Overview
Best practices for urban utility grid management focus on the integration of advanced metering, grid analytics, and smart technologies to enhance efficiency, reliability, and sustainability. The article underscores the importance of these strategies by highlighting how real-time data and intelligent networks can optimize energy distribution, engage stakeholders effectively, and build resilient infrastructure in response to increasing demand and climate challenges.
Introduction
Urban utility management is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by the convergence of advanced technologies and the pressing need for sustainability. As cities grapple with increasing energy demands and climate-related challenges, the integration of smart metering and grid analytics emerges as a pivotal strategy. These innovative tools not only facilitate real-time monitoring of energy consumption but also empower utilities to optimize resource distribution and enhance operational efficiency.
With significant investments in smart grid technologies and a focus on stakeholder engagement, urban utilities are poised to adapt to evolving consumer needs while addressing the complexities of modern infrastructure. This article delves into the critical components of urban utility management, exploring the role of technology, resilient infrastructure, and effective stakeholder communication in shaping a sustainable energy future.
Understanding Metering and Grid Analytics in Urban Utility Management
In the domain of urban service management, metering involves the systematic gathering of energy usage information through devices like advanced meters. These advanced tools offer real-time insights into usage patterns, facilitating a deeper understanding of consumer behavior. Complementarily, grid analytics involves the examination of this data to uncover trends, forecast demand, and optimize energy distribution strategies.
As of 2024, the momentum for smart meter adoption is significant, driven largely by state policies aimed at enhancing service efficiency. Organizations are now prioritizing investments in advanced metering infrastructure, improving data accuracy and granularity, which in turn bolsters energy management and customer engagement initiatives. For instance, companies utilizing data analytics can swiftly identify anomalies in consumption patterns, enabling proactive maintenance that lowers operational expenses.
Jaya Nagdeo, Research Manager for Power, Utilities & Renewables, emphasizes this trend by stating,
Rising wholesale prices, projected to increase by 19% on average between 2025 and 2028, combined with escalating distribution expenses, are likely to result in higher electricity bills for consumers.
This highlights the urgency for service providers to adopt sophisticated metering and grid analytics strategies. Moreover, the year-to-date average power price across all sectors stands at 13.09 cents per kWh, reflecting a 2.7% year-over-year increase, adding a current economic context to the discussion on smart meters and energy management.
Furthermore, companies are increasingly monitoring water stress and incorporating water risk into their financial disclosures, which is pertinent to broader management strategies. A thorough grasp of these components is essential for developing robust urban utility grid management strategies that enhance reliability and sustainability in an evolving energy landscape. The case study titled 'Strategic Choices for Utilities' further illustrates how electric power utilities are adapting to increasing demand and operational challenges, considering various strategic choices to ensure reliability, affordability, and sustainability.
