Overview
The article emphasizes the urgent need for wildlife protection during extraction projects, outlining four key strategies:
- Minimizing habitat disturbance
- Ensuring legal compliance
- Managing resources sustainably
- Engaging local communities
These strategies are crucial in addressing the alarming rates of species extinction and habitat loss. Evidence highlights the necessity for careful planning and collaboration to mitigate the negative impacts of extraction on biodiversity. By implementing these strategies, stakeholders can significantly contribute to the preservation of vital ecosystems.
Introduction
The delicate balance between resource extraction and wildlife conservation is increasingly under scrutiny as the world grapples with the alarming decline of biodiversity. With over 1,300 species in the U.S. alone facing endangerment, the urgency for effective wildlife protection strategies during extraction projects has never been more critical.
This article delves into four essential strategies that organizations can adopt to safeguard wildlife, exploring how proactive planning, community engagement, and adaptive management can mitigate the detrimental impacts of extraction activities.
How can stakeholders collaborate to ensure that economic development does not come at the expense of our planet's precious ecosystems?
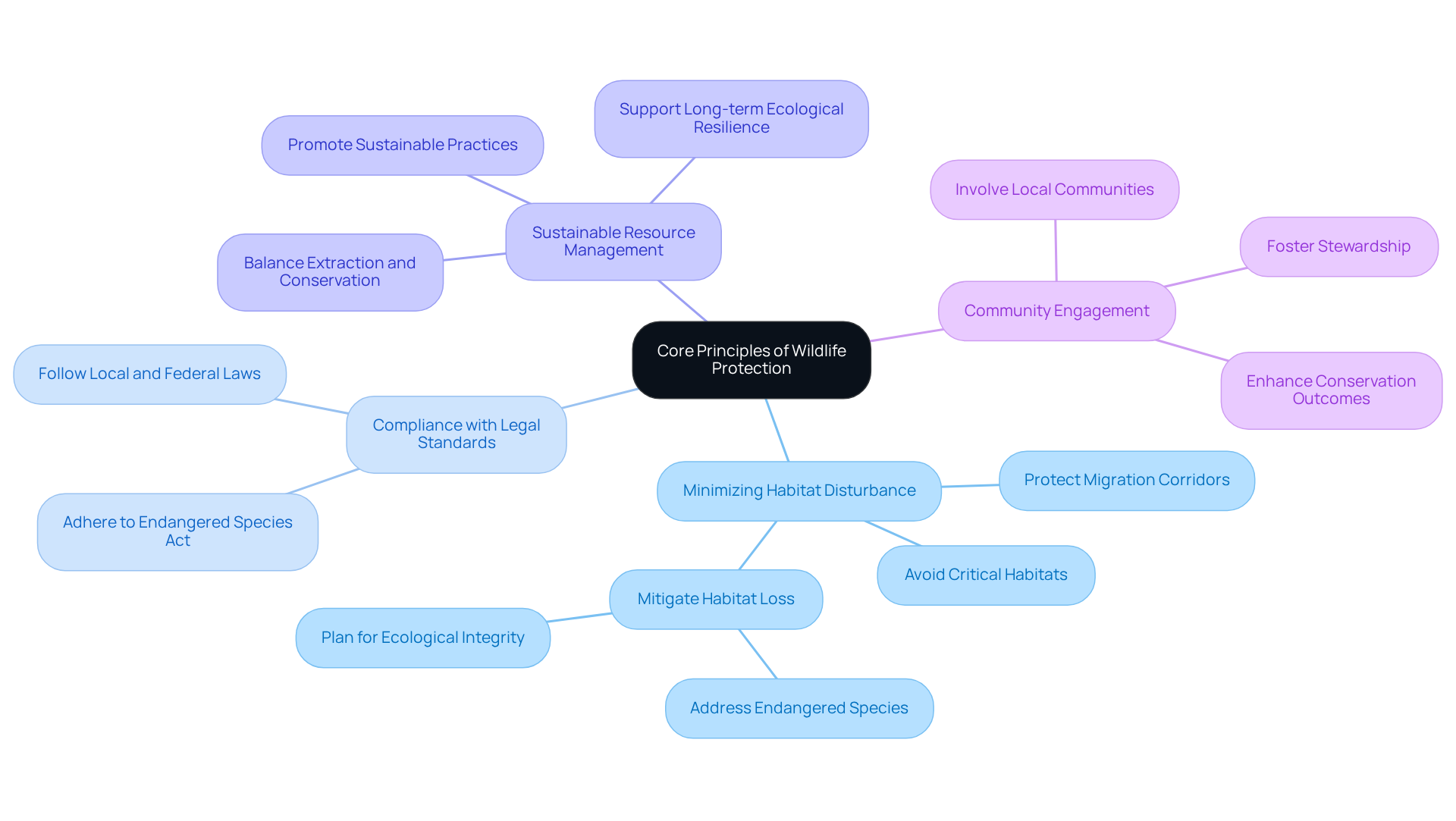
Establish Core Principles of Wildlife Protection
To effectively ensure wildlife protection during extraction initiatives, organizations must establish foundational principles that prioritize ecological integrity and biodiversity. These principles are essential for addressing the pressing challenges faced in land acquisition and ensuring wildlife protection during extraction.
