Overview
This article serves as a comprehensive guide for conducting a local solar zoning analysis, specifically designed to identify suitable areas for renewable energy installations in compliance with zoning laws. It underscores the critical need for stakeholder engagement, thorough regulation analysis, and the formulation of recommendations that promote community acceptance and streamline the permitting process. Such efforts are essential for facilitating the successful implementation of solar energy projects.
Introduction
In the quest for sustainable energy solutions, solar zoning analysis stands out as a crucial tool for aligning local regulations, land use, and community aspirations with the escalating demand for solar energy development. This systematic approach not only pinpoints suitable areas for solar installations but also guarantees compliance with existing zoning laws, fostering community acceptance and minimizing conflicts with current land uses.
Notably, a staggering 73% of contested solar projects encounter challenges at the state or local level, underscoring the necessity of understanding the nuances of solar zoning. As stakeholders navigate the intricate landscape of land rights acquisition and regulatory frameworks, effective strategies become essential for paving the way toward a more renewable-focused future, harmonizing technological advancements with community needs.
Understanding Solar Zoning Analysis: Importance and Objectives
The local solar zoning analysis serves as a vital systematic framework for assessing local regulations, land use patterns, and community objectives concerning renewable development. Its primary aim is to identify areas that are suitable for renewable energy installations and compliant with existing zoning laws. This analysis empowers local authorities to create effective frameworks, such as model ordinances, that promote the use of renewable resources while minimizing conflicts with existing land uses.
By offering clear guidelines, these ordinances assist communities in managing energy initiatives effectively and improving community acceptance by addressing local issues and aligning development with community goals. Consider the staggering statistic: 73% of contested projects between 2010 and 2021 faced challenges solely at the state or local level, as noted by Adelman. Furthermore, existing fuel efficiency standards do not guarantee ongoing advancements in lowering emissions, underscoring the significance of local solar zoning analysis in achieving broader sustainability objectives.