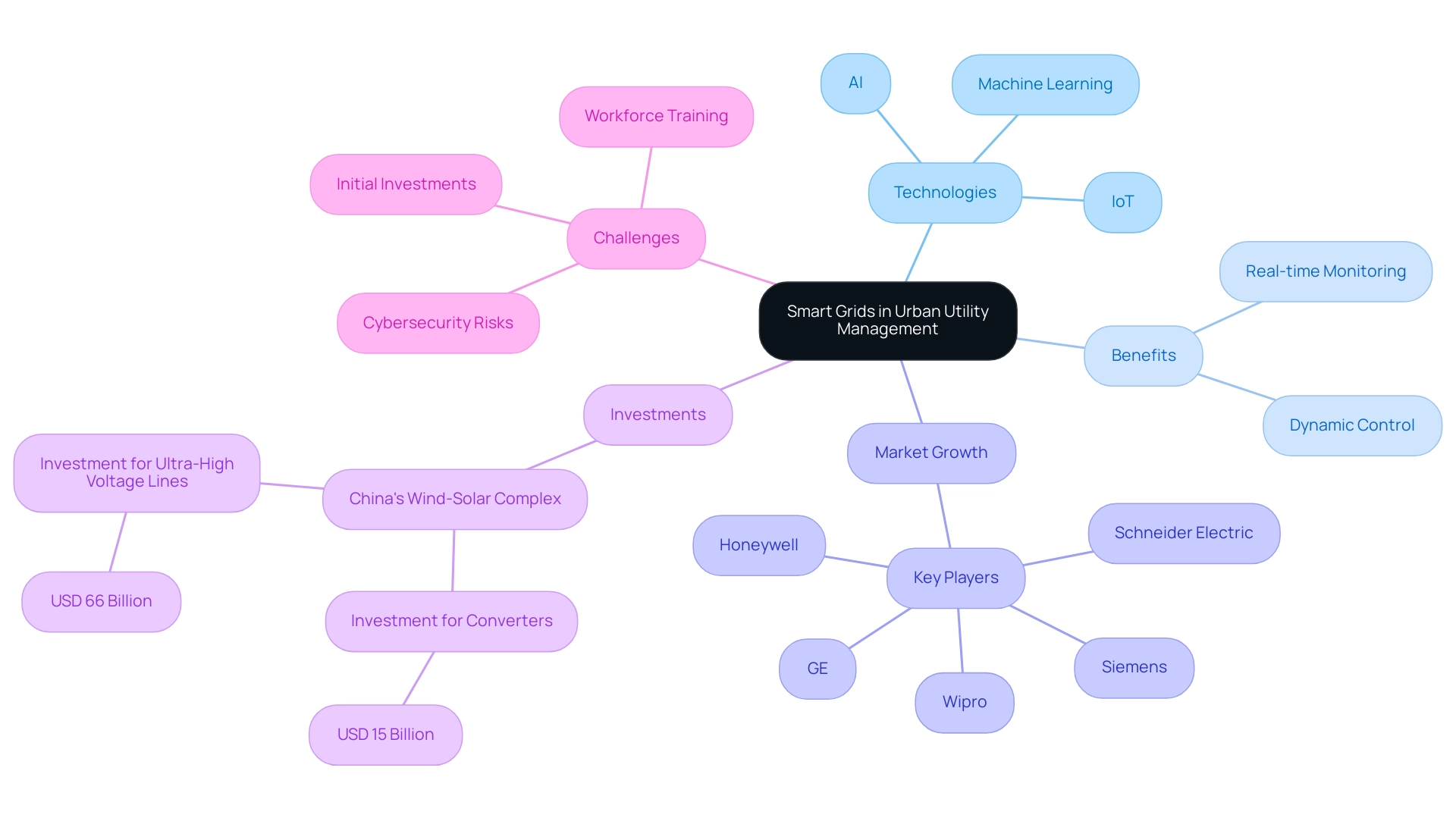
The Role of Smart Grids in Modern Urban Utility Management
Intelligent networks signify a transformative shift in energy management by utilizing advanced technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things), AI, and machine learning. These systems enable real-time monitoring and dynamic control of energy flows, which is crucial for integrating variable renewable energy sources like solar and wind. For example, intelligent networks can independently modify electricity distribution based on real-time demand and supply, greatly improving system resilience during peak usage periods or crises.
As urban areas progressively embrace these technologies, the worldwide intelligent network market is anticipated to expand significantly, with prominent companies such as Schneider Electric, Siemens, Wipro, and Honeywell at the forefront of innovation. A noteworthy instance of investment patterns in advanced energy technology is China's ambitious plan for a 455 GW wind-solar complex, which is anticipated to need investments of USD 15 billion for converters and USD 66 billion for ultra-high voltage lines by 2030. However, the journey toward extensive intelligent network implementation is fraught with challenges.
Significant initial investments are required, alongside addressing cybersecurity risks and ensuring continuous workforce training. As ABB's investment in Danish start-up OKTO GRID illustrates, the focus is on digitizing and extending the life of aging infrastructure. ABB states, 'Our investment in OKTO GRID aims to advance technology for the digitization and extension of the life of aging electrical equipment.'
Furthermore, the FirstEnergy Distribution Platform Modernization case study illustrates the role of urban utility grid management in urban service providers' endeavors to improve reliability and efficiency, directly tackling the challenges of advanced network implementation. Addressing these challenges is crucial for organizations aiming to modernize their infrastructure and enhance overall service reliability in urban areas, particularly in the realm of urban utility grid management as the demand for smart grid solutions increases in 2024.
Enhancing Stakeholder Engagement in Urban Utility Projects
Effective engagement with interested parties in utility projects is fundamentally rooted in transparent communication. Utilities must proactively communicate project objectives, timelines, and potential impacts to both the community and interested parties. Creating advisory boards or community committees acts as an essential method for promoting continuous dialogue, ensuring that a range of viewpoints, including those from under-represented and minority groups, are incorporated into the decision-making process.
Notably, the Construction Review Panel mandates at least one female representative and a representative from a minority community among its members, underscoring the importance of diversity in participant engagement. The latest developments in engagement frameworks highlight the necessity of empowering these groups to express their views, thereby enhancing project outcomes. Furthermore, establishing feedback mechanisms is crucial to inform participants how their input influenced project outcomes, demonstrating the effectiveness of engagement efforts.
