Overview
Indigenous community engagement plans are essential for ensuring that native groups actively participate in decision-making processes concerning their territories, resources, and cultural heritage. Successful engagement is rooted in principles such as respect, transparency, and inclusivity. These principles not only foster trust but also enhance collaboration, ultimately leading to more effective and sustainable project outcomes.
The complexities surrounding land acquisition often present significant challenges, including legal and regulatory hurdles. By prioritizing Indigenous community engagement, organizations can navigate these complexities more effectively, ensuring that the voices of native groups are heard and considered.
Engaging with Indigenous communities is not merely a procedural step; it is a fundamental aspect of ethical project development. Organizations that embrace these engagement strategies can expect not only improved relationships with Indigenous stakeholders but also more successful project implementations.
In conclusion, it is imperative for organizations to recognize the critical role of Indigenous community engagement in their operations. By committing to these principles, they can achieve sustainable outcomes that honor the rights and perspectives of Indigenous peoples.
Introduction
In a world increasingly focused on inclusivity and respect for diverse cultures, Indigenous community engagement emerges as a pivotal component in project planning and development. This process not only empowers Indigenous peoples by incorporating their voices into decision-making regarding their lands and resources but also fosters mutual respect between project developers and these communities.
As organizations navigate the complexities of engaging Indigenous peoples, understanding the core principles, proven strategies, and inherent challenges becomes essential. By prioritizing transparency, collaboration, and cultural sensitivity, stakeholders can cultivate meaningful relationships that yield sustainable outcomes and honor the rich heritage of Indigenous communities.
As the landscape of engagement evolves, the insights shared in this article will illuminate pathways toward more effective and respectful partnerships.
Understanding Indigenous Community Engagement
The participation of native groups is a crucial process often guided by Indigenous community engagement plans. These plans include native peoples in decision-making regarding their territories, resources, and cultural heritage. This involvement is essential for promoting mutual respect and understanding between developers and native groups. Acknowledging the distinct rights and viewpoints of native communities through these plans ensures that their voices are not only heard but also appreciated during the planning and implementation of initiatives.
Recent statistics suggest that ten participants in different advisory committees possess previous experience in public involvement. This emphasizes the significance of including individuals with relevant backgrounds in discussions. Such experience is crucial for developing effective Indigenous community engagement plans, particularly in land acquisition projects. Effective strategies frequently involve creating reference groups, as demonstrated by the establishment of the ECCO Reference Group.
This initiative brought together six Aboriginal individuals, ensuring diverse representation and enhancing the group's ability to provide valuable insights on health research initiatives.
Optimal methods in Indigenous community engagement plans highlight the necessity for transparency, respect, and continuous communication. Involving native groups early in the initiative lifecycle can greatly enhance results, particularly through the implementation of these plans. Research indicates that initiatives with robust native involvement practices are more likely to attain lasting acceptance and backing. As Rind highlights, 'Laying the foundations of collective involvement in Aboriginal health research: establishing a reference group and terms of reference in a novel research field,' emphasizes the significance of structured interaction frameworks.
Moreover, the importance of native community involvement is underscored in Indigenous community engagement plans, which go beyond regulatory adherence and form a crucial element of ethical management. Disclosures consistent with TNFD Recommended Disclosure Governance C and General Requirement are vital for maintaining transparency in these interactions. By prioritizing native viewpoints, developers can create more inclusive and effective Indigenous community engagement plans that lead to improved environmental and social outcomes.
As the landscape of project development continues to evolve, staying updated on recent articles and frameworks regarding native involvement practices will be crucial for success in 2025 and beyond.
