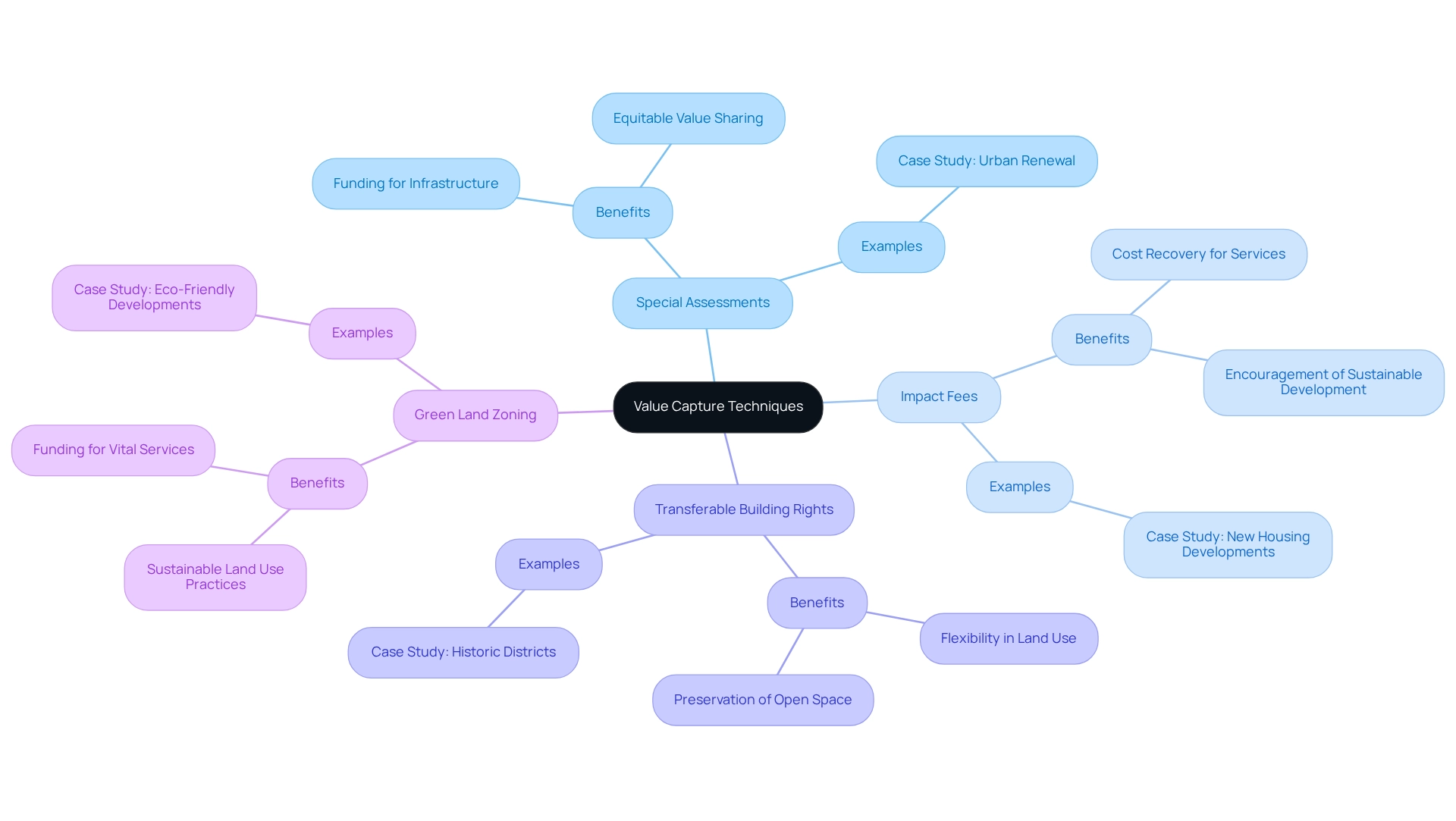
Value Capture Techniques: Leveraging Land Use Regulations for Sustainability
Value capture techniques serve as essential strategies that empower municipalities to reclaim a portion of the increased land value generated by public investments in infrastructure and services. These methods encompass a variety of tools, including special assessments, impact fees, and transferable building rights. By effectively implementing green land zoning techniques, municipalities can secure funding for vital services and infrastructure improvements while also promoting sustainable land use practices. This approach not only enhances the financial sustainability of projects but also ensures that the benefits of growth are equitably shared among all stakeholders.
