Introduction
The transition to solar energy is not just a technological shift; it is a complex journey that requires careful navigation through a myriad of regulations and permitting processes. As the demand for renewable energy surges, understanding the intricacies of solar project permitting has become essential for developers aiming to contribute to a sustainable future.
This article delves into the critical steps involved in:
- Securing the necessary permits
- Engaging with local authorities
- Adhering to zoning laws
All of which play a pivotal role in the viability of solar projects. By exploring the impact of local regulations and the value of professional assistance, this comprehensive guide provides valuable insights that can streamline the path toward successful solar energy implementation.
Understanding the Solar Project Permitting Process
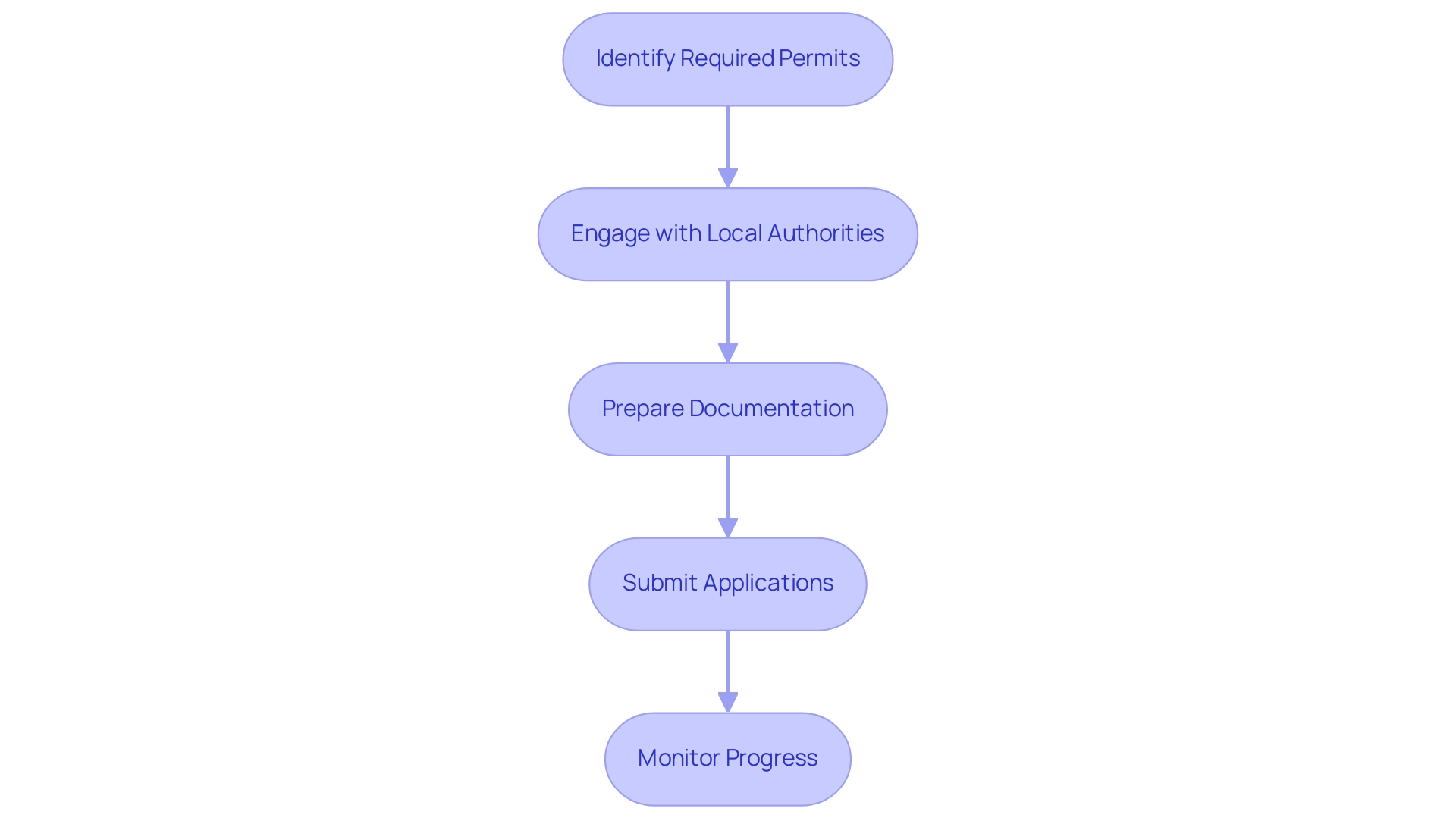
Navigating the solar initiative permitting process requires a systematic approach that encompasses several essential steps:
- Identify Required Permits: Begin by pinpointing the necessary permits based on your undertaking's location and scale. Typical permits include environmental assessments, building permits, and special use permits, which can vary significantly based on regional regulations.