The dynamics of the interconnection queue reveal that there is currently more power storage and generation capacity in the queue than operational, highlighting the urgent need for reform in the interconnection process. By leveraging Harbinger Land's expert site and right-of-way acquisition services, including advanced GIS mapping and thorough title research, stakeholders can navigate the complexities of land rights acquisition efficiently. Harbinger Land employs methodologies such as spatial analysis and data visualization in their GIS modeling services to identify optimal sites for energy projects, ensuring compliance with zoning regulations.
Additionally, their title research services provide critical insights into land ownership and rights, mitigating risks associated with land acquisitions. Comprehending the unique local context and the multifaceted advantages of renewable energy, along with Harbinger Land's capabilities, facilitates informed decision-making that fosters a more favorable environment for renewable energy initiatives.
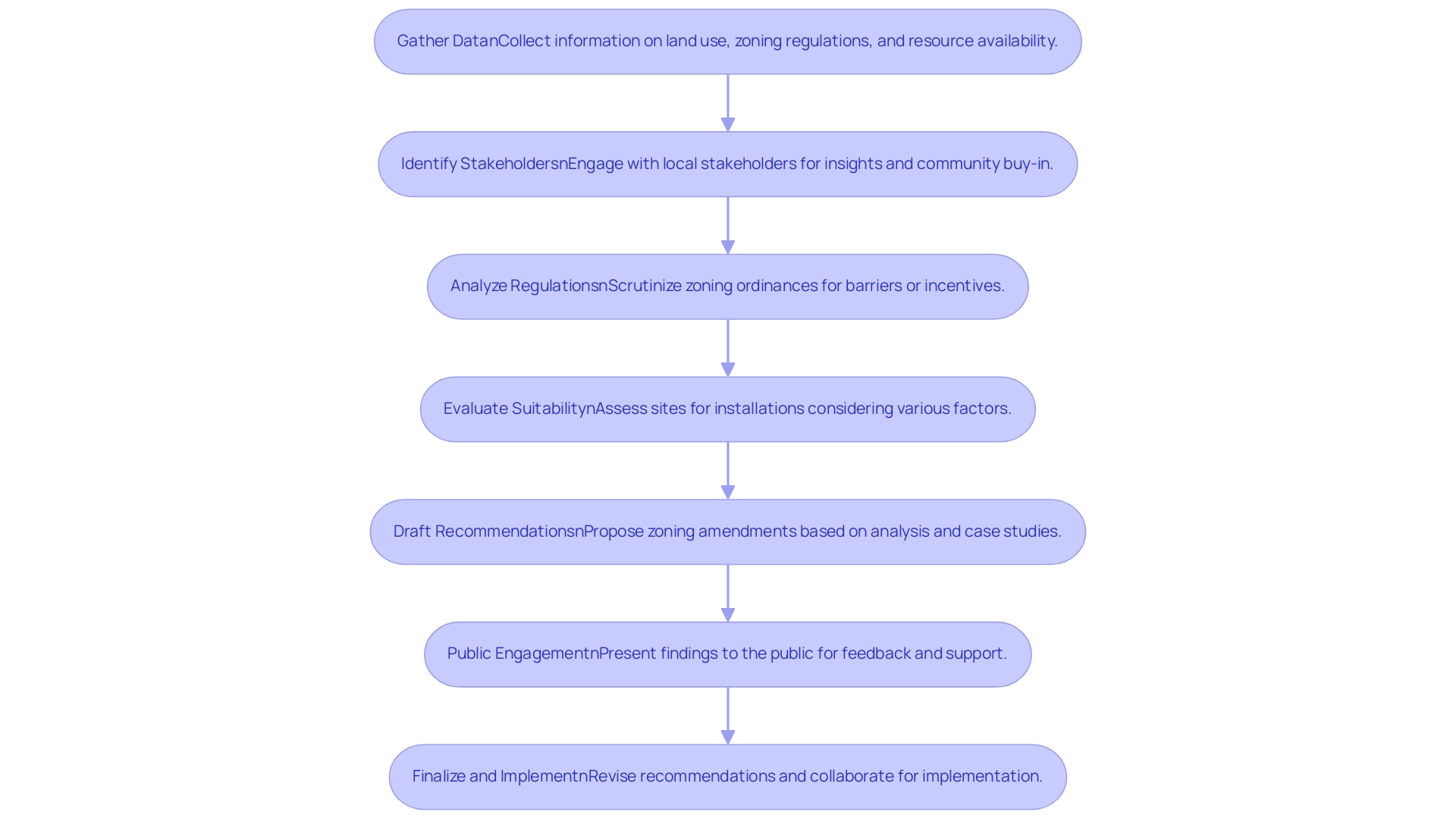
Step-by-Step Process for Conducting a Solar Zoning Analysis
-
Gather Data: Begin by collecting comprehensive information on local land use, existing zoning regulations, and resource availability. Utilize advanced GIS mapping tools to visualize potential energy sites, leveraging Solargis data, which is precisely computed for specific geographical references, ensuring high accuracy in assessments. Notably, 46 out of 66 studies were performed in temperate climates, underscoring the relevance of this data in similar regions.
-
Identify Stakeholders: Engage with local stakeholders, including government officials, residents, and renewable energy developers. This collaboration is essential for gathering insights, addressing concerns, and fostering community buy-in. As stated by Julia Matuszewska,
By applying the above data analytics lifecycle, power organizations can collect and analyze reliable data, gather meaningful insights, implement data-driven solutions, and continuously monitor and iterate to drive improvement.
-
Analyze Regulations: Conduct a local solar zoning analysis to scrutinize existing zoning ordinances and identify any barriers or incentives for renewable energy development. Focus on critical aspects such as height limitations, setbacks, and land use classifications as part of the local solar zoning analysis that may affect the feasibility of the energy initiative.
-
Evaluate Suitability: Assess the identified sites for installations, considering sunlight access, environmental impacts, and proximity to existing infrastructure. Understanding these factors is vital for evaluating the feasibility of energy projects in the area.
