Overview
This article examines best practices for effectively utilizing focus group engagement tools to enhance qualitative research outcomes. It highlights the necessity of:
- Establishing clear objectives
- Employing skilled moderation
- Ensuring participant comfort
- Implementing structured follow-up processes
Supported by case studies and expert recommendations, these practices demonstrate how they contribute to richer insights and informed decision-making.
Introduction
In a world where understanding consumer behavior is paramount, focus groups stand out as a crucial tool for gathering invaluable qualitative insights. These structured discussions, led by skilled moderators, enable participants to express their thoughts and feelings in a supportive environment. This often reveals complexities that traditional surveys fail to capture. As organizations strive to connect with their audiences, the significance of focus groups becomes increasingly evident. From market research to community engagement, these discussions not only illuminate stakeholder needs but also cultivate deeper connections, rendering them indispensable in today's data-driven landscape.
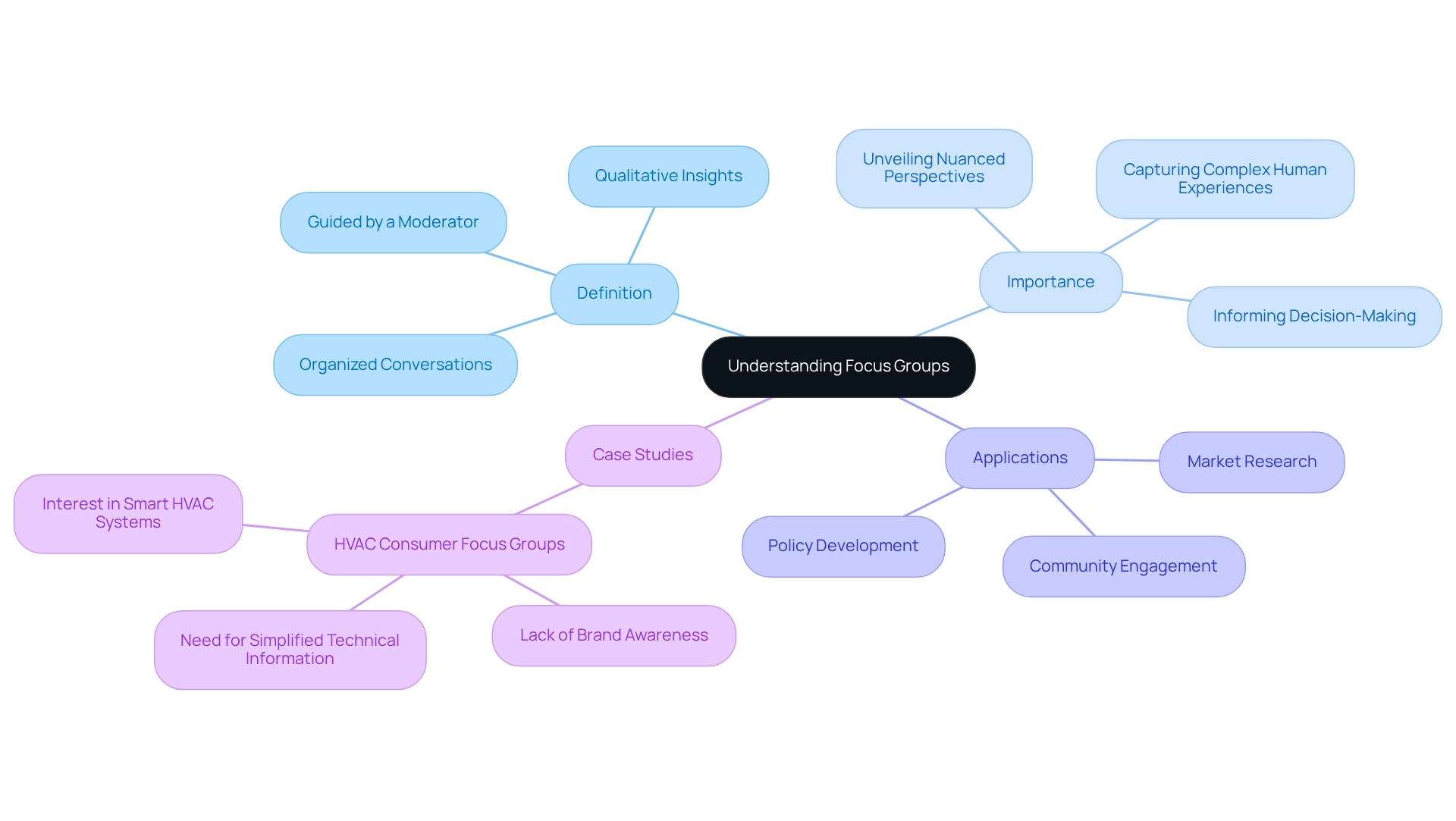
Understanding Focus Groups: Definition and Importance
Focus panels represent organized conversations involving a select group of individuals, guided by a moderator, aimed at gathering qualitative insights on specific topics. These discussions are crucial across various sectors, including market research, community engagement, and policy development. By fostering an environment of open dialogue, discussion panels empower participants to articulate their thoughts and feelings, yielding insights that often surpass those obtained through traditional surveys.