Leveraging digital platforms for public outreach has proven to significantly enhance engagement, as evidenced by a qualitative case study that identified six types of digital tools facilitating participant involvement in urban development projects. These tools, which encompass:
- Online surveys
- Social media interaction
- Virtual workshops
- Project websites
- Mobile applications
- Interactive mapping
not only offer chances for engagement but also generate value by positively impacting project success and participant satisfaction. By fostering a culture of trust and collaboration, organizations can effectively mitigate opposition and drive successful project implementation.
Whitman, Lafayette, and Roark emphasize the importance of this approach, stating,
This should therefore translate into setting up funding specifically devoted to co-creative stakeholder engagement and ensuring that all key stakeholders have been engaged and that outputs reflect local knowledge, experiences, and priorities.
Implementing Resilient Infrastructure for Urban Utilities
To cultivate resilient urban infrastructure, organizations must focus on employing durable materials and pioneering designs capable of withstanding extreme weather conditions and various stressors. For instance, implementing flood-resistant designs in high-risk areas not only mitigates potential damage but also ensures the sustainability of essential services. Incorporating redundancy in supply lines is another critical strategy that guarantees continuous service delivery during disruptions.
Regular assessments and timely upgrades of existing infrastructure are equally vital to sustaining resilience over time. Additionally, the application of Geospatial Artificial Intelligence (GeoAI) in flood prediction exemplifies innovative strategies that can enhance flood risk assessments and improve preparedness. By utilizing remote sensing, GIS, and machine learning techniques, GeoAI significantly enhances the accuracy and speed of flood predictions, facilitating better response strategies for safeguarding critical infrastructure.
Furthermore, fostering collaboration with urban planners and engineers, as well as building strong community networks, can significantly enhance the adaptability of services, allowing them to meet evolving environmental challenges effectively. As OECD Secretary-General Mathias Cormann points out, substantial investments are necessary to bolster climate resilience, highlighting the need for long-term project planning and effective risk-sharing arrangements to unlock private financing. By prioritizing these approaches, service providers can better prepare for and respond to the increasing frequency of climate-related disasters, which have escalated economic losses from an annual average of USD 198 billion in the 1970s to USD 1.6 trillion in the 2010s.
Leveraging Technology for Data-Driven Decision Making
By investing in integrated management systems that consolidate data from diverse sources like metering, grid analytics, and customer feedback, urban utility grid management can significantly enhance operational effectiveness. As the demand for technology-related roles continues to grow—evidenced by an 8 percent increase in tech job postings from 2021 to 2023—utilities must also confront a skills gap, with fewer than half of potential candidates possessing the high-demand tech skills specified in job postings. This challenge emphasizes the need for robust workforce development strategies.
Leveraging AI and big data analytics enables companies to identify patterns, accurately forecast demand, and optimize resource allocation. For example, predictive analytics can proactively address maintenance requirements, thereby minimizing downtime and reducing operational costs. Furthermore, the implementation of mobile applications for field workers can improve operational efficiency by providing real-time data access and enhancing communication channels.
As emphasized in the case study 'Navigating 2025,' energy providers are anticipated to accelerate investments in generation, transmission, and distribution to address unprecedented increases in power demand amid policy and economic uncertainty. As noted by Mike Temba, Managing Director at EY US,
Moving forward, P&U companies should look strategically at what can be capitalized and what can’t, and then spread that knowledge across the business by bettering communication, policies and training.
By adopting a technology-driven approach, including investments in customer technology and reinventing the customer operating model, urban utility grid management can help urban utilities make informed decisions that not only elevate overall performance but also enhance customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
The transformation of urban utility management is not merely a trend but a necessary evolution driven by technological advancements and the urgent need for sustainability. The integration of smart metering and grid analytics has emerged as a cornerstone of this transformation, enabling real-time monitoring and effective resource management. With utilities increasingly adopting sophisticated metering technologies, they can gain insights into consumer behavior, optimize energy distribution, and maintain operational efficiency in the face of rising costs and changing demand dynamics.
Moreover, the role of smart grids cannot be overstated. These systems are essential for enhancing resilience and integrating renewable energy sources, allowing for dynamic adjustments in energy distribution. While the journey towards widespread smart grid implementation presents challenges, the potential benefits for urban utilities and consumers alike are substantial. Investments in resilient infrastructure further underscore the commitment to sustainability, enabling utilities to withstand climate-related challenges and ensure the continuity of essential services.
Equally important is the emphasis on stakeholder engagement. By fostering transparent communication and actively involving diverse community voices in decision-making processes, utilities can enhance project outcomes and build trust. Digital engagement tools have proven effective in facilitating participation, thereby enriching the overall utility management landscape.
