Overview
The article provides a comprehensive guide on conducting effective wind energy title research, emphasizing the importance of understanding land rights, environmental regulations, and stakeholder engagement. It outlines a structured approach that includes identifying project scope, verifying title ownership, assessing environmental impacts, and documenting findings, which collectively ensure compliance and facilitate successful wind energy project development.
Introduction
The transition to renewable energy sources has become a pivotal focus in the quest for sustainable development, with wind energy emerging as a leading contender in this arena. Harnessing the power of wind through advanced turbine technology not only generates electricity but also fosters economic growth and environmental stewardship. As the demand for clean energy rises, understanding the complexities surrounding wind energy projects—ranging from the mechanics of turbine operation to the intricate legal frameworks governing land use—becomes essential for stakeholders involved in this dynamic sector.
This article delves into the fundamental aspects of wind energy, exploring the critical elements of:
- Title research
- Environmental considerations
- The role of regulatory bodies
Providing a comprehensive guide for navigating the landscape of wind energy development.
Understanding Wind Energy: Basics and Mechanisms
Air power captures the kinetic force of air through the operation of turbines, which are essential for producing electricity in a sustainable manner. The process initiates when wind flows over the blades of a turbine, causing them to rotate. This movement spins a rotor that is linked to a generator, enabling the conversion of mechanical power into electrical power—an essential aspect of modern power generation.
For those involved in wind energy title research, grasping this mechanism is vital, as it underscores the necessity for securing appropriate land rights for turbine installation and operational efficiency. The key components of this energy conversion process include:
- Wind Turbines: These devices are engineered to convert wind energy into mechanical power, with advancements in turbine design leading to efficiency gains. Notably, on-site fabrication of continuous spiral-welded towers has been demonstrated for towers up to 180 meters, showcasing significant technological progress.
- Land Requirements: Adequate space is essential not only for the installation of turbines but also for maintenance activities and access roads, ensuring unhindered operational integrity.
- Energy Production: Various factors, notably air speed and the strategic placement of turbines, play a critical role in determining overall energy output. Efficient renewable energy initiatives can greatly enhance local economies; for example, last year, these developments provided over $2 billion in state and local tax payments and land-lease agreements.
A solid understanding of these foundational elements enables more targeted and effective site identification for energy farms, which is essential for wind energy title research. As per the latest findings from the U.S. Department of Energy, "the enactment of the Inflation Reduction Act has resulted in a significant increase in near-term deployment forecasts for turbines," further highlighting the necessity of strategic planning in the area of land acquisition for such initiatives. Furthermore, insights from the 'Distributed Wind Market Report: 2024 Edition' provide valuable data on the deployment and effectiveness of distributed wind solutions, enhancing the discussion on wind mechanisms.
Navigating Legal Frameworks: Wind Turbine Titles and Ownership Issues
Wind energy initiatives frequently involve a diverse range of stakeholders, which can complicate the intricacies of title ownership. To navigate these complexities effectively, it is essential to consider several key legal aspects:
- Title Research: Conduct comprehensive investigations into existing land titles. This process ensures clear ownership and helps identify any liens or encumbrances that could hinder progress in wind energy title research.
- Easements and Rights of Way: Evaluate the need for easements to enable access to energy sites and transmission lines. Understanding the scope and implications of these easements is critical for maintaining operational efficiency.
- Lease Agreements: Familiarize yourself with the terms of property leases. These agreements often involve negotiations with landowners, and comprehending the nuances of lease conditions is vital to avoid potential conflicts.
Importantly, failure to comply with federal or state environmental regulations can result in costly delays and legal challenges, underscoring the importance of thorough legal due diligence. As Sebastian E. Winter observed, 'Few recent advancements in human medicine have been as impactful as the discovery that an imbalance (dysbiosis) of our resident microbial communities in the colon is associated with numerous chronic human diseases,' emphasizing the wider implications of systemic challenges—echoing the intricacies in renewable initiatives.
Furthermore, a case study evaluating land use and potential conflict in solar and onshore renewable sources in Japan demonstrates the real-world challenges of incorporating sustainable initiatives within existing land frameworks. Navigating these legal frameworks demands meticulous documentation and, in many cases, the involvement of legal counsel. This approach is essential for resolving any disputes that may occur during the acquisition process, especially considering recent legal issues related to turbine ownership.
As the renewable resources sector continues to evolve, staying informed about these legal aspects will facilitate smoother implementation and compliance with federal and state regulations.
Environmental Considerations in Wind Energy Title Research
Conducting title research for wind energy initiatives necessitates a comprehensive understanding of environmental regulations and assessments, which include:
- Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA): Often mandated, these evaluations assess potential effects of initiatives on local ecosystems, ensuring that developers meet biodiversity reporting requirements. Incorporating environmental DNA (Edna) analysis into EIAs can further enhance compliance and provide detailed insights into local biodiversity, a practice increasingly recognized as essential.