The significance of discussion panels lies in their capacity to unveil nuanced perspectives, making them indispensable for organizations striving to comprehend stakeholder needs and preferences. As noted by Liza Featherstone, a specialist in qualitative research, these assemblies do not adhere to a scientific and quantitative methodology for knowledge acquisition; rather, they excel at capturing the complexities of human experiences. In 2025, the relevance of discussion panels in market research will be underscored by their ability to provide valuable qualitative insights that numerical methods may overlook.
For instance, a participant in a discussion panel revealed earning $10,740 from participating in 95 sessions over the past decade, illustrating the potential benefits of engaging in these dialogues.
While there are costs associated with organizing such discussions—such as participant compensation and venue rental—these expenses are often outweighed by the advantages they confer. Focus panels serve as case studies rather than scientific surveys, offering critical insights into consumer behavior. Successful examples of discussion engagement can be found in community initiatives, where organizations have harnessed these conversations to enhance stakeholder involvement.
A notable case study involved HVAC consumer discussion panels, which revealed a widespread lack of brand awareness among buyers, despite the vital role of brand reputation in purchasing decisions. Participants expressed a need for straightforward technical information and clear explanations of energy efficiency benefits, underscoring the necessity for effective communication strategies.
In summary, focus group engagement tools, particularly discussion panels, are powerful instruments for qualitative data collection, providing organizations with the insights required to inform decision-making and foster meaningful stakeholder engagement.
Exploring Different Types of Focus Groups: A Comprehensive Overview
Focus panels can be categorized into several distinct types, each serving unique purposes in market research. Conventional discussion sessions typically involve 6-10 individuals engaging in in-person conversations, which fosters vibrant exchanges and prompt responses. Conversely, mini discussion sessions consist of fewer individuals, allowing for a deeper examination of subjects and the extraction of more subtle insights.
Online discussion forums leverage digital platforms to connect individuals remotely, broadening accessibility and facilitating participation from various geographical areas.
The selection of target demographic types is influenced by several factors, including specific research goals, participant accessibility, and financial limitations. For instance, conventional discussion panels may be more effective for sensitive subjects, where face-to-face interaction can nurture trust and transparency. However, online discussion panels have surged in popularity due to their flexibility and cost-effectiveness, particularly in reaching a broader audience.
Recent studies indicate that online discussion panels can yield outcomes comparable to conventional methods, making them a viable option for numerous researchers. Notably, the significance of native knowledge systems has been recorded in 16% of research, underscoring the importance of diverse perspectives in collective dialogues.
Expert advice highlights that the efficacy of discussion panels can vary significantly based on their structure. While conventional panels are praised for their ability to generate extensive qualitative information, they may face challenges such as intimidation among attendees and dynamics that hinder open communication, as noted in a study examining the difficulties and restrictions of panel discussions. In contrast, online panels offer advantages in terms of convenience and participant comfort, although they may lack the immediacy of face-to-face interactions.
As George, T. states, "Scope of research is established at the start of your research process, before the stage," emphasizing the critical nature of thorough planning in participant selection. Ultimately, the choice of participant assembly type should align with the research objectives and the specific context of the study, particularly considering the flexibility and adaptability of participant interactions for sensitive subjects.
Designing Effective Focus Group Discussions: Key Considerations
Creating effective conversations through focus group engagement tools demands meticulous planning and consideration of several critical factors. Setting clear objectives is paramount, as these will guide the entire conversation process. A well-structured discussion guide is vital; it should encompass open-ended questions that foster dialogue and encourage participants to express their thoughts freely, rather than confining responses to mere yes or no answers.
Team dynamics significantly influence the success of discussion panels. Cultivating a diverse combination of personalities within the team can lead to balanced and engaging discussions. This diversity often results in deeper exchanges and a broader spectrum of insights.
Research indicates that 12% of studies have addressed conservation conflicts and the application of conservation tools, underscoring the importance of discussion panels in monitoring environmental and social impacts.
Before the actual session, conducting a pilot test of the guide with a small team can prove invaluable. This practice allows for the refinement of questions and format, ensuring that the guide effectively elicits the desired information. As noted by Mary Beth Weber, "Our findings indicate that saturation was achieved after four discussion sessions, during which 94% of all codes and 96% of high-prevalence codes were identified, and the codebook had stabilized."