Recent studies reveal that municipalities employing value capture strategies have successfully funded infrastructure projects, demonstrating a significant increase in land value as a direct outcome of public investment. For example, innovative experiments with land value capture on Western state trust lands have yielded promising results, indicating that these mechanisms can foster more sustainable and financially viable land management practices. As city planners and policymakers delve deeper into green land zoning techniques, the potential for improved community development and environmental sustainability becomes increasingly evident.
How can your municipality leverage value capture techniques to enhance local infrastructure? The time to act is now; the benefits of these strategies are clear and compelling.
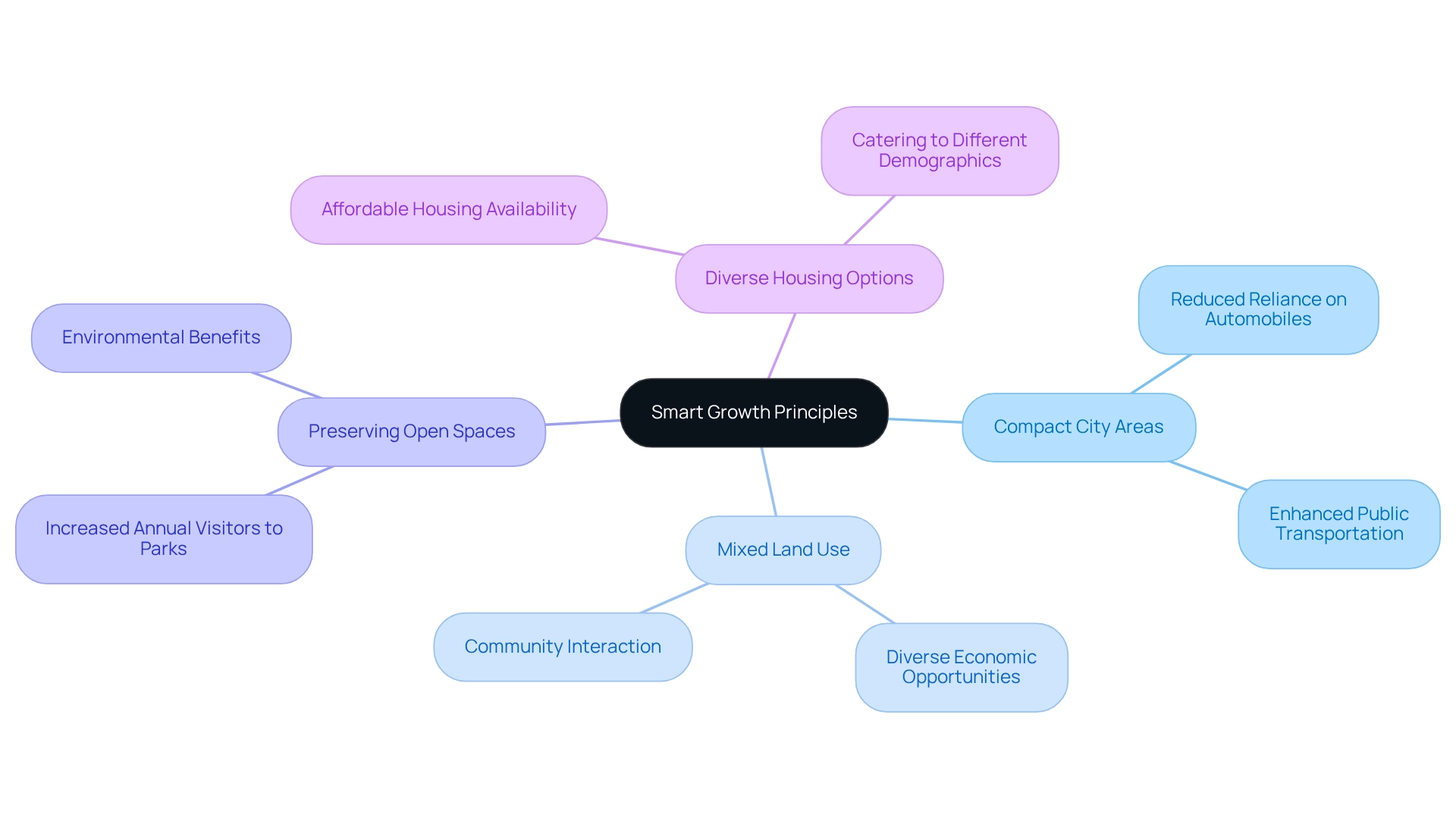
Smart Growth Principles: Zoning for Sustainable Urban Development
Smart growth principles advocate for compact, walkable city areas that reduce reliance on automobiles and promote public transportation. These principles are not merely theoretical; they encompass key strategies such as mixed land use, preserving open spaces, and creating diverse housing options. By implementing smart growth principles, cities can significantly enhance their sustainability, mitigate environmental impacts, and improve the quality of life for residents.
Consider the stark reality: over half of the global population is projected to reside in slum regions and engage in the informal economy. This underscores the critical importance of smart growth principles in city planning. Green land zoning techniques