Overview
The integration of conservation biology in planning processes is crucial for preserving biodiversity and ensuring sustainable land use. This article highlights the complexities of land acquisition, including legal and regulatory challenges, and underscores the importance of effective strategies such as:
- Conducting environmental assessments
- Engaging stakeholders
- Leveraging technology
These strategies collectively enhance decision-making and promote ecological integrity in development projects. By embracing these practices, organizations can navigate the challenges of land acquisition effectively.
What steps are you taking to ensure sustainable land use in your projects? The benefits of incorporating conservation biology are clear: improved environmental outcomes, stakeholder engagement, and a commitment to ecological integrity.
It is time to act—embrace these strategies to safeguard our natural resources for future generations.
Introduction
In an era where environmental challenges are increasingly pressing, conservation biology stands as a crucial field dedicated to safeguarding biodiversity and promoting sustainable land use. It examines the intricate relationships between human activities and natural ecosystems, providing planners and decision-makers with essential insights that can guide development initiatives towards ecological integrity.
This article explores the critical importance of integrating conservation biology into planning processes, highlighting effective strategies for stakeholder collaboration and the use of technology to enhance conservation efforts.
As the world confronts the urgent need to reverse biodiversity loss and combat climate change, embracing these principles is vital for fostering a sustainable future.
Define Conservation Biology and Its Importance in Planning
Conservation biology stands as a vital interdisciplinary field committed to the preservation of biodiversity, the study of ecosystems, and the sustainable management of natural resources. It aims to comprehend the effects of human activities on the environment and to formulate strategies that mitigate these impacts.
In organizational contexts, environmental biology is essential, providing decision-makers with insights into the ecological ramifications of land use, thereby ensuring that development projects do not jeopardize the integrity of natural habitats. By incorporating conservation biology integration in planning processes, stakeholders can effectively prioritize areas for protection, enhance ecosystem services, and promote sustainable practices that yield benefits for both the environment and society.
This integration is particularly crucial in energy and infrastructure projects, where alterations in land use can significantly impact local ecosystems and wildlife. Recent statistics reveal that 60% of our ecological footprint originates from carbon emissions associated with fossil fuels, highlighting the pressing need for sustainable land use strategies. Furthermore, the Leaders' Pledge for Nature, supported by over 90 global leaders representing 39% of world GDP, exemplifies a collective commitment to reversing the decline of ecosystems and ensuring a nature-positive planet by 2030.
Importantly, we cannot curb the loss of biological diversity without maintaining global warming below 2°C (ideally 1.5°C), necessitating rapid decarbonization across all sectors, from energy to agriculture. Such initiatives illustrate the growing recognition of ecology's significance in strategic planning, particularly as we strive to mitigate climate change and safeguard our planet's biodiversity. Additionally, the concept of a concealed levy linked to environmental degradation emphasizes the economic repercussions of neglecting preservation practices, further underscoring the urgency of incorporating ecological science into development.
