Introduction
Navigating the intricate landscape of oil and gas land management requires a comprehensive understanding of the legal, technological, and operational frameworks that govern the sector. As the industry faces mounting regulatory scrutiny and an increasing demand for sustainable practices, companies must adapt their strategies to ensure compliance while optimizing resource extraction.
Central to this endeavor is the integration of advanced technologies and robust data management practices, which not only enhance operational efficiency but also mitigate risks associated with land operations.
This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of oil and gas land management, exploring the legal frameworks, best practices, and future trends that shape the industry's trajectory in a rapidly evolving environment.
Understanding the Legal Framework for Oil and Gas Land Management
The legal framework governing oil and gas land information systems is multifaceted, encompassing a range of laws and regulations that oversee acquisition, environmental stewardship, and resource extraction. Central to this framework is the Mineral Leasing Act, which, alongside various state regulations, outlines the procedures for obtaining land rights and necessary permits. For instance, the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) implemented an annual review of lease suspensions under Permanent Instruction Memorandum 2019-007, reflecting a commitment to ongoing regulatory oversight.
This approach highlights the significance of comprehending these laws for organizations striving to navigate the complex regulatory landscape effectively. The BLM has also proposed a new surface owner protection bond section, maintaining a minimum bond amount of $1,000, which received diverse feedback yet remains unchanged, emphasizing the necessity for companies to remain informed about evolving regulations. As the BLM states, 'This information is exempt from release to the public under exemption 9 of FOIA, and the BLM will respect and maintain the confidentiality of the information.'
Furthermore, engaging with local authorities and stakeholders at the onset of the process is crucial. This proactive strategy not only helps mitigate potential legal challenges but also ensures compliance with all relevant statutes, facilitating smoother project execution. An illustrative case study involves the leasing of combined hydrocarbon leases within National Park System units.
Here, leases are permitted only if they adhere to stringent legal and environmental standards, such as those outlined by the National Park Service, with the Regional Director tasked with ensuring that no significant adverse impacts arise from such activities. The BLM will also negotiate terms of the subsurface storage agreement, including bonding and reservoir management, which are critical considerations for property acquisition. As regulations continue to evolve, particularly in 2024, staying abreast of updates to the Mineral Leasing Act and its implications is vital for successful property acquisition using oil and gas land information systems in the oil and gas industry.
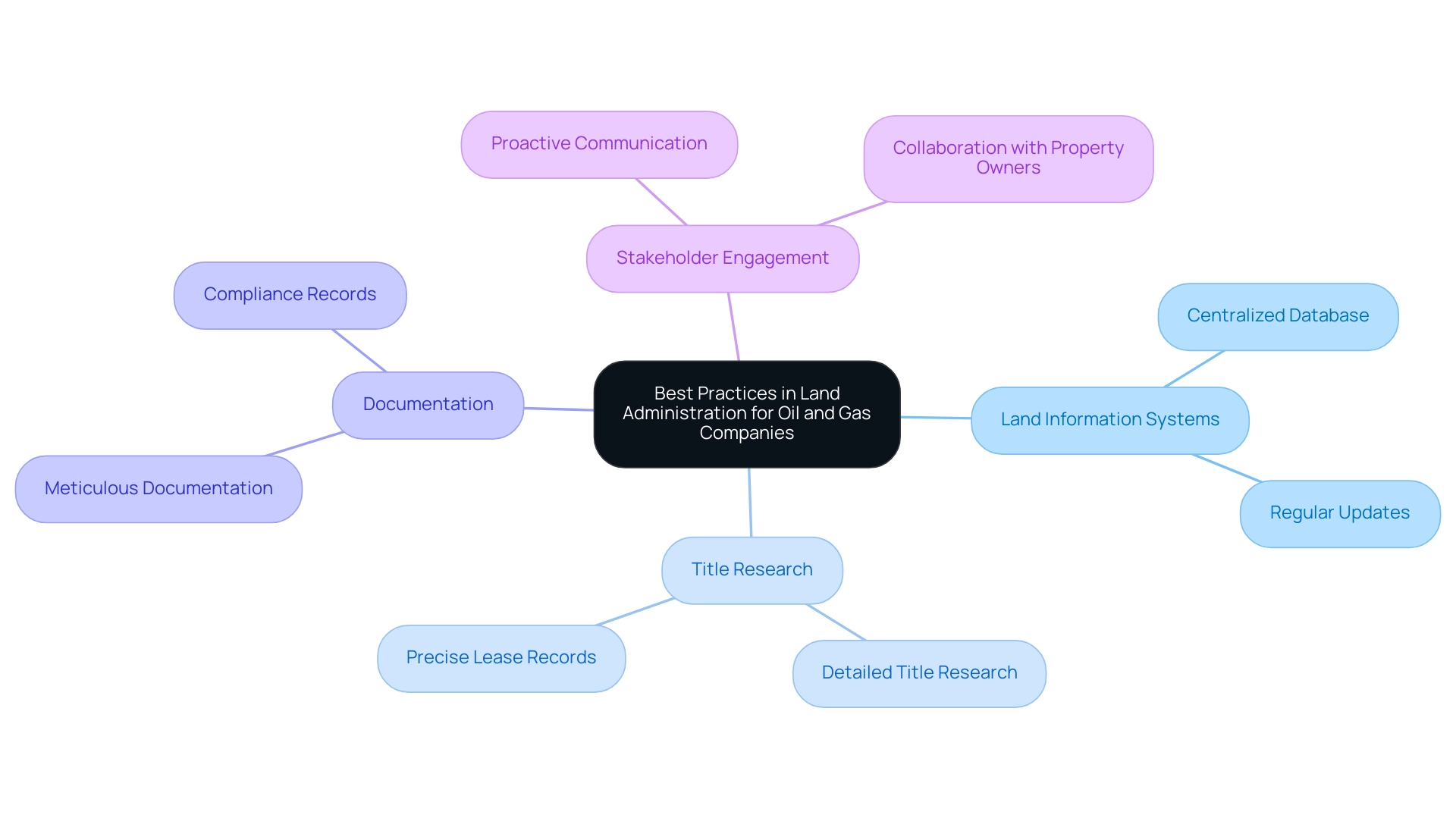
Best Practices in Land Administration for Oil and Gas Companies
