Overview
This article addresses the critical issue of noise pollution from energy hubs and outlines four effective strategies for mitigation. These strategies encompass:
- Site selection and design
- The implementation of barriers
- Technology integration
- Operational adjustments
Each approach is supported by research and real-world examples that demonstrate their effectiveness in reducing noise impact and alleviating community concerns. Furthermore, the article emphasizes the necessity of engaging stakeholders throughout the process, fostering collaboration and acceptance. This engagement is not merely beneficial; it is essential for the successful implementation of these strategies.
Introduction
Noise pollution is a significant yet often-overlooked consequence of energy production, capable of disrupting communities and adversely affecting public health. As concerns grow regarding the impact of unwanted sound from sources such as wind turbines and transportation, it becomes imperative for energy hubs to implement effective noise impact mitigation strategies.
How can energy project managers reconcile the necessity for sustainable energy production with the urgent demand for quieter environments, particularly in residential areas? This article delves into best practices and innovative approaches to tackle this challenge, ensuring that energy initiatives can coexist harmoniously with local communities.
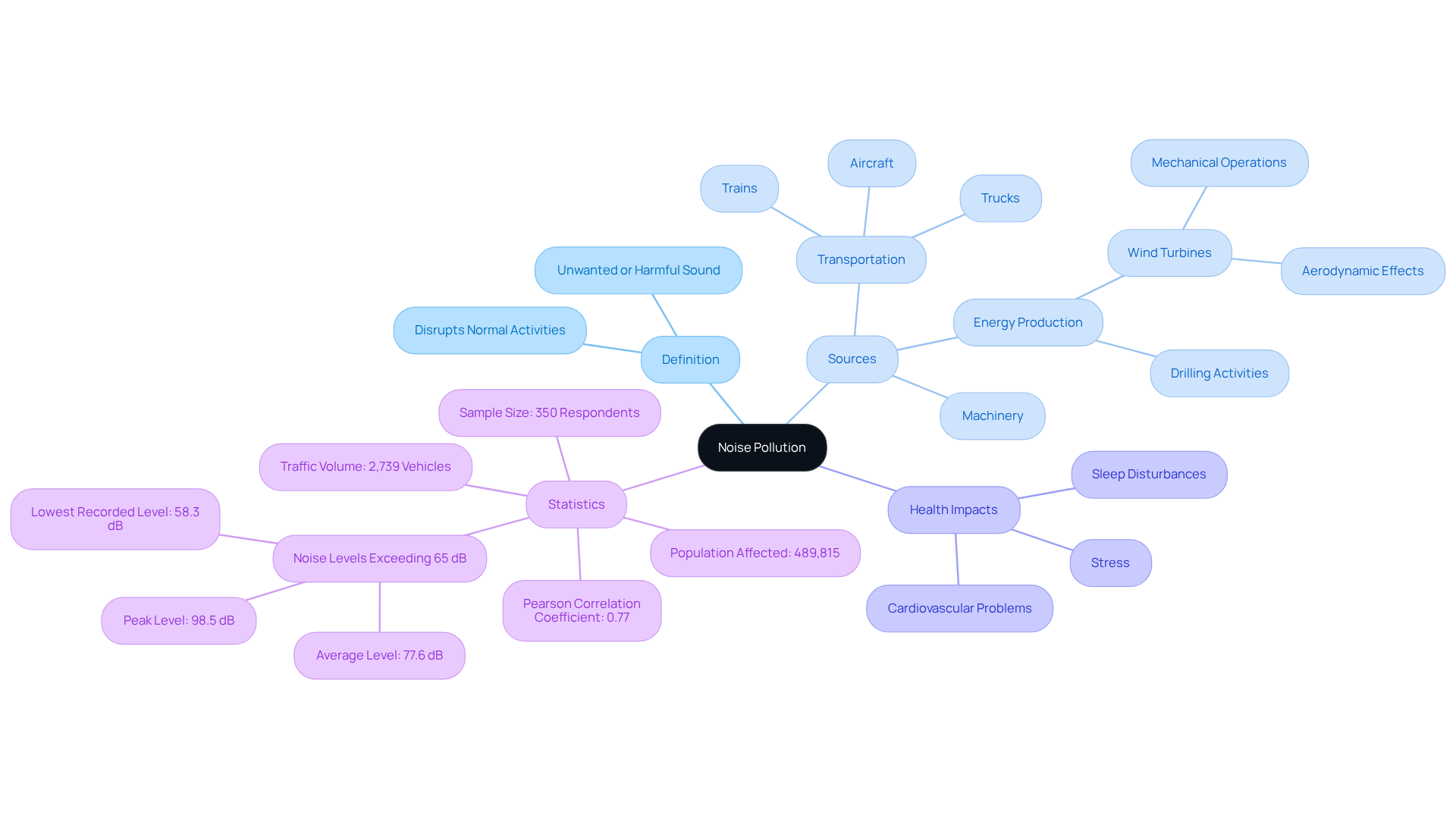
Understand Noise Pollution: Definition and Sources
Noise pollution, defined as unwanted or harmful sound that disrupts normal activities such as sleep, conversation, and recreation, highlights the need for noise impact mitigation for energy hubs. Typical sources of this sound pollution include machinery, transportation—trucks, trains, and aircraft—and operational activities