Overview
Battery decommissioning protocols are critical for ensuring safety and compliance in energy management. They focus on the systematic removal and responsible disposal of batteries containing hazardous materials.
- Adherence to safety practices and regulatory guidelines is paramount.
- The integration of technology not only mitigates environmental risks but also supports a sustainable energy lifecycle.
- This underscores the importance of informed planning and stakeholder engagement throughout the decommissioning process.
Introduction
In an era marked by a surging demand for sustainable energy solutions, the significance of effective battery decommissioning is paramount. As batteries reach the end of their life cycle, the process of safely removing and disposing of them introduces both challenges and opportunities.
With hazardous materials often present, ensuring safety and compliance with the ever-evolving regulations is essential for organizations engaged in energy management. This article explores the critical facets of battery decommissioning, encompassing:
- Safety protocols
- Robust decommissioning strategies
- Legal requirements
- Integration of technology for enhanced efficiency
By prioritizing sustainability and engaging stakeholders, companies can mitigate environmental impacts and contribute to a more resilient and responsible battery lifecycle.
Understanding Battery Decommissioning: Safety and Compliance Essentials
Battery decommissioning protocols represent a critical process, entailing the systematic removal and disposal of units that have reached the end of their useful life. The primary concern in this process is protection, as power cells often contain hazardous substances that can pose significant threats to human health and the environment. Compliance with local, state, and federal regulations is essential—not only to avoid legal repercussions but also to ensure responsible disposal practices are followed.
Key safety practices in battery decommissioning include:
- Proper handling techniques to minimize exposure to hazardous materials.
- The use of personal protective equipment (PPE) to safeguard workers during the disposal process.
- Adherence to guidelines established by regulatory bodies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
As we look ahead to 2025, the framework of energy cell disposal regulations continues to evolve, underscoring the significance of security in compliance procedures. Organizations must remain informed about these changes to ensure adherence to the latest standards. Recent statistics reveal that improper handling of hazardous materials in power sources can lead to severe environmental consequences, highlighting the urgent need for stringent safety measures.
For example, the cost of manual disassembly of electric vehicle (EV) power packs can range from USD 47 to USD 197 per pack, illustrating the financial implications of inefficient disposal methods. Furthermore, recycling costs for a Nissan Leaf unit could decrease from USD 0.64 per kg to USD 0.02 per kg with automation, showcasing the economic benefits of adopting efficient disposal practices.
Moreover, case studies emphasize the importance of adhering to battery decommissioning protocols in cell disposal. Solid-state energy storage systems, which produce minimal gas emissions upon failure due to the absence of volatile liquid electrolytes, are increasingly favored for applications in enclosed spaces like airplanes and submarines. This feature not only enhances security but aligns with contemporary trends in energy storage technology aimed at minimizing hazardous waste.
As Alexandre van de Rijt, an Associate Partner at McKinsey, states, "We strongly believe that a resilient, sustainable, and circular global energy storage value chain is not only possible but also admirable to achieve sustainable inclusive growth."
As organizations navigate the complexities of energy storage management, recognizing and applying battery decommissioning protocols for compliance is essential. This involves remaining knowledgeable about existing regulations and figures associated with hazardous substances in cells, which can significantly impact operational integrity and public welfare. By emphasizing protection and adherence, organizations can contribute to a more sustainable and responsible energy source lifecycle.