To effectively optimize property administration within the oil and gas sector, companies must implement a structured approach that incorporates:
- Oil and gas land information systems
- Detailed title research
- Meticulous documentation
- Proactive stakeholder engagement
The basis of successful property administration lies in regularly updating records and ensuring accurate mapping of leased areas, which are essential for maintaining compliance and preventing disputes. The ongoing consolidation trend in the industry, coupled with the EY-P Deal Barometer's forecast of a steady increase in deal volume in the US M&A market for 2025, underscores the urgency of these practices.
Creating a centralized database for oil and gas land information systems can significantly streamline operations, enhancing accessibility for all stakeholders involved. Furthermore, fostering clear communication channels with property owners and regulatory bodies is crucial for encouraging collaboration and mitigating potential conflicts during the acquisition process.
As highlighted in the case of State of Louisiana v. Haaland, where nearly 6 million acres were controversially removed from Lease Sale 261, the critical nature of precise lease records in upholding legal and procedural standards is paramount.
This situation highlights the need for transparency in property administration, particularly in light of the criticisms surrounding noncompetitive oil and gas land information systems and leasing practices.
Leveraging Technology for Enhanced Land Information Systems
The integration of advanced technologies is set to transform oil and gas land information systems within the sector. AI-driven title research tools are especially significant, as they drastically streamline the title examination process, thereby minimizing the time and resources required for effective property acquisition. Moreover, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) play a critical role by offering robust spatial analysis and visualization capabilities, which enable companies to assess site suitability effectively and make data-driven decisions.
A notable advantage lies in the deployment of cloud-based platforms for information storage and sharing. These platforms facilitate real-time collaboration among project teams, ensuring that every stakeholder has access to the most current and relevant information. By adopting these technologies, organizations not only enhance their operational efficiency but also mitigate the risks associated with land management, positioning themselves favorably in a competitive marketplace.
Significantly, as information centers could consume up to 9% of US electricity generation by 2030, the energy implications of these technologies are considerable. Additionally, as Keyur B. stated, 'Due to a lack of communication, workers from another shift turned on the pump, resulting in an incident that claimed 167 lives.' This underscores the importance of implementing technology to improve communication and reduce risks.
Furthermore, the Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing decision-making in the oil and gas sector by connecting devices that exchange information through oil and gas land information systems, allowing for smoother operations and proactive maintenance, leading to enhanced efficiency and cost reductions.
