Overview
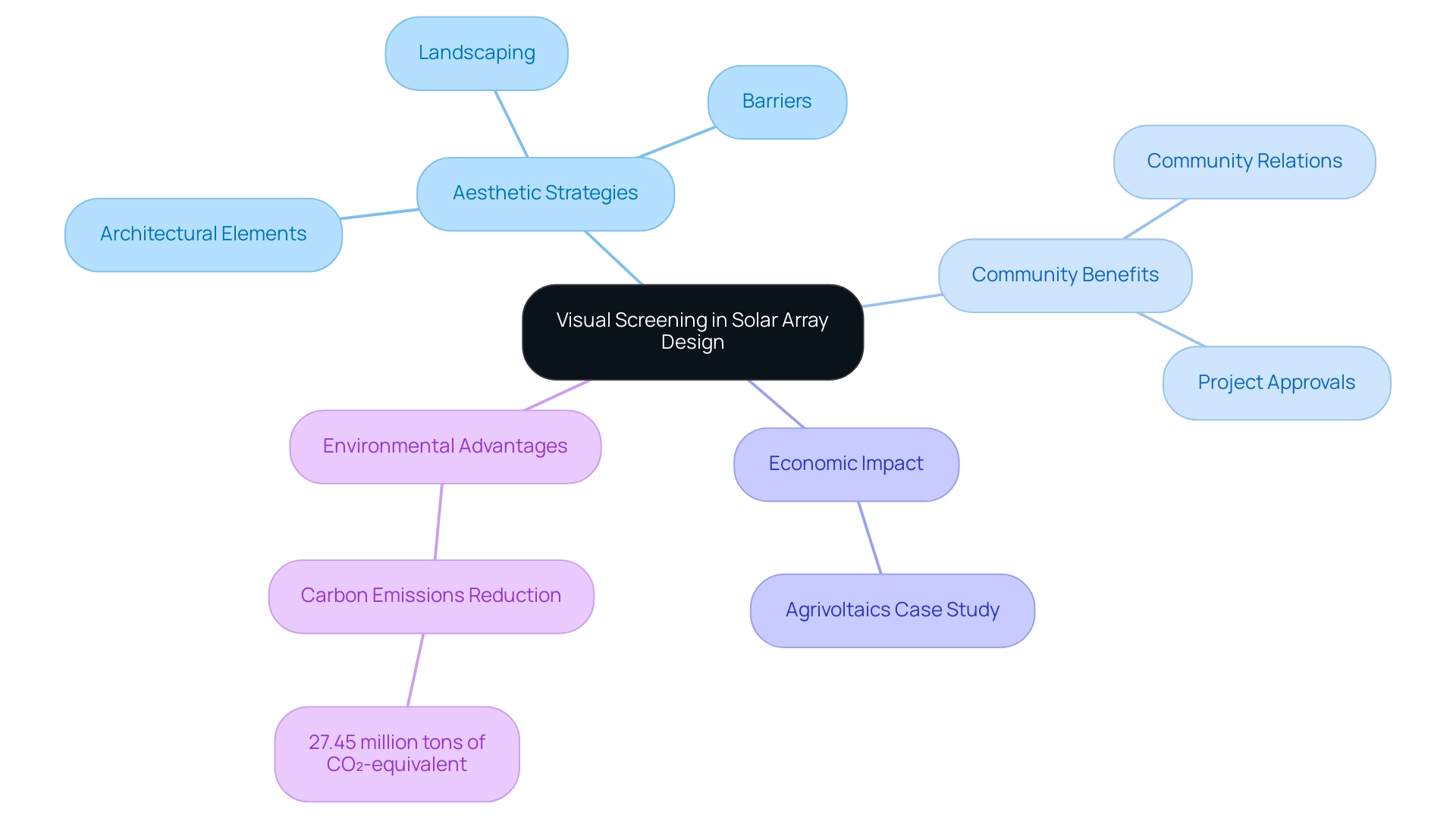
Best practices for visual screening design for solar arrays focus on using landscaping, barriers, and architectural elements to enhance aesthetic appeal and reduce community objections. The article supports this by highlighting that effective visual screening not only fosters positive community relations and project approvals but also demonstrates significant environmental benefits, such as reducing carbon emissions and improving local biodiversity.