-
Minimizing Habitat Disturbance: Initiatives must be designed to avoid critical habitats and migration corridors. Habitat loss remains the primary threat to animal survival in the United States. With over 1,300 U.S. animals currently endangered or threatened, and more than one-third of U.S. fish and animal species at risk of extinction in the coming decades, careful planning is crucial to mitigate impacts.
-
Compliance with Legal Standards: Organizations must adhere to local, state, and federal laws regarding animal protection, including the Endangered Species Act. This compliance is vital to ensure that initiatives do not infringe upon protected species and their habitats.
-
Sustainable Resource Management: Implementing practices that promote the sustainable use of natural resources is necessary. This approach balances extraction needs with conservation goals, emphasizing wildlife protection during extraction while also protecting biodiversity and supporting long-term ecological resilience.
-
Community Engagement: Involving local communities in decision-making processes fosters stewardship and support for nature conservation initiatives. Engaging stakeholders can enhance outcomes and cultivate a collective commitment to conservation.
By incorporating these principles into project planning, entities can create a framework that directs all elements of animal conservation throughout the project lifecycle. The alarming rate of species extinction, emphasized in the case study "Impact of Habitat Destruction in the US," underscores the urgent need for these principles. As highlighted by the Campaign for Nature, safeguarding 30 percent of Earth's land and ocean by 2030 is essential for reversing the biodiversity crisis. By prioritizing these strategies, organizations can significantly contribute to the preservation of vital ecosystems.
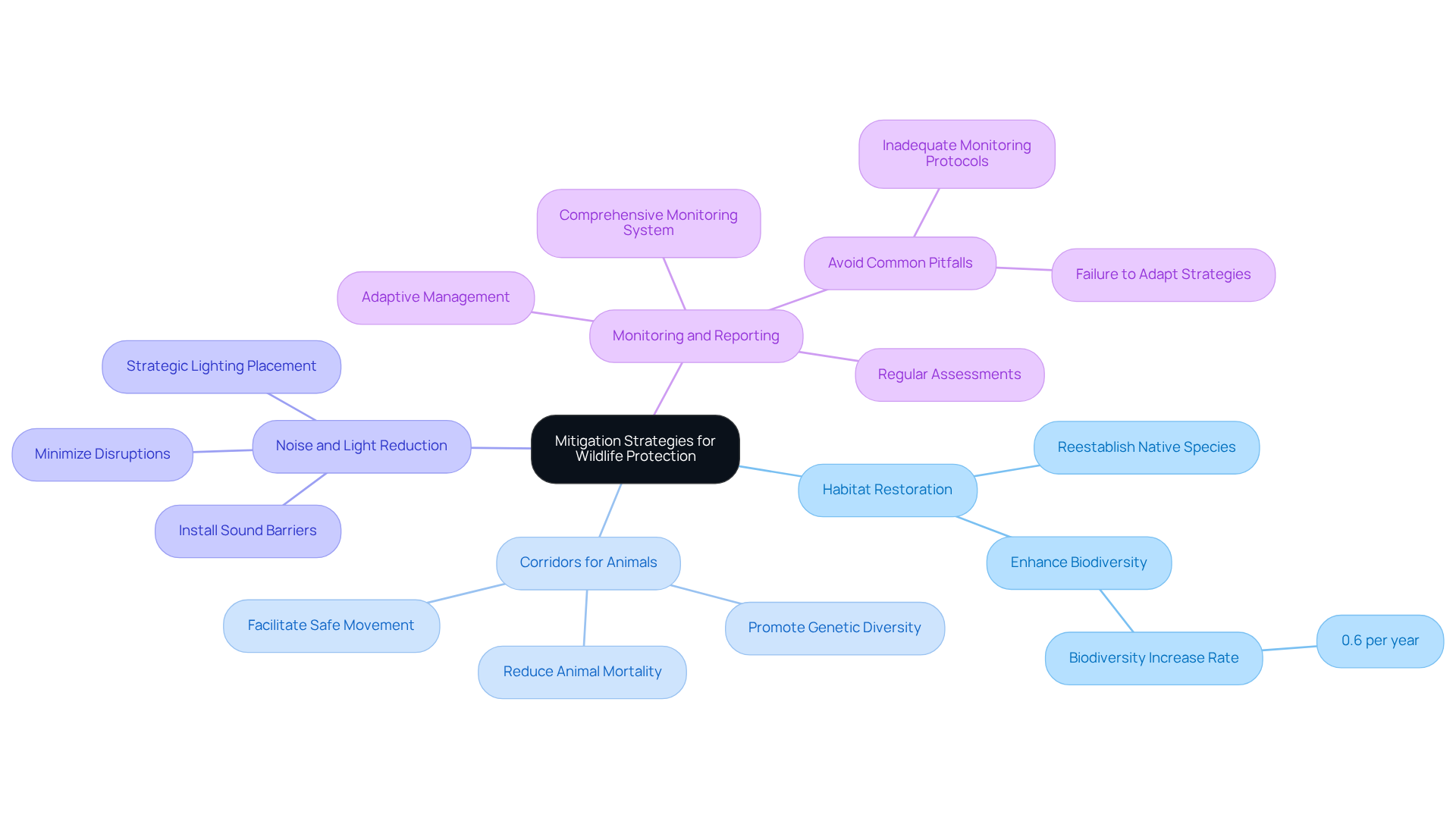
Implement Effective Mitigation Strategies
To effectively mitigate the impacts of extraction projects on wildlife, organizations must implement targeted strategies focused on wildlife protection during extraction that address specific ecological challenges.