Establishing Effective Decommissioning Protocols for Batteries
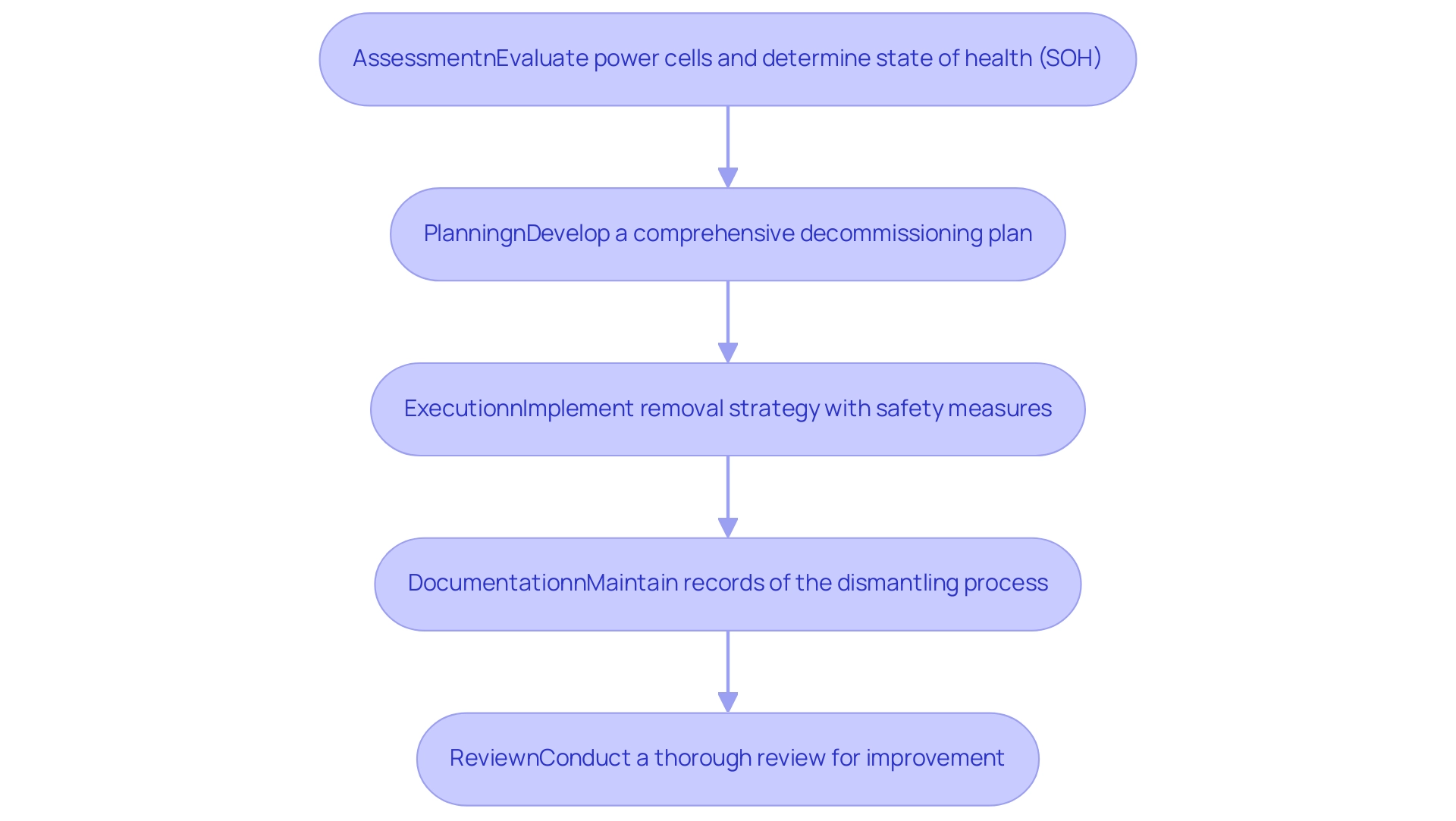
Establishing effective battery decommissioning protocols for energy storage systems is critical for ensuring safety and compliance in energy management. A robust approach involves several key steps:
- Assessment: Start with a thorough evaluation of the power cells. This assessment must determine the state of health (SOH) of each battery, which typically begins at 100% and declines over time due to natural degradation. Understanding the current situation will guide the selection of the most suitable closure method.
- Planning: Develop a comprehensive decommissioning plan that outlines necessary steps, timelines, and responsible personnel. This plan should also incorporate best practices for cell recycling, as the recycling segment of power storage materials is projected to expand more than three-fold in the next decade. As Alexandre van de Rijt, Associate Partner at McKinsey, asserts, "We strongly believe that a resilient, sustainable, and circular global energy storage value chain is not only possible but commendable to achieve sustainable inclusive growth." A well-structured plan not only facilitates smooth execution but also aligns with sustainability goals and supports the anticipated growth in the battery industry, potentially contributing to up to 18 million jobs by 2030.
- Execution: Implement the removal strategy with a strong focus on protection. Ensure that all safety measures are in place, including proper ventilation and containment for hazardous materials. The shift towards a circular economy in energy storage underscores the importance of reclaiming valuable materials and minimizing waste, achievable through effective disposal protocols. Innovations in recycling and modular energy storage systems aim to recover valuable materials, reduce waste, and extend overall lifespan through individual cell replacements.
- Documentation: Maintain meticulous records throughout the dismantling process. This documentation should detail any incidents or deviations from the plan, which are essential for compliance and future reference. Accurate records also support the growing demand for transparency in the battery lifecycle.
