Introduction
Navigating the intricate landscape of wind energy development requires an in-depth understanding of regulatory frameworks that govern this rapidly evolving sector. At the federal, state, and local levels, numerous regulations dictate the operations of wind energy projects, with key regulatory bodies such as the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) and the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) playing pivotal roles in overseeing compliance.
As developers embark on their projects, they must grapple with diverse state-specific regulations, local zoning laws, and environmental assessments, all of which can significantly influence project timelines and costs. The economic implications of these regulations are underscored by recent data, revealing substantial increases in power purchase agreement prices.
Furthermore, the importance of stakeholder engagement and community relations cannot be overstated, as these factors are crucial in ensuring the success and sustainability of wind energy initiatives.
This article delves into best practices for compliance, environmental impact assessments, community engagement strategies, and the ongoing monitoring necessary for maintaining regulatory adherence, ultimately highlighting the vital interplay between regulatory frameworks and the advancement of renewable energy resources in the United States.
Understanding Regulatory Frameworks for Wind Energy Compliance
The development of wind energy land compliance operates under a complex web of regulatory frameworks at federal, state, and local levels, necessitating a comprehensive understanding by developers. Key regulatory bodies include:
- The Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM), which oversees offshore initiatives.
- The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC), responsible for issuing permits.
It is crucial for developers to navigate state-specific regulations, including aspects of wind energy land compliance, which can differ significantly and may encompass local zoning laws, environmental assessments, and land use policies.
As noted by an industry expert, understanding wind energy land compliance regulations is vital, as they can significantly impact project timelines and costs. Recent statistics highlight the economic implications of these regulations, with:
- Solar PPA prices rising 21% year over year.
- Wind PPA prices increasing by 16%.
Moreover, cultivating positive connections with stakeholders and local communities is crucial for the success of any wind power initiative.
Recent developments, including updates from BOEM and FERC, underscore the evolving nature of regulations related to wind energy land compliance. Furthermore, case studies on recent innovations in blade design and configuration illustrate how technological advancements can improve adherence to regulatory frameworks, ultimately aiding the growth of renewable power resources in the United States.
