Overview
The article outlines seven key benefits of rural solar energy expansion, highlighting its economic, environmental, social, technological, and land use aspects. It emphasizes that rural solar energy not only stimulates local economies through job creation and reduced utility costs but also contributes to sustainability by decreasing carbon emissions and enhancing energy independence, ultimately positioning rural communities as vital players in the renewable energy landscape.
Introduction
The expansion of solar energy in rural areas is not merely a trend; it represents a transformative shift with far-reaching economic, environmental, and social implications. As communities harness the power of the sun, they unlock opportunities for job creation, enhance local economies, and contribute significantly to sustainability efforts.
This comprehensive exploration delves into the multifaceted benefits of solar energy, highlighting its role in revitalizing rural landscapes, reducing carbon footprints, and fostering energy independence. Through technological advancements and innovative land use strategies, the solar sector is poised for remarkable growth, addressing both current challenges and future demands.
The implications of this transition extend beyond mere energy production, positioning rural areas as pivotal players in the global movement towards a cleaner, more sustainable future.
Economic Advantages of Rural Solar Energy Expansion
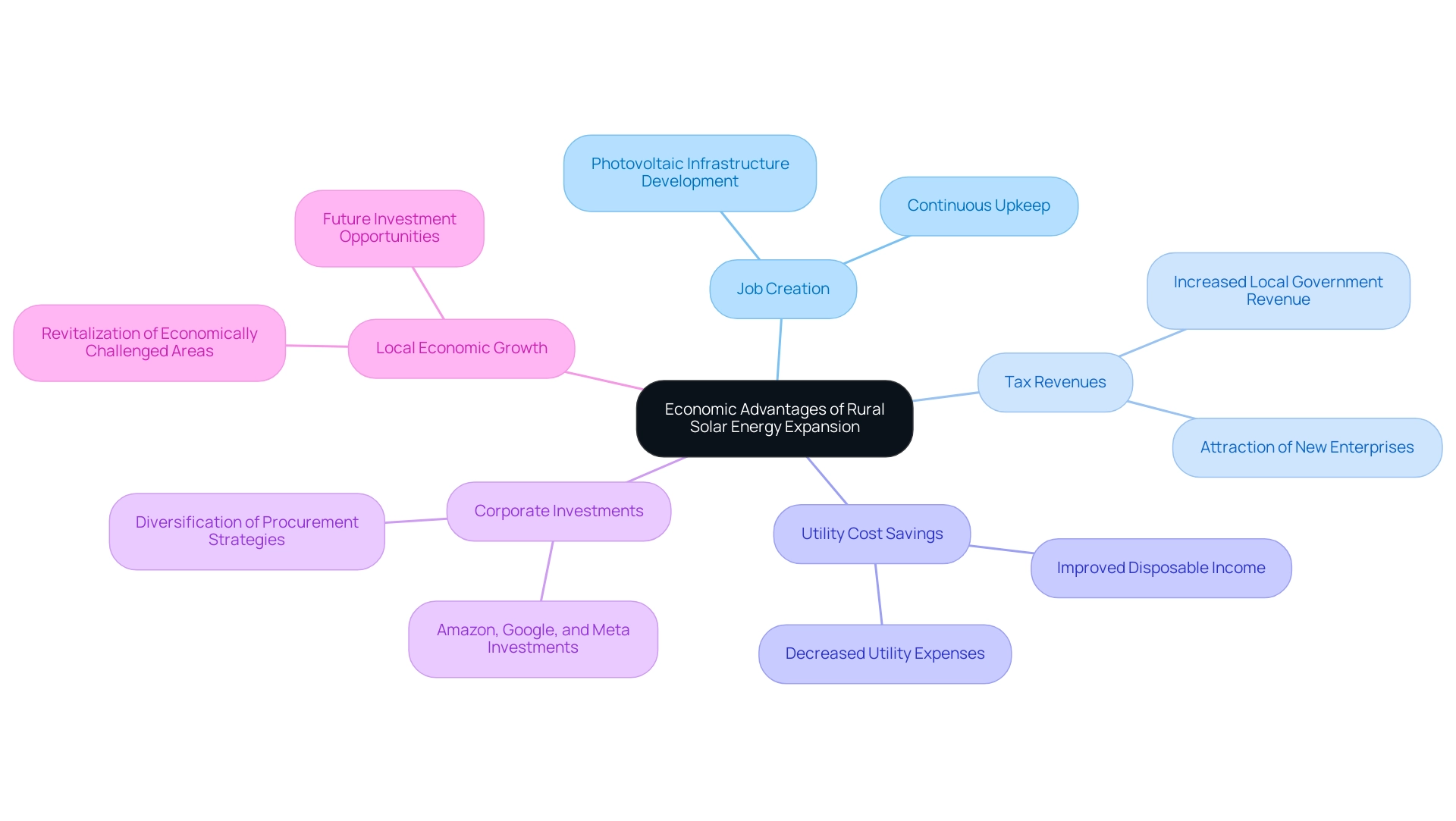
The growth of rural solar energy expansion offers significant economic benefits, especially in the fields of job creation and enhanced tax revenues for regional governments. As photovoltaic infrastructure is developed, rural solar energy expansion can enable countryside communities to attract new enterprises, thereby stimulating economic growth. The development and continuous upkeep of photovoltaic farms are vital for rural solar energy expansion, creating numerous job openings and indicating a substantial advantage for regional employment.