-
Habitat Restoration: Initiating restoration projects is crucial for rehabilitating areas affected by extraction activities. The focus should be on reestablishing native species and ecosystems, thereby enhancing biodiversity and ecological resilience. Research indicates that biodiversity at restored sites can increase by approximately 0.6% per year compared to unrestored sites, highlighting the significance of these efforts.
-
Corridors for Animals: Designing and maintaining passages that facilitate safe movement for species across fragmented landscapes is essential. These corridors play a vital role in reducing animal mortality and promoting genetic diversity among populations. Successful implementations in various energy projects have demonstrated their effectiveness in maintaining animal connectivity.
-
Noise and Light Reduction: Organizations should adopt technology and design modifications to minimize noise and light pollution, which can disrupt wildlife behavior and habitat use. Strategies may include the installation of sound barriers and strategic lighting placement to mitigate disturbances. Experts from the NOAA Restoration Center emphasize that reducing these stressors is crucial for protecting sensitive species.
-
Monitoring and Reporting: Establishing a comprehensive monitoring system is necessary to evaluate the effectiveness of mitigation measures. Regular assessments enable adaptive management, ensuring that strategies remain effective in addressing the unique challenges posed by the local environment. However, organizations must be cautious of common pitfalls, such as inadequate monitoring protocols or failure to adapt strategies based on monitoring results, particularly in the context of wildlife protection during extraction.
These strategies should be tailored to the specific ecological context of each project, ensuring they effectively address the distinct challenges presented by the local environment.