- Protected Areas: Identifying any land designated as protected is crucial, as these areas may impose restrictions on development activities. Developers must navigate these regulations carefully to avoid potential conflicts with conservation efforts.
- Wildlife Considerations: Assessing the impact on local wildlife and habitats is vital, as these factors significantly influence site selection and the likelihood of approvals. A recent study, titled 'Use of EIA Data for Wildlife Management', highlights the significance of employing data from EIAs and post-construction monitoring to guide planning choices concerning wind-related developments and their impact on wildlife. The research observed that although the information can guide land management choices, constraints arise from accessibility challenges, the observational character of the data, and discrepancies in survey activities across locations.
Integrating these ecological factors into wind energy title research not only ensures adherence to regulations but also fosters community support for renewable initiatives. As emphasized by Philip J. K. McGowan, an initiative backed by the World Pheasant Association illustrates the cooperative efforts required to balance power development and wildlife preservation. The ongoing discussion regarding wildlife effects is reflected in the latest 'Global Wind Report 2024' published by the Global Wind Energy Council, which highlights the necessity for thorough assessments in the renewable sector, especially considering historical data indicating that the earliest site in the study became operational in 1995, with the most recent in 2010.
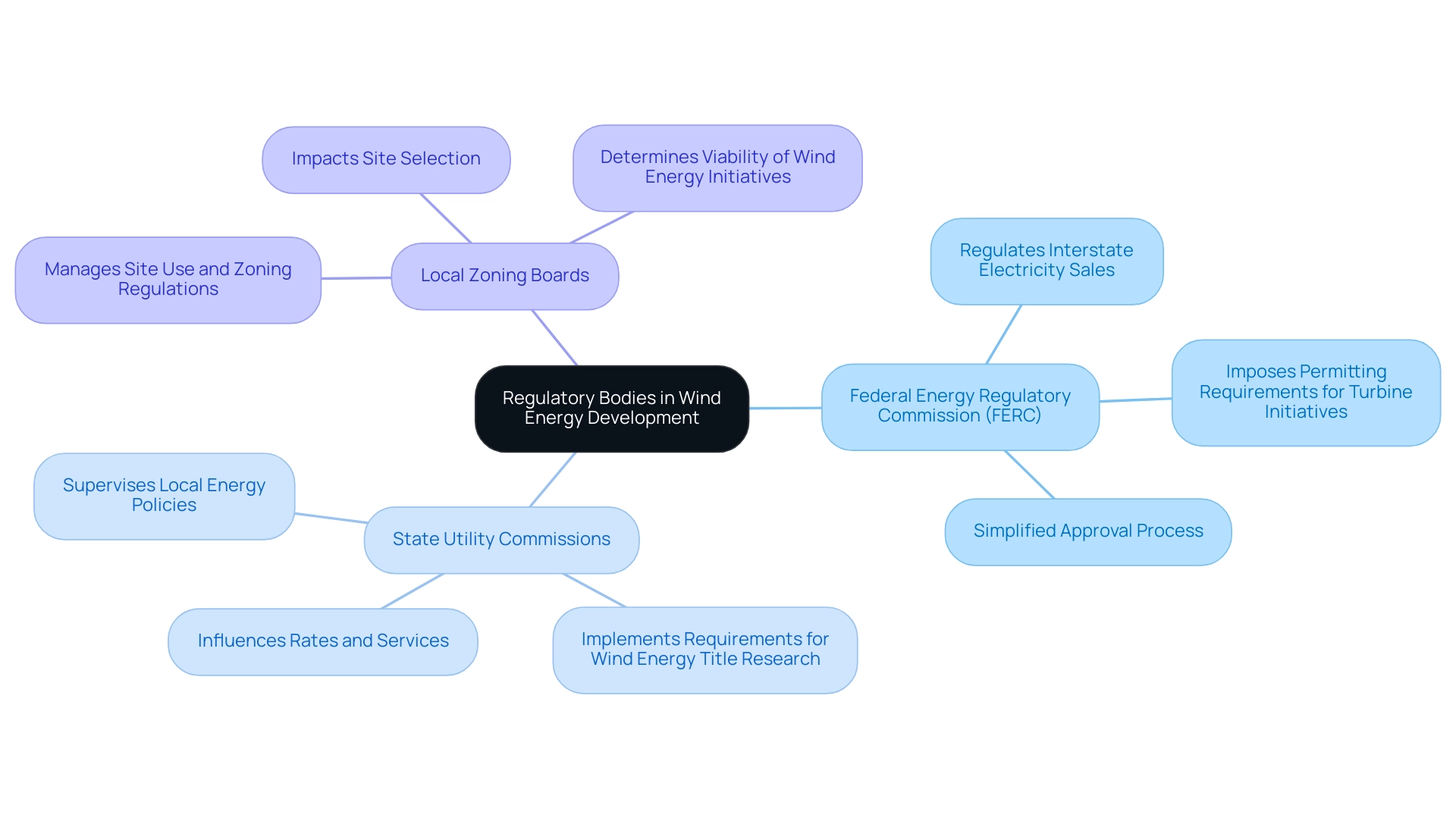
The Role of Regulatory Bodies in Wind Energy Development
Regulatory authorities are crucial in the supervision of renewable power development, ensuring that initiatives conform to legal and environmental standards. The key entities involved include:
- Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC): This commission is responsible for regulating interstate electricity sales and may impose permitting requirements for turbine initiatives. Recent changes to FERC regulations have been crafted to simplify the approval process for such initiatives, reflecting the evolving landscape of renewable energy.