-
Draft Recommendations: Following the local solar zoning analysis, propose recommendations for zoning amendments or new regulations that promote renewable energy development while considering local needs. Use findings from the Regional Solar Resource Assessment Methodology case study, which demonstrated improved solar resource availability maps in Évora, Portugal, as a guide for developing similar methodologies. Ensure that these recommendations are supported by comprehensive, accurate, and robust data management practices, including systematic validation procedures for data inputs to maintain data integrity.
-
Public Engagement: Present your findings to the public through meetings or workshops. This step is crucial for collecting feedback and fostering support for proposed changes, ensuring that the public feels involved in the planning process.
-
Finalize and Implement: Revise the recommendations based on public input, finalize the zoning amendments, and collaborate with local authorities to implement the changes. This structured approach not only enhances the likelihood of successful project outcomes but also fosters a sense of ownership among community stakeholders.
Navigating Legal and Regulatory Frameworks for Solar Development
Effectively navigating the legal and regulatory frameworks for renewable energy development necessitates a comprehensive understanding of local, state, and federal requirements. Key considerations in this process include:
- Zoning Ordinances: A thorough review of local zoning laws is essential to ascertain where photovoltaic installations are permitted. This entails conducting a local solar zoning analysis to identify any restrictions that could impede energy development, such as height limitations and specific land use classifications. For example, Wyoming currently determines its agricultural land use taxation based on the capacity to generate agricultural products, indicating that local solar zoning analysis may present unique zoning challenges if land designated for agricultural use transitions to renewable generation.
- Permitting Procedure: Familiarity with the permitting procedure is critical for renewable initiatives. This may involve obtaining building permits, conducting environmental assessments, and engaging in public hearings. Timely and precise navigation of these steps can significantly influence timelines and costs. Notably, New York's Article 10 establishes a siting review process for major electric generating facilities with a capacity of 25 megawatts or more, exemplifying the regulatory scrutiny photovoltaic initiatives may face.
- State Incentives and Regulations: It is advisable to investigate state-level incentives that bolster renewable development, such as Delaware's Green Energy Program, which provides grants to offset costs of renewable energy technologies, subject to fund availability. Comprehending these regulations can enhance the financial viability of initiatives. Furthermore, it is crucial to recognize that specific circumstances may allow for the manual setting of the Compensation Rate of a Tariff Generation Unit (STGU), as clarified by EOEEA and DOER, offering nuanced insight into tariffs.
- Environmental Regulations: Adherence to environmental regulations is vital for installations. Developers must secure necessary permits regarding land disturbance and wildlife protection regulations to avert potential legal complications.
- Community Engagement: Proactively engaging the community is essential for addressing concerns and fostering support for renewable energy initiatives. This strategy can facilitate a smoother regulatory process and bolster program acceptance.
Additionally, examining case studies such as California's Renewable Portfolio Standard, which mandates a gradual increase in the percentage of electricity generated from renewable sources, underscores the impact of state-level regulations on promoting renewable installations. As renewable energy development continues to evolve, remaining informed about the current legal frameworks and incentivizing policies is imperative for successful project implementation, particularly in light of updates for 2024.
