Introduction
In the realm of transmission land management, the complexities of project execution necessitate a multifaceted approach that blends strategic foresight with operational precision. As organizations navigate the intricate landscape of stakeholder engagement, regulatory compliance, and technological integration, the importance of effective land management becomes increasingly evident. This article delves into essential strategies that not only enhance project outcomes but also foster sustainable relationships with stakeholders.
From leveraging advanced technologies to implementing comprehensive training programs, the insights presented herein aim to equip professionals with the tools necessary for successful land management in an ever-evolving environment.
Essential Strategies for Effective Transmission Land Management
Effective resource management in transmission initiatives necessitates a comprehensive approach that harmonizes strategic planning with operational execution through transmission land management solutions. Below are several essential strategies:
-
Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging stakeholders—including landowners, community members, and regulatory bodies—early and continuously is imperative.
Establishing open communication channels can address concerns, foster collaboration, and mitigate project opposition. As noted by CS/OS,
We aim for an integrative approach that includes use activities with a certain significance, such as forestry, in order to preserve a cultural landscape.
This illustrates the need to consider various land use aspects in stakeholder discussions.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Navigating the intricate framework of local, state, and federal regulations is vital for success. Conducting extensive research to understand applicable laws and securing all necessary permits before starting the endeavor is essential to avoid delays and legal complications.
-
Site Evaluation: Thorough site evaluations are essential for assessing site suitability for transmission initiatives.
This process should involve examining topography, environmental impacts, and current usage to preempt potential conflicts. Case studies have demonstrated that concentrating on particular spatial and temporal scales—such as those mentioned by agricultural participants in Uelzen—can improve the comprehension of usage sustainability and its effect on project results. The differences in perceptions of long-term sustainability, with forestry participants considering spans of 100 years compared to agricultural participants' shorter focuses, highlight the need for tailored engagement strategies.
-
Negotiation Skills: Strong negotiation skills are crucial for securing land rights and easements. Comprehending landowners' needs and motivations allows for the development of mutually beneficial scenarios that promote agreements and improve participant satisfaction.
-
Risk Management: Identifying potential risks early in the initiative lifecycle and developing proactive mitigation strategies can prevent costly delays and ensure smoother execution.
This approach aligns with findings from stakeholder discussions, emphasizing the need for reliability in political programs to support long-term planning for farmers and other users of the terrain.
-
Documentation and Record-Keeping: Maintaining accurate records of all communications, agreements, and regulatory submissions is vital for compliance. Proper documentation serves as a reference for resolving disputes or audits, ensuring that all parties are aligned and informed.
By implementing these strategies and integrating theoretical insights from Wiltbank et al. (2006) regarding nonpredictive strategies in strategic management, organizations can significantly enhance their transmission resource management processes, ultimately leading to more favorable project outcomes.
Leveraging Technology for Enhanced Land Management Solutions
Incorporating advanced technology into resource management solutions significantly enhances efficiency and accuracy. Here are several transformative technologies and best practices:
-
GIS Mapping: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) offer an invaluable toolkit for visualizing use of territory, identifying potential conflicts, and analyzing spatial data with precision.
By leveraging GIS, project teams can streamline site selection and optimize planning for transmission land management solutions, thereby enhancing overall project outcomes. As noted by Putnam, D., high-precision GIS mapping is essential for understanding resource availability and suitability, underscoring its critical role in effective management.
-
AI-Powered Title Research: The integration of AI tools in title research automates the identification of land ownership and easement rights, greatly reducing manual efforts and improving accuracy.
This technological advancement expedites the due diligence process, allowing initiatives to be initiated more swiftly and efficiently.
-
Management Software: The use of management tools facilitates enhanced coordination among team members, streamlining communication and ensuring adherence to timelines and budgets. These platforms often include features for task tracking, document sharing, and comprehensive reporting, which are essential for effective project execution.
-
Remote Sensing Technology: Utilizing drones and satellite imagery for area assessments yields high-resolution data crucial for environmental impact studies and site evaluations. This modern technology can drastically decrease the time and costs typically associated with traditional surveying methods, making it an attractive option for management professionals.
