Overview
Best practices for energy corridor management include ecological management, stakeholder engagement, and the use of advanced technologies to ensure efficient and sustainable infrastructure development. The article emphasizes that these strategies are critical for minimizing environmental impacts, fostering community support, and navigating complex regulatory frameworks, thereby enhancing the overall success of energy projects.
Introduction
Energy corridors serve as vital arteries within the global energy landscape, facilitating the movement and distribution of essential resources such as electricity, natural gas, and renewable energy. Their importance transcends logistical functions, demanding a thorough understanding of the intricate geographical, regulatory, and environmental frameworks that govern their development.
As the world grapples with the pressing need for sustainable energy solutions, the management of these corridors emerges as a critical focus area. This article delves into the strategies necessary for effective energy corridor management, emphasizing:
- Ecological sensitivity
- Stakeholder engagement
- Regulatory compliance
By exploring proven methodologies and recent advancements, it highlights the imperative of fostering collaboration among diverse stakeholders to ensure these corridors not only meet current energy demands but also contribute to a sustainable future.
Understanding the Energy Corridor: A Strategic Overview
Power pathways are vital channels for the transportation and distribution of various resources, encompassing electricity, natural gas, and renewable sources. They play a pivotal role in connecting producers with consumers, thus bolstering the economic stability of regions. The significance of these passages extends beyond mere logistics; it necessitates a comprehensive understanding of energy corridor management in relation to their geographical, regulatory, and environmental contexts.
For instance, creating power corridors necessitates meticulous evaluations of land use, environmental effects, and compliance with both local and federal regulations. Engaging stakeholders early in the planning process is crucial for identifying potential conflicts and fostering collaboration among landowners, government entities, and utility companies. As Dr. Nick Wayth, Chief Executive of the Energy Institute, points out,
The progress of the transition is slow, but the big picture masks diverse stories related to various resources playing out across different geographies.
This holistic approach is essential to ensuring that energy corridor management is not only efficient but also sustainable and socially responsible. Moreover, recent statistics indicate that grid investment needs to nearly double by 2030 to over USD 600 billion per year, highlighting the urgency of developing these infrastructures. As we approach 2024, recent advancements highlight the integration of new power sources with existing industries, such as the coal chemical sector, to significantly reduce carbon emissions and enhance production efficiency.
A case study on Asia Pacific's power demand illustrates this dynamic; in 2023, the region consumed 292 EJ of primary resources, accounting for 47% of the world’s total demand, yet its oil production met only 19% of its consumption, while gas production met 74%. As a result, energy corridor management is crucial for the efficient administration of power pathways in navigating the changing environment of resource supply and demand worldwide.
Proven Strategies for Effective Energy Corridor Management
Effective energy corridor management necessitates a comprehensive strategy that emphasizes ecological sensitivity, stakeholder engagement, and adherence to regulatory frameworks. As the global goal of doubling the average annual rate of energy efficiency improvements by 2030 underscores, the urgency of these strategies is paramount. Below are several proven strategies:
-
Ecological Management: Conducting thorough environmental assessments is critical to identifying sensitive habitats and species within development areas. Implementing targeted mitigation strategies—such as adjusting routing or developing habitat restoration plans—can significantly minimize ecological disruption. For instance, in pipeline construction endeavors, integrating wildlife corridors can facilitate safe passage for animals, thereby preserving biodiversity.
Notably, IBM’s facility in Quebec was estimated to save 43,000 gigajoules of energy over several years, showcasing the potential benefits of effective ecological management.
-
Stakeholder Engagement: Establishing open lines of communication with all stakeholders—including landowners, local communities, and regulatory bodies—is essential. Arranging public forums and workshops offers a venue for tackling issues and collecting valuable feedback, ensuring that initiatives align with community interests.
A well-structured stakeholder engagement plan fosters trust and helps secure necessary approvals, which are pivotal for project success. The implementation of Property Assessed Clean Energy (PACE) programs in various nations exemplifies how such initiatives facilitate investments in efficiency improvements and enhance community engagement.
Regulatory compliance in energy corridor management involves staying abreast of local, state, and federal regulations governing energy corridor development, which is crucial. Working together with legal specialists can simplify the permitting process, while the development of a compliance checklist guarantees that all necessary permits and environmental regulations are thoroughly addressed before starting.