In conclusion, the convergence of technology, resilient infrastructure, and stakeholder engagement is pivotal for shaping a sustainable energy future. Urban utilities that strategically leverage these components will not only enhance their operational capabilities but also meet the evolving needs of their communities. As the landscape continues to change, the commitment to innovation and collaboration will be the key to navigating the complexities of urban utility management and achieving long-term sustainability goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of metering in urban service management?
Metering involves the systematic gathering of energy usage information through advanced meters, which provide real-time insights into usage patterns and help understand consumer behavior.
How does grid analytics complement metering?
Grid analytics examines the data collected from metering to uncover trends, forecast demand, and optimize energy distribution strategies.
What factors are driving the adoption of smart meters as of 2024?
The significant momentum for smart meter adoption is largely driven by state policies aimed at enhancing service efficiency and organizations prioritizing investments in advanced metering infrastructure.
How does data analytics benefit energy management?
Companies utilizing data analytics can quickly identify anomalies in consumption patterns, enabling proactive maintenance that lowers operational expenses.
What economic context is influencing electricity bills for consumers?
Rising wholesale prices, projected to increase by 19% on average between 2025 and 2028, along with escalating distribution expenses, are likely to result in higher electricity bills for consumers.
What is the significance of monitoring water stress in urban utility management?
Companies are increasingly monitoring water stress and incorporating water risk into their financial disclosures, which is essential for developing robust urban utility grid management strategies focused on reliability and sustainability.
What technologies are involved in intelligent networks for energy management?
Intelligent networks utilize advanced technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things), AI, and machine learning for real-time monitoring and dynamic control of energy flows.
How do intelligent networks improve system resilience?
Intelligent networks can independently modify electricity distribution based on real-time demand and supply, enhancing system resilience during peak usage periods or crises.
What challenges do organizations face in implementing intelligent networks?
Organizations face significant initial investment requirements, cybersecurity risks, and the need for continuous workforce training.
What is the focus of ABB's investment in OKTO GRID?
ABB's investment aims to advance technology for the digitization and extension of the life of aging electrical equipment.
How does the FirstEnergy Distribution Platform Modernization case study relate to urban utility grid management?
The case study illustrates the role of urban utility grid management in improving reliability and efficiency, addressing challenges associated with advanced network implementation.
List of Sources
- Understanding Metering and Grid Analytics in Urban Utility Management
- 2025 Power and Utilities Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/power-and-utilities/power-and-utilities-industry-outlook.html)
- eia.gov (https://eia.gov/tools/faqs/faq.php?id=108&t=3)
- The Role of Smart Grids in Modern Urban Utility Management
- Smart grids - IEA (https://iea.org/energy-system/electricity/smart-grids)
- Smart Grid Market to Touch US$86.6 Billion by 2024 (https://tdworld.com/grid-innovations/smart-grid/article/20972252/smart-grid-market-to-touch-us866-billion-by-2024)
- fortunebusinessinsights.com (https://fortunebusinessinsights.com/smart-grid-market-102157)
- Enhancing Stakeholder Engagement in Urban Utility Projects
- inclusiveinfra.gihub.org (https://inclusiveinfra.gihub.org/action-areas/stakeholder-identification-engagement-and-empowerment)
- Digital tools for stakeholder participation in urban development projects (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666721522000138)
- Towards a co-creative stakeholder engagement in Smart City projects: a life-cycle approach (https://tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13511610.2023.2266579)
- Implementing Resilient Infrastructure for Urban Utilities
- Sustainable and resilient infrastructure (https://oecd.org/en/topics/sub-issues/sustainable-and-resilient-infrastructure.html)
- Building urban infrastructure resilience through network governance (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2664328623000232)
- Urban Resilience Index for Critical Infrastructure: A Scenario-Based Approach to Disaster Risk Reduction in Road Networks (https://mdpi.com/2071-1050/16/10/4143)
- Massive investment is needed in sustainable infrastructure to build climate change resilience (https://oecd.org/en/about/news/press-releases/2024/04/massive-investment-is-needed-in-sustainable-infrastructure-to-build-climate-change-resilience.html)
- Leveraging Technology for Data-Driven Decision Making
- 2025 Power and Utilities Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/power-and-utilities/power-and-utilities-industry-outlook.html)
- mckinsey.com (https://mckinsey.com/capabilities/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/the-top-trends-in-tech)
- 2025 Utilities sector outlook (https://ey.com/en_us/insights/power-utilities/utilities-sector-outlook)