linked to energy production, such as drilling and turbine operation. For instance, wind turbines produce sound from both mechanical operations and aerodynamic effects, with these noises often more pronounced in rural or residential areas. Recognizing these sources is essential for developing effective noise impact mitigation for energy hubs, which allows project managers to anticipate community concerns and address them proactively.
Research has shown that continuous exposure to sound pollution can lead to serious health issues, including stress, sleep disturbances, and cardiovascular problems. A study conducted in Matamoros, Mexico, revealed that sound levels at major intersections frequently exceed the World Health Organization's recommended limit of 65 decibels, with peak levels reaching 98.5 decibels. This underscores the importance of noise impact mitigation for energy hubs, as it is crucial to identify and address sound pollution in energy initiatives due to the risks it poses not only to the environment but also to public health. The research involved a sample size of 350 participants, reflecting the community's concerns regarding sound pollution, which affects approximately 489,815 individuals. Furthermore, a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.77 indicates a strong relationship between sound intensity and the number of vehicles, with an annual average daily traffic volume of 2,739 vehicles recorded. Recognizing these sound sources is the first step toward effectively reducing their impact.
Assess Noise Impact on Energy Hubs: Challenges and Considerations
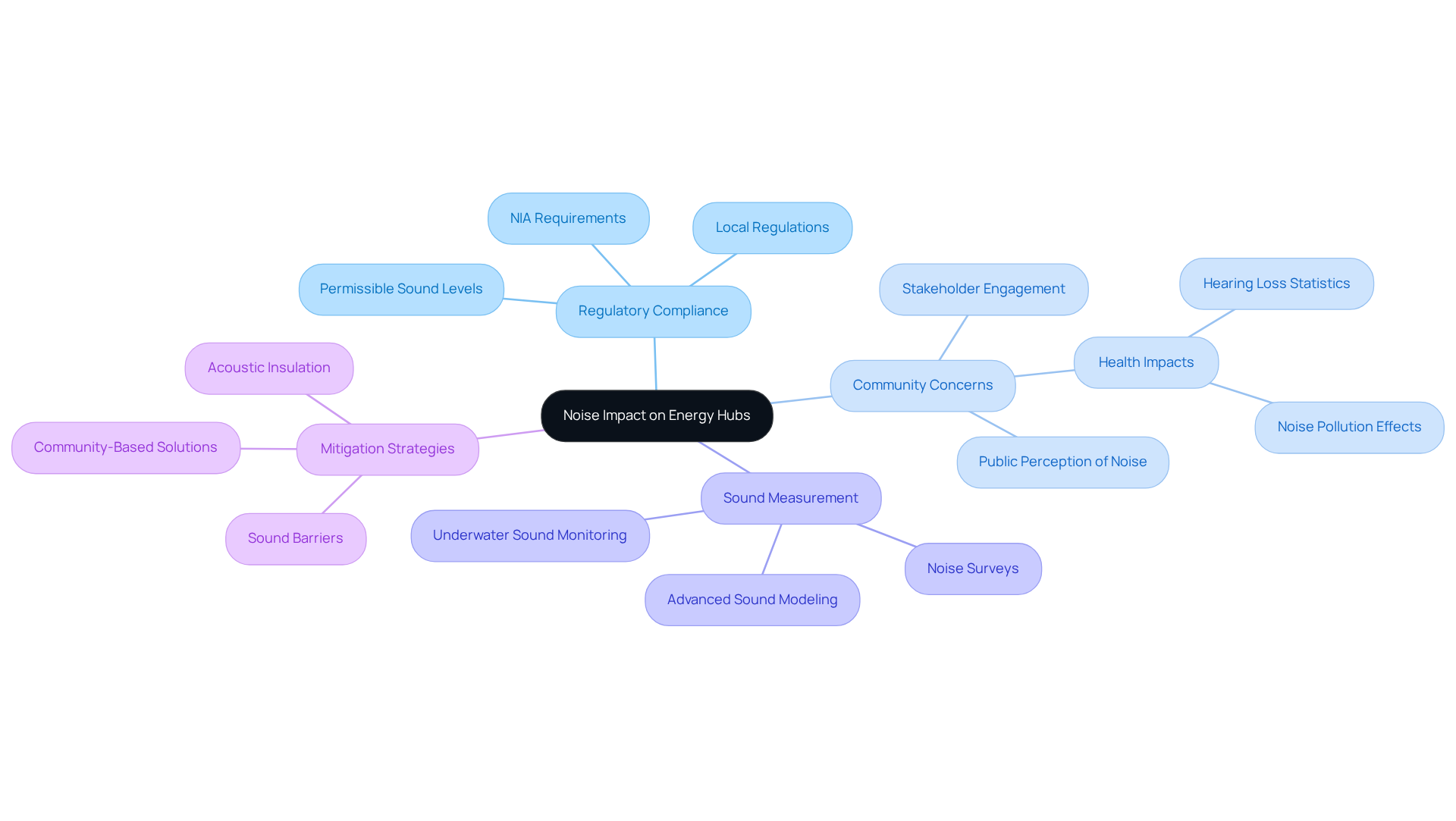