-
Technology Utilization: The integration of advanced technologies, such as GIS mapping and AI-powered software for title research, can greatly improve workflows. These tools not only enhance data precision but also enable more informed decision-making processes, ultimately resulting in more efficient execution of infrastructure projects.
-
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation: Establishing a framework for the ongoing monitoring of both environmental and social impacts throughout the initiative lifecycle is vital. This proactive approach enables timely modifications to management practices, ensuring that power pathways remain effective and sustainable in addressing evolving resource demands.
As emphasized by recent initiatives, such as Property Assessed Clean Energy (PACE) programs, the dedication to ecological management is increasingly acknowledged as a fundamental element of successful implementation.
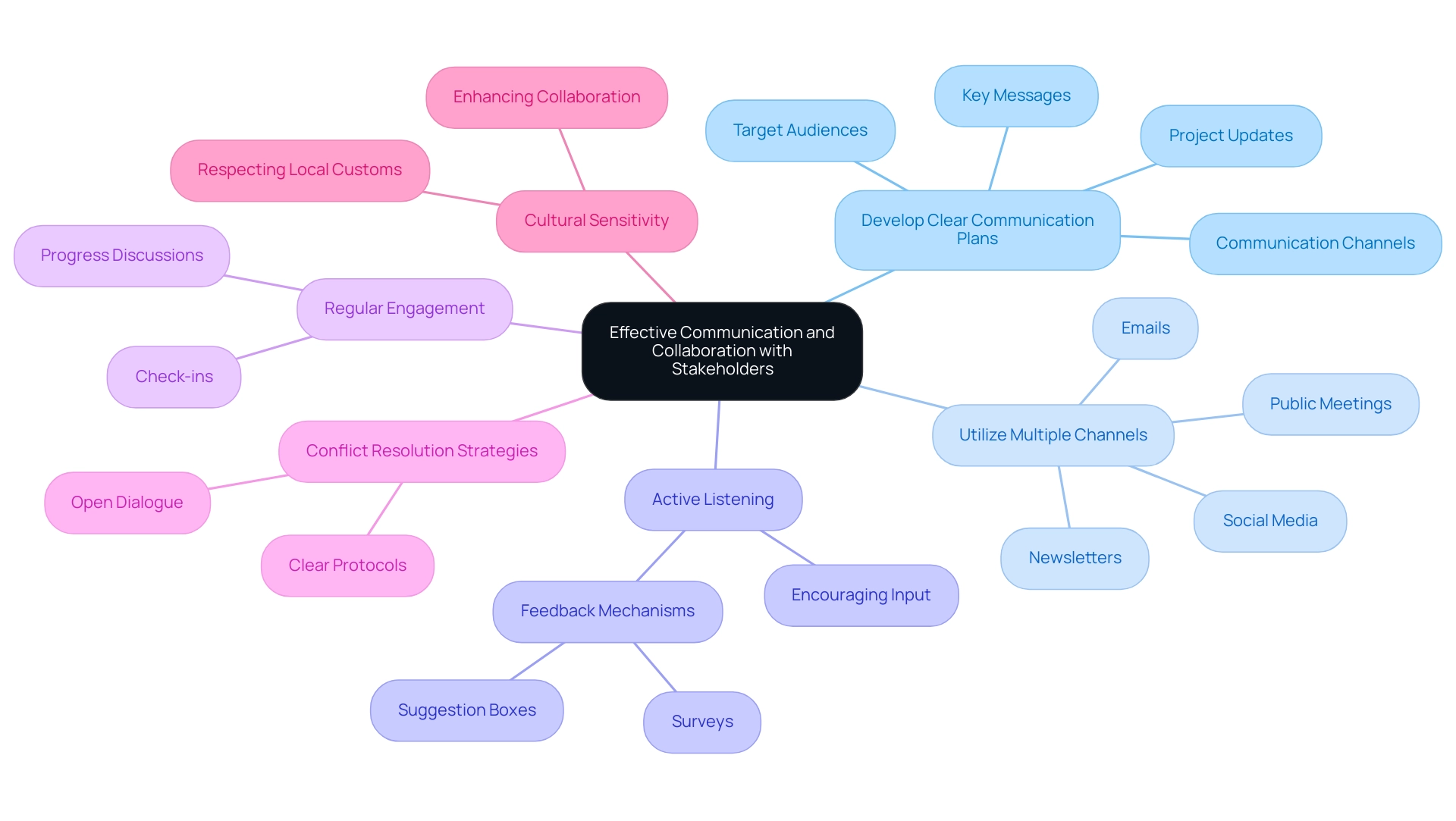
Effective Communication and Collaboration with Stakeholders
Effective communication is essential in the realm of energy corridor management, where involving a diverse group of stakeholders—from landowners to local government officials and community members—is vital for success. Implementing the following strategies can foster productive relationships and enhance overall project outcomes:
-
Develop Clear Communication Plans: Establish a comprehensive communication plan that delineates key messages, identifies target audiences, and specifies communication channels. Consistent updates regarding project timelines, potential impacts, and mitigation strategies can significantly enhance awareness and engagement of interested parties.