Based on recent studies, rural solar energy expansion, with each megawatt of photovoltaic power installed, can lead to significant growth in local economies, projected to generate thousands of jobs in countryside regions by 2024. Moreover, the implementation of rural solar energy expansion frequently leads to decreased utility expenses for both residents and enterprises, resulting in financial savings that improve disposable income within the community. This ripple effect not only aids in revitalizing economically challenged areas but also positions rural locations as attractive prospects for rural solar energy expansion and future investments.
Significantly, Amazon, Google, and Meta possess a combined contracted pipeline exceeding 25 GW, illustrating the magnitude of corporate investment in renewable resources. Additionally, the urgency of renewable energy expansion is underscored by the need for annual installations to grow to nearly 140 GW by 2030 to meet the goal of 100% carbon-free electricity by 2035. The recent trend shows that over 18% of U.S. renewable energy capacity now has a corporate offtaker, indicating a diversification of procurement strategies that further supports local economies through initiatives such as community energy and energy + storage.
It is also important to note that while the cost to install renewable energy systems has seen volatility in recent years due to inflation and supply chain challenges, recent improvements in U.S. manufacturing and easing supply chain disruptions have contributed to a continued decline in module prices year-over-year.
Environmental Impact: How Solar Energy Supports Sustainability
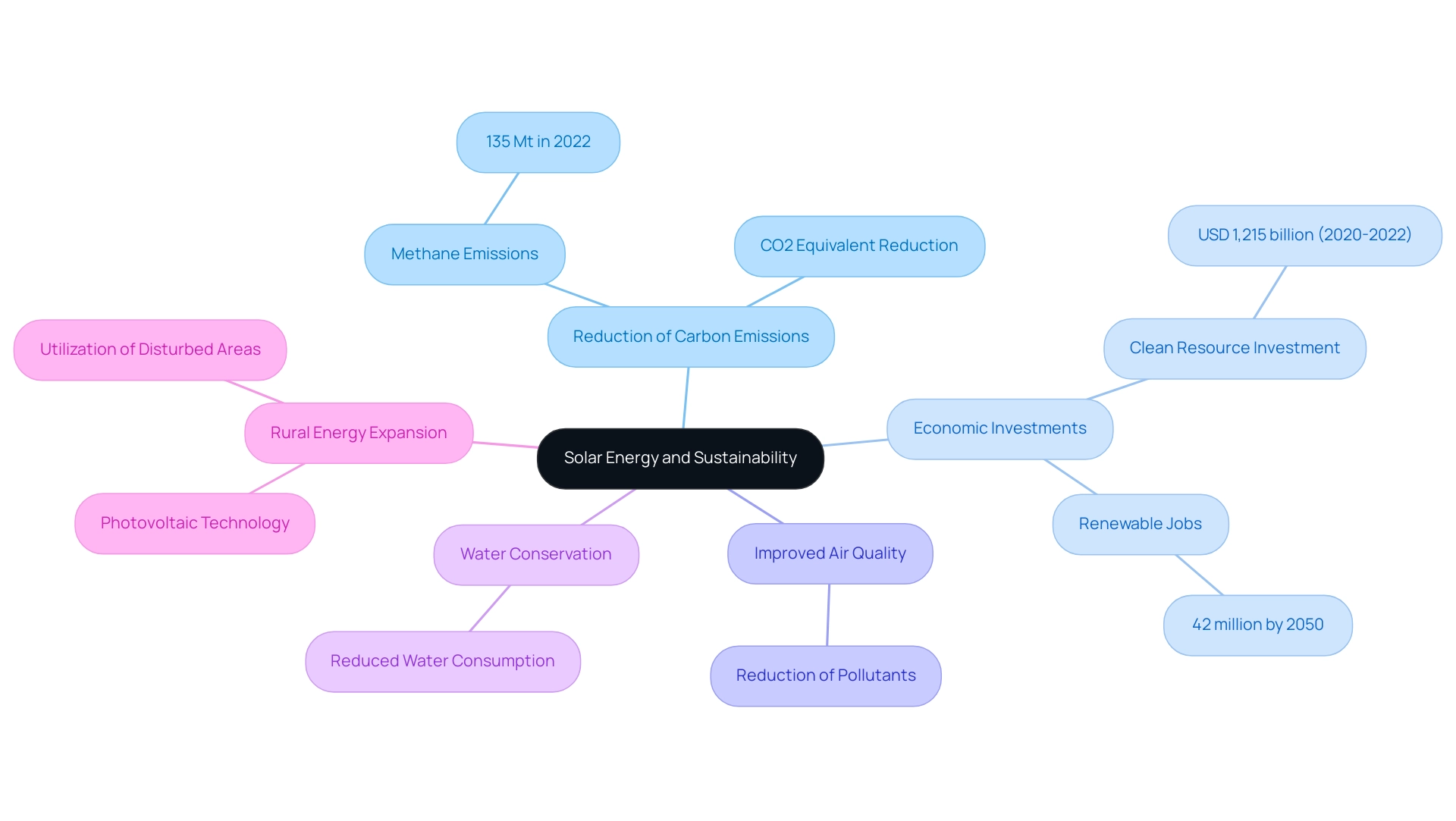
Solar power stands out as a clean and renewable resource, playing a pivotal role in significantly reducing carbon emissions when compared to fossil fuels. With methane emissions increasing to almost 135 Mt or about 4 Gt CO2-eq in 2022, the necessity to shift to cleaner power sources becomes even more evident. Rural solar energy expansion by increasing renewable installations in rural regions allows communities to reduce their reliance on non-renewable resources, directly aiding global climate change mitigation initiatives.
Recent statistics show that the use of sunlight power can significantly reduce carbon emissions, highlighting its efficacy in fostering a cleaner environment. Moreover, photovoltaic systems result in improved air quality and reduced water consumption, tackling significant issues linked to environmental deterioration. The incorporation of photovoltaic technology into rural environments is essential for rural solar energy expansion, as it promotes sustainability and safeguards natural habitats by utilizing previously disturbed areas for power generation.