Expert Tips for Ensuring Land Compliance in Wind Energy Projects
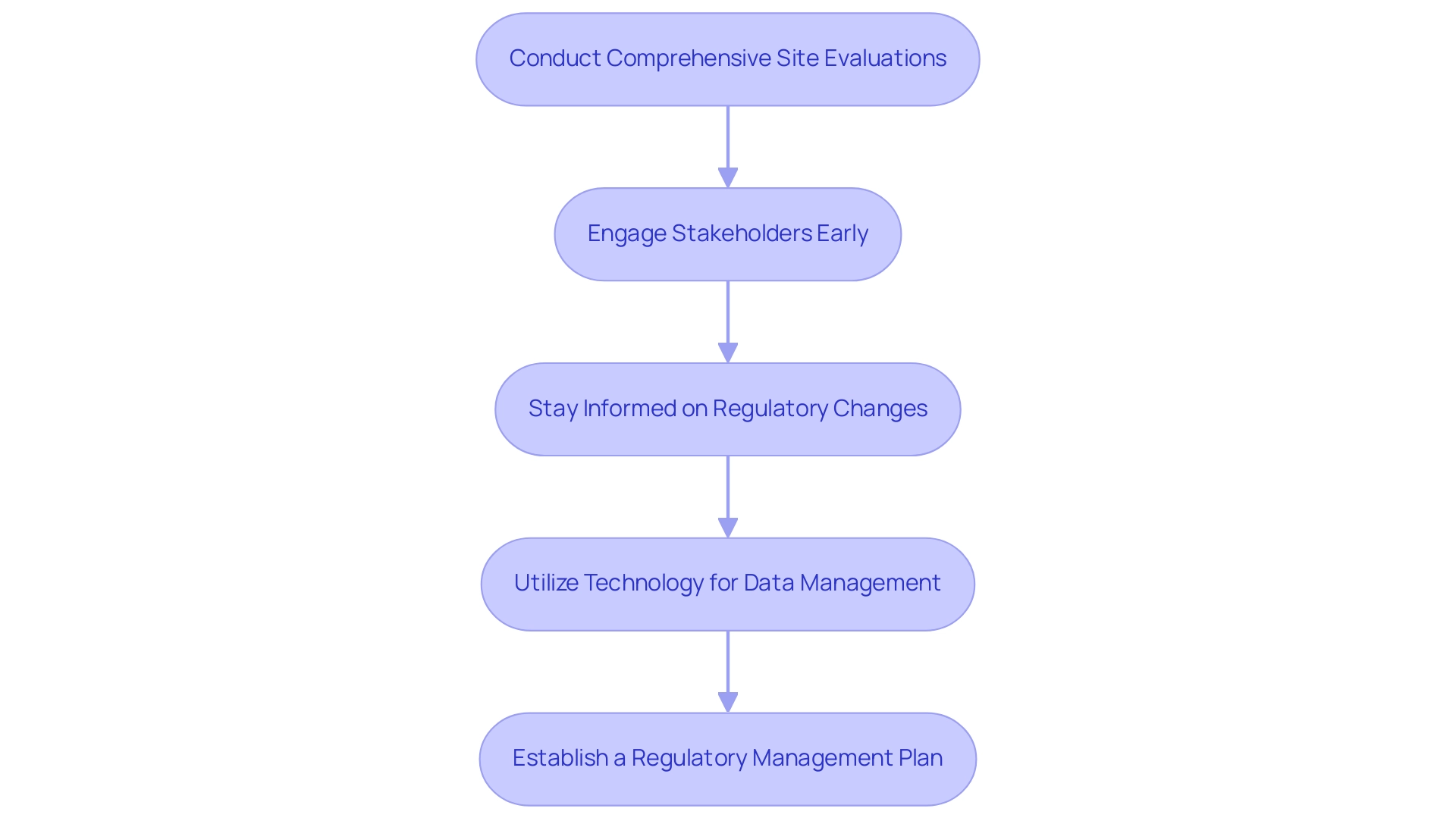
Ensuring land compliance in wind energy projects requires a strategic, multi-faceted approach that encompasses several critical practices:
- Conduct Comprehensive Site Evaluations: Before starting the endeavor, it is crucial to carry out thorough site evaluations to identify possible regulatory challenges, such as the existence of protected species or areas of environmental sensitivity. According to recent studies, approximately 70% of delays in initiatives related to wind energy land compliance can be attributed to unforeseen compliance issues, underscoring the importance of proactive measures to prevent costly delays later in the process.
- Engage Stakeholders Early: Involving local stakeholders—including landowners, regulatory agencies, and residents—at the initial stages of the initiative is essential. Early involvement helps to address concerns, fosters transparency, and builds trust within the community, which is crucial for smooth progression. As Seyed H. Aghay Kaboli states in his work on offshore wind energy assessment, "effective planning and stakeholder engagement are essential components of successful energy projects," highlighting the importance of a well-rounded strategy in this rapidly evolving sector.
- Stay Informed on Regulatory Changes: Developers must regularly monitor updates from regulatory bodies to remain compliant with evolving regulations. Changes can occur due to new environmental assessments or political shifts, making it imperative to stay informed and adapt accordingly.
- Utilize Technology for Data Management: Advanced GIS mapping tools and AI-powered software can significantly enhance data management processes, streamlining title research and documentation. Firms that have adopted these technologies have reported significant time savings and enhanced precision in their regulatory efforts.
- Establish a Regulatory Management Plan: A robust regulatory management plan is crucial. It should clearly outline procedures, assign responsibilities, and set timelines for meeting regulatory requirements. This proactive approach assists in monitoring adherence milestones and preparing for audits.
By applying these best practices, developers can effectively reduce risks related to wind energy land compliance regulations, thereby improving the overall success of their wind initiatives. The case study titled "Offshore Wind Potential Assessment" illustrates how utilizing various data sources, including ECMWF ERA5 reanalysis wind data, can inform adherence and site evaluations, filling knowledge gaps regarding offshore wind characteristics and power potential. This thorough strategy for adherence not only promotes success in endeavors but also fosters sustainable growth in the power sector.