This statement highlights the critical nature of a well-prepared approach in achieving saturation in qualitative studies. Furthermore, a comparative analysis revealed that saturation occurred consistently across various coding strategies when five focus teams were utilized, demonstrating the significance of diverse participant samples and coding techniques.
However, it is crucial to acknowledge the limitations within existing studies, such as the insufficient assessment of theme comprehension and the lack of examination regarding how team composition affects saturation. By integrating these best practices with focus group engagement tools, facilitators not only enhance the quality of conversations but also increase the likelihood of obtaining actionable insights that can inform decision-making processes. By focusing on these essential factors, facilitators can orchestrate gatherings that are both effective and impactful.
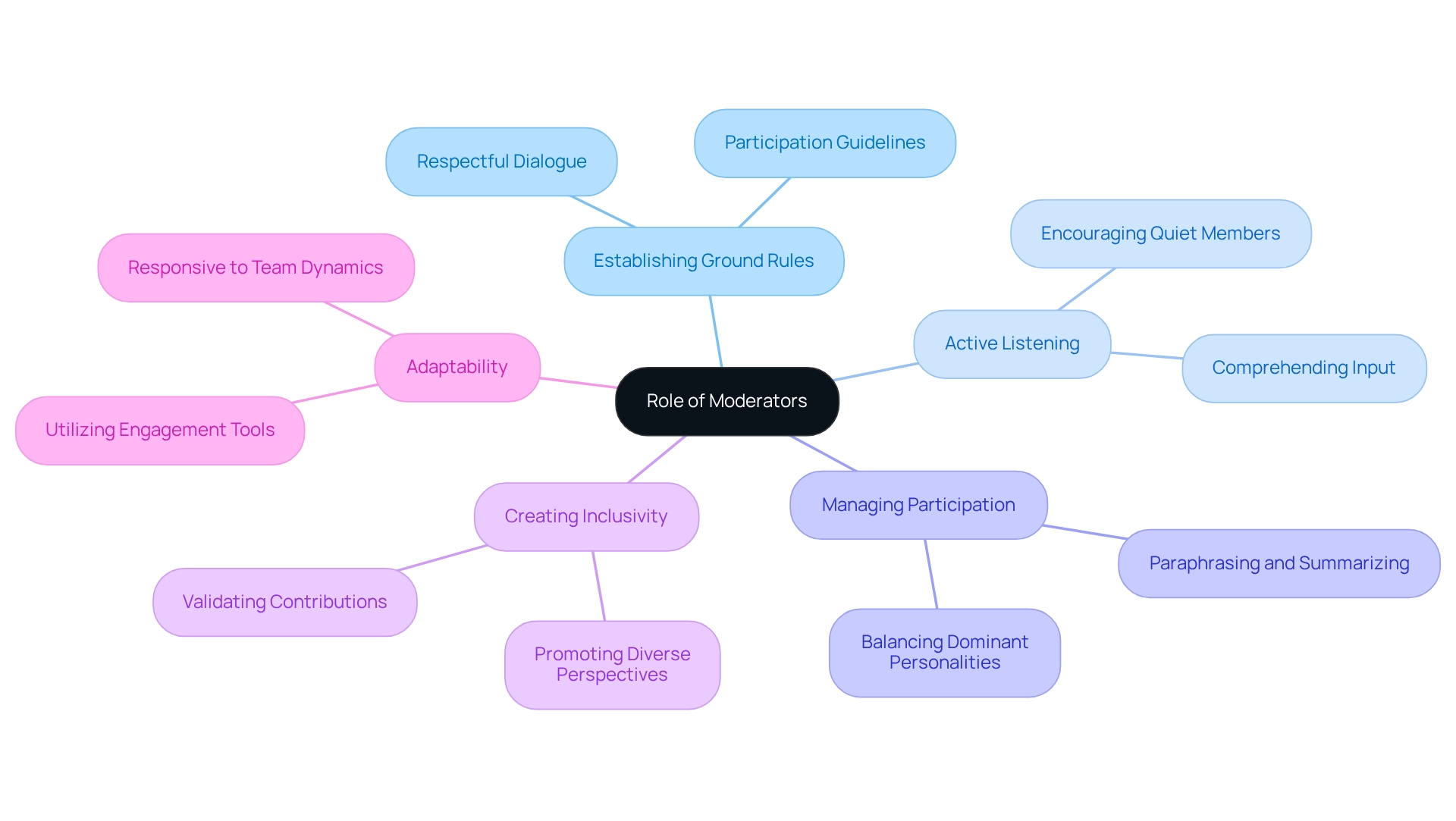
The Role of Moderators: Best Practices for Facilitating Discussions
Facilitators play a crucial role in the success of group sessions, especially when utilizing focus group engagement tools. They guide conversations and ensure that every individual has the opportunity to share their insights. To maximize effectiveness, moderators must establish clear ground rules, setting the stage for respectful and productive dialogue. Active listening is fundamental; moderators should not only hear but also comprehend contributors' input, encouraging quieter members to voice their opinions.