Implement Effective Strategies for Integrating Conservation Biology
To effectively integrate conservation biology into planning, practitioners must adopt the following strategies:
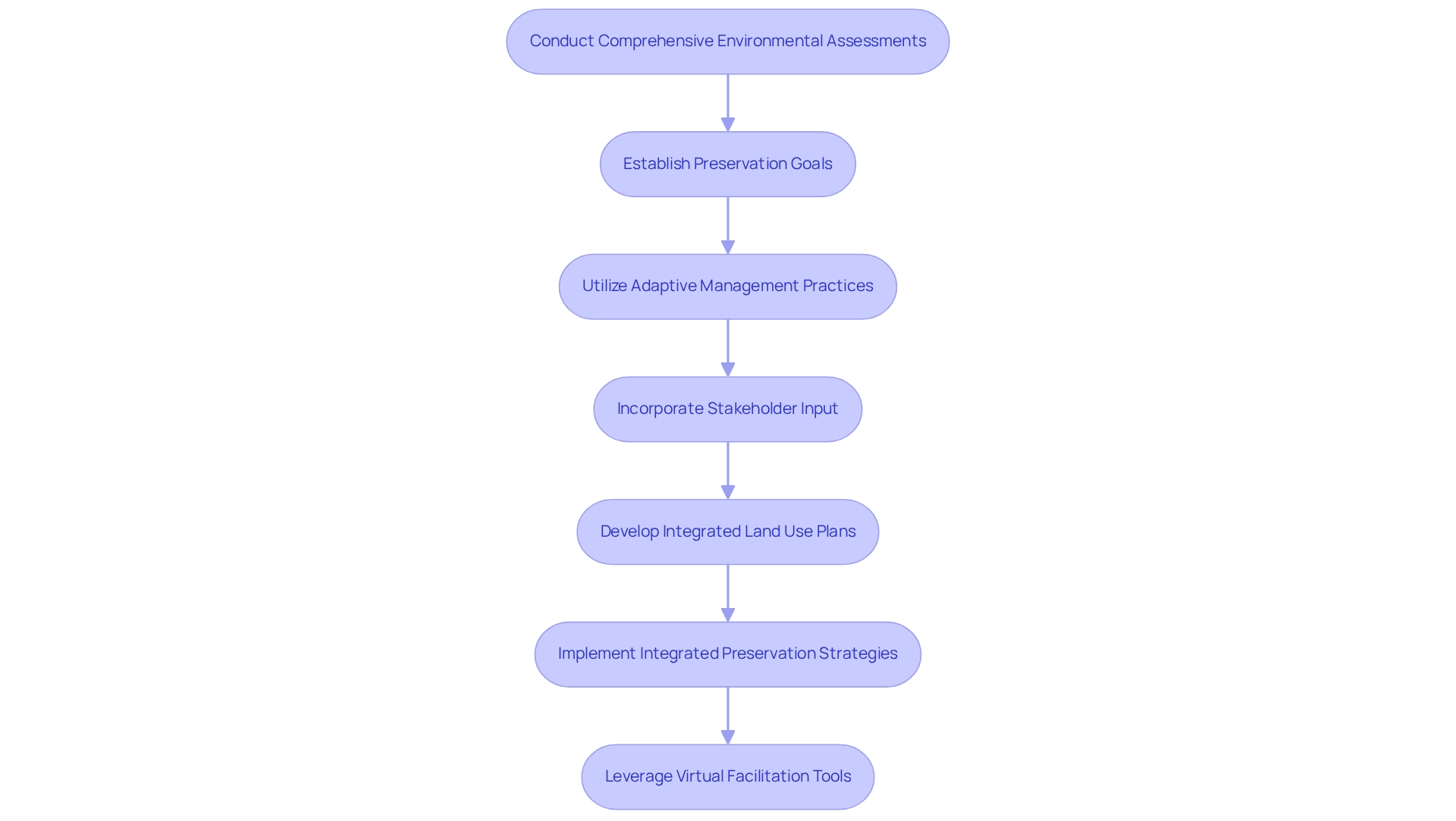
- Conduct Comprehensive Environmental Assessments: Initiate projects with thorough assessments to identify critical habitats, endangered species, and essential ecological functions. This foundational data informs decision-making and helps mitigate potential negative impacts on the environment.
- Establish Preservation Goals: Define clear preservation objectives that align with project aims. These goals should include measurable outcomes, such as specific habitat restoration targets or metrics for enhancing biodiversity, ensuring accountability and progress tracking.
- Utilize Adaptive Management Practices: Implement adaptive management frameworks that facilitate ongoing monitoring and adjustments based on ecological feedback. This dynamic approach ensures that preservation efforts remain effective and responsive to evolving environmental conditions. Flexibility in organization is crucial to accommodate new information and changing circumstances.
- Incorporate Stakeholder Input: Actively engage local communities, environmental groups, and other stakeholders throughout the planning process. Their insights can offer vital information regarding local ecological circumstances and preservation priorities, promoting collaboration and trust. As highlighted by Michael J. Manfredo, values, trust, and cultural considerations are vital in environmental governance.