Navigating Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs)
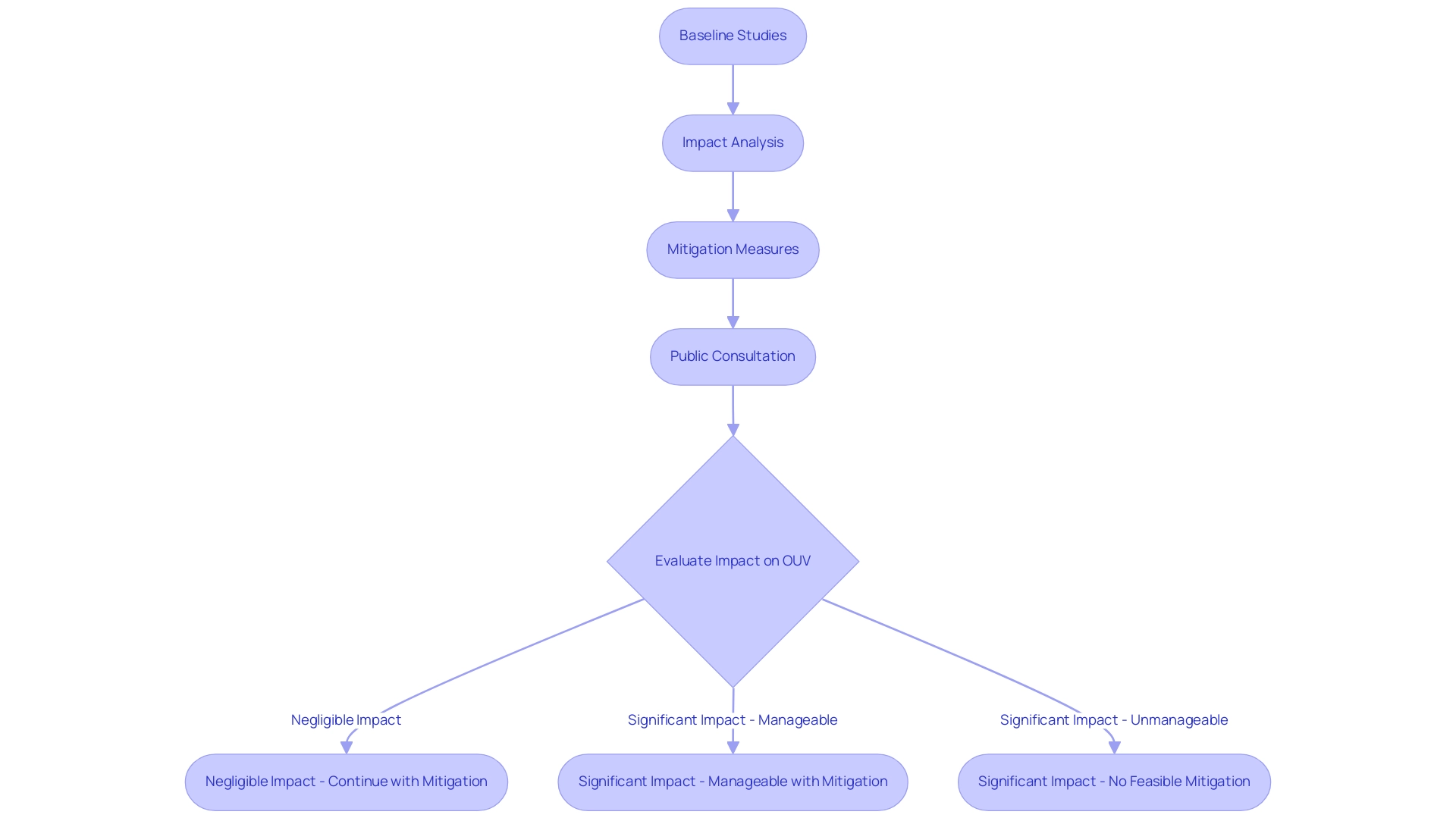
Conducting an Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) is an essential step in the planning phase of wind energy initiatives to ensure wind energy land compliance, especially given the European Union's mandate that requires member states to perform EIAs for proposals in sensitive locations, such as World Heritage sites. Engaging environmental consultants who have expertise in EIA processes is crucial for developers. A successful EIA comprises several key components:
- Baseline Studies: These studies evaluate the current environmental conditions of the proposed site, including assessments of local flora, fauna, and ecosystem dynamics.
- Impact Analysis: This step involves identifying potential impacts of the initiative on these environmental factors, taking into account both short-term disruptions and long-term consequences.
- Mitigation Measures: Developers must propose strategies to minimize adverse impacts, which may include adjusting turbine placements to avoid critical habitats or implementing wildlife protection programs.
- Public Consultation: Engaging local populations early in the EIA process is vital for gathering feedback and addressing concerns, ultimately fostering goodwill and transparency.
As articulated in Target 11.4 of the Sustainable Development Goals, efforts must be made to 'Protect the world's cultural and natural heritage.' By following these best practices in EIAs, developers not only ensure wind energy land compliance with regulatory requirements but also foster trust with stakeholders and the public, paving the way for successful implementation.