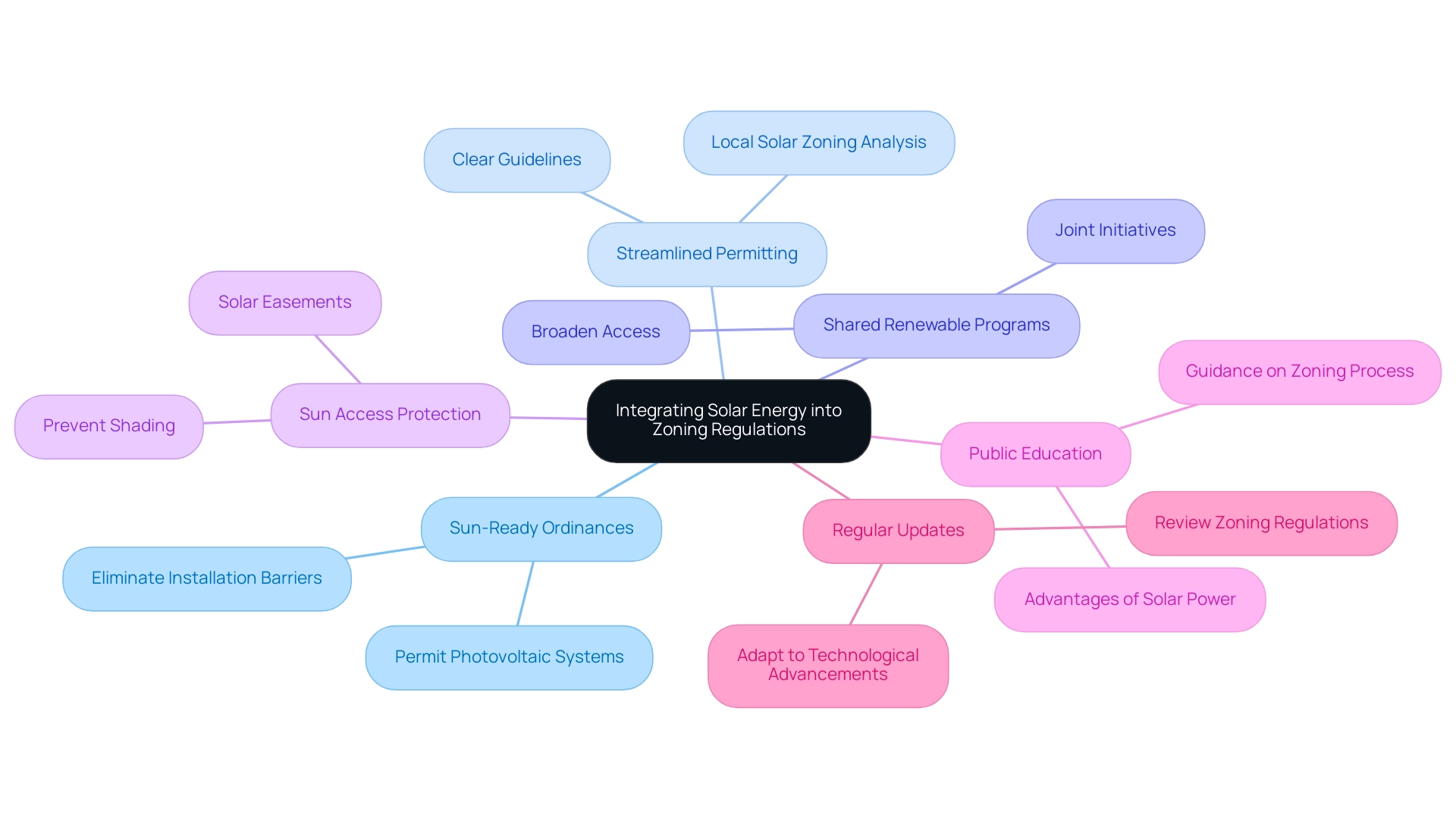
Best Practices for Integrating Solar Energy into Zoning Regulations
Incorporating renewable power into local solar zoning analysis demands a strategic approach that effectively balances the promotion of such development with the needs and concerns of local populations. The American Planning Association highlights that a significant lack of local policies concerning renewable resource use poses a major obstacle to the acceptance and implementation of these technologies. Key strategies for effective integration include:
- Sun-Ready Ordinances: Adopt regulations that explicitly permit photovoltaic systems across all zoning districts, thereby eliminating barriers to installation.
- Streamlined Permitting: Conducting a local solar zoning analysis can foster a more efficient permitting process by establishing clear guidelines that minimize unnecessary delays, facilitating developers' progress with solar projects.
- Shared Renewable Programs: Promote joint initiatives that allow multiple users to benefit from a single installation, thus broadening access to renewable resources for a larger audience.
- Sun Access Protection: Implement protective measures such as solar easements to ensure that new developments do not obstruct access through shading.
- Public Education: Provide educational resources to the public, emphasizing the advantages of solar power and offering guidance on navigating the local solar zoning analysis process for these projects.