- State Utility Commissions: These commissions supervise local energy policies and can implement specific requirements tailored to wind energy title research, which influences aspects such as rates, services, and adherence to state laws.
- Local Zoning Boards: Responsible for managing site use and zoning regulations, local boards significantly impact site selection and the overall viability of wind energy title research initiatives within their jurisdictions. Their decisions can determine the success or challenges faced by proposed developments.
Engaging with these regulatory bodies early in the land acquisition process is essential. Doing so not only ensures adherence to all necessary regulations but also facilitates a smoother approval process. As highlighted by Philip Dick, planning director of McLean County, in an interview gathered by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, a knowledgeable strategy for managing these regulatory requirements is essential for the successful execution of projects related to wind energy title research.
Moreover, the financial advantages of renewable sources are clear; for instance, residents of Sherman County, Oregon, have received yearly payments of almost $600 from renewable revenue, highlighting the beneficial economic effect of such initiatives. Furthermore, it is crucial to take into account the environmental effects of air power development. A case study titled 'Environmental Impacts of Wind Power Development' highlights that while such projects can provide significant ecological benefits, they also pose challenges such as wildlife collisions and habitat disturbances, necessitating careful assessment to mitigate risks.
Step-by-Step Guide to Conducting Wind Energy Title Research
To conduct effective renewable resource title research, adhere to the following structured approach:
- Identify Project Scope: Clearly define the geographic region targeted for energy development, along with detailed space requirements necessary for the project.
- Conduct Preliminary Research: Utilize GIS mapping tools to gather initial data on land ownership and existing titles. These tools play a crucial role in generating average air severity and power density maps, which are essential for optimal turbine placement. As noted by Huang (2024), effective wind turbine placement relies heavily on accurate resource evaluation methodologies.
- Verify Title Ownership: Access public records and databases to confirm the current land ownership status. This step also involves identifying any potential encumbrances that could affect the viability of the initiative.
- Assess Environmental Impact: Perform comprehensive environmental assessments to ensure compliance with regulatory standards and to identify any potential ecological issues that may arise during development. The case study on carbon emission savings from renewable sources highlights the significant environmental advantages, emphasizing the importance of this step in reducing carbon emissions.
- Engage with Stakeholders: Proactively communicate with landowners, regulatory bodies, and community members. Addressing concerns and negotiating agreements at this stage is vital for fostering positive relationships and ensuring support.
- Document Findings: Compile all research findings, including legal documents and agreements, into a detailed report. This comprehensive documentation will function as an essential reference for project development and compliance.
By adhering to these systematic steps, you can guarantee a thorough title research process for wind energy title research that offers a solid foundation for successful renewable project development. The publication timeline for this research—submitted on 25 November 2023, revised on 13 January 2024, accepted on 24 January 2024, and published on 26 January 2024—underscores the rigorous process involved in developing effective methodologies and technologies, such as those discussed in the article 'High-resolution large-scale onshore wind energy assessments,' which are essential for advancing sustainable energy solutions and reducing carbon emissions.
Conclusion
The exploration of wind energy as a sustainable power source has underscored its significance in the transition toward cleaner energy solutions. Understanding the fundamental mechanics of wind turbines, including their operational principles and the critical role of land requirements, is essential for stakeholders engaged in the development of wind energy projects. Additionally, the complexities surrounding title research, legal frameworks, and ownership issues highlight the necessity for thorough investigations and compliance with regulatory standards to ensure successful project execution.
Environmental considerations play a pivotal role in the planning and implementation of wind energy initiatives. Conducting Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA) and recognizing protected areas are crucial steps in mitigating potential ecological impacts and fostering community support. The integration of wildlife considerations further emphasizes the need for a balanced approach that aligns energy development with conservation efforts.