The execution of public benefit mechanisms in wind power initiatives has shown how such practices can result in heightened local investment and backing for renewable resources, further emphasizing the significance of stakeholder involvement. If negative effects on Outstanding Universal Value (OUV) are identified, three conclusions may be reached regarding its feasibility: negligible impacts allowing continuation with mitigation, significant impacts manageable through avoidance and mitigation, or significant impacts with no feasible mitigation leading to rejection.
Implementing Community Engagement Strategies
Successful involvement of the public is crucial for the achievement of wind initiatives, as it cultivates trust and cooperation between developers and local participants. To achieve this, the following strategies should be considered:
- Early and Ongoing Communication: Engaging with local residents before finalizing plans allows for valuable input and feedback, which can significantly enhance design and acceptance.
- Educational Workshops: Organizing workshops provides an opportunity to inform the public about the benefits of wind energy, dispelling misconceptions and addressing concerns directly. These sessions not only inform but also empower residents to participate in the dialogue.
- Transparency in Operations: Maintaining open lines of communication throughout the process lifecycle is critical. Keeping the public informed about progress, potential impacts, and mitigation strategies fosters trust and demonstrates accountability.
- Community Benefits: Clearly articulating how the initiative will benefit the local community—through job creation, increased tax revenue, and environmental enhancements—can significantly bolster support. According to Carolyn Amon, a research manager in the power and utilities sector, the increasing focus on public involvement is reflected in the anticipated rise of residential solar attachment rates, which are expected to jump from 14% in 2023 to a record 25% in 2024.
This emphasizes the significance of nurturing connections in renewable energy initiatives. Additionally, the forthcoming assembly of United Nations negotiators from 196 nations in Dubai from Nov. 30 to Dec. 12 emphasizes the global importance of public involvement in attaining sustainable development goals. By applying these strategies, developers can not only establish strong backing for their initiatives but also guarantee smoother adherence to wind energy land compliance requirements.
The document named 'Best Practices in Public Involvement' details recommendations for involving populations in resource initiatives, highlighting the significance of grasping local circumstances and stakeholder requirements. Effective engagement processes can result in enhanced local economies and autonomy, while also tackling potential negative effects on communities.
Monitoring and Reporting Compliance
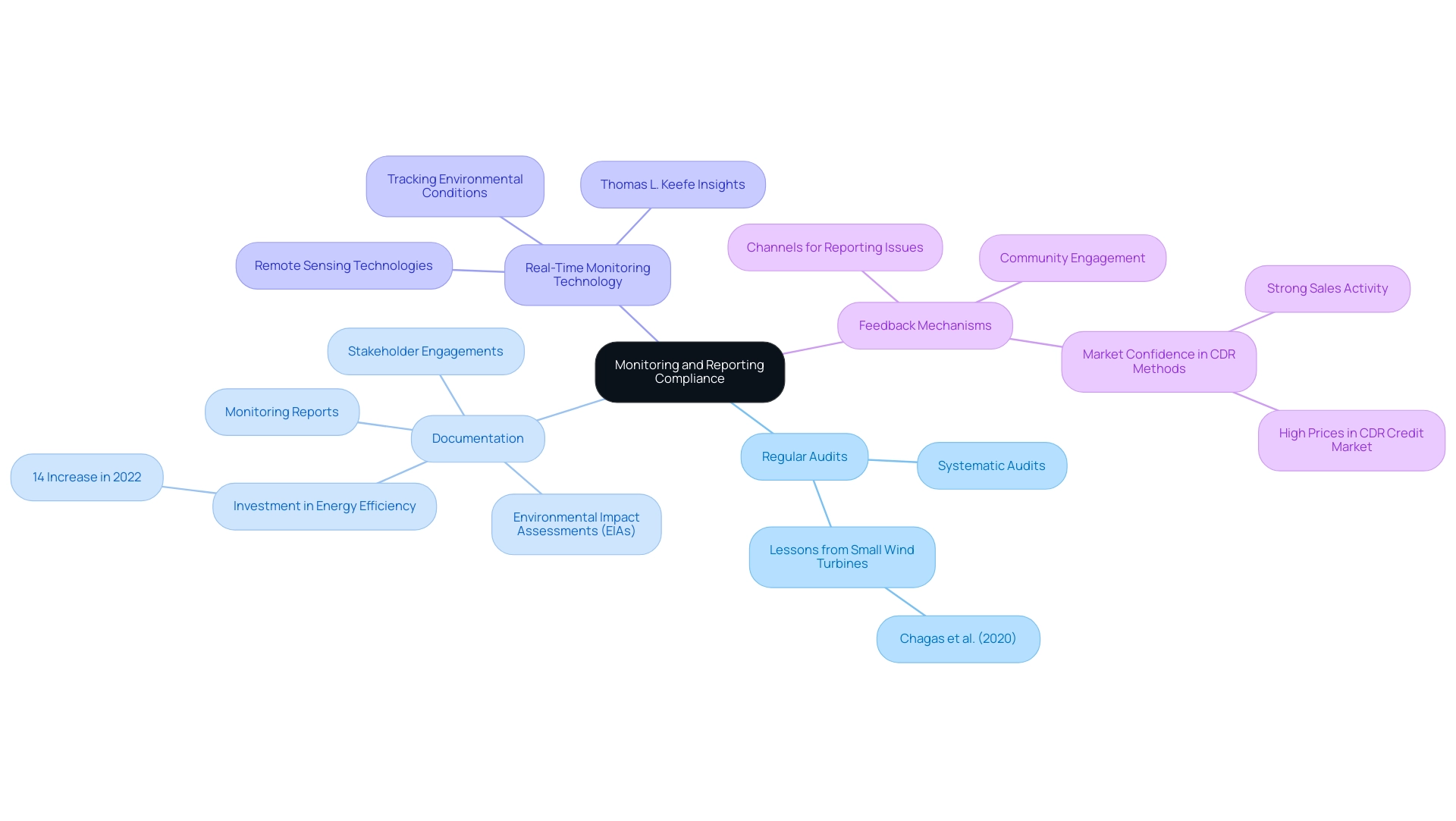
Once wind energy projects are operational, the need for continuous monitoring and reporting becomes paramount to ensure wind energy land compliance with regulatory standards. Developers are encouraged to adopt the following best practices:
-
Regular Audits: Conducting systematic audits at scheduled intervals is vital for evaluating adherence to environmental and land use regulations.