that embody these principles can effectively control sprawl and foster lively, interconnected communities. Moreover, the remarkable increase in annual visitors to National Parks and National Forests—from just over 3 million to nearly 15.5 million in 1939—highlights the benefits of preserving open spaces. As urban areas continue to develop, the integration of smart growth strategies becomes essential in shaping sustainable and resilient metropolitan environments.
Ayn Rand once remarked, 'I would trade the most magnificent sunset in the world for a glimpse of New York’s skyline,' emphasizing the aesthetic and cultural significance of thoughtfully designed city spaces. Recent updates regarding the judge halting the DOT measure against New York's congestion pricing further indicate ongoing discussions about city transportation policies that align with smart growth principles. This evolving dialogue is pivotal in addressing the challenges cities face today.
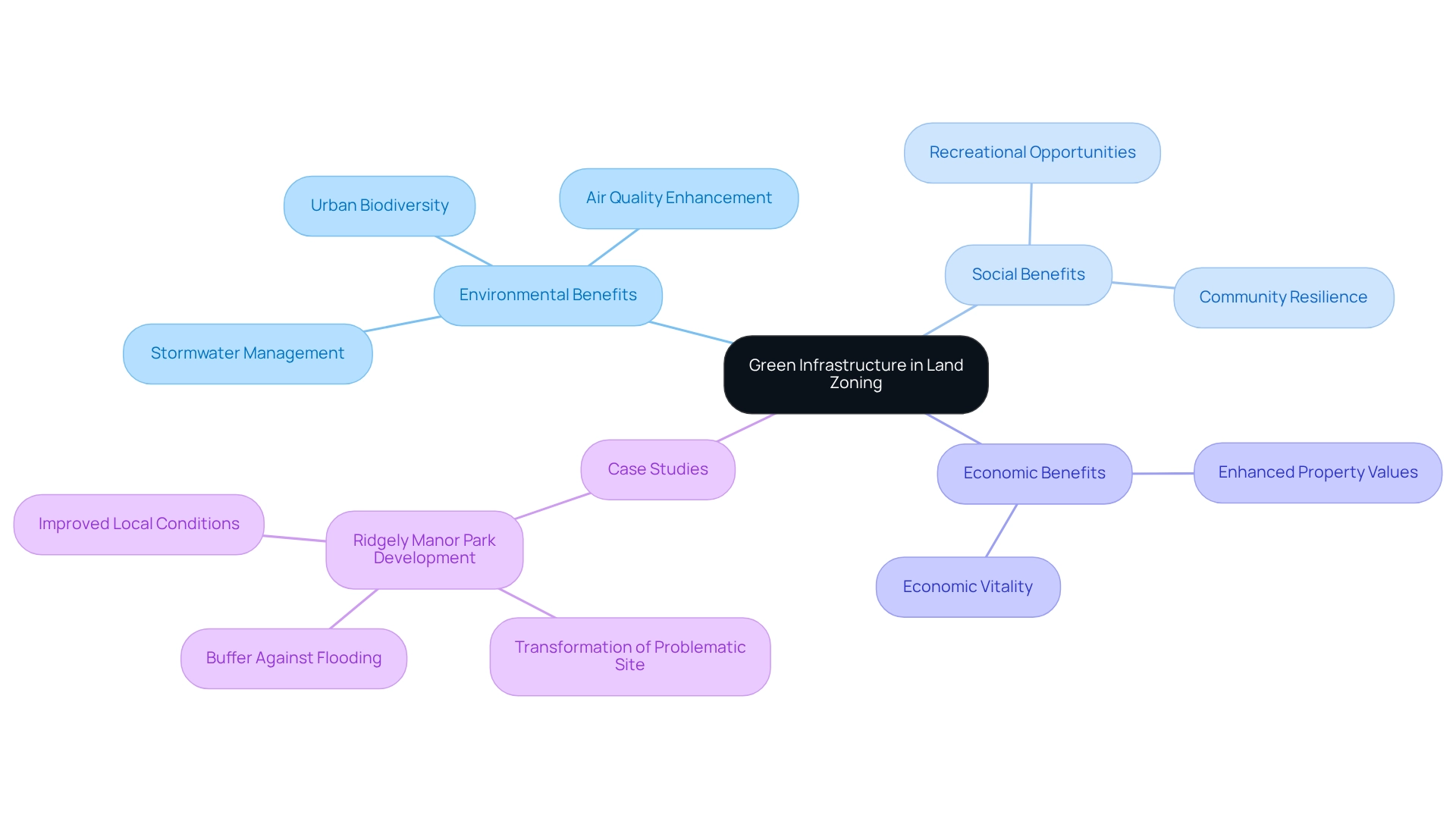
Green Infrastructure: Integrating Nature into Land Zoning Practices
Green infrastructure represents a vital network of natural and semi-natural features that deliver substantial environmental, social, and economic benefits. This includes elements such as parks, green roofs, and permeable pavements, which effectively manage stormwater, enhance air quality, and promote urban biodiversity. By incorporating green land zoning techniques into land zoning practices, municipalities can foster resilient environments that adapt to climate change while also providing valuable recreational areas for residents.
Take, for example, the Ridgely Manor Park Development, which transformed a site plagued by environmental issues into a thriving community asset. This initiative significantly improved local conditions and created recreational opportunities that serve as a buffer against flooding. Such cases exemplify how the thoughtful integration of green spaces can elevate the quality of life for residents.
Moreover, municipalities are increasingly recognizing the advantages of green infrastructure in urban planning. Research indicates that properties situated near green spaces often experience enhanced values, contributing to economic vitality. Efficient land use regulations that incorporate green land zoning techniques can facilitate the integration of these natural systems, ensuring that metropolitan areas not only meet the needs of their residents but also enhance the overall environment.
As Klaus Philipsen, President of NeighborSpace, underscores, maintaining transparency throughout these processes is crucial for establishing clear expectations among municipalities, non-profit partners, and developers alike.
Statistics reveal that initiatives like NeighborSpace's work with land trust concepts can be applied to spaces as small as 0.15 acres, demonstrating that even minor green interventions can yield significant benefits. This underscores the potential for small-scale projects to play a critical role in urban land conservation efforts. As urban areas continue to evolve, the effective incorporation of green land zoning techniques into land use practices will be essential for sustainable societal advancement, particularly in enhancing property values and promoting economic resilience.