-
Utilize Multiple Channels: Employ various communication platforms such as emails, newsletters, public meetings, and social media to reach a broad audience effectively. Each channel serves a unique purpose, whether it’s providing updates, soliciting feedback, or addressing concerns of interested parties.
-
Active Listening: Cultivating an environment of active listening is vital. Encourage input from interested parties and demonstrate that their perspectives are valued. Implementing feedback mechanisms like surveys or suggestion boxes can facilitate this process, thereby enhancing trust and collaboration.
-
Regular Engagement: Arrange regular check-ins with important participants to discuss progress and tackle emerging issues. This continuous involvement is crucial for preserving clarity and strengthening participant commitment, ultimately resulting in increased support for the initiative.
-
Conflict Resolution Strategies: Be proactive in addressing conflicts by establishing clear protocols for conflict resolution. Early identification of potential disputes, coupled with open dialogue, can often prevent issues from escalating. As noted by expert Michael Osinakachukwu Ezeh,
These strategies not only facilitate project success but also contribute to the broader goals of sustainable development and social responsibility in the energy sector.
-
Cultural Sensitivity: Recognizing and respecting local customs and values is critical. Effective engagement strategies prioritize cultural sensitivity, which enhances collaboration and fosters trust among participants. For instance, the case study titled "Developing Engagement Strategies" emphasizes that effective engagement strategies prioritize continuous feedback, transparent reporting, and cultural sensitivity to foster trust and cooperation among involved parties, ultimately enhancing participation and support.
By emphasizing these communication methods, managers can greatly improve participant involvement and backing, resulting in more successful and sustainable outcomes. Furthermore, implementing these strategies can be measured through the minimum Cronbach’s alpha of 0.907, which underscores the reliability of these communication methods in fostering effective stakeholder engagement.
Sustainable Practices in Energy Corridor Development
Embracing sustainable methods in energy infrastructure development is crucial not only for ecological conservation but also for improving the overall feasibility of initiatives. Key strategies include:
-
Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA): Conducting comprehensive EIAs is crucial for evaluating potential environmental effects prior to initiation.
These assessments help identify critical habitats, species, and other ecological features that may be affected, enabling informed decision-making that prioritizes energy corridor management and environmental integrity. Notably, there have been 64 survey years conducted across all sites, underscoring the extensive data that supports the effectiveness of EIAs in monitoring environmental impacts.
-
Sustainable Routing Options: Designing corridor routes with an emphasis on minimizing disruption to sensitive ecosystems and local communities is vital.
By employing tools such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS) mapping, planners can analyze potential routes and select alternatives that significantly lessen environmental impacts, which is essential for effective energy corridor management and aligns with the latest standards in sustainable development.
-
Restoration Practices: After construction, implementing effective restoration practices is necessary to rehabilitate disturbed areas. This includes initiatives such as replanting native vegetation, restoring wetlands, and enhancing wildlife habitats, which contribute to long-term ecological balance.
-
Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in sustainability initiatives fosters support and enhances acceptance. Informing residents about the initiative's benefits and engaging them in restoration efforts can foster a sense of shared responsibility for environmental stewardship.
-
Monitoring and Reporting: Establishing a robust monitoring program is essential for assessing the effectiveness of sustainability measures.
Regular reports to stakeholders not only show a dedication to environmental stewardship but also create chances for ongoing enhancement and adjustment to new challenges.
