Overview
The article focuses on best practices for implementing grid connectivity solutions, emphasizing the importance of infrastructure evaluation, technology integration, regulatory compliance, collaboration, and sustainability. It supports this by detailing strategies such as upgrading outdated components, engaging stakeholders, and adopting smart technologies, all of which are essential for enhancing network resilience and efficiency in response to evolving energy demands and challenges.
Introduction
In the face of an ever-evolving energy landscape, the need for effective grid connectivity solutions has never been more critical. As organizations strive to meet contemporary energy demands, a robust infrastructure becomes paramount.
This article delves into the foundational elements of grid connectivity, exploring:
- The integration of advanced technologies
- The navigation of regulatory challenges
- The significance of collaboration among stakeholders
It further examines future trends driven by innovation and sustainability, highlighting the pressing need for modernization in response to the rise of renewable energy sources.
By understanding these dynamics, organizations can better position themselves to enhance grid reliability and efficiency, ensuring a resilient energy future.
Foundations of Effective Grid Connectivity Solutions
Effective grid connectivity solutions are predicated on a robust infrastructure designed to meet contemporary energy demands. To enhance reliability and efficiency, organizations should start with a thorough evaluation of their current capabilities, identifying outdated components that require upgrades. The integration of advanced technologies, particularly smart metering and automated control systems, is crucial for optimizing network performance.
For instance, grid connectivity solutions such as universal connectivity networks allow smooth power transfer from various sources, while advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) supports real-time data gathering and observation. This capability allows for proactive management of resource distribution, ensuring that utilities can adapt swiftly to fluctuations in demand and supply. As utilities encounter crucial times ahead, especially with the uncertainties of 2025, including possible policy and economic challenges, the adoption of these technologies becomes increasingly important in strengthening the network against potential issues.
Significantly, total funding for energy initiatives by development finance institutions attained USD 470 billion from 2013 to 2021, emphasizing the considerable investment in infrastructure. Additionally, recent case studies, such as 'Grid Connection Challenges and Reforms,' illustrate how reforms aimed at reducing connection queue bottlenecks have begun to yield results, with increased capacity for projects in late stages of development, particularly in solar PV. These advancements highlight the dedication to innovation and enhancement in network integration.
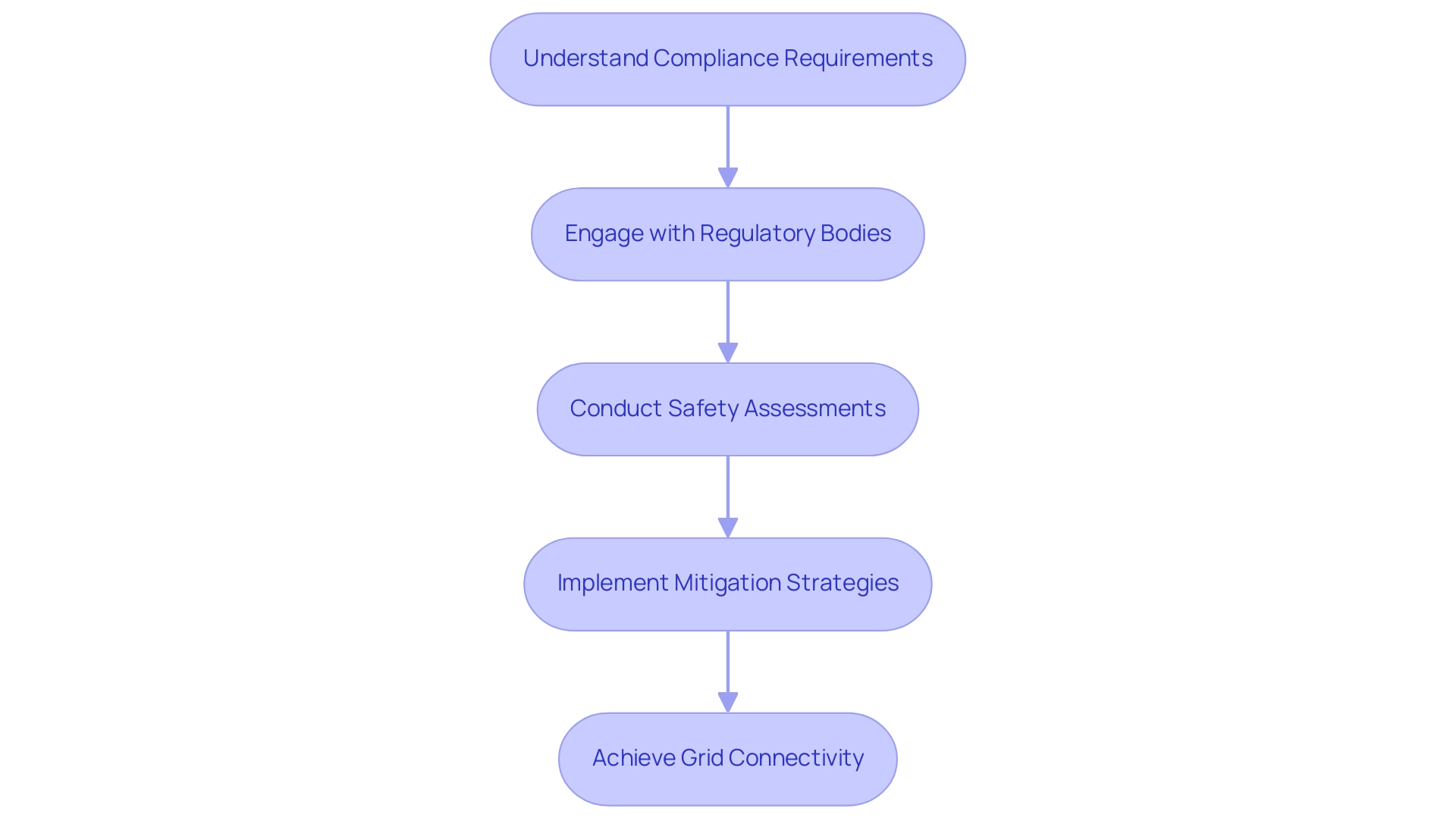
Navigating Regulatory and Safety Challenges in Grid Connectivity
Successfully executing grid connectivity solutions requires a thorough comprehension of the compliance and safety challenges inherent in the process. Organizations must navigate a complex landscape of local, state, and federal regulations that govern connections, which can differ considerably across jurisdictions. Adhering to safety standards, particularly those set forth by the National Electric Safety Code (NESC), is essential for ensuring infrastructure integrity and public safety.