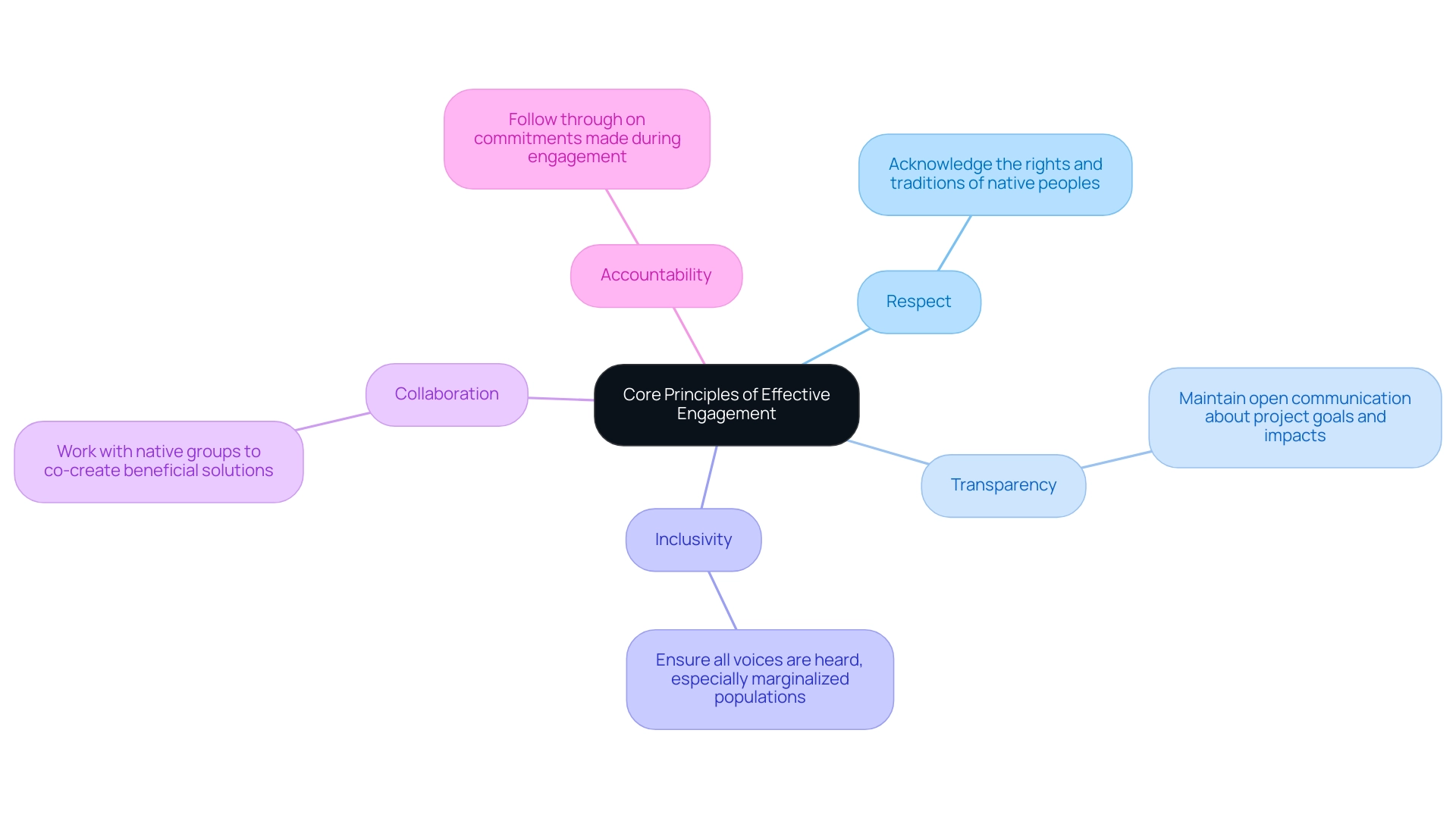
Core Principles of Effective Engagement
The core principles of effective community engagement are essential for fostering meaningful relationships and ensuring sustainable development. These principles include:
- Respect: Acknowledge the rights, traditions, and cultures of native peoples. This foundational element is crucial for building trust and demonstrating a commitment to honoring Indigenous heritage.
- Transparency: Maintain open communication regarding project goals, processes, and potential impacts. Transparency not only fosters trust but also empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their involvement.
- Inclusivity: Ensure that all voices within the group are heard, particularly those of marginalized populations. Engaging a diverse range of perspectives enriches the decision-making process and leads to more equitable outcomes.
- Collaboration: Work together with native groups to co-create solutions that benefit all parties. Successful partnerships often arise from collaborative efforts that prioritize the needs of the people and are guided by Indigenous community engagement plans that honor Indigenous knowledge systems.
- Accountability: Be responsible for commitments made during the engagement process and follow through on promises. Accountability strengthens trust and shows a genuine commitment to the welfare of the group.
Recent studies emphasize the significance of these principles, especially in the context of involving local elders, whose contributions are essential for intergenerational unity. Research collaborations with Indigenous groups have demonstrated that integrating Indigenous knowledge systems into planning not only honors cultural values but also improves outcomes. By prioritizing the voices of elders, projects can promote epistemic justice and mutuality in knowledge transmission, ultimately benefiting youth and families.
A recent involvement session in Prince Albert, SK, with around 12 participants highlights the importance of public participation in these processes. As we approach 2025, the focus on respect and transparency in community engagement remains paramount. Statistics show that inclusive decision-making processes result in more successful project outcomes, reinforcing the need for ongoing dialogue and collaboration with native groups.