- Develop Integrated Land Use Plans: Create land use plans that align environmental priorities with development needs. This holistic approach balances ecological integrity with economic growth, promoting sustainable land use practices that benefit both the environment and local economies.
- Implement Integrated Preservation Strategies: Incorporate management for habitat connectivity, genetic preservation, and assisted colonization when necessary. These strategies are essential for guaranteeing the resilience of ecosystems and improving biological variety.
- Leverage Virtual Facilitation Tools: Utilize virtual facilitation tools to enhance collaboration during environmental planning sessions, as demonstrated in the case study titled "Impact of Virtual Facilitation on Environmental Planning." This approach proved effective in maintaining participant engagement and collaboration, especially during the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic.
By adopting these strategies, conservation biology integration in planning allows energy and infrastructure projects to achieve successful preservation goals, leading to measurable outcomes that enhance biodiversity and support carbon sequestration efforts.
Foster Collaboration Among Stakeholders for Successful Outcomes
The success of conservation initiatives relies heavily on cooperation among involved parties, highlighting the importance of conservation biology integration in planning. Effective practices can significantly enhance stakeholder engagement.
-
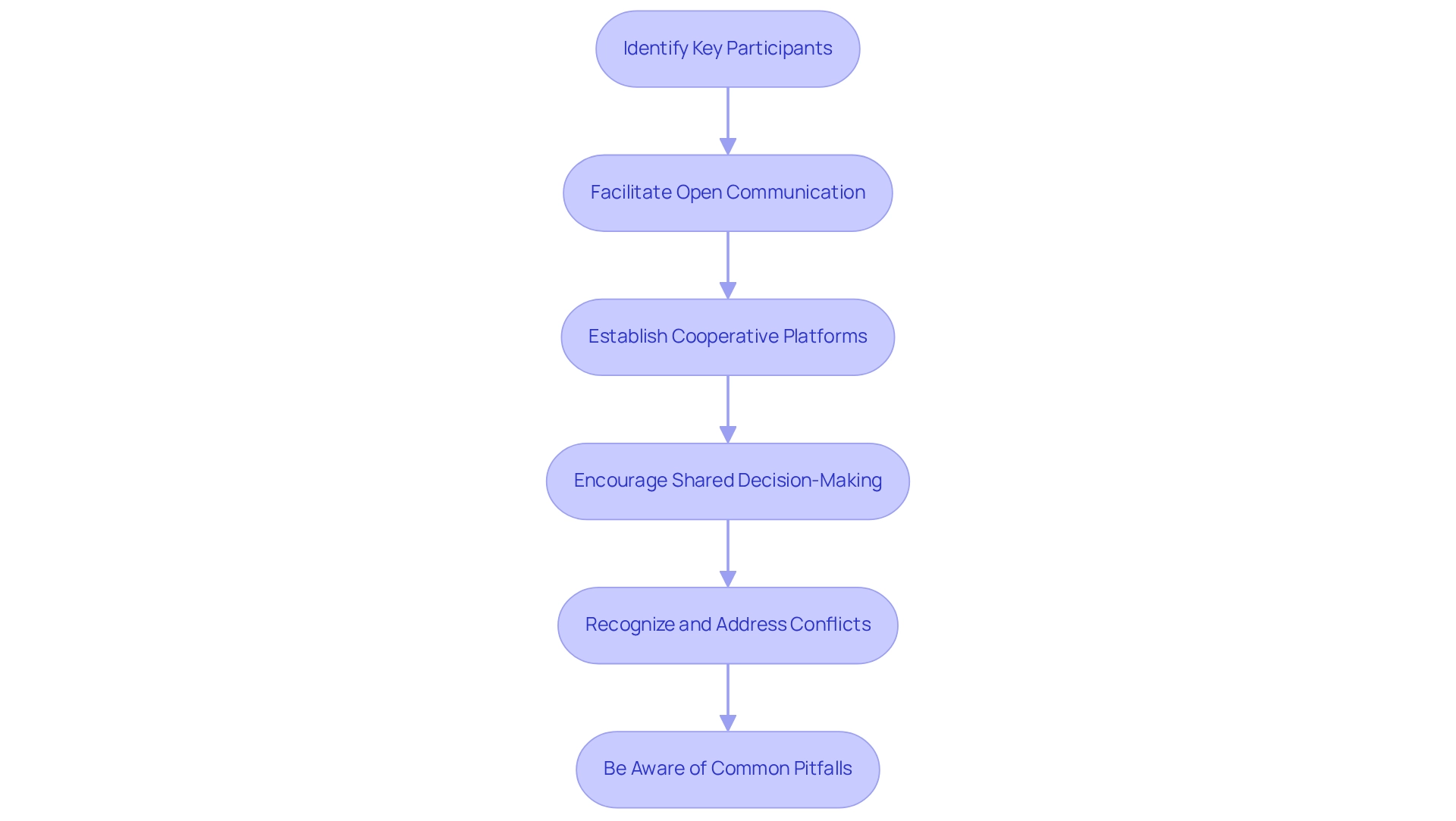
Identify Key Participants: Begin by outlining all relevant parties, including government agencies, local communities, NGOs, and industry representatives. Understanding their interests and concerns is vital for fostering effective collaboration, especially with regard to conservation biology integration in planning.
-
