Overview
Best practices for rural wind farm siting involve proactive community engagement, compliance with regulatory frameworks, and thorough environmental assessments to ensure local support and minimize ecological impact. The article emphasizes that involving residents through informational meetings and addressing their concerns fosters trust, while understanding state and local regulations, as well as conducting environmental evaluations, enhances the likelihood of successful project implementation.
Introduction
The successful siting of wind farms hinges on a multifaceted approach that prioritizes community engagement and regulatory compliance. As the demand for renewable energy surges, project developers are increasingly recognizing the importance of fostering relationships with local residents, addressing their concerns, and communicating the myriad benefits of wind energy.
This article delves into the critical aspects of wind farm siting, including:
- The necessity of proactive community involvement
- Navigating complex regulatory frameworks
- Highlighting the economic and environmental advantages of wind energy
Furthermore, it explores strategies for combating misinformation and emphasizes best practices for site selection that balance community needs with ecological considerations. By understanding and implementing these elements, developers can not only enhance project acceptance but also contribute to a more sustainable energy future.
Engaging Communities: The Key to Successful Wind Farm Siting
Efficient placement of renewable energy farms relies fundamentally on proactive public involvement in rural wind farm siting. To foster a supportive environment, project developers should conduct:
- Informational meetings
- Workshops
- Open forums aimed at educating residents about the benefits of wind energy
Involving the public through surveys enables developers to gather valuable feedback, identifying local concerns such as:
- Noise
- Aesthetics
- Land use
Significantly, on average, turbines were roughly 150 feet (46 meters) nearer to homes each year during the installation period, emphasizing local concerns regarding proximity. Moreover, forming a community advisory board can greatly improve connections with residents, promoting ongoing dialogue throughout the lifecycle. A case study titled 'Impact of Turbine Farms on Human Health' illustrates that renewable energy, as a clean source of electricity, reduces health risks associated with air pollution, with no evidence of direct health risks from turbine exposure.
This inclusive approach not only fosters trust but also reduces potential resistance to rural wind farm siting initiatives. As Sebastian E. Winter observes, the equilibrium of our resident microbial populations is connected to numerous chronic human diseases, highlighting the significance of addressing health issues. By prioritizing community engagement, developers can ensure that initiatives align with local expectations and contribute to a more sustainable future for resources.
Navigating Regulatory Frameworks: State vs. Local Control in Wind Farm Siting
Navigating the regulatory landscape for rural wind farm siting requires a comprehensive understanding of the varying frameworks that exist both at the state and local levels. Developers must familiarize themselves with overarching state policies that govern renewable initiatives, as these often dictate general guidelines and approval processes. The Public Utility Commission has authority over energy siting for facilities greater than 75 MW, while local governments exert considerable influence through their own zoning ordinances, which can significantly impact siting decisions.
According to the Siting Coordination Office, local governments have authority over most siting decisions related to turbines, but the Siting Coordination Office has primary authority over siting power generating facilities with capacity of 75 MW or more. This delineation underscores the necessity for developers to engage local planning boards early in the lifecycle to ensure compliance with these regulations.
Research shows that the quantity of ordinances adopted has increased significantly, with 16 times as many implemented in 2021 compared to 2003, indicating a rising trend toward localized management of renewable initiatives. Specific local zoning regulations can determine the rural wind farm siting of renewable energy initiatives and the conditions under which they can be established, making it essential for developers to conduct thorough research on these laws. Furthermore, the case study titled 'Distributed Wind Animation – Text Version' highlights potential use cases for distributed power generation, emphasizing the significance of access to information on these applications for a broader audience.
By promoting transparent dialogue with local authorities and aligning their initiatives more closely with public expectations and legal standards, developers can enhance the likelihood of gaining local support—an essential element for successful renewable energy development.