- Review: After completing the disassembly process, conduct a thorough review to identify areas for improvement. This reflective practice is vital for enhancing future cessation efforts and ensuring that protocols remain effective and compliant with evolving regulations.
By adhering to battery decommissioning protocols, organizations can guarantee a secure and compliant removal process, ultimately supporting a resilient and sustainable energy value chain. Industry experts emphasize that achieving a circular energy storage economy is not only feasible but essential for fostering sustainable growth in the sector.
Navigating Legal and Regulatory Requirements in Battery Decommissioning
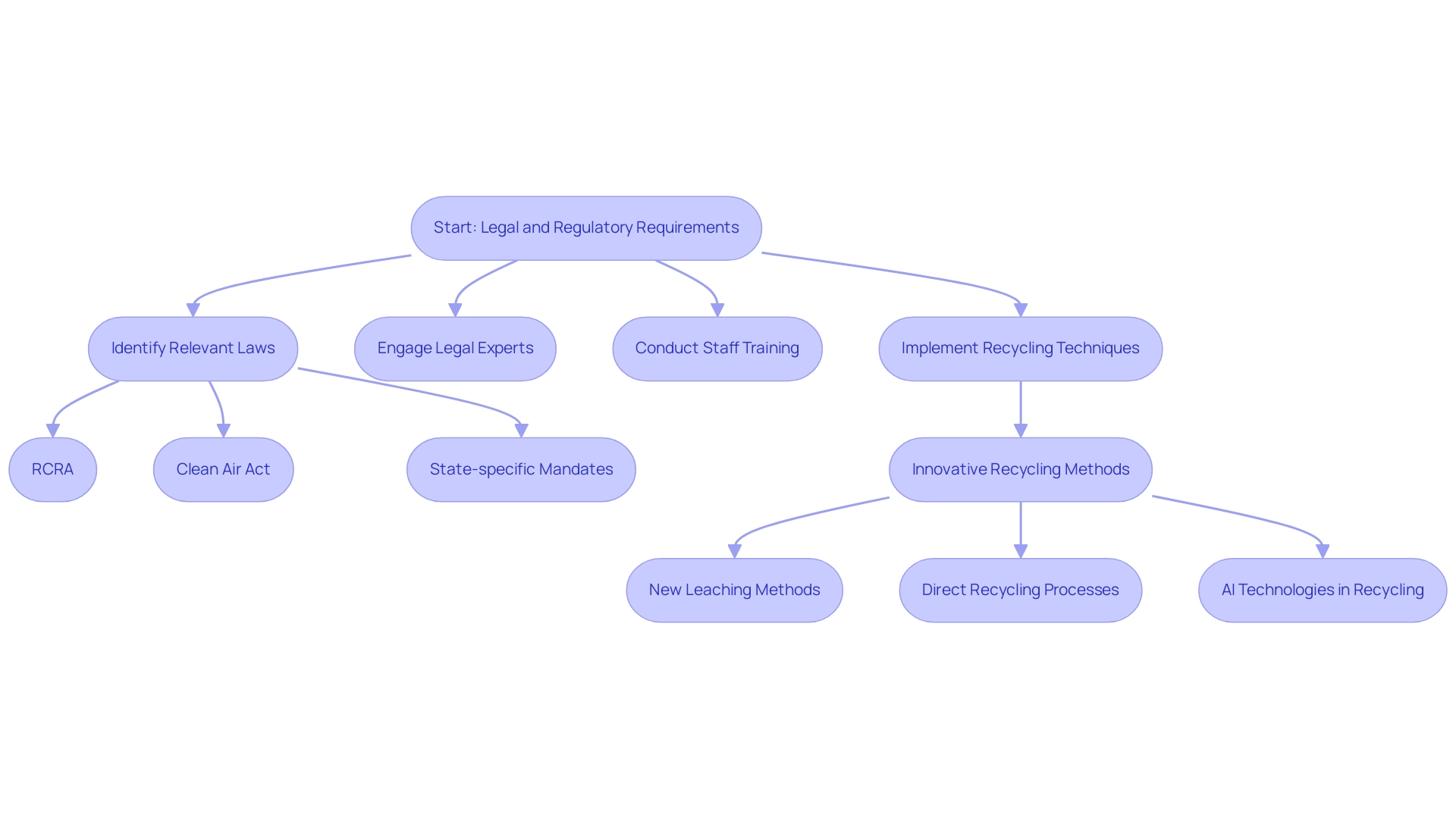
Navigating the legal and regulatory landscape for battery disposal necessitates a comprehensive understanding of various federal, state, and local laws. Central to this framework are the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) and the Clean Air Act, both of which play critical roles in hazardous waste management and emissions control during the process of shutting down operations. As of 2025, organizations must remain vigilant about evolving regulations, including state-specific mandates that may impose additional compliance requirements.