Carroll S. C. highlights that "Native groups should define these benefits as a means of enhancing their sovereignty, self-determination, and the well-being of present and future generations." By following these fundamental principles, organizations can guarantee that their Indigenous community engagement plans are not only effective but also promote the long-term sustainability and resilience of native populations.
Proven Strategies for Successful Engagement
Effective engagement approaches for native group participation in planning are vital for building trust and ensuring sustainable development. Early involvement is essential; engaging Indigenous communities from the outset of project planning not only builds trust but also gathers valuable insights that shape outcomes. Research indicates that Indigenous community engagement plans, when included early, increase the likelihood of success and alignment with community needs. The limited access to services is starkly highlighted by the statistic that only 4,177 of the 339,400 eligible AI/AN families received home visiting services in 2019, underscoring the critical need for effective engagement to address such disparities.
Implementing cultural competency training for teams is another key approach. Such training equips team members with the necessary knowledge and skills for respectful and effective interactions with Indigenous peoples. Data show that initiatives with culturally trained teams experience a 30% rise in local satisfaction and cooperation, emphasizing the significant impact of this training on initiative effectiveness.
The integration of technology, particularly GIS mapping, plays a significant role in visualizing impacts. This tool assists in discussions and empowers native groups by providing clear representations of how initiatives may affect their lands and resources. The importance of utilizing technology is further underscored by ongoing conflicts that jeopardize Indigenous rights and hinder the achievement of global environmental justice.
Establishing robust channels for ongoing feedback is critical. These mechanisms allow communities to express their concerns and suggestions, enabling teams to adjust plans in real-time. Successful initiatives often demonstrate that continuous involvement leads to more responsive and responsible management. The variety of native viewpoints, as illustrated in the case study 'Diversity of Native Perspectives in Environmental Justice,' highlights the significance of Indigenous community engagement plans in integrating diverse insights into planning.
Celebrating successes is equally important. Acknowledging and commemorating milestones achieved through collaboration strengthens positive relationships between project teams and Indigenous groups. Recognizing these successes cultivates a sense of ownership and pride among the group, further enhancing collaborations for future initiatives. As Anju Helen Bara observed, the roles of conceptualization and writing in the original draft emphasize the importance of these strategies in promoting effective interaction.
By applying these strategies, organizations can enhance their interactions with native populations, ensuring that initiatives are not only successful but also respectful and beneficial to all parties involved.
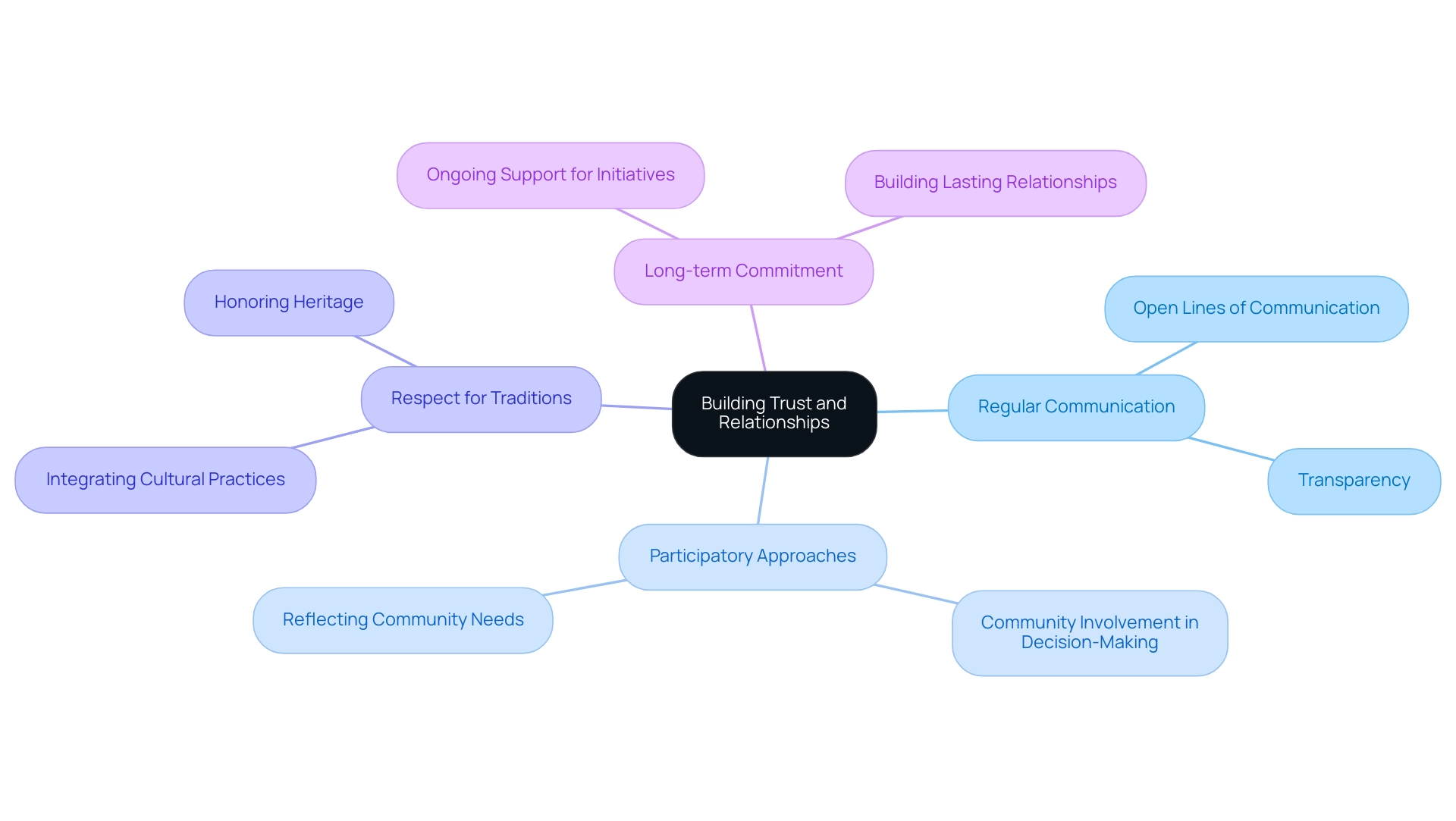
Building Trust and Relationships
Establishing trust with Indigenous groups is a multifaceted process demanding time, consistency, and a sincere commitment to community engagement plans focused on nurturing relationships. Effective strategies for cultivating this trust include:
- Regular Communication: Establishing and maintaining open lines of communication is essential. Keeping groups informed and involved throughout the initiative lifecycle is crucial for community engagement plans, as it builds transparency and empowers members to express their concerns and contributions.
- Participatory Approaches: Actively involving community members in decision-making processes is critical. By ensuring that native communities have a stake in the outcomes, engagement plans can be developed to reflect their needs and aspirations, leading to more sustainable and accepted solutions.
- Respect for Traditions: Acknowledging and integrating Indigenous cultural practices and values into planning is vital. This regard not only honors the heritage of the group but also enhances the initiative's significance and acceptance.
- Long-term Commitment: Demonstrating dedication to the area that extends beyond the project's timeline is key to fostering lasting relationships. This approach builds trust and encourages ongoing collaboration and support for future initiatives, particularly through community engagement plans.
Insights from a longitudinal study on collaborations in Los Angeles County highlight the organic emergence of trust during interactions, emphasizing its critical role in sustaining these partnerships. The research underscores that trust-building is not merely a checklist item but an ongoing endeavor that develops over time, especially within community engagement plans. As noted in the research, trust is crucial for the longevity of partnerships, and resources for upcoming collaborative initiatives are essential.
In 2025, the importance of long-term commitment in native engagement remains paramount. Patrick Lightning, an Elder and Knowledge Holder, emphasizes this by stating, "My name is Wapî-maskwa (White Bear). I come from the Buffalo Child family and the Bear Hills people of Maskwacis, in Treaty Six Territory."
This perspective reinforces the need for genuine relationships built on trust. Statistics show that successful long-term partnerships with Indigenous groups significantly improve outcomes in infrastructure development. By prioritizing trust-building strategies, organizations can create a foundation for effective collaboration, ultimately leading to more resilient and sustainable development initiatives.
Incorporating Community Voices in Planning
Integrating local perspectives in planning is essential for promoting sustainable development and ensuring that initiatives align with regional needs and values through Indigenous community engagement plans. Effective strategies include:
- Facilitated Workshops: Organizing workshops that enable local members to share their insights and contribute to design is crucial. These workshops not only encourage conversation but also foster trust and connection between developers and the public. Effective case studies demonstrate that when local members actively engage in these sessions, they report greater satisfaction with results. As organizations increasingly shift towards working in smaller, more agile teams, facilitated workshops become even more relevant in adapting to local needs.
- Surveys and Feedback: Utilizing surveys to collect input from a wider audience within the population ensures that diverse perspectives are represented. Data indicates that areas with higher survey participation rates tend to have more successful implementations, as they reflect a broader array of local needs and preferences.