Introduction
In the quest for sustainable energy solutions, solar installations often face scrutiny from local communities concerned about their visual impact on the landscape. Visual screening emerges as a vital strategy, employing landscaping, barriers, and architectural features to seamlessly integrate solar arrays into their surroundings. This practice not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of solar projects but also fosters positive community relations, paving the way for smoother project approvals.
By exploring the principles of effective visual screening, developers can mitigate objections and promote harmonious coexistence with local environments. From utilizing native vegetation to advanced design technologies, the potential for visual screening to transform public perception and support for solar energy initiatives is immense, underscoring its importance in the broader renewable energy landscape.
Understanding Visual Screening in Solar Array Design
Aesthetic assessment includes the strategic use of landscaping, barriers, and architectural elements as part of the visual screening design for solar arrays to reduce their impact on the environment. This practice is crucial for ensuring that installations seamlessly integrate into the landscape, significantly reducing community objections. Efficient imagery concealment methods may involve the use of thick greenery, earth mounds, or ornamental fencing intended to hide views of renewable energy systems from adjacent properties and public spaces.
Such measures not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of energy projects but also foster positive community relations and facilitate smoother project approvals. As emphasized in recent studies, understanding and employing visual screening design for solar arrays can lead to a more harmonious coexistence between energy installations and local environments, ultimately benefiting both developers and the communities they serve. Expert insights, such as those from Heon Jeong, emphasize that refining control algorithms for tracking can complement these efforts by optimizing energy capture while considering specific geographic factors.
Additionally, the long-term economic and environmental advantages of photovoltaic projects are underscored by the significant reduction in carbon emissions—estimated at 27.45 million tons of CO₂-equivalent over 25 years. This statistic emphasizes the necessity for careful design approaches that focus on appearance filtering. Additionally, the case study named 'Environmental and Economic Implications of Agrivoltaics' demonstrates how efficient barriers can improve land use effectiveness and decrease carbon footprints, offering a persuasive illustration of its significance in energy systems.
Benefits of Effective Visual Screening for Solar Arrays
Efficient graphical evaluation through visual screening design for solar arrays plays an essential part in enhancing the aesthetic attractiveness of energy panels, thereby boosting their acceptance within nearby communities. By strategically decreasing the prominence of photovoltaic panels, initiatives can alleviate worries associated with landscape disruption and aesthetic pollution. The visual screening design for solar arrays, when well-executed, serves as a buffer, fostering positive community relations and increasing the chances of approval.
For instance, communities that have implemented visually appealing energy installations often demonstrate greater support for future renewable energy initiatives. Notably, the potential for sunlight energy has been included in the descriptions of over 40 million homes, illustrating the extensive reach and relevance of energy projects. The inclusion of native plants in landscaping not only enhances the area but also aids local biodiversity, which can further foster community goodwill.
As one community leader observed, The long-term vision is a key factor in the advancement of renewable technology, highlighting the significance of aesthetics in the broader context of innovation. This method corresponds with the current initiatives in 2024, where various case studies have highlighted successful applications of visual screening design for solar arrays that enhance community acceptance, illustrating how aesthetics can complement improvements in panel efficiency and design.
Materials and Techniques for Visual Screening
The visual screening design for solar arrays can utilize a diverse range of materials and techniques to achieve both aesthetic and ecological benefits. Indigenous trees and shrubs are outstanding options as they not only offer barriers but also support local wildlife habitats, thus enhancing biodiversity. Earth mounds or berms can be strategically implemented to enhance natural barriers and improve the site's topography, creating a more integrated landscape.