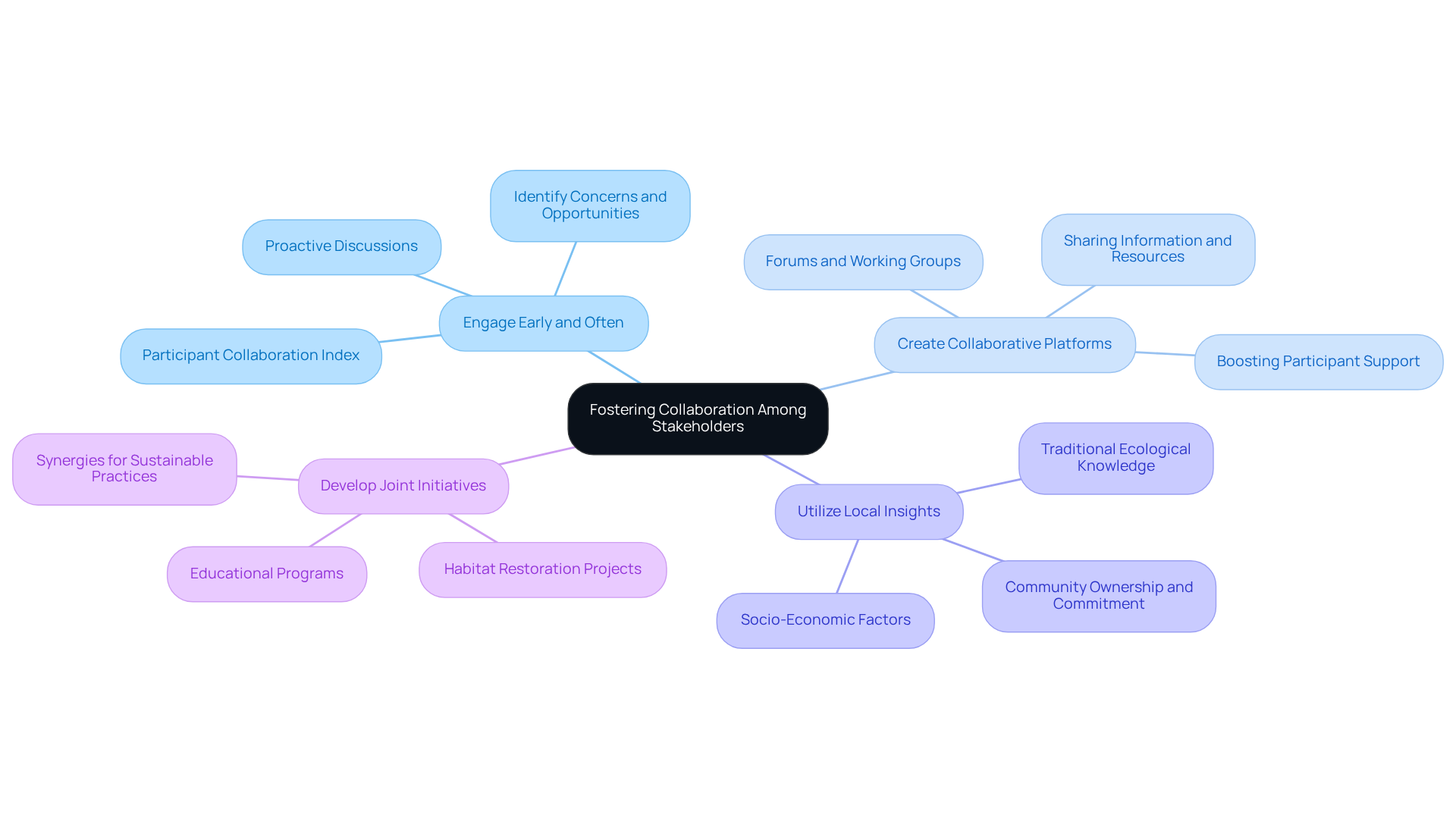
Foster Collaboration Among Stakeholders
To foster collaboration among stakeholders, organizations must implement strategic approaches that yield tangible results.
-
Engage Early and Often: It is essential to initiate discussions with involved parties during the planning phase. This proactive engagement allows for the identification of concerns and opportunities for collaboration, significantly enhancing project outcomes. The participant collaboration index, which gauges perceptions of significance in ecosystem management, underscores the effectiveness of this approach.