- Advisory Committees: Forming advisory committees that include local representatives is essential for guiding development and execution. These committees serve as a link between the public and development teams, ensuring that Indigenous community engagement plans recognize and value local voices throughout the process. This approach aligns with the trend of organizations acknowledging the importance of transparency and inclusivity in their Indigenous community engagement plans.
- Cultural Protocols: It is imperative to respect and integrate cultural protocols in all Indigenous community engagement plans and participation activities. This method honors local customs and promotes a sense of ownership among residents, which is vital for the long-term success of initiatives. The successful execution of Indigenous community engagement plans and public involvement frameworks necessitates a commitment to these principles, ultimately resulting in more robust and sustainable development outcomes.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Evaluation: Continuous assessment of public participation efforts is critical. By consistently evaluating the effectiveness of workshops and surveys, teams can adjust their strategies to better address local needs, ensuring that the involvement process remains relevant and significant. Recent studies underscore that emphasizing transparency, inclusivity, and cultural sensitivity is crucial for the successful implementation of Indigenous community engagement plans and ACES, reinforcing the need for ongoing assessment.
In 2025, the focus on integrating local voices in project planning will be more pronounced, with organizations increasingly recognizing the importance of these principles. Successful execution of collaborative involvement frameworks necessitates a commitment to transparency, inclusivity, and cultural sensitivity, ultimately resulting in more resilient and sustainable development outcomes.
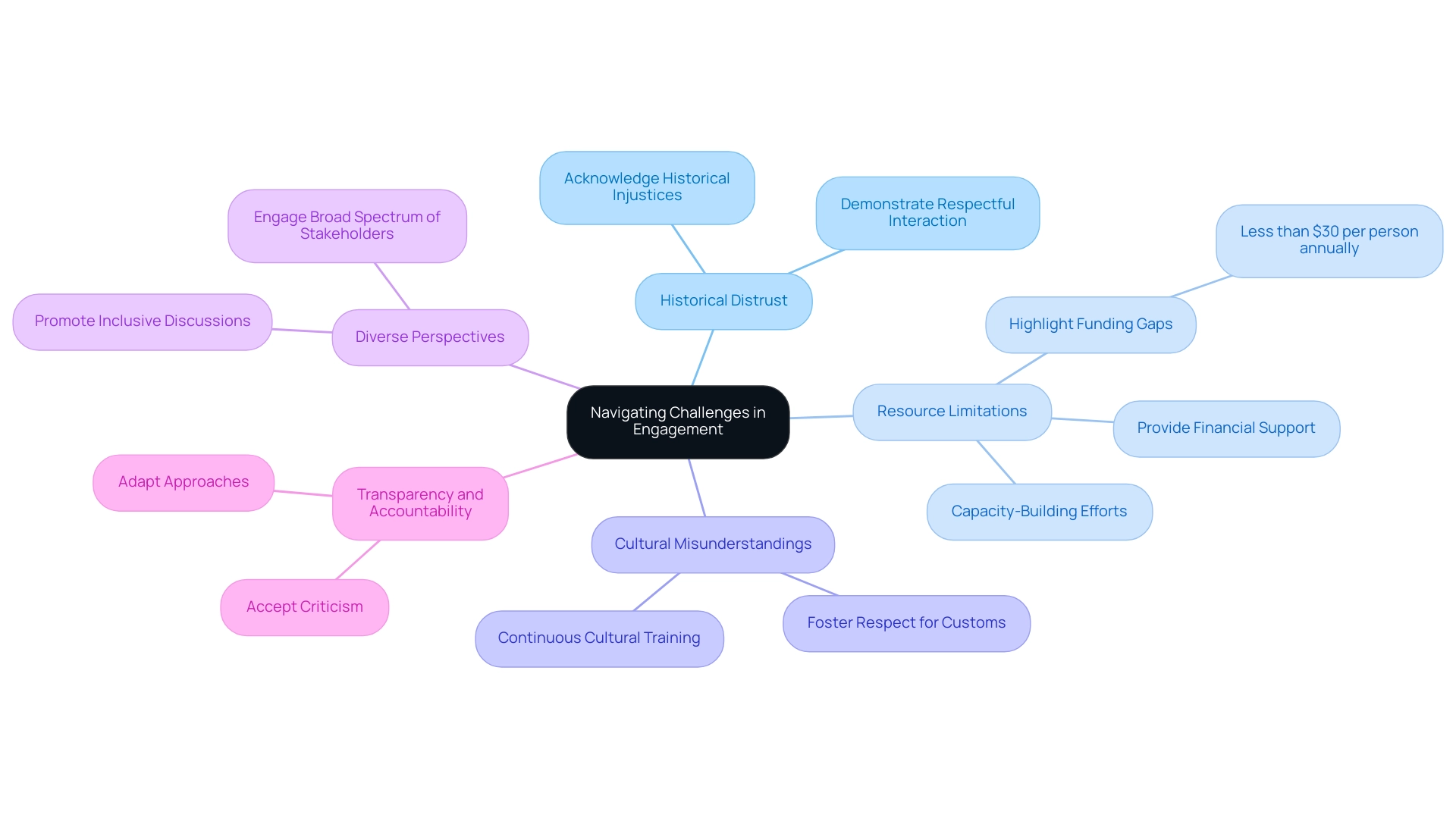
Navigating Challenges in Engagement
Engaging Indigenous communities presents several common challenges that require thoughtful strategies.