Facilitate Open Communication: Establish transparent communication channels to share information and updates. Regular meetings and workshops can build trust and ensure that all voices are heard, cultivating a more inclusive environment.
-
Establish Cooperative Platforms: Create platforms that enable participants to collaborate towards shared environmental objectives. This may involve forming joint task forces, working groups, or online forums where participants can exchange resources and strategies.
-
Encourage Shared Decision-Making: Involve participants in the decision-making process, allowing them to contribute to the development of conservation strategies. This participatory approach fosters ownership and can lead to more widely accepted and effective outcomes through conservation biology integration in planning.
-
Recognize and Address Conflicts: Proactively identify potential disputes among involved parties and work towards resolving them through negotiation and compromise. Acknowledging differing perspectives can result in innovative solutions that benefit all parties involved.
-
Be Aware of Common Pitfalls: Recognizing potential challenges in engaging interested parties, such as lack of trust, miscommunication, or differing priorities, is crucial. Addressing these issues early can prevent setbacks in collaboration.
Continued engagement with interested parties is critical for securing the essential participation and backing for effective conservation biology integration in planning initiatives. As Phil Rabinowitz states, "Like any community building activity, collaboration with involved parties must persist over the long term to achieve the level of participation and support necessary for a successful effort." Reflecting on stakeholder involvement, as highlighted in the case study "Evaluating Stakeholder Involvement," can enhance future initiatives, ensuring that collaboration remains effective and community-focused.