Mixed-Use Zoning: Promoting Sustainability through Diverse Land Use
Mixed-use planning effectively combines various land uses within a single project, fostering a vibrant community environment. By integrating residential, commercial, and recreational spaces, these developments encourage walking and cycling, thereby significantly reducing reliance on automobiles. This zoning strategy not only enhances neighborhood livability but also strengthens local economies by providing a variety of services and amenities in close proximity.
For example, the Riverwalk San Diego project exemplifies this approach, featuring:
- 4,300 residential units
- Over 150,000 square feet of retail space
- 1 million square feet of office space
All designed to cultivate a sustainable environment. As developer Hines stated, "With plans for diverse housing options, a retail center, office spaces, improved infrastructure, and a new transit stop, Riverwalk San Diego aims to create a vibrant and sustainable community in Mission Valley."
Furthermore, mixed-use projects have been shown to attract a diverse tenant mix, including families, entrepreneurs, and professionals, which enhances innovation and economic competitiveness. This aligns with the case study titled "Greater Cultural and Intellectual Diversity," emphasizing how mixed-use projects draw a varied tenant mix that fosters innovation and economic growth.
Consequently, successful mixed-use projects contribute to more sustainable urban environments that effectively meet the needs of all residents. Forecasts indicate that 27 million Americans will be motivated to engage in increased physical activity by 2027, underscoring the health benefits of such advancements and the importance of integrating mixed-use planning into future initiatives.
Community Engagement: Involving Stakeholders in Sustainable Zoning Decisions
Effective public engagement is crucial for involving residents and stakeholders in the zoning decision-making process. This engagement can manifest through public meetings, surveys, and workshops, allowing local members to express their opinions and preferences. For instance, Jalisco's public involvement strategy successfully engaged over 45,000 residents, showcasing the potential for large-scale participation.
By fostering inclusive discussions, municipalities can align land use regulations with local values and priorities by implementing green land zoning techniques. This approach not only enhances the legitimacy of land use decisions but also cultivates a sense of ownership and accountability among residents. The ongoing commitment to public involvement, as evidenced by Merriam's investments in health, infrastructure, and public safety, is anticipated to improve overall quality of life and support sustainable outcomes.
Furthermore, the 2024 State of Community Engagement Report highlights emerging trends and adaptations in stakeholder participation, underscoring the importance of these practices in forming effective planning strategies. Involving stakeholders in sustainable land-use planning and employing green land zoning techniques not only leads to improved decision-making but also positively influences land-use outcomes, emphasizing the significance of public participation in these critical processes.
As Anna Broberg noted, encouraging children's independent mobility and active transportation is essential for developing vibrant neighborhoods, further stressing the necessity for comprehensive local engagement strategies. Additionally, integrating best practices from entities such as Maptionnaire can enhance digital community engagement initiatives, ensuring that all perspectives are considered in the planning process.
Zoning Overlays: Prioritizing Environmental Protection in Land Use
Green land zoning techniques represent essential regulatory instruments that introduce specific governance layers within zoning districts, targeting critical environmental issues. These overlays, particularly environmental protection overlays, impose necessary restrictions on construction in sensitive habitats or flood-prone areas, thus preserving vital natural resources. The effective implementation of green land zoning techniques enables municipalities to strike a balance between growth demands and the imperative of environmental conservation. This strategy not only fosters sustainable land use practices but also incorporates green land zoning techniques to protect ecosystems while facilitating responsible development.
Recent updates in 2025 have prompted municipalities to adopt innovative land-use regulations that prioritize environmental protection, reflecting an increasing commitment to sustainable objectives (SDGs). Statistics indicate that climate change poses one of the most significant long-term threats to investments, underscoring the importance of land use overlays in mitigating these risks. Regions that implement green land zoning techniques demonstrate a marked reduction in habitat degradation, emphasizing their role in promoting a harmonious relationship between development and conservation.