Engaging with legal experts and regulatory agencies at the outset of the decommissioning process is crucial for clarifying obligations and ensuring a streamlined compliance pathway. This proactive approach not only aids in understanding the legal landscape but also helps in identifying best practices tailored to specific project needs.
Regular training sessions for staff on these regulations are essential to foster adherence and mitigate risks associated with non-compliance. With approximately 48 million jobs in the U.S. linked to the energy sector, the implications of compliance extend beyond legal obligations; they impact workforce stability and environmental sustainability.
As noted in the Avicenne Energy Report, "As providers of over 60% of the world’s rechargeable energy storage capacity, lead accumulators are an established, economical technology that is essential to meeting our growing energy storage needs." This underscores the significance of adhering to legal obligations in energy storage disposal.
Emerging case studies highlight innovative strategies in energy storage decommissioning that incorporate battery decommissioning protocols in alignment with RCRA compliance. For instance, recent advancements in recycling techniques, such as new leaching methods and direct recycling processes, demonstrate a commitment to minimizing environmental impact while enhancing the recovery of high-purity metals from electric vehicle power sources. Additionally, AI technologies are revolutionizing EV cell recycling by automating sorting and identification processes, leading to improved resource recovery and reduced environmental impact.
These practices not only decrease dependence on virgin materials but also enhance the overall efficiency of the recycling process, demonstrating a sustainable approach to lifecycle management.
In summary, comprehending and following the legal obligations for energy system disposal is essential for organizations engaged in energy management. By emphasizing adherence and utilizing specialist knowledge, firms can navigate the intricacies of energy storage disposal efficiently, ensuring both security and sustainability.
Leveraging Technology for Efficient Battery Decommissioning
Technology is paramount in enhancing battery decommissioning protocols, significantly boosting both efficiency and safety. AI-powered tools lead the charge, enabling precise assessments of energy storage conditions and predicting potential hazards, which empowers organizations to implement proactive measures. For example, AI-driven predictive maintenance can diminish downtime by forecasting equipment failures before they occur, ensuring that shutdown operations unfold seamlessly.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) further bolster these initiatives by refining site planning and logistics. By 2025, the integration of GIS technology in battery disposal logistics has demonstrated its ability to streamline operations, facilitating improved resource allocation and minimizing delays. This technology not only elevates operational efficiency but also ensures compliance with regulatory requirements through accurate mapping and data visualization.
Moreover, digital documentation tools are vital in tracking decommissioning progress in real-time, guaranteeing adherence to battery decommissioning protocols and regulatory standards. The deployment of cognitive recycling networks powered by AI optimizes waste collection and processing based on real-time data and predictive analytics, marking a significant advancement in the field.
Case studies underscore the effectiveness of these technologies. For instance, AI-driven hybrid energy management systems have achieved a 50% enhancement in the performance of multi-source configurations, delivering greater value and reducing overall energy expenses. This highlights the tangible benefits of integrating advanced technology into energy storage disposal strategies.
Expert opinions stress the importance of harmonizing operational efficiency with safety and environmental responsibility in recycling. As Roodsari articulates, "the use of system dynamics in financial modeling to simulate and optimize decision-making under uncertainty allows companies to make informed decisions in volatile environments." This insight underscores that as the industry evolves, leveraging innovative technologies while maintaining this balance will be crucial for organizations aiming to refine their disposal protocols, particularly battery decommissioning protocols, while ensuring compliance and sustainability.
Sustainability in Battery Decommissioning: Environmental Considerations
Battery decommissioning protocols are essential for ensuring sustainability and minimizing environmental impact through responsible practices. This encompasses the recycling and repurposing of cell materials, which not only reduces waste but also conserves valuable resources. Recent statistics reveal that Ganfeng Lithium's recycling capacity has significantly increased from 2021 to 2023, underscoring the rising demand for lithium-ion cell recycling.
Organizations must critically assess the carbon footprint of their decommissioning activities by selecting battery decommissioning protocols that effectively minimize emissions and energy consumption. Are your current practices aligned with sustainability goals?