-
Create Collaborative Platforms: Establishing forums or working groups is vital for facilitating the sharing of information, resources, and best practices among interested parties. These platforms have proven successful in boosting participant support and collaboration, resulting in more effective conservation efforts.
-
Utilize Local Insights: Integrating the traditional ecological understanding of local communities into planning and execution is crucial. This strategy not only respects local insights but also fosters a sense of ownership and commitment among community members, enhancing conservation outcomes. Understanding the socio-economic elements that affect participant engagement is paramount for this approach.
-
Develop Joint Initiatives: Collaborating on conservation initiatives that benefit both nature and local communities—such as habitat restoration projects or educational programs—creates synergies that promote sustainable practices and strengthen community ties. A case study on the advantages of effective participant engagement illustrates how such collaborations can lead to positive outcomes.
By emphasizing these cooperative strategies, organizations can significantly improve their animal protection initiatives, ensuring wildlife protection during extraction while cultivating enduring connections with partners, ultimately leading to more effective conservation results. As Sarah Lee noted, stakeholder analysis is essential for identifying and engaging key stakeholders who can impact the success of conservation efforts.
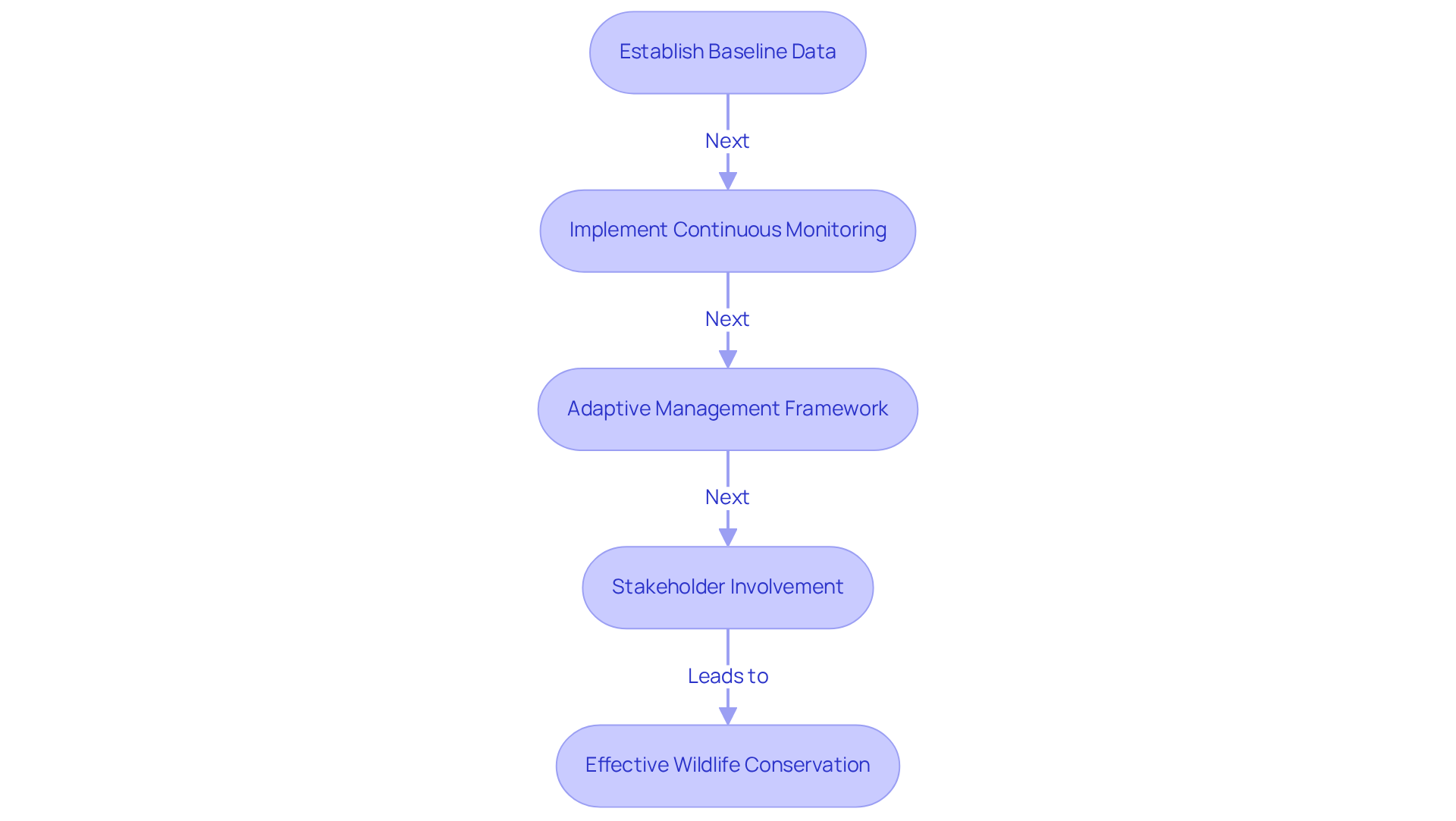
Utilize Monitoring and Adaptive Management Techniques
To effectively monitor wildlife protection efforts and adapt strategies as needed, organizations must employ a series of targeted approaches:
-
Establish Baseline Data: Gathering comprehensive baseline information on animal populations and habitats prior to initiating the program is crucial. This foundational data not only informs future assessments but also aids in evaluating the impact of extraction activities on local ecosystems, emphasizing the importance of wildlife protection during extraction.
-
Implement Continuous Monitoring: The integration of advanced technologies, such as remote sensing, GPS tracking, and camera traps, allows entities to observe fluctuations in animal populations and habitat conditions throughout the project's lifecycle. These tools deliver real-time data, enabling timely responses to emerging challenges. Furthermore, incorporating immigration and emigration data into these models is vital for accurate predictions of population trends, as it enhances the understanding of ecosystem dynamics.
-
Adaptive Management Framework: Establishing an adaptive management framework empowers organizations to maintain flexibility in their strategies. By consistently reviewing monitoring outcomes, they can make informed adjustments to their tactics, ensuring that wildlife protection during extraction measures remain effective and responsive to changing circumstances. For instance, research indicates that utilized animal populations have declined by an average of 50% from 1970 to 2016, underscoring the critical need for adaptive management.