Managing dominant personalities is another essential responsibility. Effective moderators employ strategies to balance participation, ensuring that no single voice overshadows others. Techniques such as paraphrasing and summarizing are invaluable, as they clarify points and help maintain focus on the discussion objectives.
Creating an inclusive environment is paramount. A skilled moderator fosters open dialogue by validating all contributions and promoting diverse perspectives. This approach not only enhances the quality of the data gathered but also cultivates a sense of community among contributors, leading to deeper insights.
Given that glossophobia is the most prevalent fear among Americans, it is vital for moderators to create a comfortable atmosphere that encourages participation. Fear of public speaking can significantly hinder contributions.
As we look to 2025, the role of moderators continues to evolve, with an increasing emphasis on adaptability and responsiveness to team dynamics. Successful moderation techniques, such as utilizing focus group engagement tools like visual aids or interactive tools, can further engage participants and enrich discussions. However, it is crucial to recognize that discussion techniques may not be suitable for all research settings, and facilitators should be mindful of potential constraints.
Case studies, such as 'Focus Group Discussions as a Tool for Indigenous Knowledge,' demonstrate that when moderators effectively manage team dynamics, outcomes are significantly enhanced, leading to more comprehensive and actionable insights. Adequate planning and arrangement are essential for productive collective conversations, which can serve as an economical and swift method for data gathering. As noted by a Customer Intelligence Director, "Kadence were an excellent partner on this project; they took time to really understand our business challenges and developed a research approach that would tackle the exam question from all directions. The impact of the work is still being felt now, several years later." This underscores the importance of effective moderation in achieving lasting results.
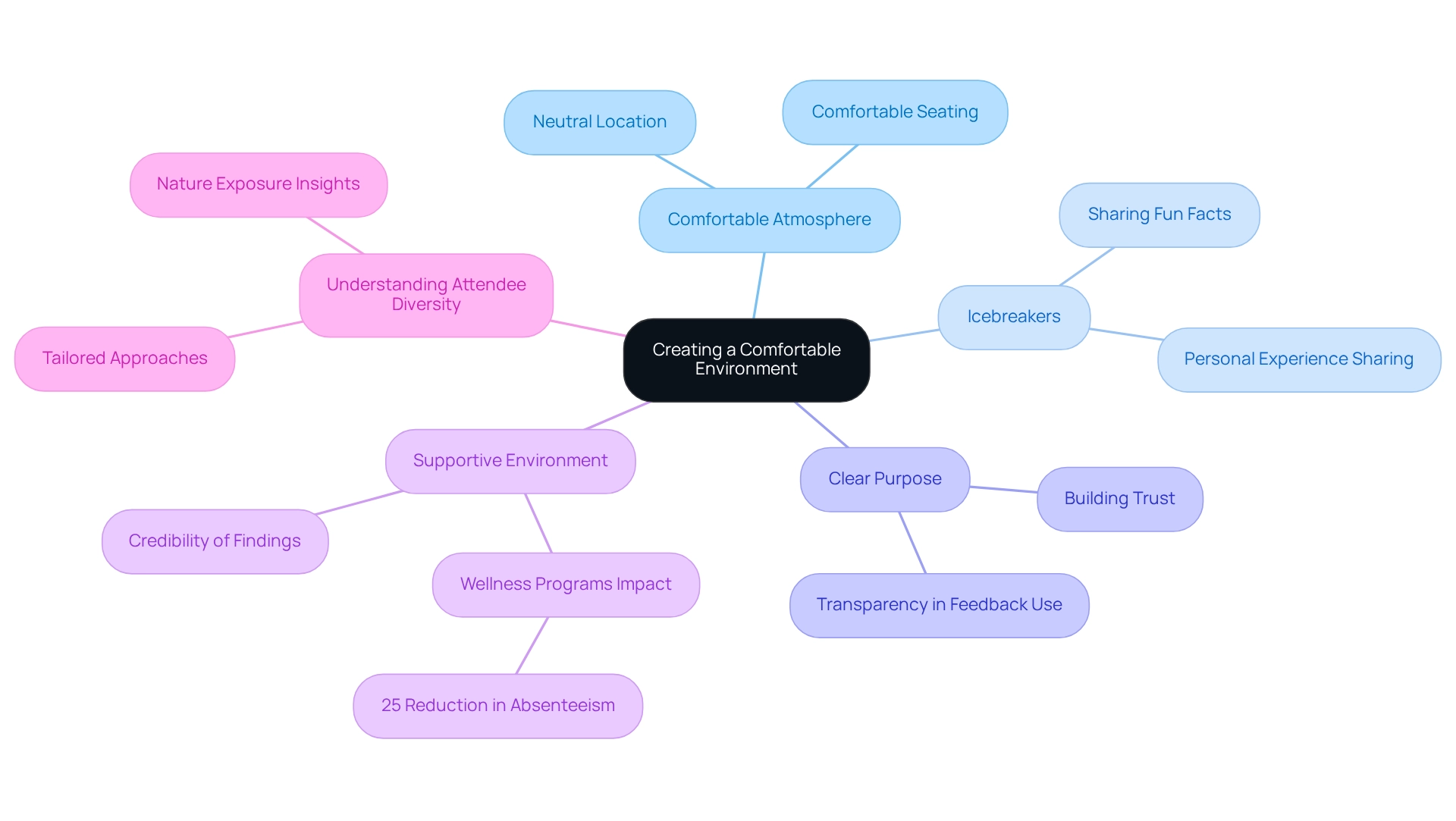
Creating a Comfortable Environment: Enhancing Participant Engagement
Establishing a comfortable atmosphere for focus group members is crucial for fostering open and honest communication. A neutral, quiet location paired with comfortable seating arrangements lays the groundwork for a productive discussion. Initiating the session with icebreakers significantly aids individuals in easing into the conversation, allowing them to relax and build rapport.