Engaging with certified recycling facilities and adhering to established battery decommissioning protocols is crucial for the safe and responsible management of hazardous materials, further safeguarding the environment. The U.S. Department of Energy has outlined strategies to integrate recycling into a circular economy framework, emphasizing, "The need to reduce reliance on new raw materials and mitigate environmental impacts is paramount." By prioritizing sustainability, organizations not only enhance their reputation but also contribute positively to the evolving energy sector, fostering a culture of environmental stewardship and compliance.
A pertinent case study is IMARC, praised for its timeliness and accuracy in delivering market research reports related to energy storage disposal practices. Their meticulous attention to detail and ability to meet tight deadlines solidify their reputation as a reliable industry partner. By adopting similar effective practices, organizations can ensure that their battery decommissioning protocols for energy removal processes are both sustainable and compliant.
Engaging Stakeholders: Communication Strategies for Successful Decommissioning
Effectively engaging stakeholders throughout the battery removal process is essential for achieving successful outcomes. Organizations must identify all pertinent stakeholders, including local communities, regulatory agencies, and environmental advocacy groups. A well-organized communication strategy is crucial; it should clearly describe how and when stakeholders will be informed about shutdown activities, thereby fostering trust and transparency.
Regular updates and opportunities for stakeholder feedback not only enhance collaboration but also address any concerns that may arise during the process.
Statistics indicate that nearly 60 percent of lithium is currently mined for battery-related applications, a figure projected to rise to 95 percent by 2030. This shift highlights the urgency of establishing strong battery decommissioning protocols that prioritize sustainability. Furthermore, effective communication strategies can significantly influence the success of project shutdowns.
For instance, organizations that implement comprehensive communication plans often report higher levels of stakeholder satisfaction and reduced conflicts.
The Battery Partnership Agreement (BPA) and Battery Production Regulation (BPR) support the transition towards more sustainable and resilient energy systems, underscoring the importance of robust battery decommissioning protocols. As Guy Éthier, Past Chairman of the Board of Directors, noted, "Three years ago McKinsey supported GBA and demonstrated the importance of a pre-competitive transparent energy storage value chain to drive the energy transformation; today’s updated report magnifies not only the importance but also the magnitude and urgency."
Additionally, decarbonizing production of energy storage systems is critical, as manufacturing emissions for electric vehicles (BEVs) are currently higher than for internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. This emphasizes the need for sustainable practices in battery decommissioning protocols. Case studies reveal that proactive stakeholder engagement can lead to more resilient and sustainable value chains for energy storage.
The battery industry is projected to create up to 18 million jobs by 2030, driven by increased demand for batteries and related technologies. This growth highlights the potential economic advantages of a transparent and collaborative method for dismantling. By prioritizing stakeholder engagement and communication, organizations can navigate potential challenges and enhance the overall effectiveness of their battery decommissioning protocols.
Conclusion
The significance of effective battery decommissioning is paramount, especially in a time when sustainability is a critical global concern. This article underscores vital elements of the decommissioning process, highlighting safety protocols, robust strategies, and strict adherence to legal requirements. By implementing comprehensive assessment, planning, execution, documentation, and review processes, organizations can guarantee a safe and compliant battery lifecycle.
Technological advancements are instrumental in bolstering the efficiency and safety of battery decommissioning. Innovations such as AI-driven predictive maintenance and the integration of Geographic Information Systems can lead to substantial enhancements in operational performance and regulatory compliance. Moreover, sustainability should be central to decommissioning strategies, prioritizing the recycling and repurposing of materials to reduce environmental impact.
Engaging stakeholders through transparent communication is essential for building trust and collaboration. By emphasizing stakeholder involvement, organizations can more effectively navigate challenges and foster a culture of environmental stewardship. The ever-evolving landscape of battery decommissioning presents both challenges and opportunities; by adopting best practices and innovative solutions, companies can contribute to a resilient and sustainable battery ecosystem.
In conclusion, the future of battery decommissioning hinges on a steadfast commitment to safety, compliance, and sustainability. As the demand for batteries continues to escalate, organizations must rise to the occasion, ensuring that their decommissioning practices embody a responsible approach to energy management and environmental preservation. By doing so, they not only secure their operational integrity but also play a vital role in shaping a sustainable future for the battery industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is battery decommissioning and why is it important?
Battery decommissioning refers to the systematic removal and disposal of power cells that have reached the end of their useful life. It is important for protecting human health and the environment since batteries often contain hazardous substances.
What regulations must be followed during battery decommissioning?