Engaging with regulatory bodies early in the planning phase is critical, as it helps mitigate potential delays and facilitates the acquisition of all necessary permits. Furthermore, organizations should prioritize conducting thorough safety assessments and risk analysis. These evaluations not only identify potential hazards but also enable the implementation of effective mitigation strategies, fostering a safer working environment.
Considering recent trends, such as Consolidated Edison employing over 1,600 new staff in 2024—the highest since 1973—this workforce expansion highlights the industry's dedication to grid connectivity solutions. Furthermore, areas such as sub-Saharan Africa have experienced considerable advancements in connections, with the count of new links more than doubling since the 2020-2022 decline. This emphasizes the significance of following legal frameworks and safety standards.
As compliance specialist Rahul Bagotia highlights, 'The changing environment of network integration necessitates careful adherence efforts to tackle the governance challenges encountered in 2024,' stressing the importance for organizations to maneuver through these intricacies skillfully.
The Importance of Collaboration in Implementing Grid Solutions
Collaboration serves as a fundamental element in the success of network connectivity implementations. Engaging a diverse range of stakeholders—including engineering consultants, technology providers, and regulatory agencies—can yield innovative solutions tailored to the unique challenges of each project. For instance, collaborations with technology companies specializing in smart network solutions enable the integration of advanced tools designed to optimize system performance and reliability.
Michael Drtil, a lead author in the field, noted that smart technologies can assist in managing this transition while decreasing the necessity for expensive new infrastructure, and can also help to enhance systems to be more resilient and dependable. The significance of collaboration is further emphasized by the statistic that interconnected WAPP countries exchanged 6 TWh in 2021, which accounted for 7% of total power generated, highlighting the importance of power exchanges in enhancing grid reliability. Moreover, the World Economic Forum's Center for Energy and Materials is working towards a sustainable energy future through initiatives like the solar project in Indonesia, demonstrating successful collaboration in clean energy efforts.
Actively involving community stakeholders during the planning stages fosters transparency and builds public support, essential for mitigating potential opposition and navigating regulatory hurdles. Effective collaboration, characterized by regular communication and joint problem-solving efforts, not only streamlines project execution but also enhances overall outcomes, ultimately contributing to a more resilient network system with grid connectivity solutions. As highlighted in recent statistics, joint initiatives in network projects are expected to increase considerably in 2024, underscoring the growing acknowledgment of the worth that these alliances provide.
Moreover, the clean power transition requires substantial digitalization across all network domains to improve resilience and access.
Future Trends in Grid Connectivity: Innovations and Sustainability
As the power landscape continues to change, organizations are compelled to integrate innovation and sustainability into their connectivity strategies. The increase of renewable power sources, such as solar and wind, necessitates a thorough modernization of infrastructure to effectively manage the variability of these power inputs. Smart network technologies, which include decentralized power management systems and advanced analytics, are crucial for optimizing system performance and enhancing overall resilience.
Moreover, sustainability practices—such as reducing losses in power and enhancing operational efficiency—are becoming increasingly central to effective grid connectivity solutions. Investing in these advancements not only aids organizations in meeting regulatory requirements but also positions them as leaders in the shift toward a sustainable future. According to the latest insights from industry experts, the average power price across all sectors has reached 13.09 cents per kWh as of August 2024, reflecting a 2.7% year-over-year increase.
This underscores the urgent requirement for efficiency in resource management. Jaya Nagdeo, Research Manager in Power, utilities & renewables, notes, 'Rising wholesale prices, projected to increase by 19% on average between 2025 and 2028, combined with escalating distribution expenses, are likely to result in higher electricity bills for consumers.' Advancements in intelligent networks will be crucial in tackling these issues and providing a more dependable power supply.