For example, simple activities such as sharing a fun fact or a personal experience related to the topic can effectively break the ice.
Moreover, clearly articulating the purpose of the focus group and how the feedback will be utilized is essential. This transparency cultivates trust and encourages individuals to share their authentic views, ultimately yielding deeper insights through focus group engagement tools. Research indicates that when individuals feel comfortable and valued, their engagement levels rise significantly, enhancing the overall quality of the discussion.
In fact, wellness programs that foster supportive environments have been shown to reduce employee absenteeism by 25%. This suggests that the comfort of participants can lead to increased engagement and productivity.
Creating a supportive atmosphere not only enhances communication but also bolsters the credibility of the findings derived from focus group engagement tools. Case studies demonstrate that tools designed to prioritize attendee comfort yield more reliable data, as individuals are more likely to express genuine opinions in a welcoming environment. The case study titled 'Guidelines for Future Applications of Discussion Sessions' underscores the importance of clear reporting and methodological rigor, reinforcing the necessity for a well-organized approach in discussion settings.
Additionally, understanding the diverse backgrounds of attendees is vital. A recent study on nature exposure revealed that individuals conceptualize nature in deeply personal ways, suggesting that facilitators should tailor their approaches to accommodate varying perceptions. This understanding can enhance attendees' comfort levels, leading to more meaningful discussions.
Finally, a survey from Hays reveals that 47% of active job seekers consider leaving their jobs due to poor company culture. This statistic underscores the importance of cultivating a positive atmosphere, drawing a parallel to the necessity of participant comfort. Therefore, dedicating time and effort to create a comfortable environment is a best practice that can significantly impact the success of discussion sessions.
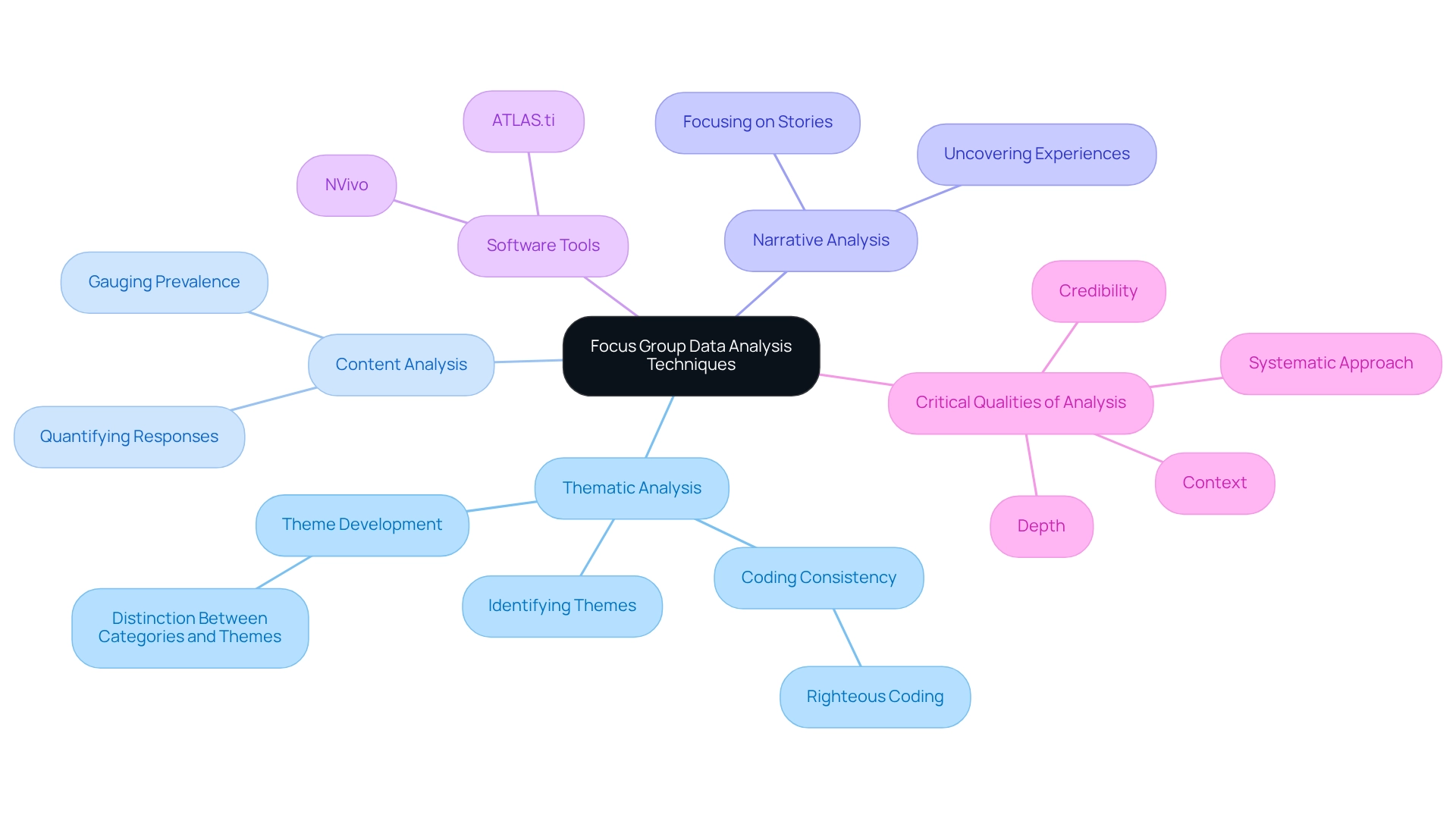
Analyzing Focus Group Data: Techniques and Tools for Insight Extraction
Analyzing focus group data demands a multifaceted approach to extract valuable insights that propel decision-making. A particularly effective method is thematic analysis, which involves identifying recurring themes and patterns within discussions. This technique not only illuminates the underlying meanings in the data but also connects them to the research questions, crafting a coherent narrative that enhances understanding.
As Attride-Stirling emphasizes, "Righteous coding ensures codes logically fit within the larger coding and align with the research’s purpose; they maintain consistency and understanding of the decisions made during coding."