Experts assert that these techniques are vital for addressing the urgent challenges posed by climate change, empowering communities to make informed decisions that benefit both the environment and local economies. As Sylvia Earle poignantly stated, 'Far and away, the greatest threat to the ocean, and thus to ourselves, is ignorance. But we can do something about that.' This highlights the critical nature of informed decision-making in land use and environmental protection. Furthermore, as John Steinbeck wisely noted, 'People don't take trips, trips take people,' reminding us that meticulous planning is essential in shaping our societies and their futures.
Performance-Based Zoning: Flexibility with Sustainability Goals
Performance-based land use planning prioritizes development outcomes over specific land uses, enabling municipalities to establish performance standards that align with sustainability goals. This innovative approach facilitates the integration of energy efficiency, stormwater management, and community impact into the planning process. By granting developers the freedom to meet these standards through diverse methods, performance-based zoning fosters creativity and adaptability in land use.
For instance, Fremont, California, successfully implemented this strategy in a 900-acre project, allowing for flexibility while achieving objectives such as job creation and affordable housing. Consequently, this approach not only encourages sustainable practices suited to the distinct characteristics of each project but also reflects a broader trend towards more cohesive urban planning.
Recent statistics reveal a rising acceptance of performance-oriented land-use planning throughout the United States, with over 45 projects crafted by specialists in the field. This highlights its capacity to promote ecological sustainability and improve societal resilience. As Lachlan McClure noted, planners respond to problematic conditions by engaging alternative authorities and establishing regional coordination forums. This further emphasizes the adaptability of performance-based zoning in addressing contemporary challenges.
Adaptive Reuse: Zoning for Sustainability through Repurposing Existing Structures
Adaptive reuse stands as a strategic necessity in today's urban landscape, where repurposing existing buildings not only extends their lifespan but also mitigates the demand for new construction. This practice preserves invaluable resources while safeguarding the cultural and historical significance of our built environment.
Recent studies reveal that adaptive reuse can achieve a remarkable 21% reduction in eutrophication potential, underscoring its substantial environmental benefits in fostering sustainability. The implementation of green land zoning techniques that promote adaptive reuse is essential for transforming underutilized properties into vibrant spaces that meet contemporary needs.
By prioritizing such initiatives, municipalities can enhance sustainability, minimize waste, and enrich the character of their communities. Furthermore, continuous evaluation of adaptive reuse projects is critical to ensuring their long-term viability and effectiveness, as highlighted in recent research.
Insights from practitioners in UNESCO cities shed light on the challenges and opportunities inherent in green adaptive reuse, emphasizing the role of green land zoning techniques in sustainable urban growth. As articulated by the city of Zabrze, 'The project aims to enhance city space competitiveness through the development of scientific, educational, social, and economic functions.'
This integration of adaptive reuse strategies is vital for promoting resource conservation and revitalizing urban landscapes.
Conclusion
The exploration of sustainable land use practices reveals a transformative landscape where innovative strategies are reshaping urban environments. Harbinger Land’s commitment to tailored land services underscores the necessity of integrating advanced technology and adaptive approaches to meet the escalating demands for sustainability in energy and infrastructure projects. Coupled with BREEAM certification, these practices not only enhance project marketability but also align development with rigorous sustainability standards, ensuring long-term benefits for both the environment and communities.
Value capture techniques and smart growth principles further illustrate the potential for municipalities to leverage land use regulations that promote equitable growth. By fostering vibrant, mixed-use developments and engaging communities in the decision-making process, cities can cultivate a sense of ownership and responsibility among residents. This inclusive approach not only enhances the legitimacy of zoning decisions but also contributes to the overall quality of life.
Moreover, the integration of green infrastructure and adaptive reuse strategies emphasizes the critical role of environmental stewardship in urban planning. By prioritizing ecological balance and resource conservation, municipalities can create resilient spaces that adapt to climate change while preserving their cultural heritage. The successful implementation of zoning overlays and performance-based zoning exemplifies a commitment to sustainable development goals, ensuring that growth does not come at the expense of the environment.
