Overview
The article provides a comprehensive step-by-step guide for conducting an environmental review for utilities, emphasizing its importance in evaluating ecological impacts and ensuring compliance with regulations like NEPA. It highlights key steps such as identifying the initiative scope, engaging stakeholders, conducting preliminary assessments, and maintaining thorough documentation, which collectively enhance the effectiveness of the review process and facilitate better project outcomes.
Introduction
In the complex landscape of utility project development, environmental reviews play a pivotal role in ensuring compliance with essential regulations such as the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA). These reviews not only assess potential environmental impacts but also serve as a proactive measure to identify and mitigate risks early in the planning process.
As utilities navigate increasing pressures from regulatory complexities and public opposition—particularly concerning renewable energy initiatives—effective environmental reviews become crucial for fostering transparency and building public trust.
The intricate interplay between stakeholder engagement, thorough documentation, and the integration of advanced technologies underscores the importance of these assessments in achieving successful project outcomes while adhering to evolving regulatory frameworks.
This article delves into the critical components of environmental reviews, providing insights into best practices, necessary documentation, and the nuances of the NEPA review process that utilities must master to thrive in today's environmentally conscious landscape.
Understanding the Importance of Environmental Reviews for Utilities
Environmental review for utilities serves as a cornerstone, providing a thorough evaluation of potential ecological impacts and ensuring adherence to crucial regulations like the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA). An environmental review for utilities is crucial in recognizing ecological issues early in the planning phase, thus allowing them to tackle challenges proactively and reduce risks. Clarity and community confidence are vital elements for the successful execution of utility initiatives, and thorough environmental review for utilities helps promote both.
Recent conversations regarding power marketing rates and the noticeable rise in the ratio of queued to online capacity in California—from three to seven in 2022—highlight the growing pressures utilities encounter in managing regulatory challenges and stakeholder expectations effectively.
Public resistance to renewable energy initiatives, especially wind and solar, demonstrates the importance of these evaluations. A study revealed that 73% of contested endeavors encounter challenges at the state or local level rather than federally, indicating that localized opposition can complicate the permitting process for clean energy initiatives. By conducting an environmental review for utilities, comprehensive assessments of the surroundings can help them better foresee and tackle local issues, thus decreasing the chances of dissent.
Moreover, the differing completion rates of energy initiatives—11% for battery initiatives compared to 31% for gas—underscore the importance of an environmental review for utilities. As Rand et al. note, the average completion rate for battery initiatives is considerably lower, highlighting that without efficient assessments, utilities may find it challenging to attain successful results.
By prioritizing NEPA compliance and conducting comprehensive assessments, utilities not only fulfill regulatory requirements but also engage in an environmental review for utilities, thereby improving their capacity to execute initiatives efficiently, in accordance with the OECD's promotion of unrestricted access to ecological data and information.
Initial Steps for Preparing an Environmental Review
- Identify the Initiative Scope: Clearly defining the initiative's objectives, location, and potential ecological impacts is essential. This initial step establishes the basis for a successful environmental review for utilities and enhances the clarity of its purpose. Experts emphasize that a well-articulated scope not only guides the assessment process but also facilitates effective stakeholder communication. Significantly, the analysis mentions 158 sources and has been referenced by 2924 other papers, highlighting the significance of comprehensive scope identification in ecological evaluations.
- Engage Stakeholders: Early engagement with stakeholders—such as local communities, regulatory agencies, and other relevant organizations—is crucial for gathering valuable input and addressing potential concerns. As emphasized by Susan Wiener from the Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, understanding stakeholder perspectives can significantly inform decisions. Collaborative efforts, as seen in recent guidance on stakeholder engagement practices, can enhance the effectiveness of these interactions. Project teams should consider collaborating with other organizations to further improve engagement effectiveness, as emphasized in the key points.
- Conduct Preliminary Assessments: Evaluating current environmental conditions and collecting baseline data is essential to guide the evaluation process. This step enables teams to identify potential impacts and ensures that the assessment is based on precise, contextual information, ultimately leading to more informed decision-making.