In addition to thematic analysis, researchers frequently employ content analysis, quantifying specific responses to gauge the prevalence of certain opinions or sentiments. Narrative analysis serves as another valuable technique, focusing on the stories shared by contributors to uncover deeper insights into their experiences and motivations.
To streamline the analysis process, software tools such as NVivo and ATLAS.ti prove invaluable. These platforms facilitate efficient coding and visualization of data, enabling researchers to manage large volumes of qualitative information effectively. By leveraging these tools, analysts ensure that their findings are robust and supported by empirical evidence, culminating in the development of a solid conceptual model.
Ultimately, the objective of these analytical techniques is to utilize focus group engagement tools to translate qualitative insights into actionable strategies. By systematically investigating individuals' views and motivations, organizations can make informed choices that align with stakeholder needs and enhance public involvement. It is crucial to consider the four critical qualities of discussion analysis: depth, context, credibility, and a systematic approach, which guarantee a thorough exploration of individuals' opinions.
Furthermore, the process of theme development in thematic analysis underscores the distinction between categories and themes, emphasizing the importance of grouping related codes to uncover abstract patterns that yield insights into the research questions.
Post-Discussion Follow-Up: Implementing Insights and Tracking Progress
Post-discussion follow-up is essential for maximizing the impact of insights derived from focus group engagement tools. Initiating this process with thank-you notes to contributors conveys gratitude for their input and fosters a sense of engagement. Summarizing key findings and clearly articulating how their feedback will influence decision-making processes is vital for ensuring transparency and trust.
Establishing metrics to track the implementation of insights allows for an assessment of their effectiveness over time. This structured approach guarantees that feedback is not only acknowledged but actively utilized. Regular updates to contributors about the progress achieved from their input reinforce their significance in the process and encourage continued involvement through focus group engagement tools.
Expert recommendations underscore that effective follow-up can significantly enhance the quality of data collected. In fact, statistics reveal that 144 out of 170 studies employed collective conversations alongside other methods, highlighting the importance of qualitative insights. Moreover, the influence of participant feedback on decision-making processes cannot be overstated; when participants witness their contributions leading to tangible outcomes, it bolsters their commitment to future engagements.
As Morgan noted, "Listening to the opinions of the other team (or by watching their interactions) frequently guides the second team to distinct conclusions than those it might have arrived at otherwise," illustrating the dynamic nature of such interactions.