Highlighting Benefits: Economic and Environmental Advantages of Wind Energy
Wind power offers numerous economic and ecological advantages that are essential in gaining public backing for new initiatives. From a financial perspective, the building and functioning stages of renewable energy farms greatly aid in job generation within nearby areas. In fact, the renewable power sector has proven to be a catalyst for employment, with numerous jobs created throughout the duration of these initiatives.
Furthermore, these installations can lead to increased tax revenues for local governments, which are vital for funding public services and enhancing community welfare. For example, in 2022, renewable projects on private land produced roughly $935 million in land lease payments to rural landowners, highlighting the financial influx that comes with these developments. Additionally, large distributed renewable energy had a levelized cost of $78 per megawatt-hour, providing a clearer economic context for the discussion around land requirements for such projects.
Environmentally, this energy source stands out as a clean, renewable resource that diminishes reliance on fossil fuels, leading to a notable decrease in greenhouse gas emissions. Recent studies indicate that turbine farms not only contribute to cleaner air but also positively influence local tourism. Researchers at the University of Rhode Island discovered that tourism near Rhode Island’s Block Island Energy Farm rose after the establishment of the energy facility, demonstrating the wider advantages that such projects can offer to local areas.
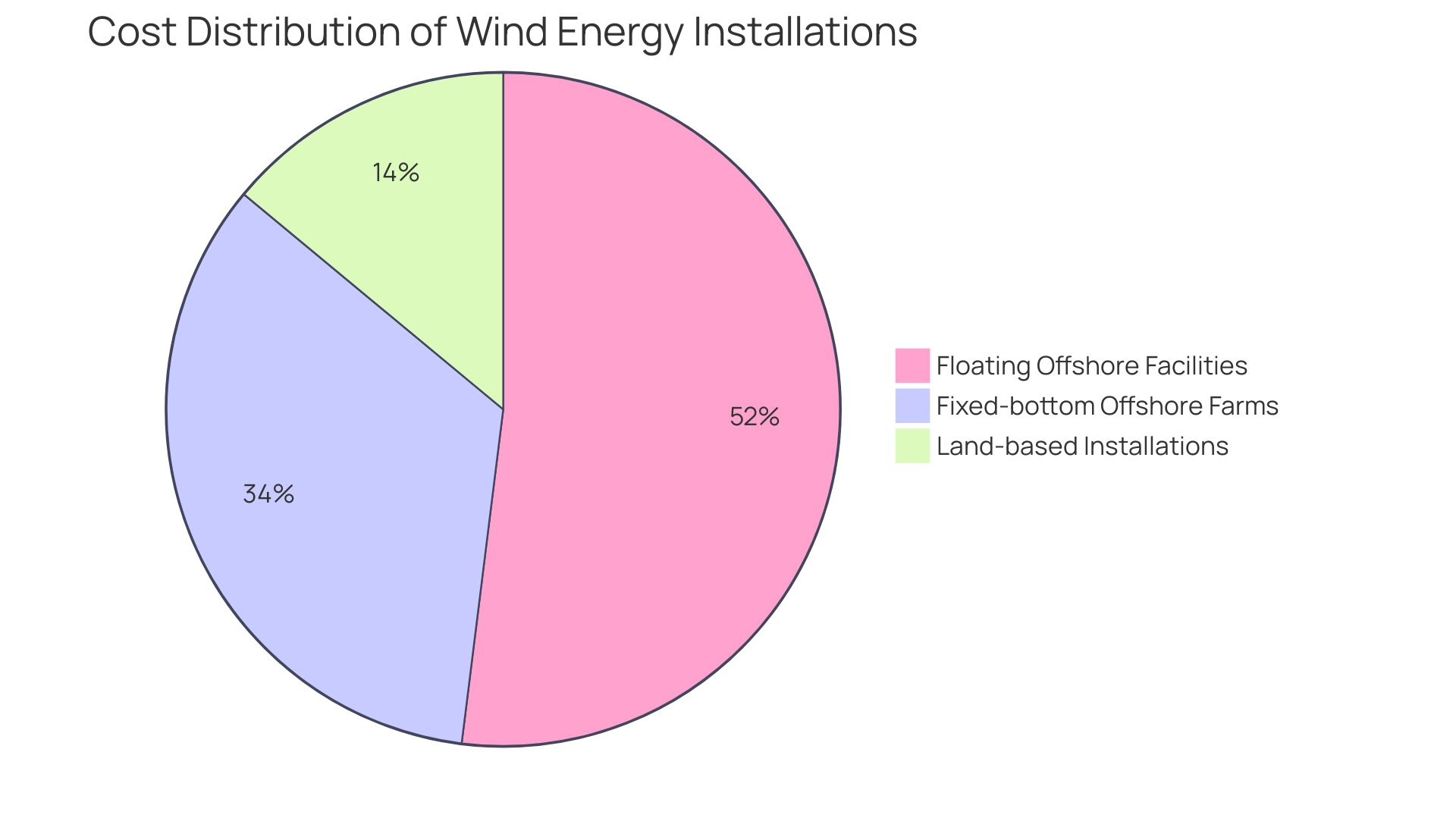
Additionally, the pricing for aerogeneration fluctuates considerably depending on the type of setup; for instance:
- The levelized cost of power for land-based installations was $39 per megawatt-hour.
- Fixed-bottom offshore farms averaged $95 per megawatt-hour.
- Floating offshore facilities had a cost of $145 per megawatt-hour.
By effectively conveying these economic and environmental benefits in local presentations, stakeholders can foster strong backing for renewable initiatives and showcase a firm dedication to sustainable development.
Combatting Misinformation: Building Trust in Wind Energy Projects
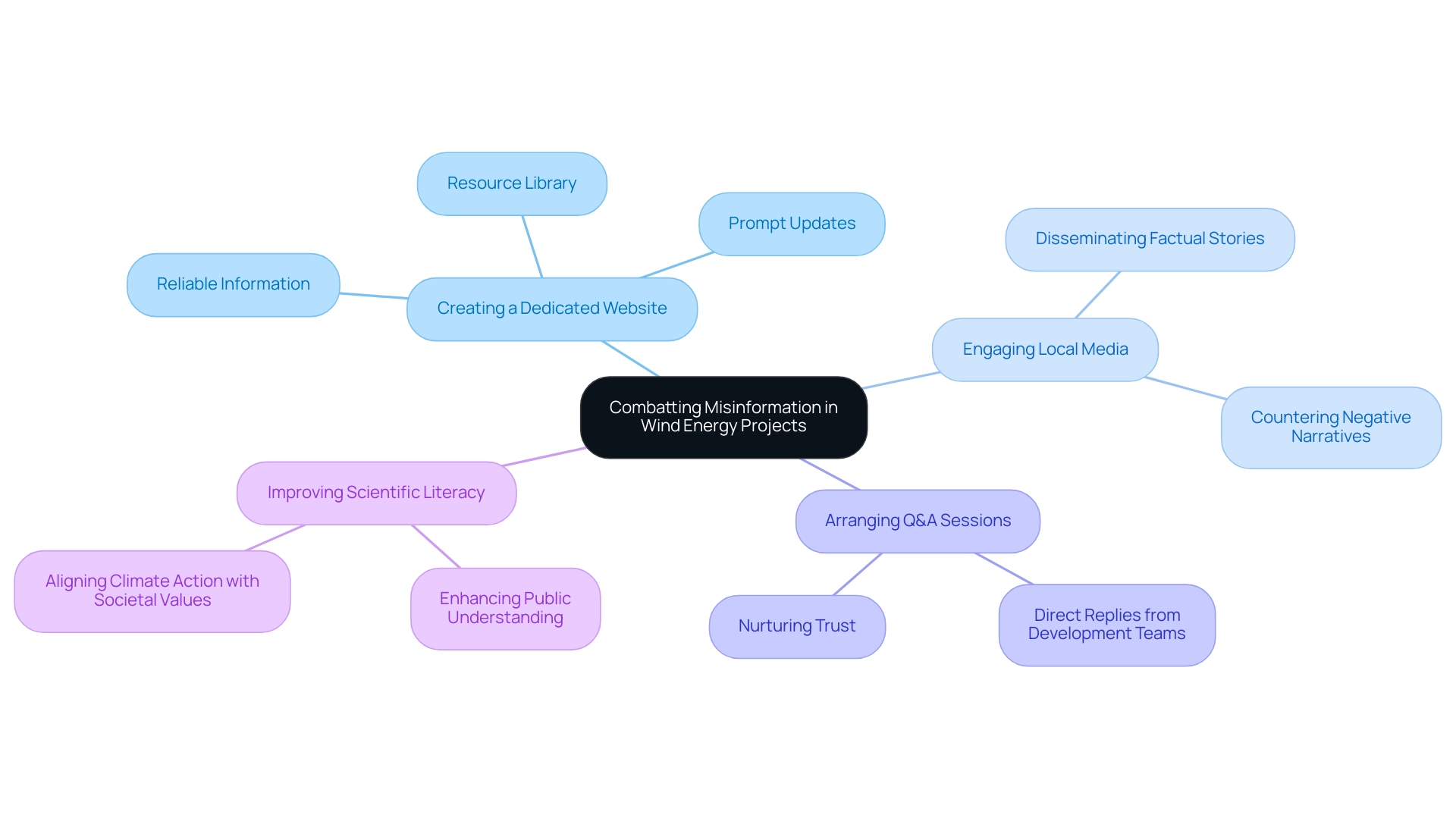
To effectively address misinformation surrounding renewable initiatives, developers must prioritize openness and educational efforts. Creating a dedicated website that provides reliable information, prompt updates, and an extensive resource library can act as a trusted source for the public. Engaging local media outlets to disseminate factual stories about the benefits and safety of wind energy is essential in countering negative narratives.
Moreover, arranging Q&A sessions enables participants to express their concerns and obtain direct replies from development teams, thus nurturing a climate of trust. Such initiatives not only enhance public understanding but also address the underlying attitudes that contribute to misinformation. Communication specialists highlight that addressing these attitudes is vital for effective outreach, suggesting that future strategies should concentrate on enhancing scientific literacy and aligning climate action with various societal values.