- Develop a Timeline: Creating a detailed timeline that outlines key milestones and deadlines for the evaluation process is essential for ensuring alignment among all parties involved. This timeline should incorporate stakeholder engagement activities and allow sufficient time for feedback and adjustments. By setting clear expectations, project teams can promote smoother interactions and improve the overall quality of the assessment process. These practices not only streamline the assessment timeline but also contribute to better stakeholder satisfaction, as effective engagement strategies have been shown to improve outcomes in environmental review for utilities. The case study titled "Recommendations for Effective Engagement" underscores the importance of transparency, clarity of roles, and the establishment of grievance mechanisms, serving as a valuable reference for best practices in stakeholder engagement.
Key Documentation Required for NEPA Compliance
For utilities to ensure compliance with the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA), several key documents must be meticulously prepared:
- Environmental Assessment (EA): This crucial document evaluates the potential ecological effects linked to a proposed initiative. It serves as a foundational analysis, determining whether the initiative might have significant environmental effects.
- Finding of No Significant Impact (FONSI): Following the EA, if the evaluation indicates that the undertaking will not have significant adverse effects on the environment, a FONSI is issued. This document effectively conveys the conclusion of the EA, allowing the initiative to proceed without the need for a more comprehensive Environmental Impact Statement (EIS).
- Impact Statement (EIS): For initiatives expected to have considerable ecological effects, an EIS is required. This extensive report delves into the potential effects of the project, outlining mitigation measures and alternatives to minimize environmental harm.
- Public Involvement Documentation: The National Environmental Policy Act emphasizes stakeholder engagement, necessitating the collection of records from public meetings and comments during the review process. For instance, a public meeting held in Eastern in August 1987 exemplifies the historical importance of public involvement in NEPA processes. This documentation is crucial for showcasing transparency and accountability, reflecting the initiative's responsiveness to public concerns.
Additionally, as President Obama pointed out, the objective is "to significantly decrease the overall time needed to make decisions in the permitting and assessment of infrastructure projects by the Federal Government." This emphasizes the significance of efficiency in environmental compliance.