Proper planning and organization are critical for effective collective dialogues, which can leverage focus group engagement tools as a cost-effective data-gathering method. However, it is crucial to avoid organizing dialogues in situations where attendees may feel uncomfortable or where statistical information is required, as this can undermine the method's effectiveness.
Case studies exemplify the benefits of well-structured follow-up strategies. For instance, organizations that have implemented systematic post-discussion follow-ups report richer qualitative insights that inform targeted problem-solving. The case study titled 'The Advantages of Collaborative Sessions' demonstrates that these gatherings facilitate personal conversations, allowing participants to express their concerns in their own words.
By thoughtfully organizing panels and ensuring diverse involvement, organizations can harness these conversations to drive significant transformation.
Best Practices for Focus Group Engagement: Expert Recommendations
To achieve successful participant engagement, organizations must adhere to several best practices:
- Define Clear Objectives: Establish specific goals for the discussion group to guide conversations and ensure that the insights gathered align with organizational needs. This clarity significantly impacts the overall success of the focus group.
- Select Suitable Individuals: Carefully choose individuals based on criteria that reflect the target audience. A varied assembly can offer a wider array of viewpoints, enriching the depth of the conversation. Focus teams can also comprise three participants and a moderator, referred to as triads, which can be effective for more intimate discussions.
- Develop a Structured Discussion Guide: Prepare a well-organized guide featuring open-ended questions that encourage in-depth responses. This structure helps keep the conversation focused while allowing for organic dialogue.
- Create a Comfortable Environment: Foster an atmosphere that promotes open communication. Participants should feel safe to express their thoughts without fear of judgment, leading to more honest and valuable feedback.
- Employ Skilled Moderators: Utilize experienced moderators who can effectively manage group dynamics, ensuring that all voices are heard and that the dialogue remains productive.
- Analyze Data Effectively: Implement appropriate data analysis techniques to extract actionable insights from the discussions. This step is crucial for translating qualitative feedback into strategic recommendations.
- Follow Up with Attendees: After the session, engage with attendees to share findings and demonstrate how their input will be utilized. Research indicates that follow-up can significantly increase participant engagement; those who receive updates are 12 times more likely to feel involved. Kristin Ryba's research shows that employees who report follow-up after a survey are 12 times more engaged than those who do not.
- Test Marketing and Advertising Messages: Use panels to evaluate marketing and advertising messages prior to making substantial investments. This approach guarantees that campaigns connect with the intended audience and may result in more impactful marketing strategies.
By adopting these optimal methods, organizations can improve the efficiency of their discussion efforts through focus group engagement tools. This results in better-informed decision-making and enhanced outcomes in marketing and engagement strategies. For instance, before launching a marketing or advertising campaign, businesses can utilize focus group engagement tools to test their messaging and visuals, making necessary adjustments based on feedback to align with customer expectations.
Conclusion
Understanding and implementing focus groups is not merely beneficial; it is essential for organizations aiming to gain deeper insights into consumer behavior and stakeholder needs. Focus groups unveil nuanced perspectives that traditional surveys often overlook, highlighting their critical role in qualitative research. By categorizing various types of focus groups—from traditional to online formats—it becomes clear that the choice of method significantly influences the richness of the data collected.
The effective design and facilitation of focus group discussions depend on several key considerations. Establishing clear objectives, creating a comfortable environment, and employing skilled moderators are paramount. These practices foster open dialogue, enabling participants to express their thoughts freely and contribute to more meaningful discussions. Furthermore, analyzing focus group data through thematic and content analysis techniques ensures that valuable insights are extracted and transformed into actionable strategies.
Equally critical is the post-discussion follow-up, which reinforces participant engagement and demonstrates the impact of their contributions on decision-making processes. By maintaining transparency and communicating outcomes, organizations can cultivate a sense of community and encourage ongoing participation in future discussions.
Ultimately, focus groups serve as a powerful tool for qualitative data collection, allowing organizations to connect more profoundly with their audiences. By adhering to best practices and prioritizing participant comfort and engagement, organizations can leverage focus groups to inform their strategies and drive meaningful change. In today’s data-driven landscape, capturing the complexities of human experience through focus groups is not just advantageous; it is indispensable for success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are focus panels?
Focus panels are organized conversations involving a select group of individuals, guided by a moderator, aimed at gathering qualitative insights on specific topics. They are crucial in sectors like market research, community engagement, and policy development.
Why are discussion panels significant?
Discussion panels unveil nuanced perspectives and provide insights that often surpass those obtained through traditional surveys. They help organizations understand stakeholder needs and preferences, capturing the complexities of human experiences.
How do discussion panels differ from traditional surveys?
Unlike traditional surveys, discussion panels do not adhere to a scientific and quantitative methodology; they excel at capturing qualitative insights and the intricacies of participants' thoughts and feelings.