In city settings, decorative fencing or trellises embellished with climbing plants can act as effective barriers, softening the overall look of energy installations. Furthermore, the advent of advanced technologies, including AI-powered design tools like reV, facilitates the visual screening design for solar arrays by aiding in the selection of optimal materials and layouts tailored to site-specific conditions. This tool enables calculations of renewable energy capacity and generation, ensuring that graphical assessment aligns with the project's objectives, budgetary limitations, and environmental effects.
It is also essential to consider that system voltages in the United States are typically limited to 600 volts, influencing design decisions. Furthermore, the EPA's findings that photovoltaic panels do not contain sufficient metals to be regarded as scrap metal highlight the ecological implications of the materials employed in aesthetic barriers. As stated by Ahmed Elnozahy:
The anti-static effect of the hydrophobic SiO nanomaterial coating can spread away from the water droplets and produce a thin layer with less resistance for photons, highlighting the potential for innovative materials to enhance array design.
Navigating Regulations and Compliance in Visual Screening
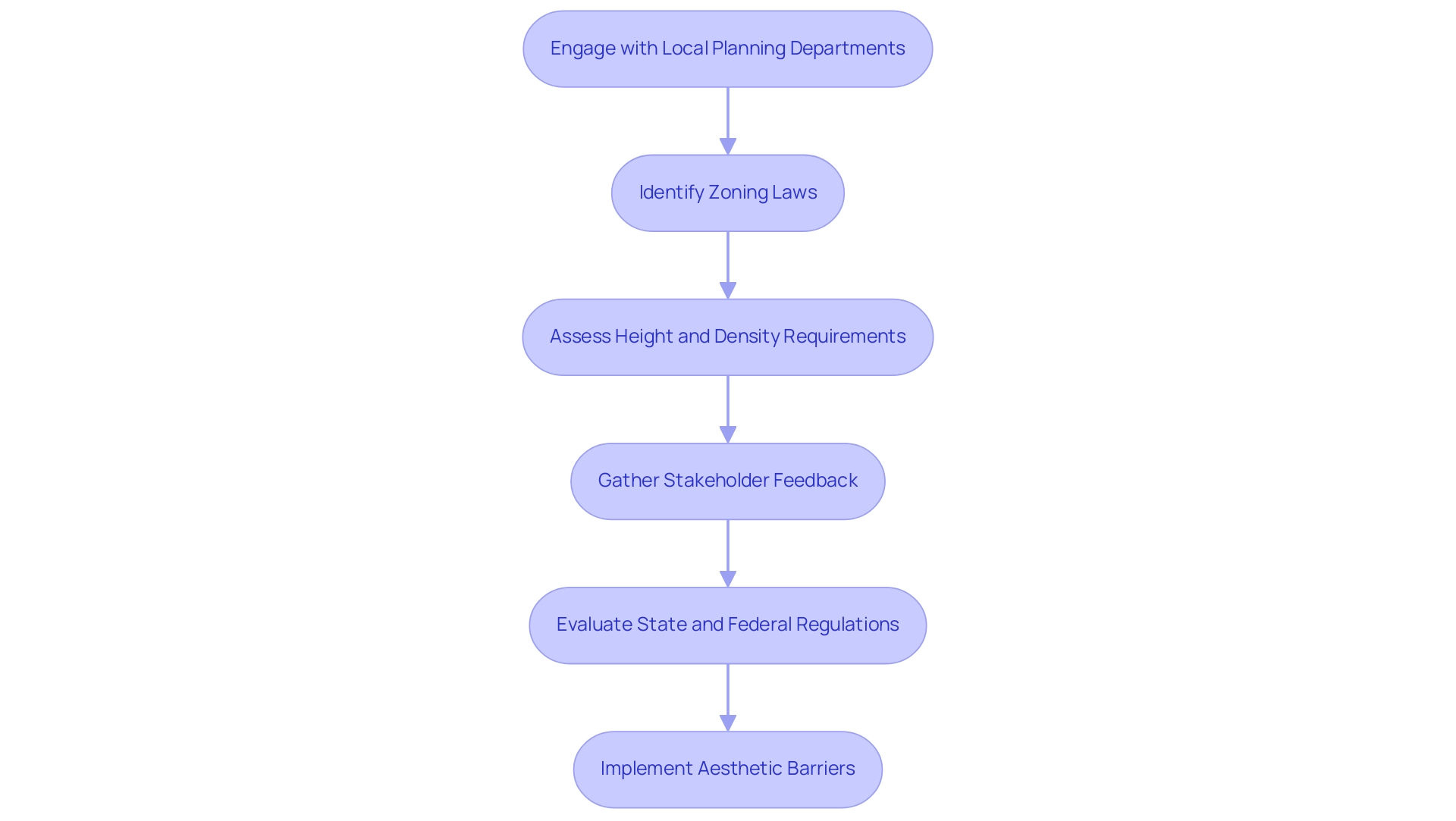
When developing visual screening design for solar arrays, adherence to local zoning laws and regulations is paramount. To implement an effective visual screening design for solar arrays, project developers must navigate specific requirements concerning height, density, and material types. Engaging proactively with local planning departments at the outset of the design process can uncover potential regulatory challenges.
Additionally, seeking feedback from community stakeholders not only improves compliance strategies but also aligns designs with local preferences and concerns. As mentioned by the American Society of Civil Engineers, engineers must stay current with the latest engineering principles, standards, and codes to deliver effective and safe energy solutions. Moreover, conducting consistent evaluations of state and federal regulations is crucial to guarantee that the initiative stays compliant during its development stages, reducing risks related to compliance challenges in array aesthetics.