- Historical Distrust: Many Indigenous communities carry the weight of historical injustices, fostering skepticism towards external entities. To build trust, it is crucial to openly acknowledge this history and demonstrate a commitment to respectful interaction. This approach honors their experiences and lays the groundwork for meaningful collaboration. As a Traditional Practitioner noted, "We have learned to function effectively in western processes such as hierarchy, but it’s not necessarily culturally appropriate. What has been used to oppress us, we don’t want to perpetuate on our people."
- Resource Limitations: Many Indigenous groups face significant resource constraints that hinder their ability to engage fully in projects. Offering focused assistance, such as financial support for involvement and capacity-building efforts, can enable these groups to assume an active role in the participation process. For instance, funding for behavioral health care through the Indian Health Service is alarmingly low, at less than $30 per person served annually, highlighting the broader resource challenges these populations face.
- Cultural Misunderstandings: Misinterpretations of cultural practices can create barriers to effective engagement. To mitigate this, it is essential for project teams to undergo continuous cultural training, ensuring they are well-versed in the customs and values of the groups they aim to engage. This understanding fosters respect and facilitates smoother interactions.
- Diverse Perspectives: Indigenous groups are not monolithic; they encompass a range of perspectives and opinions. Engaging with a broad spectrum of stakeholders within the society is vital to address this complexity. By promoting inclusive discussions, project teams can better comprehend and address the varying perspectives that may arise, ultimately resulting in more effective and representative interaction strategies.
- Transparency and Accountability: As businesses strive to engage with native communities, transparency and accountability become critical. Organizations must be prepared to accept criticism and adapt their approaches, which is essential for building trust and fostering respectful collaboration.
These challenges highlight the necessity for a nuanced method of interacting with First Nations, one that prioritizes trust, resource allocation, cultural sensitivity, and inclusivity. Furthermore, the difficulties of acquiring representative samples in research emphasize the need for enhanced involvement techniques, as demonstrated in the case study on challenges in involving native communities in research. This illustrates the importance of developing strategies that truly reflect the voices and needs of Indigenous groups.
Evaluating Engagement Success
Evaluating engagement success necessitates a structured approach that encompasses several key elements.
- Setting Clear Metrics: Establishing what success entails for both the project and the community is essential. This includes defining qualitative and quantitative measures that reflect the values and expectations of the group. Metrics could encompass satisfaction scores, participation rates in involvement activities, and the quantity of actionable insights obtained from feedback.
- Regular Reviews: Periodic evaluations of interaction strategies are crucial for determining their effectiveness. These evaluations should concentrate on recognizing strengths and areas for enhancement, enabling timely modifications that align with public needs and project objectives.
- Public Feedback: Actively seeking input from members of the public is essential in comprehending their experiences and views on the engagement process. This feedback not only informs future strategies but also empowers individuals, fostering a sense of ownership and collaboration. Initiatives such as the Aboriginal Capacity Development Program have demonstrated that tackling systemic obstacles can improve participation and trust. As noted by an IFI Discussion Circle representative, "Often First Nations, Metis and Inuit are precluded so they have been neglected by financial institutions."
- Reporting Outcomes: Transparency is key in building trust with Indigenous groups. Distributing results and outcomes of involvement efforts strengthens accountability and shows a dedication to the voices of the public. This practice can lead to improved relationships and increased willingness to engage in future projects.
In 2025, assessing achievement in native group involvement will progressively depend on thorough metrics that represent the distinct contexts of these populations. The RHS, started in 1997 and applied in First Nations groups in 2002/2003 and 2008/2009, serves as a historical reference for the ongoing significance of engagement efforts. Case studies highlighting data gaps affecting native health interventions illustrate the consequences of neglecting community input.