Evaluating the noise impact mitigation for energy hubs presents significant challenges, including compliance with local regulations, understanding community concerns, and accurately measuring sound intensity. Regulatory frameworks often dictate permissible sound levels, which can vary greatly depending on location and project type, particularly concerning noise impact mitigation for energy hubs. For example, wind farms may face more stringent sound regulations in residential areas compared to rural settings.
Moreover, community perceptions of sound can differ widely. Recent data indicates that approximately 30 million Americans live in areas where sound pollution exceeds safe standards, an increase of 10 million in recent years. Furthermore, 51% of urban residents express concerns about sound levels, underscoring the necessity of engaging local stakeholders early in the noise impact mitigation for energy hubs evaluation process.
Utilizing advanced sound modeling software can aid in predicting sound levels and their potential impacts on surrounding areas, thereby enabling more informed decision-making. Additionally, incorporating measures such as sound barriers and acoustic insulation is crucial for noise impact mitigation for energy hubs.
Real-world examples, such as sound assessments conducted for offshore wind projects, highlight the importance of thorough evaluations. These projects often employ underwater sound monitoring to assess impacts on marine life, emphasizing the need for comprehensive evaluations that consider all potential effects. Regulatory experts stress the significance of adhering to established sound level standards as part of noise impact mitigation for energy hubs to mitigate adverse effects on both communities and ecosystems. As the demand for energy projects continues to grow, the importance of noise impact mitigation for energy hubs through effective sound reduction strategies that align with local regulations and community expectations becomes increasingly vital.