With the global photovoltaic market anticipated to reach 3.5 TW by the end of 2027, the significance of compliance becomes even more critical as projects expand. A case study named 'Comparison of Solar and Agricultural Land Use' showed that such development takes up a relatively small share of land use in most counties, especially in farming areas, indicating that effective aesthetic barriers can mitigate local issues while promoting this type of expansion. Additionally, the regulatory environment plays a vital role in enabling growth in renewable energy, underscoring the need for robust permitting and grid capacity improvements.
Engaging Stakeholders in Visual Screening Design
Timely involvement of stakeholders in the design process is vital for the success of solar initiatives, particularly given that local opposition is one of the primary reasons for solar initiative cancellations in the United States. This engagement should encompass a diverse range of participants, including:
- local residents
- municipal officials
- environmental organizations
- [other interested parties
Community workshops](https://blog.harbingerland.com/best-practices-for-community-partnerships-for-storage-projects-proven-strategies-for-success) act as a beneficial platform for these stakeholders to express their concerns and preferences concerning visual screening design for solar arrays.
By incorporating visual screening design for solar arrays, developers can significantly enhance stakeholder comprehension of proposed designs. This approach not only fosters open communication but also builds trust, which is essential in minimizing local opposition to solar installations. To further strengthen this relationship, developers can utilize a structured stakeholder engagement plan that includes:
- establishing goals
- getting acquainted with stakeholders
- determining methods of engagement
- establishing a feedback strategy
- maintaining long-term engagement
Consistent email communication, customized updates, and a feedback strategy can ensure stakeholders remain informed about milestones and feel empowered to contribute their insights. As noted by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Solar Energy Technologies Office, 'We thank the U.S. Department of Energy’s Solar Energy Technologies Office for their support of this work, as well as the 54 interviewees who gave generously of their time to offer these insights.' Involving the community throughout the process can yield valuable perspectives that honor the experiences of farmers and landowners while promoting successful outcomes.