The Role of Data Management in Oil and Gas Land Operations
In the oil and gas sector, robust oil and gas land information systems are not merely advantageous; they are essential for ensuring operational efficiency and compliance with regulatory mandates. As the industry evolves, companies are increasingly recognizing the critical need for a comprehensive governance framework that guarantees the accuracy, consistency, and security of oil and gas land information systems. Routine evaluations and proactive information cleansing procedures are essential for detecting and correcting discrepancies, which can avert complications during property leasing and regulatory reporting.
According to expert Qiana Matthew, effective information management is crucial in oil and gas land information systems within the oil and gas sector. It enhances efficiency, ensures compliance, mitigates risks, and drives innovation. Furthermore, the integration of analytics solutions is projected to enhance productivity by 6-8% for oil and gas companies, offering valuable insights into land utilization patterns.
This capability enables firms to optimize resource allocation and enhance operational efficiency. Additionally, Rebellion Energy Solutions collaborates with a coalition of partners to address the complex legacy well challenge, demonstrating the importance of teamwork in tackling industry issues. In June 2021, Schlumberger and IBM launched the first commercial hybrid cloud Enterprise Data Management Solution for the OSDU Data Platform, which aims to expand global customer access and enhance analysis speed and decision-making.
This advancement highlights the industry's shift towards innovative information management solutions. By referencing the case study titled 'The Evolving Landscape of Oil and Gas Information Management Market,' we can observe that while the industry faces challenges such as security and high technology adoption costs, there are significant opportunities for differentiation and innovation. By prioritizing data management in oil and gas land information systems, organizations can not only make more informed decisions but also reduce the risks associated with ground operations, positioning themselves for success in a rapidly changing environment.
Future Trends and Challenges in Oil and Gas Land Management
The oil and gas sector is presently undergoing a phase of considerable change, propelled by emerging trends that require a proactive stance from organizations. Increasing regulatory scrutiny is at the forefront, with new regulations pushing for enhanced environmental responsibility in land use and resource extraction. This shift compels organizations to adopt sustainable practices that not only comply with these regulations but also demonstrate a commitment to environmental stewardship.
As highlighted by industry expert Kate Hardin,
Sustainable initiatives are no longer optional; they are essential for long-term viability in the sector.
This insight underscores the challenges and opportunities faced by companies striving to align with sustainability goals. Furthermore, the integration of renewable energy sources into traditional operations is becoming a standard practice, necessitating a comprehensive reevaluation of resource management strategies.
Technological advancements are also reshaping the landscape, with innovations in data analytics, automation, and artificial intelligence revolutionizing oil and gas land information systems. By embracing these technologies, organizations can enhance their operational efficiency and responsiveness to market changes. Additionally, as the oil demand growth shifts towards non-OECD countries, businesses must be agile in adapting to these international market dynamics.
For instance, China's oil demand growth is projected to decline significantly from 1.7 mb/d in 2023 to just 620 kb/d in 2024, reflecting broader shifts in the global energy landscape. Moreover, the case study on non-OECD oil demand growth illustrates how companies can adapt to these changing market conditions, positioning themselves effectively in an evolving industry landscape. By anticipating and strategically responding to these trends and challenges, organizations can position themselves for success.
Conclusion
The intricate landscape of oil and gas land management necessitates a thorough understanding of the legal frameworks, best practices, and technological advancements that shape the industry. As highlighted, the legal framework, particularly the Mineral Leasing Act and various state regulations, is crucial for navigating land acquisition and ensuring compliance with environmental standards. Companies must engage proactively with local authorities to mitigate legal challenges and uphold stringent environmental practices, which have become increasingly vital in light of regulatory scrutiny.
Best practices in land administration, including meticulous title research and stakeholder communication, are essential for optimizing operations. The ongoing consolidation within the industry emphasizes the need for accurate and transparent land records to prevent disputes and enhance collaboration among stakeholders. The integration of advanced technologies, such as AI-driven tools and Geographic Information Systems, has the potential to revolutionize land information systems, significantly improving operational efficiency and decision-making.
Furthermore, robust data management practices are indispensable for ensuring compliance and operational effectiveness. By prioritizing data governance and leveraging analytics, companies can enhance productivity and mitigate risks associated with land operations. As the industry faces evolving challenges, including sustainability mandates and technological advancements, organizations must remain agile and responsive to these changes.