Implement Effective Noise Mitigation Strategies: Best Practices for Energy Hubs
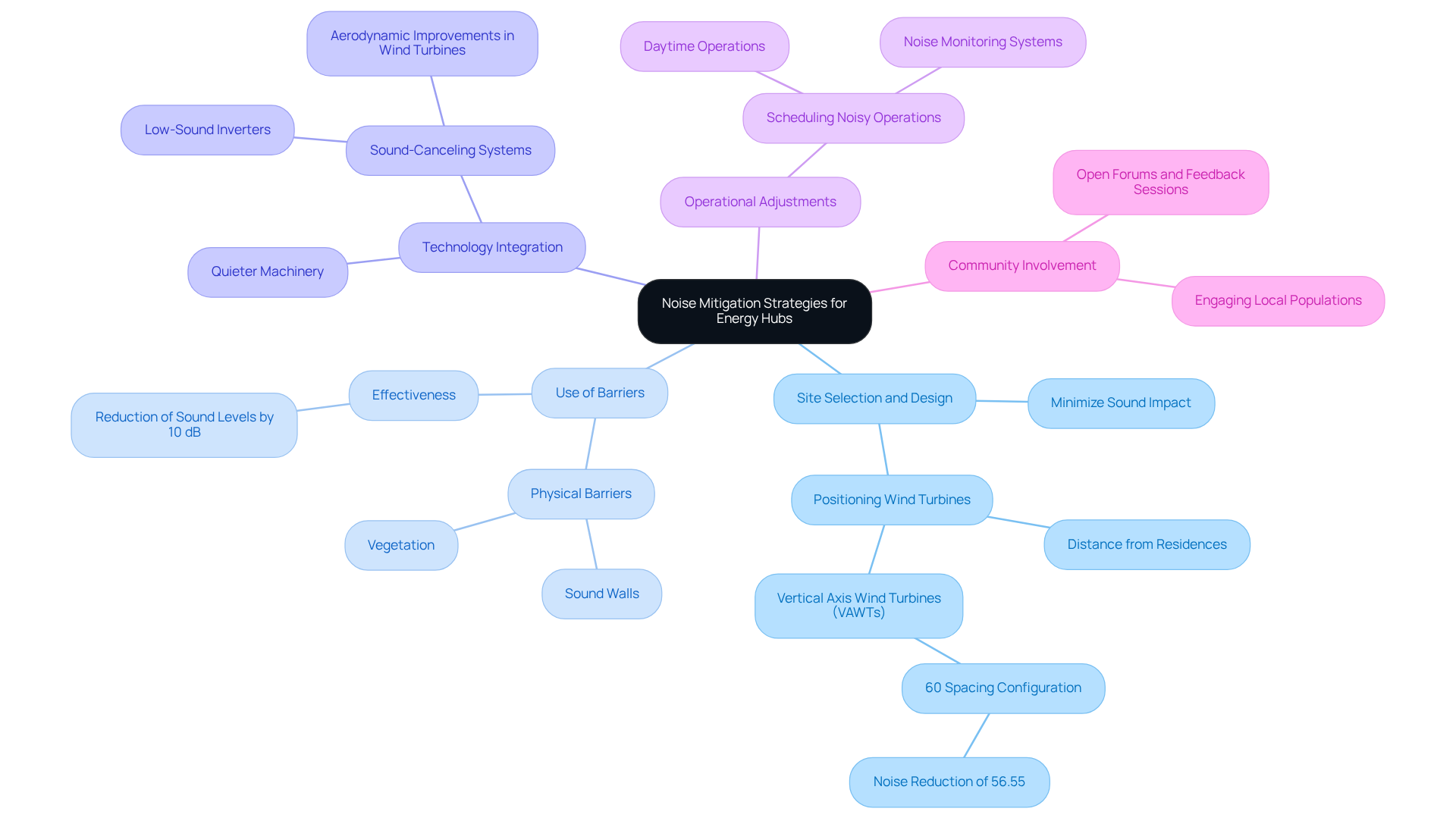
To effectively mitigate noise pollution from energy hubs, several best practices can be implemented:
-
Site Selection and Design: Choosing locations that minimize sound impact on sensitive receptors, such as residential areas, is crucial. For instance, noise impact mitigation for energy hubs can be achieved by positioning wind turbines further from residences, which can significantly reduce perceived sound levels. A case study on the innovative design of vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs) demonstrates that a 60% spacing configuration between airfoils can decrease generated sound by 56.55%, rendering them suitable for urban settings.