Compliance with local, state, and federal regulations is essential to avoid legal repercussions and ensure responsible disposal practices.
What are key safety practices in battery decommissioning?
Key safety practices include proper handling techniques to minimize exposure to hazardous materials, using personal protective equipment (PPE), and adhering to guidelines from regulatory bodies like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
How are battery decommissioning protocols evolving by 2025?
The framework of energy cell disposal regulations is evolving, emphasizing the need for organizations to stay informed about changes to ensure compliance with the latest standards.
What are the financial implications of improper battery disposal methods?
The cost of manually disassembling electric vehicle (EV) power packs can range from USD 47 to USD 197 per pack. Additionally, recycling costs for a Nissan Leaf unit could decrease significantly with automation.
What is the significance of solid-state energy storage systems in battery decommissioning?
Solid-state energy storage systems produce minimal gas emissions upon failure and are increasingly favored for applications in enclosed spaces, enhancing security and aligning with trends in energy storage technology.
What are the key steps involved in establishing effective battery decommissioning protocols?
The key steps include: 1. Assessment of the battery's state of health. 2. Planning a comprehensive decommissioning strategy. 3. Execution of the removal strategy with a focus on safety. 4. Documentation of the entire dismantling process. 5. Review of the process to identify areas for improvement.
How can organizations contribute to a sustainable energy source lifecycle?
By adhering to battery decommissioning protocols and remaining knowledgeable about regulations, organizations can ensure a secure and compliant removal process, contributing to a more sustainable and responsible energy lifecycle.
List of Sources
- Understanding Battery Decommissioning: Safety and Compliance Essentials
- High-Volume Battery Recycling: Technical Review of Challenges and Future Directions (https://mdpi.com/2313-0105/11/3/94)
- Outlook for battery and energy demand – Global EV Outlook 2024 – Analysis - IEA (https://iea.org/reports/global-ev-outlook-2024/outlook-for-battery-and-energy-demand)
- Battery 2030: Resilient, sustainable, and circular (https://mckinsey.com/industries/automotive-and-assembly/our-insights/battery-2030-resilient-sustainable-and-circular)
- Grid-scale battery safety showing signs of progress amid growth (https://pv-magazine-usa.com/2025/01/06/grid-scale-battery-safety-showing-signs-of-progress-amid-growth)
- Battery Fire Risks: How Safe Are Lithium-Ion and Solid-State Batteries? (Failure Rate Stats) (https://patentpc.com/blog/battery-fire-risks-how-safe-are-lithium-ion-and-solid-state-batteries-failure-rate-stats)
- Establishing Effective Decommissioning Protocols for Batteries
- Battery 2030: Resilient, sustainable, and circular (https://mckinsey.com/industries/automotive-and-assembly/our-insights/battery-2030-resilient-sustainable-and-circular)
- EV Battery Health Insights: Data From 10,000 Cars | Geotab (https://geotab.com/blog/ev-battery-health)
- What is battery degradation and how to prevent it – gridX (https://gridx.ai/knowledge/what-is-battery-degradation-and-how-to-prevent-it)
- Navigating Legal and Regulatory Requirements in Battery Decommissioning
- batterycouncil.org (https://batterycouncil.org/sources)
- High-Volume Battery Recycling: Technical Review of Challenges and Future Directions (https://mdpi.com/2313-0105/11/3/94)
- Leveraging Technology for Efficient Battery Decommissioning
- Recent Advancements in Artificial Intelligence in Battery Recycling (https://mdpi.com/2313-0105/10/12/440)
- The Impact of AI on Battery Technology: How AI Is Improving Battery Performance (Key Stats) (https://patentpc.com/blog/the-impact-of-ai-on-battery-technology-how-ai-is-improving-battery-performance-key-stats)
- Sustainability in Battery Decommissioning: Environmental Considerations
- Global battery recycling capacity by region 2023-2030 | Statista (https://statista.com/statistics/1495719/global-battery-recycling-capacity-by-region)
- imarcgroup.com (https://imarcgroup.com/united-states-battery-recycling-market)
- Engaging Stakeholders: Communication Strategies for Successful Decommissioning
- Battery 2030: Resilient, sustainable, and circular (https://mckinsey.com/industries/automotive-and-assembly/our-insights/battery-2030-resilient-sustainable-and-circular)
- (PDF) Stakeholder engagement and influence: Strategies for successful energy projects (https://researchgate.net/publication/382514218_Stakeholder_engagement_and_influence_Strategies_for_successful_energy_projects)