-
Stakeholder Involvement: Incorporating input from interested parties, including local communities and conservation groups, enriches the monitoring process. Engaging diverse perspectives fosters collaborative decision-making and enhances the overall efficiency of conservation strategies. Case studies, such as the global analysis of animal population trends, exemplify the effectiveness of these monitoring techniques and the significance of stakeholder engagement.
By implementing these techniques, organizations can markedly enhance their capacity to protect wildlife while adapting to evolving environmental conditions and integrating new information.
Conclusion
Establishing effective wildlife protection during extraction projects is not merely an ethical responsibility; it is a crucial necessity for preserving biodiversity and ecological integrity. By prioritizing core principles such as:
- Minimizing habitat disturbance
- Adhering to legal standards
- Promoting sustainable resource management
- Engaging local communities
organizations can create a robust framework that safeguards wildlife while meeting extraction needs.
Key strategies, including:
- Habitat restoration
- The creation of animal corridors
- Reducing noise and light pollution
- Implementing comprehensive monitoring systems
offer actionable steps for mitigating the adverse effects of extraction activities. Tailored to specific ecological contexts, these approaches ensure that wildlife protection remains at the forefront of project planning and execution. Moreover, fostering collaboration among stakeholders through early engagement, creating platforms for information sharing, and integrating local insights further enhances conservation efforts.
Ultimately, the significance of these strategies extends beyond individual projects; they represent a collective commitment to ethical resource extraction that honors both the environment and the communities that depend on it. By adopting these practices and continually adapting to new information, organizations can play a pivotal role in reversing the alarming trends of species extinction and habitat loss. This commitment contributes to a more sustainable future for wildlife and humanity alike.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the core principles of wildlife protection during extraction initiatives?
The core principles include minimizing habitat disturbance, compliance with legal standards, sustainable resource management, and community engagement.
Why is minimizing habitat disturbance important?
Minimizing habitat disturbance is crucial to avoid critical habitats and migration corridors, as habitat loss is the primary threat to animal survival, with many species endangered or at risk of extinction.