-
Use of Barriers: Physical barriers, including sound walls or vegetation, can effectively block sound from reaching nearby communities. Research indicates that strategically placed barriers are effective for noise impact mitigation for energy hubs, as they can reduce sound levels by as much as 10 dB, enhancing the overall auditory environment for residents.
-
Technology integration that includes advanced technologies, such as quieter machinery and sound-canceling systems, is essential for noise impact mitigation for energy hubs. For example, utilizing low-sound inverters in solar energy systems minimizes sound emissions, while innovative designs in wind turbines focus on aerodynamic improvements to reduce auditory intensity. As Vladislovas Katinas notes, 'The level of the wind turbine sound rises as wind velocity increases,' underscoring the importance of design in sound management.
-
Operational Adjustments: Scheduling noisy operations during less sensitive times (e.g., daytime rather than nighttime) can help alleviate disturbances. Furthermore, implementing noise monitoring systems contributes to noise impact mitigation for energy hubs by providing real-time data to adjust operations as necessary, ensuring compliance with local noise regulations.
-
Community Involvement: Engaging local populations in the planning process can lead to more acceptable solutions. Open forums and feedback sessions can help identify community concerns and preferences, resulting in tailored mitigation strategies that foster positive relationships between energy projects and residents.
Engage Stakeholders: Foster Collaboration for Successful Mitigation
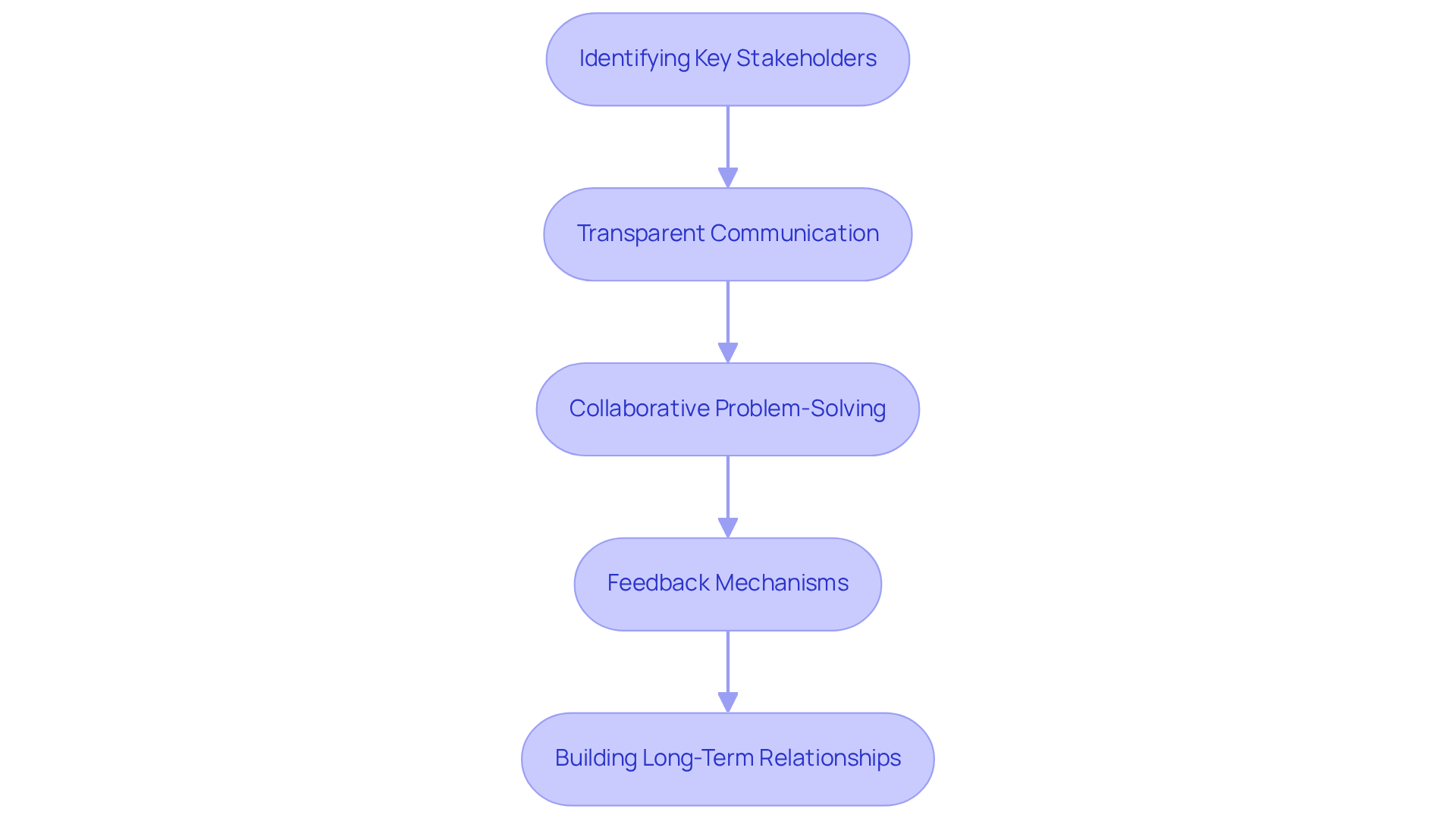
Involving stakeholders is essential for noise impact mitigation for energy hubs to effectively reduce disturbances. Successful stakeholder engagement encompasses several key strategies that can significantly enhance project outcomes.
-
Identifying Key Stakeholders: Recognizing those impacted by sound pollution, including local residents, businesses, and regulatory agencies, is the first critical step. Understanding their concerns is vital for effective engagement and for the noise impact mitigation for energy hubs, addressing the complexities of noise management.
-