- Engage with Local Authorities: Initiate contact with local government offices or planning departments to gain a thorough understanding of specific requirements. Local officials can provide valuable insights into current regulations and the documentation needed for solar land regulatory compliance, especially in light of recent changes in solar permitting processes for 2024.
- Prepare Documentation: Gather all necessary documents, such as site plans, environmental impact assessments, and detailed descriptions of the endeavor. It is crucial that all information submitted is accurate and comprehensive to mitigate the risk of delays; incomplete applications can lead to significant setbacks.
- Submit Applications: File your permit applications with the appropriate authorities. Be prepared for potential requests for additional information or modifications, as local jurisdictions may require clarifications based on the specific context of your endeavor.
- Monitor Progress: After submission, maintain regular communication with the authorities to track the status of your applications. Proactive involvement can help tackle any issues promptly and ensure a smoother approval experience.
Comprehending the average length of the approval process is crucial; statistics show that it can differ significantly, frequently requiring several months to more than a year, based on the area and intricacy of the undertaking. For instance, in California, the approval process has demonstrated considerable variability, with some undertakings requiring over a year due to regulatory complexities. As emphasized in case studies, successful applications for renewable energy initiatives often arise from thorough preparation and cooperation with regional authorities to achieve solar land regulatory compliance, paving the way for efficient execution.
The Hamilton Project and Energy Policy Institute at the University of Chicago emphasize that 'Given the immense threat that climate change represents, it is crucial that policymakers implement efficient solutions that minimize climate damages from our use of energy.' This perspective underscores the importance of navigating the permitting process effectively to contribute to a sustainable energy future.
Navigating Local Regulations and Zoning Laws for Solar Projects
Successfully maneuvering through local regulations and zoning laws for renewable energy initiatives requires a systematic approach, especially considering the Biden Administration's goal for 100% renewable electricity by 2035, which highlights the urgency of compliance. Here are key steps to follow:
-
Research Local Zoning Codes: Start by thoroughly reviewing the zoning codes relevant to your project area.
These codes govern land use and are critical in determining the type of solar installation that is permissible.
-
Consult Regional Planning Departments: Engage with regional planning departments to clarify any uncertainties regarding zoning laws.
These departments can provide significant insights into restrictions, requirements, and the overall regulatory landscape.
-
Identify Variances or Special Permits: If your endeavor does not align with existing zoning regulations, it may be necessary to apply for a variance or special permit.
Familiarize yourself with the application process and the specific requirements to facilitate this step.
-
Community Engagement: Actively interacting with the surrounding community can be advantageous in addressing potential concerns and nurturing support for your initiative.
This proactive approach can be instrumental in navigating regulatory hurdles that may arise.
It's also important to note that associations such as homeowners associations, condominium owners associations, and cooperative housing associations hold the authority to prohibit the installation and use of energy collection devices, as stated in the District of Columbia Code § 8–1774.51:
'The authority of homeowners associations, condominium owners associations, and cooperative housing associations to prohibit the installation and use of energy collection devices.'
By adhering to these steps, you can effectively place your renewable energy initiative for success amid the challenges of regional regulations.
Furthermore, examine the case study of Holy Cross Energy's collaboration with Virtual Peaker, which illustrates effective management of distributed energy resources and emphasizes the significance of compliance in navigating regional zoning laws.
The Role of Professional Help in Solar Permitting
Involving expert assistance in energy approvals is essential for improving the success rate of projects. Here are key strategies to consider:
-
Identify Qualified Consultants: Choose consultants who have a demonstrated history in solar approval and a comprehensive knowledge of local regulations.
Their expertise can significantly smooth the permitting process, ensuring solar land regulatory compliance and reducing delays.
-
Evaluate Services Offered: Review the comprehensive range of services provided by potential consultants, including permit application preparation, regulatory compliance assessments, and community engagement strategies.
These elements are vital for navigating the complex landscape of energy regulations.
-
Discuss Requirements: Clearly articulate your initiative's specific needs and timelines when engaging with consultants.
Effective communication of your expectations is essential to align their capabilities with your goals.
-
Maintain Communication: Foster open lines of communication with your consultant throughout the approval process.
Regular updates and discussions can help address emerging issues promptly and keep the project on track.
As highlighted in the Lapeer Solar Park Development case study, professional assistance can streamline environmental assessments and permitting processes, ultimately contributing to your clean energy objectives. Despite market constraints affecting resource allocation, such as the tension between profitability and the desire to invest in DEIA initiatives, recognizing the value of expert guidance is crucial for navigating solar land regulatory compliance effectively.