What legal standards must organizations comply with for wildlife protection?
Organizations must adhere to local, state, and federal laws regarding animal protection, including the Endangered Species Act, to ensure that their initiatives do not infringe upon protected species and their habitats.
How does sustainable resource management contribute to wildlife protection?
Sustainable resource management promotes the balanced use of natural resources, ensuring that extraction needs do not compromise conservation goals, thereby protecting biodiversity and supporting long-term ecological resilience.
What role does community engagement play in wildlife protection initiatives?
Community engagement fosters stewardship and support for conservation initiatives by involving local communities in decision-making processes, which can enhance outcomes and cultivate a collective commitment to conservation.
Why is there an urgent need for these wildlife protection principles?
The alarming rate of species extinction highlights the urgent need for these principles, as safeguarding ecosystems is essential for reversing the biodiversity crisis and ensuring long-term ecological health.
List of Sources
- Establish Core Principles of Wildlife Protection
- Habitat Loss | National Wildlife Federation (https://nwf.org/Educational-Resources/Wildlife-Guide/Threats-to-Wildlife/Habitat-Loss)
- How Habitat Loss Imperils US Wildlife | Earth.Org (https://earth.org/lost-species-the-impact-of-habitat-destruction-in-the-us)
- 23% of Earth's natural habitats could be gone by 2100, study finds (https://weforum.org/stories/2020/11/earth-natural-habitats-destroyed-biodiversity-loss)
- The Global Impacts of Habitat Destruction (https://news.nationalgeographic.org/the-global-impacts-of-habitat-destruction)
- The greatest threats to species (https://conbio.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/csp2.12670)
- Implement Effective Mitigation Strategies
- Enhanced but highly variable biodiversity outcomes from coastal restoration: A global synthesis (https://cell.com/one-earth/fulltext/S2590-3322(24)00096-4)
- 13 Thought-Provoking Endangered Species Quotes to Inspire Action | Earth.Org (https://earth.org/endangered-species-quotes)
- Monitoring and Evaluation for Restoration Projects (https://fisheries.noaa.gov/national/habitat-conservation/monitoring-and-evaluation-restoration-projects)
- Assessing the success of marine ecosystem restoration using meta-analysis - Nature Communications (https://nature.com/articles/s41467-025-57254-2)
- Terrestrial ecosystem restoration increases biodiversity and reduces its variability, but not to reference levels: A global meta‐analysis - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9320827)
- Foster Collaboration Among Stakeholders
- Wildlife Conservation market Size & Industry Growth 2030 (https://futuredatastats.com/wildlife-conservation-market?srsltid=AfmBOop2kufebxBKqcsiHm9gOqhAqHG9aFO9EvYxa83dfWq_Op7tkH_5)
- Wildlife Stakeholder Analysis Guide (https://numberanalytics.com/blog/wildlife-stakeholder-analysis-guide)
- Stakeholder collaboration: evaluating community-based conservancies in Kenya | Oryx | Cambridge Core (https://cambridge.org/core/journals/oryx/article/stakeholder-collaboration-evaluating-communitybased-conservancies-in-kenya/24F86F695953E4BA6D2941CB7B999881)
- Frontiers | Stakeholder Support for Wildlife Conservation Funding Policies (https://frontiersin.org/journals/conservation-science/articles/10.3389/fcosc.2021.767413/full)
- Initiating Relationships with Stakeholders in Wildlife Conservation (https://wildteam.org.uk/post/initiating-relationships-with-stakeholders-in-wildlife-conservation)
- Utilize Monitoring and Adaptive Management Techniques
- A global indicator of utilized wildlife populations: Regional trends and the impact of management (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2590332222001476)
- Improving statistical methods to protect wildlife populations (https://phys.org/news/2024-05-statistical-methods-wildlife-populations.html)
- Wildlife Population Assessment: Changing Priorities Driven by Technological Advances - Journal of Statistical Theory and Practice (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42519-023-00319-6)
- Large scale wildlife monitoring studies: Statistical methods for design and analysis (https://usgs.gov/publications/large-scale-wildlife-monitoring-studies-statistical-methods-design-and-analysis)