Case Studies: Successful Visual Screening in Solar Projects
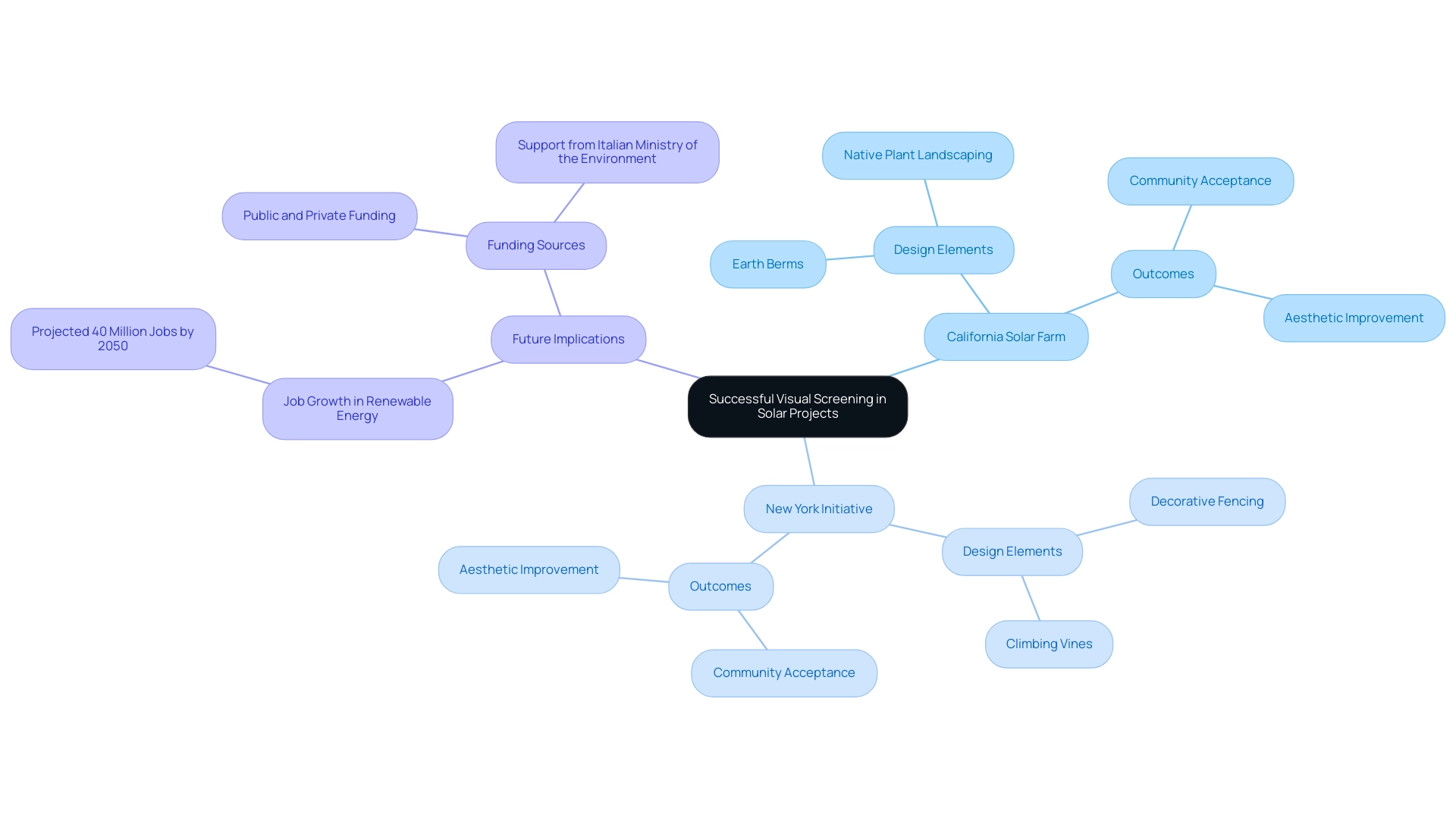
Many renewable energy initiatives have effectively utilized visual screening design for solar arrays, providing important insights for upcoming developments. A notable example comes from a solar farm in California, where a blend of native plant landscaping and earth berms was utilized to create an effective visual barrier between the installation and nearby residential areas. This considerate method led to remarkable community acceptance, emphasizing the importance of considering local aesthetics in planning.