-
Collaboration Platforms: The utilization of digital collaboration tools facilitates real-time communication among project stakeholders, which accelerates decision-making processes and reduces the chances of misunderstandings.
By adopting these innovative technologies, organizations can significantly improve their transmission land management solutions, resulting in better project outcomes and increased stakeholder satisfaction. Notably, recent advancements in GIS mapping have shown substantial effectiveness in resource management, providing a framework for integrating space syntax into urban morphology analysis, as demonstrated by Jing B. in 2002.
Furthermore, expert opinions highlight the importance of high-precision GIS mapping in understanding space availability and suitability. This is especially pertinent considering that the home ownership rate in Yazoo was 68.8% in 2000, illustrating the need for precise property management strategies. Additionally, the case study on 'Training and Data Accuracy in GIS' emphasizes that proper training and accurate data are essential for effective GIS implementation, reinforcing the importance of investing in reliable data sources and collaboration with local authorities.
Comprehensive Risk Assessment and Management
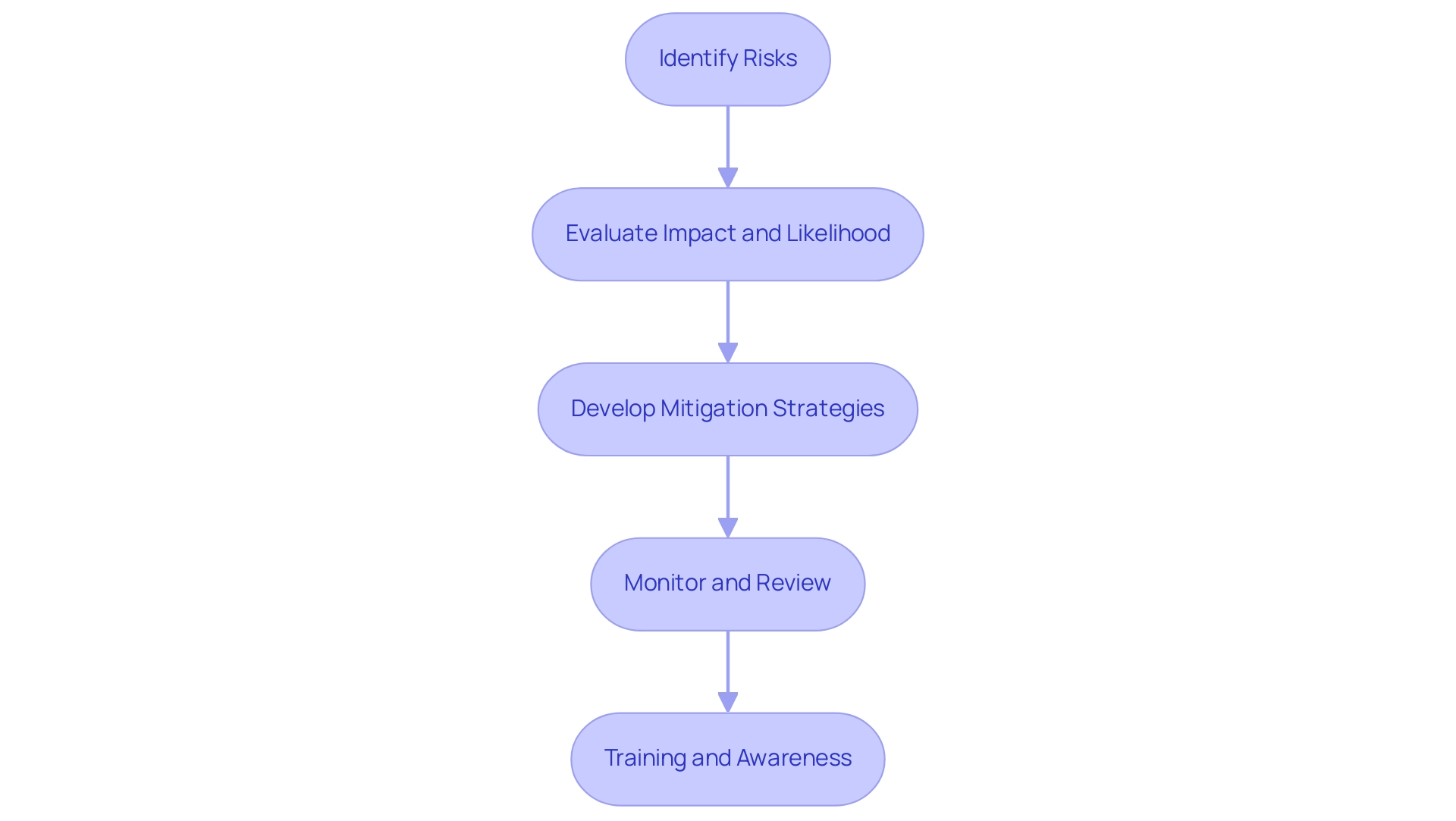
Efficient hazard management is essential for successful land administration, especially in transmission land management solutions where various challenges can emerge. A systematic approach to hazard evaluation includes the following key steps:
- Identify Risks: Begin with a comprehensive analysis to pinpoint potential challenges, such as regulatory changes, environmental impacts, landowner disputes, and project delays. Interacting with stakeholders at this stage can uncover concealed threats that may not be readily apparent.