As the International Energy Agency (IEA) continues to release updated data on electricity access, it becomes clear that the integration of renewable sources is not just beneficial; it is imperative for achieving future sustainability. The IEA's annual reports emphasize the ongoing challenges in achieving universal electricity access by 2030, underscoring the importance of integrating renewable energy and smart grid technologies in addressing these issues.
Conclusion
The exploration of effective grid connectivity solutions highlights the critical need for a robust infrastructure to meet modern energy demands. Integrating advanced technologies such as smart metering and automated control systems is essential for enhancing grid reliability and efficiency. Organizations must assess their current capabilities and adopt innovative tools to optimize performance and adapt to energy fluctuations.
Navigating regulatory and safety challenges is also vital. Engaging with regulatory bodies early in the process ensures compliance with safety standards, facilitating smoother project execution. The growth in workforce and the increase in new connections in regions like sub-Saharan Africa emphasize the importance of adhering to established frameworks that protect both infrastructure integrity and public safety.
Collaboration among stakeholders is fundamental to successful grid implementations. Partnering with technology providers and involving community stakeholders enables organizations to develop tailored strategies that enhance grid performance and build public support. This collaborative approach not only streamlines execution but also strengthens the resilience of the grid system.
As the energy landscape evolves, integrating innovation and sustainability into grid connectivity strategies becomes imperative. The transition to renewable energy requires modernization of infrastructure to manage energy variability effectively. Prioritizing sustainability practices and investing in smart grid technologies will help organizations meet regulatory requirements and position them as leaders in the sustainable energy sector.
In conclusion, modernizing grid connectivity is essential for a resilient energy future. By embracing advanced technologies, navigating regulatory complexities, fostering collaboration, and prioritizing sustainability, organizations can effectively address the challenges of an evolving energy landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is essential for effective grid connectivity solutions?
Effective grid connectivity solutions require a robust infrastructure that meets contemporary energy demands, starting with a thorough evaluation of current capabilities to identify outdated components that need upgrades.
How can organizations enhance the reliability and efficiency of their grid connectivity?
Organizations can enhance reliability and efficiency by integrating advanced technologies such as smart metering and automated control systems, which optimize network performance.
What role does advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) play in grid connectivity?
Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) supports real-time data gathering and observation, allowing for proactive management of resource distribution and enabling utilities to adapt swiftly to fluctuations in demand and supply.
Why is the adoption of advanced technologies important for utilities?
The adoption of advanced technologies is crucial for strengthening the network against potential issues, especially given the uncertainties anticipated in 2025, including policy and economic challenges.
How much funding for energy initiatives was provided by development finance institutions from 2013 to 2021?
Development finance institutions provided a total of USD 470 billion for energy initiatives from 2013 to 2021, highlighting significant investment in infrastructure.
What do recent case studies indicate about grid connection challenges?
Recent case studies, such as 'Grid Connection Challenges and Reforms,' show that reforms aimed at reducing connection queue bottlenecks have begun to yield results, increasing capacity for projects, particularly in solar PV, that are in late stages of development.
What are the key phases in the process of improving grid connectivity?
The key phases in the process include Evaluation (blue), Technology Integration (green), and Funding (orange), which are crucial steps in enhancing grid connectivity solutions.
List of Sources
- Foundations of Effective Grid Connectivity Solutions
- 2024 Wrap-Up: Advancing a More Powerful Grid (https://energy.gov/gdo/articles/2024-wrap-advancing-more-powerful-grid)
- 2025 Power and Utilities Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/power-and-utilities/power-and-utilities-industry-outlook.html)
- Overview and key findings – World Energy Investment 2024 – Analysis - IEA (https://iea.org/reports/world-energy-investment-2024/overview-and-key-findings)
- Electricity – Renewables 2024 – Analysis - IEA (https://iea.org/reports/renewables-2024/electricity)
- Navigating Regulatory and Safety Challenges in Grid Connectivity
- 2025 Power and Utilities Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/power-and-utilities/power-and-utilities-industry-outlook.html)
- Electricity access continues to improve in 2024 - after first global setback in decades – Analysis - IEA (https://iea.org/commentaries/electricity-access-continues-to-improve-in-2024-after-first-global-setback-in-decades)
- The Importance of Collaboration in Implementing Grid Solutions
- Smart grids - IEA (https://iea.org/energy-system/electricity/smart-grids)
- The ICT sector needs to drive energy innovation to handle growing data volumes sustainably. Here’s how. (https://weforum.org/stories/2024/05/data-growth-drives-ict-energy-innovation)
- 2025 Power and Utilities Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/power-and-utilities/power-and-utilities-industry-outlook.html)
- Future Trends in Grid Connectivity: Innovations and Sustainability
- Electricity access continues to improve in 2024 - after first global setback in decades – Analysis - IEA (https://iea.org/commentaries/electricity-access-continues-to-improve-in-2024-after-first-global-setback-in-decades)
- 2025 Power and Utilities Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/power-and-utilities/power-and-utilities-industry-outlook.html)
- Top 10 Smart Grid Trends in 2025 | StartUs Insights (https://startus-insights.com/innovators-guide/smart-grid-trends)