As regulatory structures develop, especially with conversations regarding openness in the process, upholding a comprehensive and clear documentation strategy is crucial for utilities involved in the environmental review for utilities managing ecological assessments. The Trump Administration's suggested modifications to the environmental policy, intended to set time constraints for evaluations and limit the range of ecological assessments, demonstrate the ongoing conversation regarding these regulations and their effects on environmental evaluations.
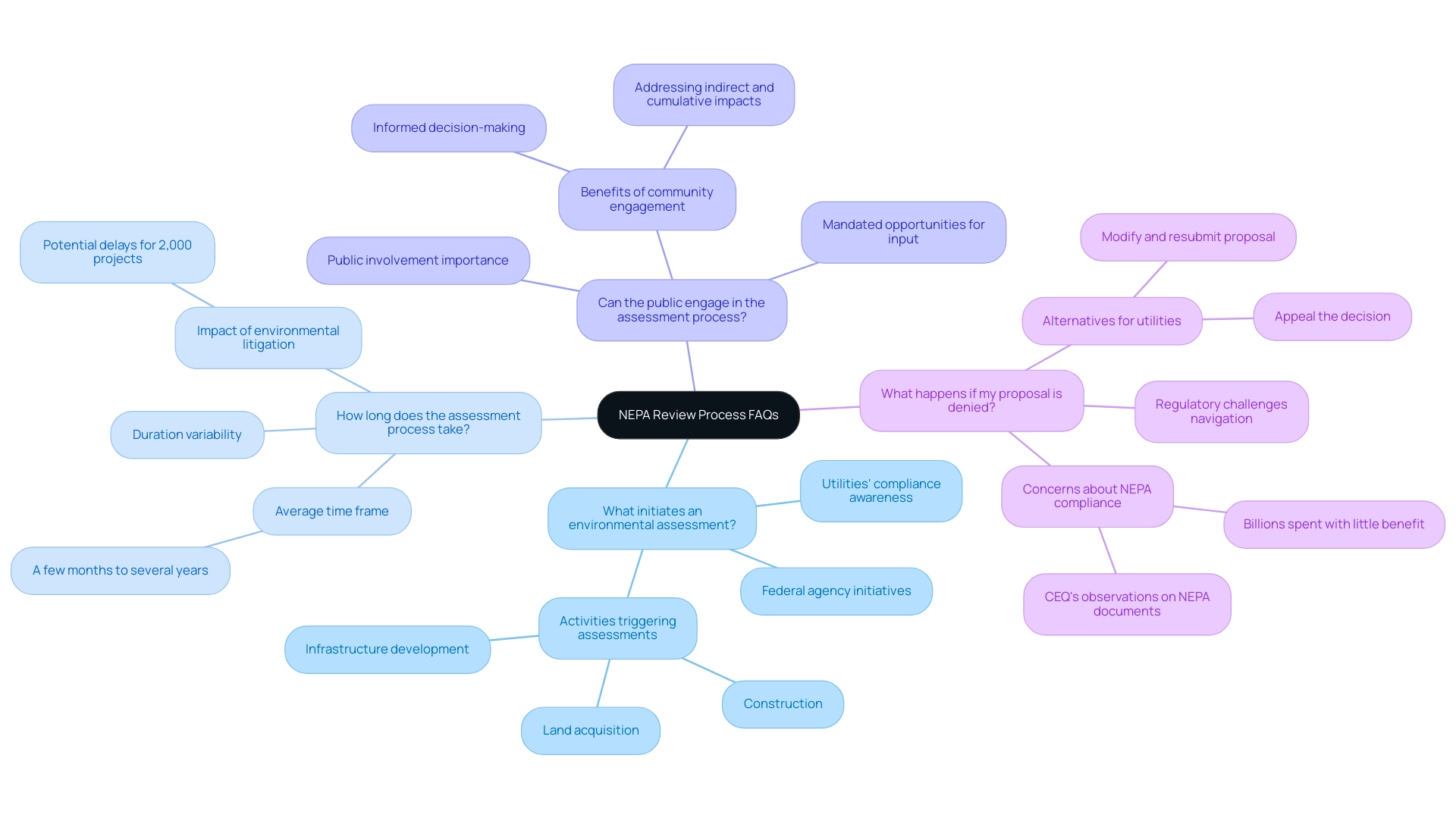
Frequently Asked Questions About the NEPA Review Process
- What initiates an environmental assessment? An environmental assessment is required when a federal agency undertakes an initiative that could greatly affect the environment. This can include a wide range of activities, such as construction, land acquisition, and infrastructure development. It is essential for utilities to be aware of these triggers in the environmental review for utilities to ensure compliance and timely advancement.
- How long does the assessment process take? The length of the assessment process varies significantly, shaped by the intricacy of the undertaking and the extent of environmental issues. On average, these evaluations can take anywhere from a few months to several years. Recent statistics indicate that if the current trend continues, approximately 2,000 government projects may face delays or halts due to environmental litigation, underscoring the importance of efficient project planning.
- Can the public engage in the environmental review for utilities assessment process? Public involvement is a cornerstone of the NEPA assessment process. It is not only encouraged but also mandated, requiring utilities to provide ample opportunities for stakeholder input throughout the review. Engaging the community in an environmental review for utilities can lead to more informed decision-making and potentially enhance outcomes, as public insights can effectively address indirect and cumulative impacts.
- What happens if my proposal is denied? If an initiative is rejected during the environmental review for utilities, utilities have several alternatives. They can appeal the decision, seeking a re-evaluation based on additional information or adjustments to the original proposal. Alternatively, they may modify the project to resolve the concerns identified in the review process and resubmit it for approval. This flexibility allows utilities to navigate regulatory challenges while striving to meet environmental standards. However, it is important to note that despite the billions spent on compliance with environmental regulations, as highlighted in the case study titled "Unmeasured Benefits of Expenditures," there is no evidence that these expenditures have produced tangible benefits for the American public. This raises questions about the effectiveness of NEPA compliance in decision-making processes, a concern echoed in the quote from Andrus regarding the President’s authority to delegate power to CEQ.