- Evaluate Impact and Likelihood: Once threats are identified, assess both their potential impact and likelihood. This evaluation helps prioritize which threats demand immediate attention and resource allocation, ensuring a focused approach to mitigation.
- Develop Mitigation Strategies: For threats considered high-priority, formulate targeted strategies to alleviate their effects. This may involve creating contingency plans, securing necessary permits, or enhancing communication with stakeholders to maintain transparency and foster collaboration.
- Monitor and Review: Implement a robust monitoring system to keep track of hazard factors throughout the project lifecycle. Frequent evaluations are crucial, as they enable the modification of management strategies in response to emerging challenges. As stated in a report by McGraw-Hill, comprehending the major challenges in construction projects—such as budget overruns, schedule delays, and regulatory compliance—can greatly improve management practices, especially in property acquisition.
- Training and Awareness: It is vital to educate team members about common threats and the significance of adhering to established protocols. A knowledgeable team is better equipped to identify and address challenges proactively, fostering a culture of vigilance and responsiveness.
By systematically assessing and managing threats, organizations can confidently navigate the complexities of transmission land management solutions. Recent developments in evaluation emphasize the growing significance of comprehensive strategies. For example, a study on commercial real estate valuation amid leasing uncertainty discovered that preleasing can act as a safeguard against leasing challenges, thus affecting development choices in changing market conditions.
This demonstrates the practical use of mitigation strategies in real-world situations. Furthermore, statistics indicate that common risks in property management projects include environmental compliance issues, which have been reported to affect 30% of projects, underscoring the need for effective risk management practices.
Building Strong Relationships with Stakeholders
Effective transmission land management solutions are fundamentally reliant on the cultivation and maintenance of strong relationships with involved parties. Here are essential strategies to enhance these relationships:
-
Open Communication: Establishing transparent communication channels among all stakeholders—landowners, governmental agencies, and community groups—is paramount.
Regular updates and open forums invite dialogue and help foster trust. Research indicates that when involved parties perceive meaningful engagement, their trust in leadership increases dramatically—by as much as 75%.
-
Proactive Concern Addressing: Actively listen to the concerns of involved parties and address them with foresight.
By offering concrete solutions or compromises, organizations can alleviate apprehensions and demonstrate a genuine commitment to community well-being. As noted by Officevibe, 69% of employees stated that they’d exert more effort if they were more valued, emphasizing the significance of appreciation in relationships with involved parties.
-
Early Participant Involvement: Engaging contributors from the initiative's inception is crucial.
Including them in conversations about objectives and potential impacts offers valuable insights and encourages greater support.
-
Educational Resources: Provide involved parties with comprehensive materials that clarify the initiative, its advantages, and the strategies implemented to reduce negative impacts.
Clear, factual information can effectively dispel misconceptions and cultivate a positive perception.
The Pumble Employee Communication App serves as a practical example of how effective communication tools can enhance engagement by organizing conversations through direct messages, threads, and channels.
-
Celebrate Milestones: Acknowledging and celebrating significant achievements with involved parties strengthens these connections.