Moreover, economic recovery packages globally have encompassed USD 1,215 billion in clean resource investment backing between April 2020 and October 2022, highlighting the financial dedication to enhancing renewable initiatives. As mentioned by Susan Tierney, the International Renewable Resources Agency's 'Transforming Energy Scenario' indicates that the count of renewable employment opportunities globally might surpass 42 million by 2050, further emphasizing the significant advantages of enhancing initiatives related to sunlight. This development not only bolsters regional economies but also establishes renewable power as a fundamental element in the battle against climate change.
Social Benefits: Job Creation and Energy Independence
The rural solar energy expansion is crucial for driving significant job creation across various sectors, including construction, installation, and the ongoing maintenance and operation of solar facilities. This surge in employment opportunities is vital for local economies, providing stable jobs that contribute to economic stability and community development. In fact, the clean power sector has been a strong driver of job growth, accounting for 4-6% of overall job expansion in advanced economies, including the United States and the European Union, in 2023.
Furthermore, rural solar energy expansion enhances independence by empowering communities to generate their own electricity. This capability decreases dependence on remote power sources, thereby enhancing regional power security. Such independence becomes critically important during crises or fluctuations in fossil fuel prices, allowing communities to take control of their power future.
As Kate Magill pointed out, First Solar chooses Louisiana as the site for its next panel factory, this decision highlights the increasing trend of investment in renewable infrastructure, which not only promotes local job creation but also supports rural solar energy expansion and enhances autonomy in rural regions. Additionally, the case study titled 'Gender Balance in the Workforce' highlights the potential for improving gender representation within the clean sector, which is essential for a diverse and skilled workforce. Furthermore, recent news indicates a 1% increase in utility-scale system pricing for fixed-tilt and a 2% increase for single-axis tracking year-over-year, illustrating the economic landscape in which these projects operate.