This proactive measure allows for early identification of potential issues, thereby ensuring wind energy land compliance and reducing the risk of non-compliance. As highlighted by Chagas et al. (2020), lessons learned from small wind turbine applications can inform these audit processes, leading to enhanced adherence practices.
-
Documentation: Documentation of wind energy land compliance involves maintaining comprehensive records of adherence activities, including Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs), stakeholder engagements, and monitoring reports.
Such documentation not only serves as proof of wind energy land compliance during regulatory inspections but also facilitates transparent communication with stakeholders.
The recent 14% increase in investment in energy efficiency in buildings underscores the financial implications of thorough documentation and compliance monitoring.
-
Real-Time Monitoring Technology: The integration of advanced monitoring technologies enables developers to track environmental conditions and effects in real-time.
For instance, remote sensing technologies can effectively monitor wildlife activity around turbine sites, facilitating timely adjustments to project operations. Recent advancements in these technologies highlight their increasing importance in ensuring environmental adherence. As Thomas L. Keefe, Vice Chair of US Power, Utilities, and Renewables at Deloitte & Touche LLP, notes, understanding these trends is crucial for navigating the evolving landscape of the wind energy sector.
-
Feedback Mechanisms: Creating clear channels for members to express concerns or report adherence issues improves transparency and accountability.
Engaging with the community not only enables developers to swiftly address potential problems but also fosters trust and collaboration.
The case analysis on market trust in carbon removal techniques demonstrates the significance of monitoring and verification in adherence practices, reflecting how robust sales activity and elevated prices in the CDR credit market can enhance confidence in such initiatives.
By prioritizing these monitoring and reporting practices, developers can ensure ongoing wind energy land compliance, strengthen relationships with regulators, and contribute to the sustainable development of wind energy projects.
Conclusion
Navigating the regulatory landscape of wind energy development is a complex task that demands a thorough understanding of compliance requirements at various levels of government. This article emphasizes the critical roles of the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) and the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC), along with the necessity of familiarizing oneself with state-specific regulations and environmental assessments that can impact project timelines and costs.
To achieve successful land compliance, developers should implement strategic practices such as:
- Comprehensive site assessments
- Proactive stakeholder engagement
- Robust compliance management plans
Utilizing technology for data management and real-time monitoring can significantly enhance the ability to address compliance risks. Additionally, conducting thorough Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) and building strong community relations are essential for fostering trust and support for renewable energy initiatives.
Ongoing monitoring and reporting are crucial for ensuring adherence to regulatory standards. By conducting regular audits and maintaining detailed compliance documentation, developers can demonstrate their commitment and strengthen relationships with stakeholders.