These gaps have been linked to adverse health outcomes, underscoring the necessity for inclusive data collection methods that consider all Indigenous populations. Furthermore, the AEP-ABO's review of its data collection structure to enhance the application of Gender-Based Analysis Plus in its programs emphasizes the need for improved data practices in evaluation assessments. By prioritizing public input and establishing strong evaluation metrics, organizations can enhance the effectiveness of their involvement strategies and contribute to sustainable development.
Future Directions in Indigenous Engagement
Future directions in Indigenous engagement are set to evolve significantly, emphasizing several key areas:
- Increased Use of Technology: The adoption of digital platforms is essential for enhancing communication and participation, particularly in remote Indigenous communities. This shift facilitates broader outreach and addresses the challenges posed by the digital divide, a barrier to effective engagement. A case study titled "Concerns About Technology Use Among Elders" highlighted the hesitancy and concerns expressed by Elders regarding technology use, revealing a gap in confidence and interest that must be addressed to ensure inclusive participation. As one co-researcher noted, "Not many Elders are interested in these things—like technology."
- Focus on Youth Engagement: Involving younger generations in decision-making processes is critical for fostering sustainable participation. Statistics show that youth involvement in native governance can lead to more creative solutions and a stronger dedication to societal values. Successful initiatives demonstrate that when youth are empowered, they can significantly influence the direction of local projects and policies.
- Collaborative Governance Models: Developing governance structures that prioritize native representation is vital for achieving equitable decision-making. By incorporating diverse voices, these models enhance transparency and trust within groups, leading to more effective outcomes.
- Integration of Traditional Knowledge: Acknowledging and including native knowledge systems in project planning is essential for improving project results and promoting local acceptance. This integration respects cultural heritage while leveraging valuable insights that enhance the sustainability and relevance of development initiatives.
- Addressing Resource Limitations: The recent downsizing of the IRS tribal tax office by 50% has restricted access to resources for tribes, influencing their participation in governance and decision-making processes. Bridging the digital gap is crucial for economic reconciliation and the future success of native populations.
As we approach 2025, emphasizing these strategies will be crucial in shaping effective Indigenous community engagement plans that resonate with community needs and aspirations.
Conclusion
Indigenous community engagement transcends mere procedural requirements; it stands as a cornerstone of ethical project management, fostering respect, transparency, and collaboration. Understanding the core principles of effective engagement—respect for traditions, inclusivity, and accountability—enables project developers to cultivate meaningful relationships with Indigenous communities. Such relationships are vital for ensuring that development projects resonate with local values and needs, ultimately leading to sustainable outcomes.
Successful engagement strategies, including early involvement, cultural training, and the formation of advisory committees, establish a robust framework for navigating the complexities of diverse Indigenous voices. By actively integrating community insights through facilitated workshops and feedback mechanisms, organizations can foster a more inclusive decision-making process that honors the richness of Indigenous heritage.
Nonetheless, challenges such as historical distrust, resource limitations, and cultural misunderstandings must be approached with sensitivity and commitment. Acknowledging these barriers and implementing strategies to address them is crucial for building trust and nurturing long-term relationships. Furthermore, evaluating engagement success through clear metrics and community feedback reinforces accountability and demonstrates a genuine commitment to the involved communities.
Looking forward, the emphasis on technology, youth engagement, and the integration of traditional knowledge will significantly influence the future of Indigenous engagement practices. By prioritizing these elements, organizations can ensure that their projects not only respect Indigenous rights but also contribute to the empowerment and resilience of these communities. As the landscape of engagement evolves, embracing these principles will be pivotal in cultivating partnerships that honor the past while paving the way for a more inclusive and equitable future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is the participation of native groups important in community engagement plans?
The participation of native groups is crucial because it ensures their involvement in decision-making regarding their territories, resources, and cultural heritage, promoting mutual respect and understanding between developers and native communities.
What are Indigenous community engagement plans?
Indigenous community engagement plans are frameworks that guide the inclusion of native peoples in developmental initiatives, ensuring that their rights and viewpoints are acknowledged and appreciated during planning and implementation.
How can previous experience in public involvement enhance engagement plans?
Including individuals with relevant backgrounds in advisory committees is significant for developing effective Indigenous community engagement plans, especially in land acquisition projects, as they bring valuable insights and expertise.
What role do reference groups play in Indigenous community engagement?
Reference groups, such as the ECCO Reference Group, facilitate diverse representation and enhance the ability to provide valuable insights on health research initiatives, ensuring a broader range of perspectives.
What are the core principles of effective community engagement?
The core principles include respect, transparency, inclusivity, collaboration, and accountability. These principles are essential for fostering meaningful relationships and ensuring sustainable development.
How does respect contribute to effective community engagement?