As noted by Philip J. K. McGowan, > Our results show that black grouse found generally within 500 m of planned turbines moved locally after construction, emphasizing the significance of considering wildlife movement patterns in planning. Furthermore, the recent launch of the Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA) program by the Environment Agency Abu Dhabi in April 2023 emphasizes the growing recognition of integrating environmental considerations into strategic projects. The incorporation of sustainable methods in energy corridor management is progressively acknowledged as a best practice, ensuring that both ecological and community interests are balanced.
Navigating Regulatory Frameworks and Compliance
Navigating the regulatory landscape is essential in the management of power pathways. As the Department of Energy (DOE) prepares to allocate approximately $2 billion to national interest initiatives through the Transmission Facility Financing program, understanding compliance and legal frameworks becomes increasingly critical. To ensure adherence to regulations and mitigate legal risks, consider these key strategies:
- Stay Informed: Regularly monitor local, state, and federal regulations affecting utility corridor initiatives. Subscribing to industry newsletters and participating in professional organizations can provide timely updates on regulatory changes and compliance requirements.
- Engage Legal Experts: Collaborating with legal advisors who specialize in energy and land use regulations is essential. Their expertise can guide you through the complexities of the permitting process and ensure that all legal requirements are met, significantly enhancing success rates.
- Develop a Compliance Checklist: A detailed compliance checklist outlining all required permits and approvals can streamline the application process. This tool not only assists in tracking necessary steps but also reduces the risk of oversight, contributing to more efficient management.
- Document Everything: Maintaining comprehensive documentation of all communications, permits, and assessments throughout the initiative lifecycle is crucial. This meticulous record-keeping demonstrates compliance during audits and inspections, providing a clear trail of adherence to regulatory requirements.
- Prepare for Inspections: Familiarize yourself with the inspection process and prepare for potential site visits from regulatory agencies. Conducting internal audits can identify and address compliance issues proactively, ensuring readiness and reducing the likelihood of delays.
A relevant case study, "Right-Sizing Transmission Facilities," illustrates how transmission providers can modify existing facilities to increase transfer capability while allowing incumbent owners the right to refuse such modifications. This example underscores the importance of transparency in local planning information and stakeholder engagement during the regional planning cycle, which is crucial for compliance.
As recent updates indicate, the DOE is on track to finalize capacity contract negotiations for three transmission initiatives aimed at adding 3.5 GW of grid capacity. This highlights the importance of legal expertise in navigating complex regulatory frameworks, particularly in light of reforms such as Order No. 1920, which aims to provide a more certain trajectory for transmission planning.
These reforms highlight the necessity for resource route managers to adjust their compliance strategies accordingly. However, it’s essential to be wary of the political context; Commissioner Mark Christie cautioned against rushing the adoption of such orders for partisan policy goals, reminding us that careful navigation of these challenges is vital. By employing these strategies, energy corridor management can effectively navigate the evolving regulatory landscape, ensuring compliance and advancing project goals.
Conclusion
Energy corridors are indispensable to the global energy framework, serving as crucial channels for the distribution of electricity, natural gas, and renewable energy. The management of these corridors involves a multifaceted approach that prioritizes ecological sensitivity, stakeholder engagement, and regulatory compliance. By implementing proven strategies such as:
- Thorough environmental assessments
- Proactive communication with stakeholders
- Maintaining adherence to legal standards
stakeholders can enhance the effectiveness and sustainability of these vital infrastructures.
The emphasis on sustainable practices in energy corridor development cannot be overstated. Incorporating:
- Environmental impact assessments
- Community involvement
- Robust monitoring systems
not only preserves ecological integrity but also fosters public support. As the energy landscape continues to evolve, the integration of advanced technologies and continuous adaptation to regulatory frameworks will play a pivotal role in ensuring the successful management of energy corridors.
Ultimately, the collaborative efforts of all stakeholders—ranging from local communities to regulatory bodies—will determine the success of energy corridors in meeting the pressing energy demands of today while safeguarding the environment for future generations. A commitment to these strategies is essential for navigating the complexities of energy corridor management, ensuring that they contribute positively to both economic stability and environmental sustainability in an increasingly interconnected world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are power pathways, and why are they important?