- Regular Updates: Continuously review and update zoning regulations, including local solar zoning analysis, to adapt to technological advancements, shifts in market conditions, and evolving community needs.
Moreover, the impact of utility-scale solar facilities on neighboring property values is typically negligible, alleviating public concerns regarding potential negative effects. Local examples, such as the Greensville County Energy Applications case, demonstrate the effectiveness of these strategies in addressing challenges related to scale and community impact, ultimately resulting in the approval of three out of four energy applications. These best practices are essential for cultivating an environment conducive to renewable energy development.
Overcoming Challenges in Solar Zoning Analysis and Land Acquisition
Successfully navigating the complexities of local solar zoning analysis and land acquisition demands a proactive approach that integrates strategic planning with effective communication. Key challenges include:
- Stakeholder Resistance: Early and meaningful engagement with stakeholders is crucial. Arranging public gatherings and workshops can establish a forum for open conversation, permitting issues to be tackled and backing for renewable energy initiatives to be fostered.
- Regulatory Barriers: A comprehensive grasp of regulatory environments is essential. Proactively identify and address zoning ordinances that may obstruct renewable energy development by conducting a local solar zoning analysis in collaboration with local authorities to amend such restrictions. As Michael Greenstone proposes, streamlining these regulations can result in more efficient task completion.
- Land Suitability Issues: Conducting thorough site assessments is vital for evaluating land appropriateness for renewable installations. Factors such as soil quality, drainage capabilities, and proximity to existing power lines should be meticulously analyzed to ensure optimal placement of the initiative.
- Community Opposition: Combatting community opposition can be effectively managed through education and involvement. Informing residents about the advantages of photovoltaic systems and actively involving them in the planning process fosters a sense of ownership and acceptance.
- Negotiation Challenges: Strong negotiation strategies are essential for successful land acquisition. Clearly articulating the initiative’s benefits while addressing landowner concerns can facilitate smoother negotiations and build trust.
- Legal Complexities: Navigating the intricate landscape of land use laws requires expert legal counsel. Involving legal experts guarantees adherence to all relevant regulations, reducing the likelihood of obstacles arising from legal issues.
The widespread nature of local bans and moratoria—over 300 counties have implemented limitations on wind and solar projects—emphasizes the necessity of tackling community concerns and regulatory structures to promote clean power initiatives. Furthermore, permitting-related challenges have increased the time initiatives spend in the interconnection queue, with fewer than 25 percent of requests resulting in operation within four years as of 2023. As the landscape of U.S. climate policy evolves, particularly with the critical year of 2025 approaching, implementing these strategies will be vital for overcoming barriers and achieving renewable energy goals.
Efficient planning is crucial, especially considering that transmission projects triggering an EIS take seven times longer to complete than typical projects.
Conclusion
Solar zoning analysis stands as a crucial instrument for the integration of solar energy within local communities. By evaluating local regulations and land use patterns, stakeholders can pinpoint optimal sites for solar installations that adhere to zoning laws. This method not only mitigates conflicts with existing land uses but also fosters community acceptance—an essential element given the myriad challenges solar projects encounter at the local level.
This article delineates a systematic approach to executing solar zoning analysis, underscoring the significance of data collection, stakeholder engagement, and regulatory assessment. Engaging community members is vital; it addresses their concerns and cultivates support, which is indispensable for achieving successful project outcomes. By implementing best practices such as solar-ready ordinances and streamlined permitting processes, the adoption of solar energy can be significantly enhanced.
As the demand for renewable energy escalates, addressing challenges related to solar zoning and land acquisition becomes increasingly imperative. Effectively managing stakeholder resistance, navigating regulatory complexities, and ensuring land suitability are pivotal steps in this endeavor. Robust communication and negotiation strategies are essential in fostering a conducive environment for solar development.
In conclusion, the integration of solar energy into local zoning regulations necessitates collaboration among stakeholders to reconcile community needs with renewable energy objectives. By prioritizing solar zoning analysis, stakeholders can optimize the potential of solar energy, ensuring that development aligns with both regulatory requirements and community aspirations. This, in turn, contributes to a more sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the local solar zoning analysis?