Arranging community events or offering progress updates can reinforce communal ties and improve overall support.
By prioritizing stakeholder relationships, organizations can cultivate a collaborative atmosphere that greatly aids the success of transmission land management solutions initiatives. Effective communication not only enhances project outcomes but also builds a foundational relationship that supports long-term success.
Implementing Comprehensive Training Programs
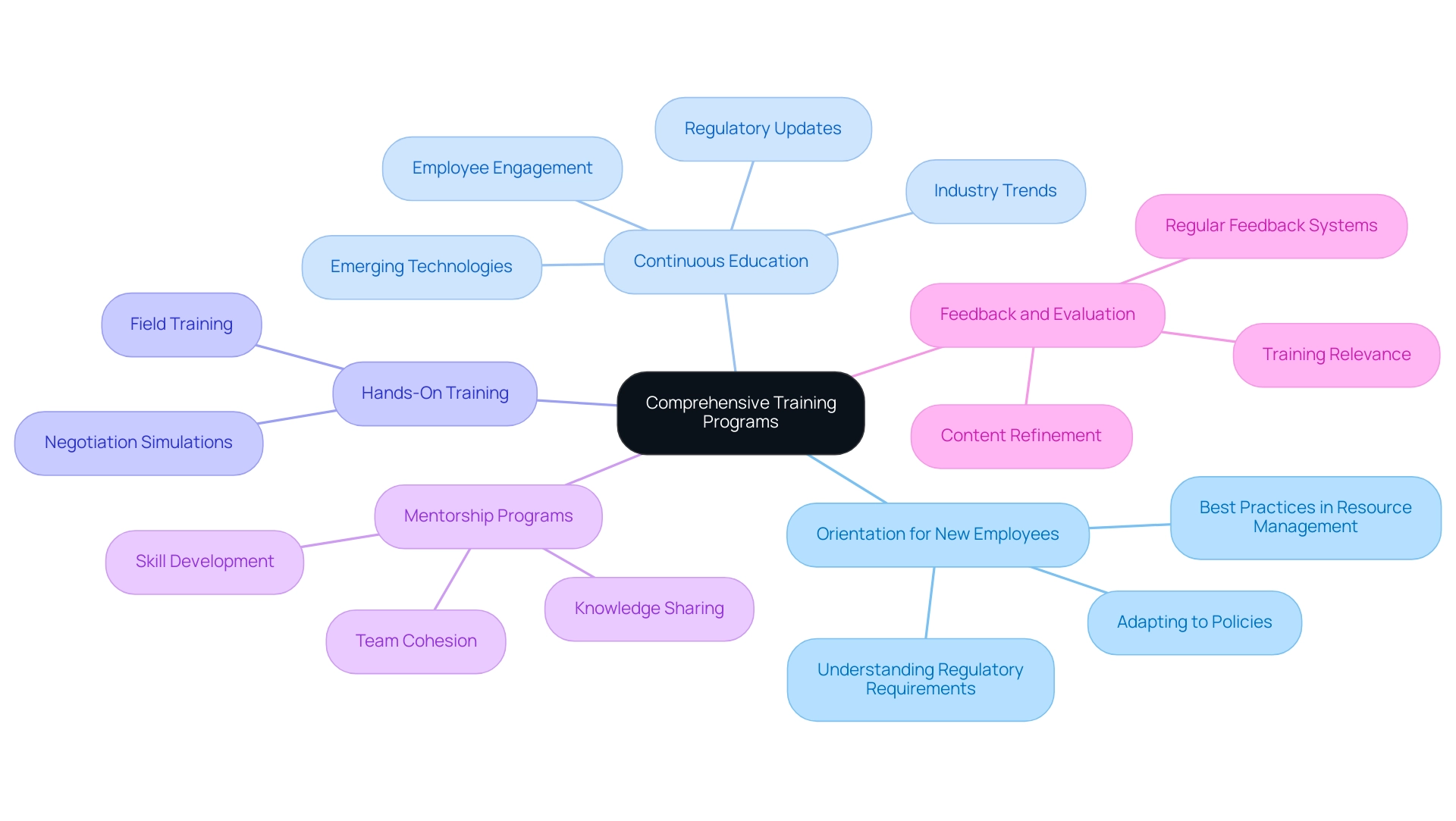
Investing in comprehensive training programs is essential for empowering team members with the necessary skills and knowledge for effective resource management. Here are key components to consider:
-
Orientation for New Employees: A comprehensive orientation program is essential for new hires, assisting them in adapting to organizational policies, regulatory requirements, and the best practices in resource management.