For instance, Cronbach’s α was found to be 0.94 in studies assessing public perceptions, indicating high reliability in the information presented. Moreover, it's significant that usually, two individuals can maintain a dialogue at regular voice levels even while positioned directly beneath a turbine, highlighting the safety and social involvement aspects of renewable projects. The case study titled 'Implications for Communication Strategies' highlights that addressing these underlying attitudes is crucial for effective communication, reinforcing the need for transparency initiatives.
By openly tackling misunderstandings and prioritizing transparency, developers can alleviate fears, foster informed discussions, and ultimately enhance support for energy initiatives.
Best Practices for Site Selection: Balancing Community Needs and Environmental Impact
During the rural wind farm siting process for renewable energy farms, developers must carefully balance community needs with environmental impacts. Conducting comprehensive environmental assessments is vital to evaluate potential effects on local ecosystems during rural wind farm siting. Advanced GIS mapping technology plays a crucial role in rural wind farm siting, enabling developers to identify areas that maximize resource availability while avoiding sensitive habitats.
A recent study emphasizing rural wind farm siting by applying a 1000-meter buffer distance to protected areas in Spain highlights the importance of these assessments in identifying potential conflicts and optimizing site selection practices. Additionally, insights from the case study 'Common Siting Factors in WiFSS' reveal that factors such as:
- Distance to urban centers
- Wind speed
- Ocean depth
are frequently employed but often lack clear justification in their selection. Actively engaging with local members regarding rural wind farm siting to gauge their preferences and address concerns fosters a collaborative decision-making process.