The local solar zoning analysis serves as a systematic framework for assessing local regulations, land use patterns, and community objectives regarding renewable energy development. Its primary aim is to identify areas suitable for renewable energy installations that comply with existing zoning laws.
How does the local solar zoning analysis benefit local authorities?
It empowers local authorities to create effective frameworks, such as model ordinances, that promote renewable resources while minimizing conflicts with existing land uses. This helps communities manage energy initiatives effectively and improves community acceptance by addressing local issues.
What challenges do renewable energy projects face at the state or local level?
A staggering 73% of contested renewable energy projects between 2010 and 2021 faced challenges solely at the state or local level, highlighting the importance of local regulations in the planning and implementation of these projects.
What is the significance of the interconnection queue in renewable energy projects?
The interconnection queue currently has more power storage and generation capacity than what is operational, indicating an urgent need for reform in the interconnection process to facilitate timely and effective energy project implementation.
How does Harbinger Land assist in land rights acquisition for energy projects?
Harbinger Land offers expert site and right-of-way acquisition services, including advanced GIS mapping and thorough title research, to help stakeholders navigate the complexities of land rights acquisition efficiently.
What methodologies does Harbinger Land use in their GIS modeling services?
Harbinger Land employs methodologies such as spatial analysis and data visualization in their GIS modeling services to identify optimal sites for energy projects while ensuring compliance with zoning regulations.
What steps are involved in the solar zoning analysis process?
The solar zoning analysis process involves gathering data, identifying stakeholders, analyzing regulations, evaluating site suitability, drafting recommendations, engaging the public, and finalizing and implementing changes based on feedback.
Why is public engagement important in the solar zoning analysis process?
Public engagement is crucial for collecting feedback and fostering support for proposed changes, ensuring that the community feels involved in the planning process and enhancing the likelihood of successful project outcomes.
List of Sources
- Understanding Solar Zoning Analysis: Importance and Objectives
- Eight facts about permitting and the clean energy transition - The Hamilton Project (https://hamiltonproject.org/publication/economic-fact/eight-facts-permitting-clean-energy-transition)
- Regulating Utility-Scale Solar Projects on Agricultural Land (https://kleinmanenergy.upenn.edu/research/publications/regulating-utility-scale-solar-projects-on-agricultural-land)
- Step-by-Step Process for Conducting a Solar Zoning Analysis
- An observational method for determining daily and regional photovoltaic solar energy statistics (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0038092X21007416)
- Data Analytics in Solar Energy: Business Benefits | Miquido Blog (https://miquido.com/blog/data-analytics-in-solar-energy)
- Procedures for solar radiation data gathering and processing and their application to DNI assessment in southern Portugal (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0960148120316414)
- Solar, meteorological, and environmental data (https://kb.solargis.com/docs/solar-meteorological-and-environmental-data)
- Navigating Legal and Regulatory Frameworks for Solar Development
- farmandenergyinitiative.org (https://farmandenergyinitiative.org/projects/farmland-solar-policy/policy-design-toolkit/land-use-permitting-processes)
- Farmland Solar Policy State Law Database (https://farmandenergyinitiative.org/projects/farmland-solar-policy/state-law-database)
- Best Practices for Integrating Solar Energy into Zoning Regulations
- nrel.gov (https://nrel.gov/state-local-tribal/blog/posts/best-practices-in-zoning-for-solar.html)
- Planning for Utility-Scale Solar Energy Facilities (https://planning.org/pas/memo/2019/sep)
- Overcoming Challenges in Solar Zoning Analysis and Land Acquisition
- brookings.edu (https://brookings.edu/articles/eight-facts-about-permitting-and-the-clean-energy-transition)
- Eight facts about permitting and the clean energy transition - The Hamilton Project (https://hamiltonproject.org/publication/economic-fact/eight-facts-permitting-clean-energy-transition)