Looking ahead, the residential photovoltaic market is anticipated to rebound in 2025, propelled by stabilizing markets and interest rate reductions, further highlighting the significance of rural solar energy expansion for job creation and energy independence. The advantages of independence in power resources extend beyond just local control; they pave the way for sustainable development and resilience in the face of evolving challenges in this sector.
Technological Innovations Driving Solar Energy Growth
Technological advancements are essential for promoting rural solar energy expansion and growth in renewable sources, particularly in rural regions. Recent advancements in photovoltaic technology have yielded panels that boast increased efficiency, enabling them to generate more power while occupying less physical space. For instance, as of late October 2024, imports of over 9.4 GW of photovoltaic cells reflected a significant demand, with 75% of the tariff-rate quota already utilized.
This increase signifies strong interest in enhancing sunlight power generation amid current market difficulties. Barry Elad, a technology enthusiast, emphasizes, "Making complex tech information easy and accessible for everyone is essential for driving adoption and innovation in the energy sector." Furthermore, the emergence of advanced power storage solutions, such as lithium-ion batteries, empowers communities to capture excess power produced during peak sunlight hours, making it accessible during low-light conditions or at night.
Additionally, innovations in smart grid technology enhance energy management and distribution, significantly improving the reliability of photovoltaic energy systems. However, the renewable energy sector faces challenges such as equipment shortages and tariff uncertainties, which can hinder progress. For instance, a recent case study emphasized that in Q3 2024, residential energy installations experienced a 4% decline due to high electricity bills and changes in California's net metering regulations.
As these technologies keep progressing, they promise to reduce expenses and enhance the feasibility of projects in countryside locations, thereby supporting rural solar energy expansion while tackling both existing challenges and upcoming possibilities in the renewable landscape.
Navigating Land Use Challenges for Solar Projects
Navigating the complexities of land use is a critical consideration for renewable energy projects, particularly in rural regions, where rural solar energy expansion encounters significant hurdles due to land availability and zoning regulations. Conducting comprehensive site assessments and engaging local stakeholders early in the planning stages are crucial steps in identifying optimal locations for renewable energy installations. Recent research highlights that effective management of land as pastures in India could reduce land-use change (LUC) emissions per kilowatt-hour of electricity by 3 to 5 times, emphasizing the importance of responsible land stewardship.
Moreover, strategies such as utilizing previously disturbed lands and collaborating with agricultural entities for dual-use farming can significantly support rural solar energy expansion and reduce land use conflicts. As observed by Maguire, K., "Payments to farmers fluctuate based on farm size, market conditions, and location," which highlights the potential for mutually advantageous collaborations between renewable developers and landowners. Furthermore, adherence to regional zoning regulations is essential to avoid complications during the installation process.
Recent developments suggest that establishing minimum efficiency standards for photovoltaic modules may assist in reducing land requirements, potentially generating opportunities for rural solar energy expansion and more extensive renewable power deployment. Regional microclimate effects of photovoltaic installations remain uncertain and rely on various factors, including land management practices, which can influence both power generation and nearby ecosystems. By proactively addressing these challenges, renewable energy developers can secure necessary land for their projects while minimizing disruptions to local communities and ecosystems.
Moreover, case studies on land availability confirm that while certain regions possess potential for solar energy development, significant constraints arise due to land competition and environmental protections.
Conclusion
The expansion of solar energy in rural areas brings substantial economic, environmental, and social advantages. Economically, it generates job opportunities and boosts local tax revenues, attracting businesses and revitalizing communities. Projections indicate that thousands of jobs will be created by 2024, leading to lower energy costs for residents and enhancing disposable income.
Environmentally, solar energy is crucial for reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainability. By transitioning to solar power, rural areas can lessen their reliance on fossil fuels, contributing positively to climate change mitigation while improving air quality and conserving water.
Socially, the growth of solar energy enhances energy independence, allowing rural communities to control their energy sources and improve local energy security. This independence is vital during energy crises, enabling communities to manage fluctuations in fossil fuel prices. Furthermore, the clean energy sector is poised to create stable jobs and promote diversity within the workforce.