This method of rural wind farm siting reduces ecological disturbances and aligns initiatives with local values, ultimately boosting acceptance and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. Furthermore, considering the broader policy support classified as:
- Social
- Cultural
- Economic
- Safety factors
can provide a more rounded perspective on the influences shaping site selection decisions. By prioritizing sustainable practices and community involvement, developers can significantly improve the overall success of their projects related to rural wind farm siting.
Conclusion
Effective siting of wind farms is inherently linked to the principles of community engagement and adherence to regulatory frameworks. Through proactive outreach, developers can establish trust and transparency with local residents, addressing their concerns while illustrating the tangible benefits of wind energy. By fostering open dialogue and incorporating community feedback, project developers not only mitigate opposition but also ensure that their initiatives align with local expectations and values.
Navigating the complex regulatory landscape is equally crucial. Understanding the interplay between state and local regulations allows developers to effectively position their projects within legal parameters, increasing the likelihood of community support. As local governance continues to evolve, it is imperative for developers to stay informed and engaged with planning boards and local officials.
Furthermore, the economic and environmental advantages of wind energy cannot be overstated. From job creation and increased tax revenues to significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, the positive impacts of wind energy projects resonate well beyond the immediate vicinity of the installations. Addressing misinformation through transparency and education further solidifies public support, enabling communities to make informed decisions based on accurate information.
Ultimately, by balancing community needs with environmental considerations, and by adopting best practices in site selection, developers can lead the way toward a sustainable energy future. The journey toward successful wind farm siting is not merely about infrastructure; it is about building lasting partnerships and fostering a shared vision for clean energy that benefits all stakeholders involved.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is public involvement important in the siting of rural wind farms?
Public involvement is crucial for fostering a supportive environment for renewable energy projects. It helps to educate residents about the benefits of wind energy and addresses local concerns, thereby reducing resistance to siting initiatives.
What methods can project developers use to engage the public?
Developers can engage the public through informational meetings, workshops, and open forums aimed at educating residents. Additionally, conducting surveys allows developers to gather valuable feedback on local concerns.
What are some common local concerns regarding wind farms?
Common concerns include noise, aesthetics, and land use. These issues are often raised by residents during public engagement efforts.
How does the proximity of wind turbines to homes affect public perception?
On average, turbines have been installed roughly 150 feet (46 meters) closer to homes each year, highlighting local concerns about proximity and its impact on residents' quality of life.
What role does a community advisory board play in the wind farm siting process?
A community advisory board can improve connections with residents and promote ongoing dialogue throughout the lifecycle of the project, fostering trust and collaboration.
What health benefits are associated with renewable energy, according to case studies?
Renewable energy, as a clean source of electricity, reduces health risks associated with air pollution, and there is no evidence of direct health risks from turbine exposure.
What is the significance of addressing health issues in the context of renewable energy?
Addressing health issues is important as the equilibrium of resident microbial populations is linked to numerous chronic human diseases, which underscores the need for community engagement in renewable energy initiatives.
What regulatory frameworks must developers understand for rural wind farm siting?
Developers must navigate both state and local regulations, including overarching state policies and local zoning ordinances, which can significantly impact siting decisions.
What authority do local governments have regarding wind farm siting?
Local governments have considerable authority over most siting decisions related to turbines, while the Siting Coordination Office has primary authority over facilities with a capacity of 75 MW or more.
How has the trend in local zoning regulations for wind farms changed over time?
The number of local ordinances adopted has significantly increased, with 16 times as many implemented in 2021 compared to 2003, indicating a trend toward localized management of renewable initiatives.
Why is transparent dialogue with local authorities important for developers?
Transparent dialogue helps developers align their initiatives with public expectations and legal standards, enhancing the likelihood of gaining local support, which is essential for successful renewable energy development.