Leverage Technology to Enhance Conservation Planning Efficiency
Utilizing technology is essential for enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of resource management planning. The following are several ways to leverage technology in this context:
-
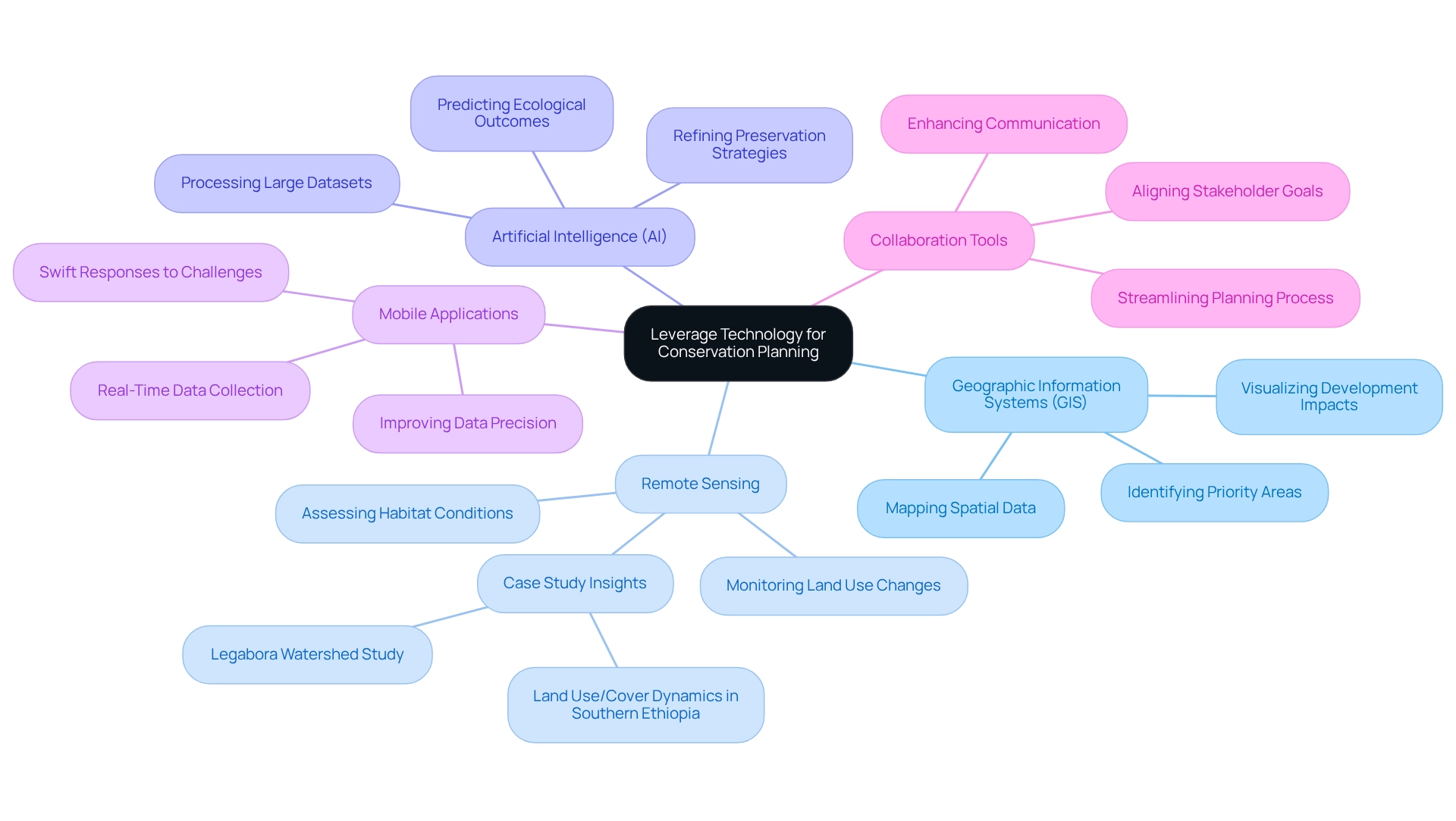
Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS plays a pivotal role in mapping and analyzing spatial data related to biological diversity, land use, and ecological features. This tool aids in identifying priority areas for preservation and visualizing potential impacts of development projects, thereby facilitating informed decision-making.
-
Remote Sensing: Remote sensing technologies are invaluable for monitoring land use changes, habitat conditions, and biodiversity over time. For instance, a study in the Legabora watershed revealed a significant reduction in shrublands by 144 hectares annually from 1976 to 2022. This underscores the necessity for effective monitoring to guide adaptive management strategies and evaluate the success of preservation efforts. Additionally, a case study titled "Remote Sensing and GIS-Based Study of Land Use/Cover Dynamics in Southern Ethiopia" illustrates the practical application of these technologies in analyzing land use changes and their driving factors.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms can process large datasets to predict ecological outcomes and refine preservation strategies. By offering insights that may not be immediately apparent through traditional analysis, AI strengthens decision-making processes, making them more robust and data-driven.