Notably, while recent utility-scale photovoltaic prices range from $16/MWh to $35/MWh, making this energy competitive, firms often find it challenging to dedicate resources to training and community engagement, as many DEIA training resources remain optional. As one industry participant noted, while a commitment to training and community engagement is ideal, profitability challenges often hinder firms from dedicating necessary resources.
Assessing the Impact of Local Regulations on Solar Project Viability
To effectively navigate the influence of regional regulations on solar land regulatory compliance and the viability of solar initiatives, consider the following steps:
-
Conduct a Regulatory Review:
Begin by thoroughly analyzing local regulations concerning solar land regulatory compliance to understand their implications for your initiative. Identify any restrictions that may limit the scope or scale, as these can significantly affect feasibility.
-
Evaluate Financial Implications:
It is crucial to grasp how compliance costs—such as fees for permits or mandatory environmental studies—can influence your budget. Understanding these financial implications is vital, especially in light of the significant potential tax revenues projected from initiatives like the Ohio Community Solar Pilot Program, which could yield between USD 318,500,000 and USD 409,500,000 over its lifetime.
Furthermore, take into account the anticipated expenses and economic effects for different renewable energy initiatives, as these elements will further guide your budgeting process.
-
Consider Timeline Impacts:
Assess how the regulatory approval processes may extend timelines, directly affecting your return on investment.
Delays related to solar land regulatory compliance can obstruct the financial feasibility of renewable initiatives, particularly when accounting for the U.S. goals of attaining 100% clean electricity by 2035 and a net-zero carbon economy by 2050. The anticipated growth in solar installations, which has already seen over 30 GW completed through Q3 2024, underscores the urgency of addressing these timelines, especially given ongoing challenges such as interconnection issues and labor availability.
-
Engage Stakeholders Early:
Involve key stakeholders early in the planning process to collaboratively address potential regulatory challenges. Early engagement can facilitate smoother navigation of solar land regulatory compliance hurdles, which is essential for successful implementation.
As noted by Anthony Lopez, a senior geospatial data scientist at NREL,
The data can inform discussions about balancing local clean energy deployment decisions with mitigating global climate change.
This balance is essential for the successful execution of energy initiatives amid changing regulatory environments. Furthermore, the Solar PV Growth Forecast suggests that while photovoltaic technology is at the forefront of new capacity, challenges persist that could influence feasibility and timelines.
Essential Land Use and Infrastructure Requirements for Solar Power
To navigate regulatory compliance concerning land use and infrastructure requirements for renewable energy initiatives effectively, adhere to the following guidelines:
-
Identify Suitable Land: Assess land suitability by considering critical factors such as sunlight exposure, proximity to existing infrastructure, and environmental impacts. For instance, community energy facilities, which typically have less than five megawatts of electrical capacity, are often situated on leased land. This model enables residents and small enterprises to obtain credits on their electricity bills for the power generated from their portion of a solar array, thereby reducing their electricity expenses, making land selection a key factor in feasibility.
-
Understand Land Use Designations: Thoroughly review local land use designations to ensure alignment with permitted uses. Comprehending the regulations concerning solar land regulatory compliance is vital, as they can differ greatly by state and locality, affecting timelines and approvals. For instance, certain states may have particular requirements for agricultural land conversion or zoning regulations that could affect renewable energy project development.
-
Plan for Infrastructure Needs: Evaluate necessary infrastructure, including access roads, power lines, and maintenance water supply. According to G. Heath,
The direct area comprises land directly occupied by photovoltaic arrays, access roads, substations, service buildings, and other infrastructure.
Properly addressing these needs is essential for the successful integration of solar energy installations.
-
Conduct Environmental Assessments: Depending on the scope of the undertaking, it may be necessary to conduct environmental assessments to evaluate potential impacts on local ecosystems. Such assessments are commonly a requirement for permitting and can help mitigate future regulatory challenges. Furthermore, staying informed about the most recent land use regulations, particularly regarding solar land regulatory compliance for renewable energy initiatives, is essential, as these can change and may vary considerably by area.
By following these guidelines, project developers can ensure compliance with land use and infrastructure requirements while contributing to the growing solar energy landscape, which saw 11 gigawatts of new solar module manufacturing capacity come online in the United States during Q1 2024.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of solar project permitting is crucial for developers aiming to contribute effectively to the renewable energy landscape. By understanding the essential steps—identifying required permits, engaging with local authorities, preparing comprehensive documentation, and monitoring application progress—developers can significantly enhance their chances of success. Each of these steps plays a vital role in ensuring compliance with local regulations, which can vary widely depending on the project's location.
Local regulations and zoning laws further complicate the permitting process, necessitating thorough research and proactive community engagement. Recognizing the importance of these regulations is essential, particularly in light of national goals for renewable energy. Engaging with local planning departments and understanding the implications of zoning codes can help mitigate potential obstacles, paving the way for smoother project execution.