This foundational knowledge sets the tone for their future performance.
-
Continuous Education: Developing ongoing training modules that address emerging technologies, regulatory updates, and industry trends is crucial. This approach ensures employees remain informed and adaptable, which is vital in a rapidly changing landscape.
Recent data reveals that 52% of workers recognize the need to learn new skills within the next year, highlighting the urgency for continuous development. Furthermore, organizations must adapt their training strategies to meet the evolving needs of the modern workforce, enhancing employee engagement and performance.
-
Hands-On Training: Incorporating practical, hands-on training enhances skill retention and application.
For instance, field training on site assessments or negotiation simulations can significantly reinforce theoretical knowledge and prepare employees for real-world challenges.
-
Mentorship Programs: Establishing mentorship programs that pair experienced team members with newer employees promotes knowledge sharing and skill development in a supportive environment. This initiative not only aids junior staff but also strengthens team cohesion and organizational culture.
-
Feedback and Evaluation: Implementing a robust system for regular feedback and evaluation of training programs is essential. Gathering input from participants allows organizations to continuously refine content and delivery methods, ensuring that training remains relevant and effective, especially in the area of transmission land management solutions.
As LinkedIn's 2023 Workplace Learning Report indicates, 94% of employees would remain in their roles if offered development opportunities, underscoring the critical link between training and employee retention.
Additionally, the case study titled 'Development Opportunities and Retention' emphasizes that 90% of employees are less likely to quit if they receive development opportunities, reinforcing the necessity of investing in employee training.
Conclusion
Effective transmission land management hinges on a multifaceted approach that integrates:
- Strategic planning
- Stakeholder engagement
- Regulatory compliance
- Technological advancements
By prioritizing stakeholder engagement, organizations can foster collaboration and mitigate project opposition through transparent communication and early involvement. Navigating the complex regulatory landscape is essential to avoid legal pitfalls, while comprehensive site assessments ensure that land suitability is thoroughly evaluated.
Leveraging advanced technologies such as GIS mapping and AI-powered tools enhances efficiency and accuracy in land management processes. These innovations streamline project execution and improve coordination among stakeholders, leading to more favorable outcomes. Additionally, a systematic approach to risk assessment and management is vital for identifying potential challenges and developing targeted mitigation strategies that promote project resilience.
Building strong relationships with stakeholders through:
- Open communication
- Proactive concern addressing
- Educational resources
reinforces trust and support for transmission projects. Celebrating milestones further strengthens community bonds, ensuring collaborative success. Finally, investing in comprehensive training programs equips team members with the necessary skills and knowledge, fostering a capable workforce adept at navigating the complexities of land management.
In conclusion, the integration of these essential strategies and technologies not only enhances project outcomes but also sustains positive relationships with stakeholders. By adopting a holistic approach to transmission land management, organizations can effectively navigate the challenges of an ever-evolving environment, ultimately contributing to the long-term success and sustainability of their projects.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the importance of stakeholder engagement in transmission initiatives?
Engaging stakeholders, including landowners, community members, and regulatory bodies, early and continuously is crucial. It fosters collaboration, addresses concerns, and mitigates project opposition through open communication channels.
Why is regulatory compliance essential in transmission initiatives?
Navigating local, state, and federal regulations is vital for success. Understanding applicable laws and securing necessary permits before starting a project helps avoid delays and legal complications.
What does site evaluation involve for transmission initiatives?
Thorough site evaluations assess suitability by examining topography, environmental impacts, and current usage to prevent potential conflicts. Tailored engagement strategies may be necessary based on differing perceptions of long-term sustainability among stakeholders.
How do negotiation skills contribute to resource management?
Strong negotiation skills are essential for securing land rights and easements. Understanding landowners' needs allows for the creation of mutually beneficial agreements, enhancing participant satisfaction.