Best Practices for Conducting Effective Environmental Reviews
- Conduct Comprehensive Descriptions: Begin by clearly outlining the goals and potential impacts. A clearly outlined initiative description acts as the foundation for the environmental review for utilities, ensuring that all stakeholders comprehend the goals and implications. This clarity aids in the environmental review for utilities by identifying key areas of concern early in the process.
- Engage Early and Often: Establishing open lines of communication with stakeholders from the outset is crucial. Regular engagement helps build trust and fosters an environment where environmental review for utilities can effectively address concerns proactively. Experts stress that effective stakeholder communication not only reduces risks but also enhances the overall quality of the environmental review for utilities. For instance, incorporating feedback from local communities can lead to more informed decision-making and ultimately better project outcomes. The Ministry of Ecology and Environment states that "the Interim Rules for Carbon Emissions Trading Management were issued," highlighting the importance of regulatory frameworks in guiding stakeholder interactions, which is essential for an environmental review for utilities.
- Utilize Technology: The incorporation of technology, such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and advanced data processing tools, can significantly enhance the accuracy of data gathered during the assessment. These technologies simplify data management and visualization, which is essential for conducting an environmental review for utilities to evaluate impacts comprehensively. Recent advancements in technology have transformed the efficiency of assessments, allowing for quicker analysis and response times. For instance, utilizing the Shannon index, which is expressed as the logarithm of the total number of individuals divided by the number of species, can offer a quantitative foundation for comprehending species richness in the context of assessments.
- Document Everything: Maintaining detailed records of all communications, assessments, and decisions is essential. This documentation aims to promote transparency and accountability throughout the environmental review for utilities evaluation process. By systematically capturing all interactions and findings, practitioners not only comply with regulatory requirements but also promote just and impartial treatment of all individuals involved in the environmental review for utilities. This commitment to thorough documentation can prove invaluable in addressing any disputes or inquiries that may arise after the environmental review for utilities. Moreover, referencing case studies like Parametric and Non-Parametric Methods illustrates the practical application of various methodologies in estimating species richness, further enhancing the discussion on technology and methodologies in environmental reviews.
Conclusion
Environmental reviews are indispensable for utilities, serving as a critical mechanism for assessing potential environmental impacts and ensuring compliance with the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA). Through proactive identification and mitigation of risks, these reviews not only help in navigating the complexities of regulatory requirements but also foster transparency and build public trust. As the increasing local opposition to renewable energy projects demonstrates, effective environmental reviews can significantly reduce potential conflicts and enhance project completion rates.
The initial steps for preparing an environmental review, including:
- Defining project scope
- Engaging stakeholders
- Conducting preliminary assessments
lay the groundwork for a thorough and effective evaluation process. Key documentation, such as Environmental Assessments and Environmental Impact Statements, is essential for NEPA compliance, ensuring that all potential impacts are meticulously analyzed. Moreover, the inclusion of public involvement documentation underscores the importance of community engagement in shaping project outcomes.
Best practices for conducting environmental reviews further emphasize the significance of:
- Clear project descriptions
- Consistent stakeholder communication
- The integration of advanced technologies
By documenting all aspects of the review process, utilities can not only comply with regulations but also enhance accountability and transparency.
In conclusion, as utilities face mounting pressures from evolving regulatory frameworks and public expectations, mastering the intricacies of environmental reviews is paramount. By prioritizing thorough assessments and stakeholder engagement, utilities can navigate the complexities of project development while contributing to sustainable and responsible energy solutions. The path forward lies in recognizing the vital role these reviews play in achieving successful project outcomes and fostering a more environmentally conscious future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of an environmental review for utilities?
An environmental review for utilities serves to evaluate potential ecological impacts and ensure compliance with regulations like the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA). It helps identify ecological issues early in the planning phase, allowing utilities to address challenges proactively and reduce risks.
Why is clarity and community confidence important in utility initiatives?