Regulatory bodies, including the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission and local zoning boards, are instrumental in guiding wind energy projects through the legal landscape. Engaging with these entities early in the process can streamline approvals and facilitate compliance with both federal and state regulations.
By adhering to a structured approach in conducting title research, stakeholders can ensure the identification of suitable sites and the establishment of strong relationships with landowners and regulatory agencies. This comprehensive understanding of the wind energy sector not only promotes effective project development but also reinforces the broader goal of advancing sustainable energy solutions that benefit both the economy and the environment. As the demand for renewable energy continues to rise, the insights gained from this exploration will be vital for navigating the intricate landscape of wind energy development.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the basic mechanism of how wind energy is converted into electricity?
Wind energy is captured by turbines, which rotate when wind flows over their blades. This rotation spins a rotor connected to a generator, converting mechanical power into electrical power.
What are the key components involved in the wind energy conversion process?
The key components include wind turbines, land requirements for installation and maintenance, and factors affecting energy production such as air speed and turbine placement.
Why are land requirements important for wind energy projects?
Adequate space is necessary for installing turbines, conducting maintenance activities, and providing access roads, which are essential for operational integrity.
How do wind energy initiatives impact local economies?
Efficient renewable energy initiatives can enhance local economies significantly; for example, they contributed over $2 billion in state and local tax payments and land-lease agreements last year.
What recent developments have influenced the deployment of wind turbines?
The enactment of the Inflation Reduction Act has led to a significant increase in near-term deployment forecasts for turbines, highlighting the need for strategic land acquisition planning.
What legal aspects should be considered in wind energy title research?
Key legal aspects include conducting title research to ensure clear ownership, evaluating easements for access to energy sites, and understanding lease agreements with landowners.
Why is it important to comply with federal and state environmental regulations in wind energy projects?
Non-compliance can result in costly delays and legal challenges, making thorough legal due diligence essential for successful project implementation.
What are some challenges related to land use for renewable energy initiatives?
Incorporating sustainable initiatives within existing land frameworks can present real-world challenges, requiring meticulous documentation and often the involvement of legal counsel to resolve disputes.
How can stakeholders navigate the complexities of title ownership in wind energy projects?
Stakeholders should conduct comprehensive investigations into existing land titles, evaluate the need for easements, and familiarize themselves with lease agreement terms to avoid conflicts.
List of Sources
- Understanding Wind Energy: Basics and Mechanisms
- atb.nrel.gov (https://atb.nrel.gov/electricity/2024/land-based_wind)
- Wind Market Reports: 2024 Edition (https://energy.gov/eere/wind/wind-market-reports-2024-edition)
- Wind Power Facts and Statistics | ACP (https://cleanpower.org/facts/wind-power)
- Navigating Legal Frameworks: Wind Turbine Titles and Ownership Issues
- Wind Turbine Titles: What Are the Key Ownership and Legal Hurdles? (https://pippintitle.com/blog/wind-turbine-titles-ownership-legal-hurdles)
- mcafeetaft.com (https://mcafeetaft.com/wind-law-and-negotiations-from-a-landowners-perspective)
- pnas.org (https://pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2302313120)
- Conceptualizing the patterns of land use conflicts in wind energy development: Towards a typology and implications for practice (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2214629622004108)
- Environmental Considerations in Wind Energy Title Research
- esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com (https://esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1890/ES14-00331.1)
- inogenalliance.com (https://inogenalliance.com/blog-post/harnessing-renewable-energy-responsibly-role-environmental-impact-assessments)
- Wind Energy Factsheet (https://css.umich.edu/publications/factsheets/energy/wind-energy-factsheet)
- The Role of Regulatory Bodies in Wind Energy Development
- windexchange.energy.gov (https://windexchange.energy.gov/economic-development-guide)
- nap.nationalacademies.org (https://nap.nationalacademies.org/read/11935/chapter/7)
- The determinants of wind energy growth in the United States: Drivers and barriers to state-level development (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1364032118306063)
- Step-by-Step Guide to Conducting Wind Energy Title Research
- Research on Wind Turbine Location and Wind Energy Resource Evaluation Methodology in Port Scenarios (https://mdpi.com/2071-1050/16/3/1074)
- Analysis of Wind Data, Calculation of Energy Yield Potential, and Micrositing Application with WAsP (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1155/2018/2716868)
- High-resolution large-scale onshore wind energy assessments: A review of potential definitions, methodologies and future research needs (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0960148121014841)
- Wind energy resource assessment and wind turbine selection analysis for sustainable energy production - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11087656)