What is the role of risk management in transmission initiatives?
Identifying potential risks early and developing proactive mitigation strategies can prevent costly delays and ensure smoother execution, supporting long-term planning for stakeholders.
Why is documentation and record-keeping important in resource management?
Maintaining accurate records of communications, agreements, and regulatory submissions is vital for compliance. It serves as a reference for resolving disputes or audits, ensuring all parties are informed and aligned.
How does GIS mapping enhance resource management in transmission initiatives?
GIS mapping provides tools to visualize territory use, identify potential conflicts, and analyze spatial data, thereby streamlining site selection and optimizing planning for better project outcomes.
What benefits does AI-powered title research offer?
AI tools automate the identification of land ownership and easement rights, reducing manual efforts and improving accuracy, which expedites the due diligence process for initiatives.
How does management software facilitate project execution?
Management tools enhance coordination among team members, streamline communication, and ensure adherence to timelines and budgets through features like task tracking and document sharing.
What advantages does remote sensing technology provide in area assessments?
Utilizing drones and satellite imagery yields high-resolution data for environmental impact studies and site evaluations, significantly reducing time and costs compared to traditional surveying methods.
How do collaboration platforms improve project management?
Digital collaboration tools enable real-time communication among stakeholders, accelerating decision-making processes and reducing misunderstandings, which enhances overall project efficiency.
List of Sources
- Essential Strategies for Effective Transmission Land Management
- Why Stakeholder Engagement Matters: Building Stronger Connections for Success (https://iquasar.com/blog/why-stakeholder-engagement-matters-building-stronger-connections-for-success)
- Sustainability in Land Management: An Analysis of Stakeholder Perceptions in Rural Northern Germany (https://mdpi.com/2071-1050/7/1/683)
- Multi‐stakeholder participation for successful implementation of applied research projects in Africa (https://besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/2688-8319.12252)
- Leveraging Technology for Enhanced Land Management Solutions
- High-Precision Land-Cover-Land-Use GIS Mapping and Land Availability and Suitability Analysis for Grass Biomass Production in the Aroostook River Valley, Maine, USA (https://mdpi.com/2073-445X/4/1/231)
- GIS Applications in Land Management: The Loss of High Quality Land to Development in Central Mississippi from 1987–2002 - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3810626)
- Unlocking the Power of GIS for Land Management (https://landgate.com/news/everything-you-need-to-know-about-gis)
- Comprehensive Risk Assessment and Management
- U.S. construction: main risks for private and public projects | Statista (https://statista.com/statistics/216774/biggest-risks-for-private-and-public-construction-projects)
- Qualitative Analysis of Risks Affecting the Delivery of Land Surveying Project Activities (https://mdpi.com/2071-1050/13/22/12645)
- (PDF) Land Development: Risk, Return and Risk Management (https://researchgate.net/publication/5151913_Land_Development_Risk_Return_and_Risk_Management)
- Understanding the Risks in Property Development (https://beechholdings.co.uk/news/understanding-the-risks-in-property-development)
- Building Strong Relationships with Stakeholders
- Workplace Communication Statistics (2025) (https://pumble.com/learn/communication/communication-statistics)
- 21 Scary Internal Communication Stats - Oak Engage (https://oak.com/blog/internal-communications-statistics)
- Internal Communications Statistics for a Successful Company (https://blog.gaggleamp.com/internal-communications-statistics)
- Implementing Comprehensive Training Programs
- (PDF) Effectiveness of Training and its impact on employee performance in the Department of Lands and Survey (https://researchgate.net/publication/299584895_Effectiveness_of_Training_and_its_impact_on_employee_performance_in_the_Department_of_Lands_and_Survey)
- Top 27 Employee Training Statistics And Trends To Discover In 2024 (https://oakinnovation.com/blog/free-trainer-skills/top-27-employee-training-statistics-and-trends-to-discover-in-2024?srsltid=AfmBOorTwTxif_o_BMYUct0J9zj9xbdVinsSIIh8v1tGdnUhs7TabPAj)
- Employee Training Statistics, Trends, and Data in 2025 | Devlin Peck (https://devlinpeck.com/content/employee-training-statistics)