-
Mobile Applications: Developing mobile apps for field data collection allows practitioners to gather real-time information on species, habitats, and environmental conditions. This approach improves data precision and availability, enabling swift responses to environmental challenges.
-
Collaboration Tools: Online collaboration platforms enhance communication and information sharing among stakeholders, improving coordination and streamlining the planning process. These tools ensure that all parties are aligned on preservation goals, fostering a collaborative approach to sustainable land use.
The integration of these technologies supports biodiversity preservation and aligns with current trends in environmental protection, highlighting the importance of conservation biology integration in planning to reflect a growing global consciousness about sustainable practices. As Zainab Tahir noted, "Understanding these changes is crucial for mitigating adverse environmental impacts and promoting sustainable development." Furthermore, recent discussions have concluded with cautious optimism regarding innovative legislation and advanced technologies that can further enhance conservation planning efforts.
Conclusion
Integrating conservation biology into planning processes is not just beneficial; it is imperative for the future of our ecosystems and the well-being of our planet. The interdisciplinary nature of conservation biology equips decision-makers with vital insights into the ecological impacts of human activities, enabling them to prioritize biodiversity preservation and sustainable resource management effectively. By adopting comprehensive environmental assessments, setting clear conservation goals, and utilizing adaptive management practices, stakeholders can create a more resilient and ecologically balanced approach to development.
Collaboration among various stakeholders is equally crucial. By fostering open communication and shared decision-making, diverse interests can converge towards common conservation goals. Recognizing and addressing potential conflicts ensures that all voices are heard, leading to innovative and widely accepted solutions. The emphasis on sustained engagement highlights the long-term commitment necessary for successful conservation initiatives.
Moreover, leveraging technology enhances the efficiency of conservation planning. Tools such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS), remote sensing, and artificial intelligence provide essential data that inform decision-making and optimize strategies for biodiversity conservation. These technological advancements, combined with collaborative practices, create a robust framework for addressing the pressing environmental challenges of our time.
Ultimately, the integration of conservation biology into planning processes serves not only to combat biodiversity loss and climate change but also to foster a sustainable future for generations to come. As the urgency of these issues continues to grow, embracing these principles will be vital for achieving both ecological integrity and human prosperity. Now is the time to act, ensuring that conservation efforts are at the forefront of development initiatives worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is conservation biology?
Conservation biology is an interdisciplinary field focused on preserving biodiversity, studying ecosystems, and managing natural resources sustainably. It aims to understand the impact of human activities on the environment and develop strategies to mitigate these effects.
How does conservation biology benefit decision-makers in organizational contexts?
Conservation biology provides decision-makers with insights into the ecological impacts of land use, helping to ensure that development projects do not harm natural habitats. It aids in prioritizing areas for protection and promoting sustainable practices that benefit both the environment and society.
Why is the integration of conservation biology important in energy and infrastructure projects?
The integration of conservation biology is crucial in energy and infrastructure projects because changes in land use can significantly affect local ecosystems and wildlife. It helps to identify and mitigate potential ecological impacts, ensuring sustainable development.
What percentage of our ecological footprint is attributed to carbon emissions from fossil fuels?
Recent statistics indicate that 60% of our ecological footprint originates from carbon emissions associated with fossil fuels, highlighting the need for sustainable land use strategies.
What is the Leaders' Pledge for Nature?
The Leaders' Pledge for Nature is a commitment supported by over 90 global leaders representing 39% of the world GDP, aimed at reversing ecosystem decline and ensuring a nature-positive planet by 2030.
How does global warming relate to biodiversity loss?
To curb the loss of biological diversity, it is essential to keep global warming below 2°C, ideally at 1.5°C. This requires rapid decarbonization across all sectors, including energy and agriculture.
What does the concept of a concealed levy linked to environmental degradation imply?
The concept of a concealed levy emphasizes the economic consequences of neglecting preservation practices, underscoring the urgency of incorporating ecological science into development planning.