Technological advancements in solar energy, including improved photovoltaic systems and energy storage solutions, increase efficiency and reliability. Nonetheless, addressing challenges related to land use and regulatory frameworks is essential to maximize the benefits of solar projects.
In conclusion, the shift to solar energy in rural areas represents a transformative opportunity for economic growth, environmental sustainability, and social empowerment. By adopting solar technology, these communities can play a crucial role in advancing a cleaner, more sustainable future, highlighting their importance in the global transition to renewable energy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the economic benefits of rural solar energy expansion?
Rural solar energy expansion offers significant economic benefits, including job creation, enhanced tax revenues for regional governments, and the attraction of new enterprises, which stimulates economic growth in countryside communities.
How does rural solar energy expansion impact job creation?
The development and maintenance of photovoltaic farms create numerous job openings, contributing to substantial advantages for regional employment.
What is the projected impact of rural solar energy on local economies by 2024?
Each megawatt of photovoltaic power installed is projected to generate thousands of jobs in rural regions by 2024, indicating significant growth in local economies.
How does rural solar energy expansion affect utility expenses for residents and businesses?
The implementation of rural solar energy expansion often leads to decreased utility expenses, resulting in financial savings that improve disposable income within the community.
What role do major corporations play in renewable energy investment?
Companies like Amazon, Google, and Meta have a combined contracted pipeline exceeding 25 GW, showcasing significant corporate investment in renewable resources.
What is the target for renewable energy installations by 2030?
To meet the goal of 100% carbon-free electricity by 2035, annual installations of renewable energy need to grow to nearly 140 GW by 2030.
What percentage of U.S. renewable energy capacity now has a corporate offtaker?
Over 18% of U.S. renewable energy capacity now has a corporate offtaker, indicating a diversification of procurement strategies that supports local economies.
How have installation costs for renewable energy systems changed recently?
While installation costs have seen volatility due to inflation and supply chain challenges, improvements in U.S. manufacturing and easing supply chain disruptions have led to a continued decline in module prices year-over-year.
What environmental benefits does solar power provide?
Solar power significantly reduces carbon emissions, improves air quality, and reduces water consumption, aiding in global climate change mitigation initiatives.
How does rural solar energy expansion contribute to sustainability?
By increasing renewable installations in rural regions, solar energy expansion promotes sustainability and protects natural habitats by utilizing previously disturbed areas for power generation.
List of Sources
- Economic Advantages of Rural Solar Energy Expansion
- Solar Industry Research Data – SEIA (https://seia.org/research-resources/solar-industry-research-data)
- Environmental Impact: How Solar Energy Supports Sustainability
- CO2 Emissions in 2022 – Analysis - IEA (https://iea.org/reports/co2-emissions-in-2022)
- wri.org (https://wri.org/insights/setting-record-straight-about-renewable-energy)
- What is the Carbon Footprint of Solar Panels? (https://solar.com/learn/what-is-the-carbon-footprint-of-solar-panels)
- Social Benefits: Job Creation and Energy Independence
- Executive summary – World Energy Employment 2024 – Analysis - IEA (https://iea.org/reports/world-energy-employment-2024/executive-summary)
- Census Solar Job Trends (https://irecusa.org/census-solar-job-trends)
- Solar Market Insight Report Q4 2024 – SEIA (https://seia.org/research-resources/solar-market-insight-report-q4-2024)
- Technological Innovations Driving Solar Energy Growth
- Quarterly Solar Industry Update (https://energy.gov/eere/solar/quarterly-solar-industry-update)
- Solar Energy Statistics and Facts 2024 (https://electroiq.com/stats/solar-energy-statistics)
- Solar Market Insight Report Q3 2024 – SEIA (https://seia.org/research-resources/solar-market-insight-report-q3-2024)
- Solar Industry Research Data – SEIA (https://seia.org/research-resources/solar-industry-research-data)
- Navigating Land Use Challenges for Solar Projects
- The potential land requirements and related land use change emissions of solar energy - Scientific Reports (https://nature.com/articles/s41598-021-82042-5)
- Agricultural Land Near Solar and Wind Projects Usually Remained in Agriculture After Development | Economic Research Service (https://ers.usda.gov/amber-waves/2024/september/agricultural-land-near-solar-and-wind-projects-usually-remained-in-agriculture-after-development)