Clarity and community confidence are vital for the successful execution of utility initiatives. A thorough environmental review promotes both by ensuring that stakeholders are well-informed and engaged throughout the process.
What recent trends highlight the challenges utilities face in regulatory management?
Recent discussions regarding power marketing rates and the increase in the ratio of queued to online capacity in California—from three to seven in 2022—underscore the growing pressures utilities face in managing regulatory challenges and stakeholder expectations effectively.
How does public resistance impact renewable energy initiatives?
Public resistance, particularly to wind and solar projects, can complicate the permitting process for clean energy initiatives. Studies show that 73% of contested projects face challenges at the state or local level, emphasizing the need for comprehensive environmental evaluations to anticipate and address local concerns.
What are the completion rates for energy initiatives, and what does this indicate about environmental reviews?
The completion rates for energy initiatives differ significantly, with battery initiatives at 11% and gas initiatives at 31%. This disparity highlights that without effective environmental assessments, utilities may struggle to achieve successful project outcomes.
How does NEPA compliance benefit utilities?
By prioritizing NEPA compliance and conducting thorough assessments, utilities fulfill regulatory requirements and improve their ability to execute initiatives efficiently, aligning with the OECD's promotion of unrestricted access to ecological data and information.
What are the key steps in conducting an environmental review for utilities?
The key steps include: 1. Identify the Initiative Scope: Clearly define objectives, location, and potential ecological impacts. 2. Engage Stakeholders: Early involvement of local communities and regulatory agencies to gather input and address concerns. 3. Conduct Preliminary Assessments: Evaluate current environmental conditions and collect baseline data. 4. Develop a Timeline: Create a detailed timeline outlining key milestones and deadlines to ensure alignment among all parties involved.
How can stakeholder engagement impact the environmental review process?
Effective stakeholder engagement can enhance the review process by gathering valuable input and addressing potential concerns. Collaborative efforts improve engagement effectiveness, leading to better outcomes in environmental evaluations.
List of Sources
- Understanding the Importance of Environmental Reviews for Utilities
- Eight facts about permitting and the clean energy transition - The Hamilton Project (https://hamiltonproject.org/publication/economic-fact/eight-facts-permitting-clean-energy-transition)
- Environmental Review – NEPA – Western Area Power Administration (https://wapa.gov/about-wapa/regions/crsp/about-crsp/environment)
- oecd.org (https://oecd.org/en/topics/environmental-statistics-accounts-and-indicators.html)
- Initial Steps for Preparing an Environmental Review
- Stakeholder participation for environmental management: A literature review (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0006320708002693)
- Guidance on stakeholder engagement practices to inform the development of area-wide vector control methods - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6483156)
- Key Documentation Required for NEPA Compliance
- environment.fhwa.dot.gov (https://environment.fhwa.dot.gov/legislation/nepa/guidance_preparing_env_documents.aspx)
- National Environmental Policy Act Guidance on Consideration of Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Climate Change (https://federalregister.gov/documents/2023/01/09/2023-00158/national-environmental-policy-act-guidance-on-consideration-of-greenhouse-gas-emissions-and-climate)
- Why are we so slow today? (https://thecgo.org/benchmark/why-are-we-so-slow-today)
- Frequently Asked Questions About the NEPA Review Process
- National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) and Transportation Decisionmaking | Environmental Review Toolkit | FHWA (https://environment.fhwa.dot.gov/nepa/QAimpact.aspx)
- A Long and Winding Road: How the National Environmental Policy Act Has Become the Most Expensive and Least Effective Environmental Law in the History of the United States, and How to Fix It - Regulatory Transparency Project (https://rtp.fedsoc.org/paper/national-environmental-policy-act)
- Best Practices for Conducting Effective Environmental Reviews
- Statistical Techniques for Environmental Sciences: A Review (https://mdpi.com/2297-8747/26/4/74)
- Environmental Statistics - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics (https://sciencedirect.com/topics/earth-and-planetary-sciences/environmental-statistics)
- amstat.org (https://amstat.org/your-career/ethical-guidelines-for-statistical-practice)