In conclusion, the future of oil and gas land management lies in the effective integration of legal knowledge, best practices, and innovative technologies. By embracing these elements, companies can navigate the complexities of the sector while positioning themselves for success in an increasingly regulated and competitive environment. The commitment to sustainable practices and proactive adaptation to emerging trends will not only ensure compliance but also drive long-term viability in the industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the legal framework governing oil and gas land information systems?
The legal framework is multifaceted, involving various laws and regulations that oversee acquisition, environmental stewardship, and resource extraction, with the Mineral Leasing Act being central to this framework.
What role does the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) play in this legal framework?
The BLM implements regulations such as an annual review of lease suspensions and proposed new sections like the surface owner protection bond, which reflects its commitment to regulatory oversight.
Why is it important for organizations to understand these laws?
Understanding these laws is crucial for organizations to navigate the complex regulatory landscape effectively and ensure compliance with all relevant statutes.
What is the significance of engaging with local authorities and stakeholders?
Engaging with local authorities and stakeholders at the onset of the process helps mitigate potential legal challenges and ensures compliance with regulations, facilitating smoother project execution.
What are the legal and environmental standards for leasing within National Park System units?
Leases are permitted only if they adhere to stringent legal and environmental standards outlined by the National Park Service, ensuring that no significant adverse impacts arise from such activities.
What are critical considerations for property acquisition in oil and gas?
Critical considerations include negotiating terms of subsurface storage agreements, bonding, and reservoir management.
What practices must companies implement for effective property administration?
Companies should implement a structured approach that includes oil and gas land information systems, detailed title research, meticulous documentation, and proactive stakeholder engagement.
How can companies streamline operations in property administration?
Creating a centralized database for oil and gas land information systems can enhance accessibility for all stakeholders involved.
What was the significance of the case State of Louisiana v. Haaland?
This case highlighted the critical nature of precise lease records in upholding legal and procedural standards, particularly as nearly 6 million acres were controversially removed from Lease Sale 261.
Why is transparency important in property administration?
Transparency is vital to address criticisms surrounding noncompetitive oil and gas land information systems and leasing practices, ensuring accountability and compliance.
List of Sources
- Understanding the Legal Framework for Oil and Gas Land Management
- Fluid Mineral Leases and Leasing Process (https://federalregister.gov/documents/2024/04/23/2024-08138/fluid-mineral-leases-and-leasing-process)
- Best Practices in Land Administration for Oil and Gas Companies
- The future of land services in oil and gas (https://ey.com/en_us/insights/oil-gas/the-future-of-land-services-in-oil-and-gas)
- blog.harbingerland.com (https://blog.harbingerland.com/the-role-of-land-services-in-the-oil-and-gas-industry)
- 2025 Oil and Gas Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/oil-and-gas/oil-and-gas-industry-outlook.html)
- americanprogress.org (https://americanprogress.org/article/how-the-federal-government-can-hold-the-oil-and-gas-industry-accountable)
- Leveraging Technology for Enhanced Land Information Systems
- The future of land services in oil and gas (https://ey.com/en_us/insights/oil-gas/the-future-of-land-services-in-oil-and-gas)
- Oil and gas technology trends in 2024 (https://aveva.com/en/perspectives/blog/oil-and-gas-technology-trends-in-2024)
- 2025 Oil and Gas Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/oil-and-gas/oil-and-gas-industry-outlook.html)
- pluto-men.com (https://pluto-men.com/top-oil-gas-industry-challenges-solve)
- The Role of Data Management in Oil and Gas Land Operations
- Oil and Gas Data Management Market Size, Share - 2033 (https://alliedmarketresearch.com/oil-and-gas-data-management-market)
- The Crucial Role of Data Management in the Oil and Gas Industry - Rebellion Energy Solutions (https://rebellionenergy.com/the-crucial-role-of-data-management-in-the-oil-and-gas-industry)
- Global Oil and Gas Data Management Industry Analysis, Share, Growth, Trends, and Forecast 2024 to 2031 (https://linkedin.com/pulse/global-oil-gas-data-management-industry-analysis-share-growth-cbnbe)
- Future Trends and Challenges in Oil and Gas Land Management
- 2025 Oil and Gas Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/oil-and-gas/oil-and-gas-industry-outlook.html)
- Year-End Review: Oil and Gas Market Trends in 2024 | DW Energy Group (https://dwenergygroup.com/year-end-review-oil-and-gas-market-trends-in-2024)
- Oil Market Report - March 2024 – Analysis - IEA (https://iea.org/reports/oil-market-report-march-2024)