Similarly, an initiative in New York showcased the use of decorative fencing interwoven with climbing vines. This not only provided assessment but also improved the overall aesthetic charm of the location, showing that functionality and beauty can coexist in energy installations. These case analyses demonstrate that strategic imagery assessment can greatly enhance initiative results, encouraging community backing while reducing aesthetic effect.
As Gabriele Lobaccaro observes in his evaluation of renewable energy in urban planning, insights from such initiatives are essential for future efforts in incorporating renewable infrastructure within urban environments. Moreover, with the renewable energy sector anticipated to generate over 40 million jobs by 2050, the visual screening design for solar arrays not only enhances community acceptance but also contributes to the broader viability and support for renewable initiatives. Funding for these projects has come from a mix of public and private sources, including significant support from the Italian Ministry of the Environment, underscoring the collaborative effort needed to implement successful solar installations.
Conclusion
Effective visual screening is integral to the successful integration of solar installations within local communities. By thoughtfully employing landscaping, barriers, and architectural features, developers can significantly reduce the visual impact of solar arrays, thereby addressing community concerns and fostering positive relations. Techniques such as using native vegetation, earth mounds, and decorative fencing not only enhance aesthetic appeal but also contribute to local biodiversity, which can lead to increased community support for renewable energy initiatives.
The importance of engaging stakeholders early in the design process cannot be overstated. By incorporating feedback from local residents and officials, project developers can align their designs with community preferences, thereby minimizing opposition and facilitating smoother project approvals. Case studies have illustrated that projects employing effective visual screening strategies often experience greater acceptance, demonstrating that aesthetics and functionality can indeed coexist in solar development.
Ultimately, as the demand for sustainable energy solutions continues to grow, the role of visual screening in solar installations will be paramount. It is not merely about reducing visual pollution; it is about creating harmonious relationships between renewable energy projects and the communities they serve. The future of solar energy hinges on the ability to balance ecological benefits with community aesthetics, ensuring that both developers and residents can thrive together in a greener landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is aesthetic assessment in the context of solar arrays?
Aesthetic assessment involves the strategic use of landscaping, barriers, and architectural elements to visually screen solar arrays, reducing their environmental impact and ensuring they integrate seamlessly into the landscape.
Why is visual screening design important for solar installations?
Visual screening design is crucial as it reduces community objections, enhances the aesthetic appeal of energy projects, fosters positive community relations, and facilitates smoother project approvals.
What methods are commonly used for visual screening of solar arrays?
Common methods include using thick greenery, earth mounds, and ornamental fencing to hide views of renewable energy systems from adjacent properties and public spaces.
How does visual screening benefit community relations?
By decreasing the prominence of photovoltaic panels, visual screening alleviates concerns about landscape disruption, leading to increased community support for renewable energy initiatives.
What are the long-term economic and environmental advantages of photovoltaic projects?
Photovoltaic projects significantly reduce carbon emissions, estimated at 27.45 million tons of CO₂-equivalent over 25 years, highlighting the importance of careful design approaches.
How does the inclusion of native plants in landscaping impact solar array projects?
Including native plants enhances the area’s aesthetic appeal and aids local biodiversity, which can foster community goodwill.
What role does aesthetics play in the advancement of renewable technology?
Aesthetics are key to the long-term vision for renewable technology, as visually appealing installations can lead to greater community acceptance and support for future projects.
Are there any studies that support the effectiveness of visual screening design?
Yes, recent studies and case studies have highlighted successful applications of visual screening design for solar arrays, showing how aesthetics can improve community acceptance and complement panel efficiency and design improvements.