Transparent Communication: Transparent communication about noise impact mitigation for energy hubs and strategies fosters trust among stakeholders. Frequent updates and transparent communication channels can greatly alleviate concerns and improve relations within the group.
-
Collaborative Problem-Solving: Engaging stakeholders in the decision-making process can yield innovative solutions that address public concerns. For instance, local workshops can serve as platforms for brainstorming mutually acceptable noise reduction strategies, thus enhancing community involvement.
-
Feedback Mechanisms: Establishing continuous feedback channels enables stakeholders to share their concerns and suggestions throughout the initiative's lifecycle. This can include surveys, public meetings, or dedicated hotlines, ensuring that local voices are heard and considered.
-
Building Long-Term Relationships: Cultivating enduring connections with stakeholders enhances acceptance and support. Involving the public even after the initiative's conclusion builds trust and creates opportunities for future partnerships.
By implementing these strategies, energy projects can achieve successful noise impact mitigation for energy hubs, ultimately benefiting both the community and project stakeholders.
Conclusion
Mitigating noise pollution stands as a pivotal concern for energy hubs, directly influencing community well-being and environmental health. Understanding the origins of noise and deploying targeted strategies enables energy projects to diminish disturbances significantly and cultivate stronger relationships with local populations.
This article delineates several essential strategies for effective noise impact mitigation:
- Thoughtful site selection
- The implementation of sound barriers
- Leveraging technological advancements
- Making operational adjustments
- Fostering active community engagement
Each of these methods is instrumental in tackling the challenges posed by noise pollution, ensuring adherence to regulations, and addressing stakeholder concerns.
Ultimately, the successful mitigation of noise pollution in energy hubs hinges on a steadfast commitment to collaboration and transparency among all stakeholders. By prioritizing community involvement and embracing best practices, energy projects can achieve a harmonious balance between energy production and the quality of life for surrounding residents, thus paving the way for sustainable development in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is noise pollution?