Power pathways are essential channels for transporting and distributing resources like electricity, natural gas, and renewable sources. They connect producers with consumers, which helps bolster the economic stability of regions.
What factors must be considered when creating power corridors?
Creating power corridors requires thorough evaluations of land use, environmental impacts, and compliance with local and federal regulations. Engaging stakeholders early in the planning process is also crucial for identifying potential conflicts and fostering collaboration.
What is the significance of stakeholder engagement in energy corridor management?
Stakeholder engagement is vital as it establishes open communication with landowners, local communities, and regulatory bodies. Public forums and workshops can provide valuable feedback and help align initiatives with community interests, thereby fostering trust and securing necessary approvals.
How does ecological management contribute to energy corridor development?
Ecological management involves conducting environmental assessments to identify sensitive habitats and species. Implementing targeted mitigation strategies, such as adjusting routing or developing habitat restoration plans, can minimize ecological disruption and preserve biodiversity.
What role does technology play in energy corridor management?
Technology, such as GIS mapping and AI-powered software, enhances data precision and improves workflows. These advanced tools facilitate informed decision-making processes, leading to more efficient execution of infrastructure projects.
Why is continuous monitoring important in energy corridor management?
Continuous monitoring allows for the ongoing assessment of environmental and social impacts throughout the project lifecycle. This proactive approach enables timely adjustments to management practices, ensuring that power pathways remain effective and sustainable in meeting evolving resource demands.
What are some proven strategies for effective energy corridor management?
Proven strategies include ecological management, stakeholder engagement, technology utilization, and continuous monitoring and adaptation. These strategies emphasize ecological sensitivity, collaboration with stakeholders, and adherence to regulatory frameworks.
What are the current challenges facing energy corridor development?
Recent statistics indicate that grid investment needs to nearly double by 2030, highlighting the urgency of developing infrastructures to meet growing energy demands. Additionally, the integration of new power sources with existing industries is necessary to reduce carbon emissions and enhance production efficiency.
List of Sources
- Understanding the Energy Corridor: A Strategic Overview
- Executive summary – Electricity Grids and Secure Energy Transitions – Analysis - IEA (https://iea.org/reports/electricity-grids-and-secure-energy-transitions/executive-summary)
- Home (https://energyinst.org/statistical-review)
- REN21 Renewables Global Status Report (https://ren21.net/reports/global-status-report)
- World Energy Outlook 2021 – Analysis - IEA (https://iea.org/reports/world-energy-outlook-2021)
- Integrated energy corridor: a comprehensive proposal of the low-carbon transition for China Energy Group (https://academic.oup.com/ce/article/7/1/132/7074349)
- Proven Strategies for Effective Energy Corridor Management
- Energy Efficiency Progress Tracker – Data Tools - IEA (https://iea.org/data-and-statistics/data-tools/energy-efficiency-progress-tracker)
- Effective Communication and Collaboration with Stakeholders
- Investigating the Impact of Communication Factors and Stakeholders Engagement on Renewable Energy Projects in Pakistan (https://mdpi.com/2071-1050/15/14/11289)
- (PDF) Stakeholder communication framework for successful implementation of community-based renewable energy projects (https://researchgate.net/publication/385812540_Stakeholder_communication_framework_for_successful_implementation_of_community-based_renewable_energy_projects)
- (PDF) Stakeholder engagement and influence: Strategies for successful energy projects (https://researchgate.net/publication/382514218_Stakeholder_engagement_and_influence_Strategies_for_successful_energy_projects)
- Sustainable Practices in Energy Corridor Development
- esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com (https://esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1890/ES14-00331.1)
- thebusinessresearchcompany.com (https://thebusinessresearchcompany.com/report/environmental-impact-assessments-global-market-report)
- inogenalliance.com (https://inogenalliance.com/blog-post/harnessing-renewable-energy-responsibly-role-environmental-impact-assessments)
- Navigating Regulatory Frameworks and Compliance
- Transmission Planning Reforms Finalized in FERC Order No. 1920 | White & Case LLP (https://whitecase.com/insight-alert/transmission-planning-reforms-finalized-ferc-order-no-1920)
- US Clean Power Development Sees Record Progress, As Well As Stronger Headwinds (https://wri.org/insights/clean-energy-progress-united-states)