In summary, the interaction between regulatory frameworks and successful wind energy development highlights the need for a comprehensive approach that prioritizes compliance, stakeholder engagement, and environmental stewardship. As the demand for renewable energy resources grows, developers must navigate these complexities effectively to ensure project viability and contribute to the advancement of sustainable energy solutions in the United States.
Frequently Asked Questions
What regulatory bodies oversee wind energy land compliance?
Key regulatory bodies include the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM), which oversees offshore initiatives, and the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC), responsible for issuing permits.
Why is understanding state-specific regulations important for wind energy developers?
State-specific regulations can differ significantly and may include local zoning laws, environmental assessments, and land use policies, all of which can impact project timelines and costs.
What recent trends have been observed in wind and solar Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) prices?
Solar PPA prices have risen by 21% year over year, while wind PPA prices have increased by 16%.
What is the significance of stakeholder engagement in wind energy projects?
Engaging local stakeholders early helps address concerns, fosters transparency, and builds trust within the community, which is essential for the smooth progression of projects.
What are some critical practices for ensuring land compliance in wind energy projects?
Critical practices include conducting comprehensive site evaluations, engaging stakeholders early, staying informed on regulatory changes, utilizing technology for data management, and establishing a regulatory management plan.
How can technology improve regulatory compliance in wind energy projects?
Advanced GIS mapping tools and AI-powered software can enhance data management processes, streamline title research, and improve precision in regulatory efforts, leading to significant time savings.
What role does a regulatory management plan play in wind energy projects?
A regulatory management plan outlines procedures, assigns responsibilities, and sets timelines for meeting regulatory requirements, helping to monitor adherence and prepare for audits.
What recent case study demonstrates the importance of data in wind energy compliance?
The 'Offshore Wind Potential Assessment' case study shows how utilizing various data sources, including ECMWF ERA5 reanalysis wind data, can inform adherence and site evaluations, addressing knowledge gaps regarding offshore wind characteristics and power potential.
List of Sources
- Understanding Regulatory Frameworks for Wind Energy Compliance
- 2025 Renewable Energy Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/renewable-energy/renewable-energy-industry-outlook.html)
- US Clean Power Development Sees Record Progress, As Well As Stronger Headwinds (https://wri.org/insights/clean-energy-progress-united-states)
- Innovations in Wind Turbine Blade Engineering: Exploring Materials, Sustainability, and Market Dynamics (https://mdpi.com/2071-1050/16/19/8564)
- Expert Tips for Ensuring Land Compliance in Wind Energy Projects
- Wind data | solar data | energy resource monitoring | Resource Panorama (https://dnv.com/services/wind-data-and-solar-data-energy-resource-monitoring-resource-panorama-3813)
- Offshore Wind Energy Resource Assessment across the Territory of Oman: A Spatial-Temporal Data Analysis (https://mdpi.com/2071-1050/13/5/2862)
- Resources time footprint analysis of onshore wind turbines combined with GIS-based site selection: A case study in Fujian Province, China (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0973082623000546)
- Navigating Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs)
- whc.unesco.org (https://whc.unesco.org/en/wind-energy/impacts)
- windexchange.energy.gov (https://windexchange.energy.gov/projects/wildlife)
- Implementing Community Engagement Strategies
- 2025 Renewable Energy Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/renewable-energy/renewable-energy-industry-outlook.html)
- As States Advance Clean Energy Projects, 2024 Looms as Pivotal Year (https://pewtrusts.org/en/research-and-analysis/articles/2023/11/30/as-states-advance-clean-energy-projects-2024-looms-as-pivotal-year)
- (PDF) Stakeholder engagement and influence: Strategies for successful energy projects (https://researchgate.net/publication/382514218_Stakeholder_engagement_and_influence_Strategies_for_successful_energy_projects)
- (PDF) Community Engagement and Equity in Renewable Energy Projects: A Literature Review (https://researchgate.net/publication/373738458_Community_Engagement_and_Equity_in_Renewable_Energy_Projects_A_Literature_Review)
- Monitoring and Reporting Compliance
- Innovations in Wind Turbine Blade Engineering: Exploring Materials, Sustainability, and Market Dynamics (https://mdpi.com/2071-1050/16/19/8564)
- iea.org (https://iea.org/energy-system/buildings)
- 2025 Renewable Energy Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/renewable-energy/renewable-energy-industry-outlook.html)