Ultimately, the dynamic interplay of these strategies underscores a fundamental shift towards sustainable land use that prioritizes community needs and environmental protection. As urban landscapes continue to evolve, the commitment to innovative practices and collaborative engagement will be essential in shaping a resilient and sustainable future for all.
Frequently Asked Questions
What specialized services does Harbinger Land provide?
Harbinger Land offers specialized land services for energy and infrastructure projects, including site and right-of-way acquisition, advanced title research, GIS mapping, and document imaging solutions.
How does Harbinger Land address the complexities of land acquisition?
Harbinger Land addresses the complexities of land acquisition by leveraging cutting-edge technology, such as AI-powered title research software and integrated GIS modeling services, to enhance operational efficiency and client satisfaction.
Who are the typical clients of Harbinger Land?
Typical clients of Harbinger Land include natural gas companies, solar developers, and municipalities.
What is the significance of BREEAM certification?
BREEAM certification is a leading sustainability assessment framework that helps recognize and enhance the value of high-performing assets, promoting sustainable practices and maximizing social and economic benefits for developers.
How does BREEAM compliance benefit property owners?
Compliance with BREEAM standards helps mitigate the risk of fines, leads to long-term savings, and enhances project marketability, making it an attractive option for property owners.
What are the potential penalties for non-compliance with sustainability regulations?
Non-compliance with regulations, such as NYC Local Law 87, can result in escalating penalties, prompting building owners to take proactive measures to align with sustainability standards.
How does BREEAM certification influence property values?
Properties with higher BREEAM ratings tend to command premium prices, indicating that BREEAM certification positively influences property values.
What are value capture techniques and their purpose?
Value capture techniques are strategies that enable municipalities to reclaim a portion of increased land value generated by public investments in infrastructure and services, promoting sustainable land use practices and enhancing financial sustainability.
What tools are included in value capture techniques?
Tools included in value capture techniques encompass special assessments, impact fees, and transferable building rights.
What benefits have municipalities seen from employing value capture strategies?
Municipalities employing value capture strategies have successfully funded infrastructure projects, demonstrating increased land value as a direct outcome of public investment.
List of Sources
- Harbinger Land | Comprehensive Solutions for Land Services in Energy and Infrastructure
- Leveraging Technology For Efficient Land Acquisition Processes - FasterCapital (https://fastercapital.com/topics/leveraging-technology-for-efficient-land-acquisition-processes.html)
- Streamlining Land Acquisition with GIS Services: A Comprehensive Guide (https://blog.harbingerland.com/streamlining-land-acquisition-with-gis-services-a-comprehensive-guide)
- 2021 Land Market Survey Results (https://rliland.com/Voices/The-Voices-of-Land-blog/ArticleID/3/2021 Land Market Survey Results)
- BREEAM Certification: Setting Standards for Sustainable Land Development
- BREEAM Certification: Ultimate Sustainability Guide (https://proptechos.com/breeam-certification)
- A short guide to BREEAM green building standard certification — green healthy places (https://greenhealthyplaces.com/journal/breeam-green-building-certification-standard)
- Unlocking BREEAM Certification: Green Building Standards | VertPro® (https://blog.vertpro.com/understanding-breeam-certification-green-building-standards)
- Why Should You Obtain BREEAM Accreditation for Your Building Projects? | Encon Associates (https://enconassociates.com/news/breeam-accreditation-for-your-building-projects)
- Value Capture Techniques: Leveraging Land Use Regulations for Sustainability
- Land Value Capture in the United States - Lincoln Institute of Land Policy (https://lincolninst.edu/publications/policy-focus-reports/land-value-capture-in-united-states)