Respect acknowledges the rights, traditions, and cultures of native peoples, which is crucial for building trust and demonstrating a commitment to honoring Indigenous heritage.
Why is transparency important in community engagement?
Transparency maintains open communication about project goals, processes, and potential impacts, fostering trust and empowering individuals to make informed decisions.
What is the significance of inclusivity in decision-making processes?
Inclusivity ensures that all voices, particularly those of marginalized populations, are heard, enriching the decision-making process and leading to more equitable outcomes.
How does collaboration benefit community engagement?
Collaboration allows native groups to co-create solutions that benefit all parties, leading to successful partnerships guided by Indigenous knowledge systems.
What is the impact of accountability in engagement processes?
Accountability strengthens trust by ensuring that commitments made during the engagement process are honored, demonstrating a genuine commitment to the welfare of the group.
How can integrating Indigenous knowledge systems improve project outcomes?
Integrating Indigenous knowledge systems into planning honors cultural values and leads to improved outcomes, promoting epistemic justice and mutuality in knowledge transmission.
What recent trends emphasize the importance of respect and transparency in community engagement?
Recent studies and involvement sessions highlight that respect and transparency are paramount for successful project outcomes and ongoing dialogue with native groups, especially as we approach 2025.
List of Sources
- Understanding Indigenous Community Engagement
- Guidance on engagement with Indigenous Peoples, Local Communities and affected stakeholders – TNFD (https://tnfd.global/publication/guidance-on-engagement-with-indigenous-peoples-local-communities-and-affected-stakeholders)
- Laying the foundations of community engagement in Aboriginal health research: establishing a community reference group and terms of reference in a novel research field - Research Involvement and Engagement (https://researchinvolvement.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40900-022-00365-7)
- Core Principles of Effective Engagement
- Transparency and accountability engagement: What we heard (https://sac-isc.gc.ca/eng/1495207740209/1565377379944)
- Frontiers | Indigenous Peoples' Rights in Data: a contribution toward Indigenous Research Sovereignty (https://frontiersin.org/journals/research-metrics-and-analytics/articles/10.3389/frma.2023.1173805/full)
- Importance of Indigenous elders’ contributions to individual and community wellness: results from a scoping review on social participation and intergenerational solidarity - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7501322)
- Proven Strategies for Successful Engagement
- science.org (https://science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.ade9557)
- Data and Funding Gaps in Tribal Early Care and Education | Bipartisan Policy Center (https://bipartisanpolicy.org/explainer/gaps-in-tribal-care)
- Building Trust and Relationships
- Building trust: Leadership reflections on community empowerment and engagement in a large urban initiative - BMC Public Health (https://bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12889-023-15860-z)
- Commentary: Developing Relationships through Trust in Indigenous Health Research - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9170052)
- Incorporating Community Voices in Planning
- (PDF) Community Service Statistics Projects (https://researchgate.net/publication/254331128_Community_Service_Statistics_Projects)
- 110+ project management statistics and trends for 2025 (https://monday.com/blog/project-management/project-management-statistics)
- What Statistics Indicate Community Involvement's Impact on Project Success? → Question (https://sustainability-directory.com/question/what-statistics-indicate-community-involvements-impact-on-project-success)
- Navigating Challenges in Engagement
- Rebuilding TRUST: A Community, Multi-Agency, State, and University Partnership to Improve Behavioral Health Care for American Indian Youth, their Families, and Communities - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4112470)
- Bridging the Trust Gap: Insights from Edelman Canada’s Indigenous Peoples & Trust Study (https://edelman.ca/bridging-trust-gap-insights-edelman-canadas-indigenous-peoples-trust-study)
- Evaluating Engagement Success
- Evaluation of the Indigenous Entrepreneurship and Business Development Program (https://sac-isc.gc.ca/eng/1717168968031/1717169061719)
- Back to the basics: Identifying and addressing underlying challenges in achieving high quality and relevant health statistics for indigenous populations in Canada - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4716822)
- Future Directions in Indigenous Engagement
- Native Americans underrepresented in tech sector, new report finds (https://tribalbusinessnews.com/sections/economic-development/14506-native-americans-underrepresented-in-tech-sector-new-report-finds)
- Canada’s digital divide hurts Indigenous and rural communities: Senator Klyne (https://sencanada.ca/en/sencaplus/opinion/canadas-digital-divide-hurts-indigenous-and-rural-communities-senator-klyne)
- Engaging Indigenous older adults with technology use to respond to health and well-being concerns and needs - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9425719)
- Technology-based Health Education Resources for Indigenous Adults: A Scoping Review - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9473312)