Noise pollution is defined as unwanted or harmful sound that disrupts normal activities such as sleep, conversation, and recreation.
What are the typical sources of noise pollution?
Typical sources of noise pollution include machinery, transportation (trucks, trains, and aircraft), and operational activities linked to energy production, such as drilling and turbine operation.
How do wind turbines contribute to noise pollution?
Wind turbines produce sound from both mechanical operations and aerodynamic effects, with these noises often being more pronounced in rural or residential areas.
Why is it important to recognize sources of noise pollution?
Recognizing sources of noise pollution is essential for developing effective noise impact mitigation strategies for energy hubs, allowing project managers to anticipate community concerns and address them proactively.
What health issues can arise from continuous exposure to noise pollution?
Continuous exposure to noise pollution can lead to serious health issues, including stress, sleep disturbances, and cardiovascular problems.
What did the study conducted in Matamoros, Mexico, reveal about noise levels?
The study revealed that sound levels at major intersections frequently exceed the World Health Organization's recommended limit of 65 decibels, with peak levels reaching 98.5 decibels.
How many individuals are affected by sound pollution according to the research?
The research indicates that sound pollution affects approximately 489,815 individuals.
What does the Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.77 indicate about noise pollution?
A Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.77 indicates a strong relationship between sound intensity and the number of vehicles.
What was the annual average daily traffic volume recorded in the study?
The annual average daily traffic volume recorded was 2,739 vehicles.
What is the first step toward effectively reducing the impact of noise pollution?
Recognizing the sources of sound pollution is the first step toward effectively reducing their impact.
List of Sources
- Understand Noise Pollution: Definition and Sources
- (PDF) Investigation & Examination of Noise Pollution - Definition, Sources, Effects, Monitoring and Control (https://researchgate.net/publication/342600987_Investigation_Examination_of_Noise_Pollution_-_Definition_Sources_Effects_Monitoring_and_Control)
- Assess Noise Impact on Energy Hubs: Challenges and Considerations
- Noise Impact Assessments | Focus 360 Energy (https://focus360energy.co.uk/noise-impact-assessments)
- 25+ Noise Pollution Statistics 2025: Environment & Oceans (https://headphonesaddict.com/noise-pollution-statistics)
- Noise Pollution on Human Health and the Environment – Planetary Health in Costa Rica (https://blogs.iu.edu/ecohealth/2020/12/13/noise-pollution-on-human-health-and-the-environment)
- Implement Effective Noise Mitigation Strategies: Best Practices for Energy Hubs
- Quieting the Wind: Noise Pollution Mitigation Strategies (https://linkedin.com/pulse/quieting-wind-noise-pollution-mitigation-strategies-un6ye)
- (PDF) Analysis of the wind turbine noise emissions and impact on the environment (https://researchgate.net/publication/290522641_Analysis_of_the_wind_turbine_noise_emissions_and_impact_on_the_environment)
- Advancements In Noise Reduction Technology - FasterCapital (https://fastercapital.com/topics/advancements-in-noise-reduction-technology.html/1)
- Wind Energy Factsheet (https://css.umich.edu/publications/factsheets/energy/wind-energy-factsheet)
- The co-benefits of electric mobility in reducing traffic noise and chemical air pollution: Insights from a transit-oriented city (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0160412023003896)
- Engage Stakeholders: Foster Collaboration for Successful Mitigation
- Stakeholder and Community Engagement (https://abergeldie.com/news-and-media/stakeholder-and-community-engagement)
- Inspiring quotes to foster collaboration and teamwork (https://hellobonsai.com/blog/collaboration-quotes)
- The Power of Community Quotes (https://ellevatenetwork.com/articles/8538-quotes-about-the-power-of-community)
- Community Engagement for an Equitable Energy Transition, with Julia Haggerty (https://resources.org/resources-radio/community-engagement-for-an-equitable-energy-transition-with-julia-haggerty)
- 100+ Inspiring Quotes About Community to Foster Connection and Unity (https://aigift.alibaba.com/quotes/quotes-about-community)