- Value capture ideals and practice – Development stages and the evolution of value capture policies (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0264275120312099)
- Value Capture and Land Policies - Lincoln Institute of Land Policy (https://lincolninst.edu/publications/books/value-capture-land-policies)
- Smart Growth Principles: Zoning for Sustainable Urban Development
- (https://smartcitiesdive.com/ex/sustainablecitiescollective/twenty-best-quotes-about-sustainable-cities/176241)
- 100+ of the Best Urban Planning Quotes: Cities, Community, Urbanisation & Inspiration - This Big City (https://thisbigcity.net/quotes)
- 20 Insightful and Inspiring Quotes About Sustainability (https://jerseygirlorganics.co.nz/post/20-insightful-and-inspiring-quotes-about-sustainability)
- Green Infrastructure: Integrating Nature into Land Zoning Practices
- Enhancing Livability Through Urban Land Conservation: NeighborSpace of Baltimore County, Pocket Parks, and Retrofitting URDL - The International Partnership for the Satoyama Initiative (IPSI) (https://satoyama-initiative.org/case_studies/enhancing-livability-through-urban-land-conservation-neighborspace-of-baltimore-county-pocket-parks-and-retrofitting-urdl)
- Cities Are Investing in Green Infrastructure—Should Developers Help Foot the Bill? (https://lincolninst.edu/publications/articles/2020-01-riches-resilience-cities-investing-green-infrastructure-should-developers-foot-bill)
- Mixed-Use Zoning: Promoting Sustainability through Diverse Land Use
- Exploring the World of Mixed-Use Development (https://matthews.com/thought-leadership-mixed-use-development)
- Supporting Active Living Through Mixed-Use Developments (https://planning.org/blog/9227408/supporting-active-living-through-mixed-use-developments)
- What Is Mixed Use Development And Why Is It Important? - Blog | DBF (https://digitalbluefoam.com/post/what-is-mixed-use-development)
- Community Engagement: Involving Stakeholders in Sustainable Zoning Decisions
- How to Measure Community Engagement and Its Impact with KPIs (https://maptionnaire.com/blog/measure-community-engagement-impact-with-metrics)
- Merriam Comprehensive Plan 2040 (https://merriam.org/Government/Departments/Community-Development/Moving-Merriam-Forward/2040)
- 2024 State of Community Engagement Report | PublicInput (https://publicinput.com/wp/state-of-community-engagement-report)
- Zoning Overlays: Prioritizing Environmental Protection in Land Use
- 100+ inspirational and powerful quotes on Sustainability (clustered by topic) - Twenty Now (https://twentynow.com/sustainability-initiatives/sustainability/100-inspirational-and-powerful-quotes-on-sustainability-clustered-by-topic)
- 35 Inspiring CONSERVATION & ENVIRONMENTAL Quotes (with photos) (https://morethanjustparks.com/environmental-conservation-quotes)
- Performance-Based Zoning: Flexibility with Sustainability Goals
- Performance Based Zoning → Term (https://climate.sustainability-directory.com/term/performance-based-zoning)
- Fall Speaker Series: Using the New Performance Zoning with Lane Kendig - CAROLINA PLANNING (https://planning.unc.edu/event/fall-speaker-series-lane-kendig)
- Performance-based zoning: U.S. cities starting to loosen zoning regulations (https://bdcnetwork.com/home/news/55158752/performance-based-zoning-us-cities-starting-to-loosen-zoning-regulations)
- (PDF) Performance-Based Planning: Perspectives from the United States, Australia, and New Zealand (https://researchgate.net/publication/27474528_Performance-Based_Planning_Perspectives_from_the_United_States_Australia_and_New_Zealand)
- Adaptive Reuse: Zoning for Sustainability through Repurposing Existing Structures
- (PDF) Assessing the environmental benefits of adaptive reuse in historical buildings. A case study of a life cycle assessment approach (https://researchgate.net/publication/381993940_Assessing_the_environmental_benefits_of_adaptive_reuse_in_historical_buildings_A_case_study_of_a_life_cycle_assessment_approach)
- Assessing the environmental benefits of adaptive reuse in historical buildings. A case study of a life cycle assessment approach (https://tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/27658511.2024.2375439)