The role of professional assistance cannot be overstated. Qualified consultants provide invaluable expertise that can streamline the permitting process, ensuring adherence to regulations and facilitating effective communication with local authorities. By leveraging professional help, developers can navigate the intricate landscape of solar project permitting more efficiently.
Ultimately, understanding and addressing local regulations, engaging stakeholders early, and recognizing the financial and timeline impacts of compliance are essential for the successful implementation of solar projects. As the demand for renewable energy continues to grow, a meticulous approach to permitting will not only enhance project viability but also contribute to a sustainable energy future. The commitment to navigating these regulatory landscapes effectively is a crucial step in the collective effort to combat climate change and achieve clean energy targets.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the essential steps in the solar initiative permitting process?
The essential steps include identifying required permits, engaging with local authorities, preparing documentation, submitting applications, and monitoring progress.
How can I identify the required permits for my solar project?
You can identify the required permits by determining the necessary permits based on your project's location and scale, which typically include environmental assessments, building permits, and special use permits.
Why is it important to engage with local authorities?
Engaging with local authorities helps you understand specific requirements and current regulations, and obtain necessary documentation for solar land regulatory compliance, especially with recent changes in the permitting processes.
What documentation do I need to prepare for my solar application?
You need to gather necessary documents such as site plans, environmental impact assessments, and detailed descriptions of the project to ensure all information submitted is accurate and comprehensive.
What should I expect when submitting my permit applications?
When submitting your permit applications, be prepared for potential requests for additional information or modifications from local jurisdictions based on the specifics of your project.
How can I monitor the progress of my permit applications?
After submission, maintain regular communication with the authorities to track the status of your applications and proactively address any issues that may arise.
How long does the approval process for solar permits typically take?
The approval process can vary significantly, often taking several months to more than a year, depending on the area and complexity of the project.
What should I do if my solar project doesn't align with existing zoning regulations?
If your project does not align with existing zoning regulations, you may need to apply for a variance or special permit and familiarize yourself with the application process and specific requirements.
Why is community engagement important during the permitting process?
Actively engaging with the surrounding community can help address potential concerns and build support for your initiative, which can be beneficial in navigating regulatory hurdles.
Can homeowners associations restrict solar energy installations?
Yes, homeowners associations, condominium owners associations, and cooperative housing associations can prohibit the installation and use of energy collection devices according to local regulations.
List of Sources
- Understanding the Solar Project Permitting Process
- Eight facts about permitting and the clean energy transition - The Hamilton Project (https://hamiltonproject.org/publication/economic-fact/eight-facts-permitting-clean-energy-transition)
- Solar Industry Research Data – SEIA (https://seia.org/research-resources/solar-industry-research-data)
- Navigating Local Regulations and Zoning Laws for Solar Projects
- Regulating Utility-Scale Solar Projects on Agricultural Land (https://kleinmanenergy.upenn.edu/research/publications/regulating-utility-scale-solar-projects-on-agricultural-land)
- Wind, Solar and Siting: A Look at Recent Laws and Legislative Trends in the Midwest - CSG Midwest (https://csgmidwest.org/2024/02/29/wind-solar-and-siting)
- palmetto.com (https://palmetto.com/policy/solar-access-laws-by-state)
- Hundreds of US localities restrict renewables siting, with 293 projects currently contested: Columbia report (https://utilitydive.com/news/local-restrictions-renewables-siting-projects-solar-wind/652026)
- The Role of Professional Help in Solar Permitting
- Census Demographics and Diversity (https://irecusa.org/census-demographics-and-diversity)
- Solar Power Development | Site Permitting, Engineering (https://trccompanies.com/markets/power-and-utilities/renewables/solar-power-development)
- Solar Industry Research Data – SEIA (https://seia.org/research-resources/solar-industry-research-data)
- Assessing the Impact of Local Regulations on Solar Project Viability
- NREL Releases Comprehensive Databases of Local Ordinances for Siting Wind, Solar Energy Projects (https://nrel.gov/news/program/2022/nrel-releases-comprehensive-databases-of-local-ordinances-for-siting-wind-solar-energy-projects.html)
- Assessing the Economic Impacts of Sustainable Energy: An Analysis of Ohio’s Community Solar Program (https://mdpi.com/2071-1050/16/21/9436)
- Solar Industry Research Data – SEIA (https://seia.org/research-resources/solar-industry-research-data)
- Essential Land Use and Infrastructure Requirements for Solar Power
- seia.org (https://seia.org/solar-state-by-state)
- Community Solar – SEIA (https://seia.org/initiatives/community-solar)
- Land-Use Requirements for Solar Power Plants in the United States (https://digital.library.unt.edu/ark:/67531/metadc841450)