What are the potential benefits of participating in discussion panels?
Participants can earn compensation for their involvement, as illustrated by a participant who earned $10,740 from 95 sessions over a decade.
What are the costs associated with organizing discussion panels?
Costs can include participant compensation and venue rental, but these expenses are often outweighed by the valuable insights gained from the discussions.
What are the different types of focus panels?
The main types include conventional discussion sessions (6-10 individuals in-person), mini discussion sessions (fewer individuals for deeper insights), and online discussion forums (connecting individuals remotely).
When might a conventional discussion panel be more effective?
Conventional discussion panels may be more effective for sensitive subjects where face-to-face interaction can foster trust and transparency among participants.
What advantages do online discussion panels offer?
Online discussion panels provide flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to reach a broader audience, making them increasingly popular among researchers.
How do the outcomes of online discussion panels compare to conventional methods?
Recent studies indicate that online discussion panels can yield outcomes comparable to conventional methods, making them a viable option for many researchers.
What factors influence the selection of target demographics for discussion panels?
Factors include specific research goals, participant accessibility, and financial limitations, which guide the choice of panel type and participant assembly.
What challenges do conventional discussion panels face?
Conventional panels may encounter issues such as intimidation among attendees and dynamics that hinder open communication, affecting the quality of discussions.
How important is planning in the research process involving discussion panels?
Thorough planning in participant selection is critical, as noted by experts, to ensure the research scope aligns with the objectives and context of the study.
List of Sources
- Understanding Focus Groups: Definition and Importance
- The focus group will never die (https://vox.com/the-goods/2019/1/22/18187443/focus-groups-brand-market-research)
- The Role Of Market Research Focus Groups (https://andrewreise.com/insights/the-role-of-market-research-focus-group)
- Focus Groups: The Definitive Guide - Qualtrics (https://qualtrics.com/experience-management/research/focus-groups)
- Exploring Different Types of Focus Groups: A Comprehensive Overview
- The use of focus group discussion methodology: Insights from two decades of application in conservation (https://besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/2041-210x.12860)
- What Is a Focus Group? | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples (https://scribbr.com/methodology/focus-group)
- Designing Effective Focus Group Discussions: Key Considerations
- The use of focus group discussion methodology: Insights from two decades of application in conservation (https://besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/2041-210x.12860)
- What Influences Saturation? Estimating Sample Sizes in Focus Group Research - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6635912)
- The Role of Moderators: Best Practices for Facilitating Discussions
- 5 key goals for moderators during research | Articles (https://quirks.com/articles/5-key-goals-for-moderators-during-research)
- The use of focus group discussion methodology: Insights from two decades of application in conservation (https://besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/2041-210x.12860)
- Understanding the Role of a Focus Group Moderator. | Kadence (https://kadence.com/en-us/understanding-the-role-of-a-focus-group-moderator)
- Creating a Comfortable Environment: Enhancing Participant Engagement
- (PDF) Focus group discussion in built environment qualitative research practice (https://researchgate.net/publication/323669687_Focus_group_discussion_in_built_environment_qualitative_research_practice)
- 20 Employee Engagement Statistics You Need to Know | HR Cloud (https://hrcloud.com/blog/20-employee-engagement-statistics-you-need-to-know)
- The use of focus group discussion methodology: Insights from two decades of application in conservation (https://besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/2041-210x.12860)
- Analyzing Focus Group Data: Techniques and Tools for Insight Extraction
- A Step-by-Step Process of Thematic Analysis to Develop a Conceptual Model in Qualitative Research - Muhammad Naeem, Wilson Ozuem, Kerry Howell, Silvia Ranfagni, 2023 (https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/16094069231205789)
- Analysis Of Focus Group Data: Top 5 AI Tools For FGD Analysis (https://insight7.io/analysis-of-focus-group-data-top-5-ai-tools-for-fgd-analysis)
- Post-Discussion Follow-Up: Implementing Insights and Tracking Progress
- The use of focus group discussion methodology: Insights from two decades of application in conservation (https://besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/2041-210x.12860)
- Beyond Survey Analytics: How Dialogue & Focus Groups Can Speed Action (https://blog.perceptyx.com/beyond-survey-analytics-how-dialogue-focus-groups-can-speed-action)
- Best Practices for Focus Group Engagement: Expert Recommendations
- Focus Groups: The Definitive Guide - Qualtrics (https://qualtrics.com/experience-management/research/focus-groups)
- How to Conduct an Employee Focus Group: A Full Guide (https://aihr.com/blog/employee-focus-group)
- How to Run a Focus Group: Employee Focus Group Best Practices (https://quantumworkplace.com/future-of-work/employee-focus-groups-your-superpower-improving-employee-engagement)




