Overview
This article delves into the implementation of green infrastructure innovation within development projects, underscoring the necessity of integrating eco-friendly systems that effectively manage stormwater, enhance biodiversity, and bolster urban resilience. It articulates the complexities faced in this endeavor, particularly in land acquisition, while presenting various strategies such as employing GIS and AI technologies for effective planning.
Successful case studies are showcased, demonstrating the multifaceted benefits—environmental, social, and financial—of green infrastructure in urban settings. Ultimately, this exploration calls for a concerted effort in adopting these innovative solutions to address the pressing challenges of urban development.
Introduction
In an era where urban landscapes face increasing environmental challenges, the integration of green infrastructure stands out as a transformative solution. This innovative approach merges natural systems with urban development, yielding numerous benefits that surpass mere aesthetics. It enhances stormwater management, boosts biodiversity, and improves community well-being, effectively reshaping how cities adapt to climate change while promoting sustainable growth.
As urban planners and developers focus on these eco-friendly practices, grasping the principles and successful implementations of green infrastructure is crucial for creating resilient urban environments. This article examines the multifaceted advantages of green infrastructure, explores cutting-edge technologies that enhance its effectiveness, and underscores the importance of stakeholder engagement in driving successful outcomes.
Understanding Green Infrastructure: A Foundation for Development Projects
Green systems represent a meticulously planned network of natural and semi-natural spaces aimed at managing stormwater, enhancing biodiversity, and bolstering urban resilience. This approach employs innovative techniques, including eco-friendly roofs, rain gardens, and permeable pavements, which are essential for developers committed to sustainable practices. By emulating natural processes, these systems effectively tackle environmental challenges while elevating the aesthetic and functional quality of urban landscapes.
Recent advancements in eco-friendly systems underscore their increasing prevalence in metropolitan areas. Notably, statistics reveal a remarkable 291% surge in outdoor recreational activities in Oslo during the COVID-19 lockdown, highlighting the public's growing appreciation for natural spaces. Successful implementations of eco-friendly roofs and rain gardens across global cities exemplify their efficacy in stormwater management and urban cooling, thereby contributing to overall metropolitan resilience.
Key considerations regarding sustainable systems in development initiatives include their pivotal role in fostering biodiversity. Research indicates that these systems serve as biodiversity hotspots within urban limits. Experts emphasize the multifaceted benefits of eco-friendly systems, such as improved air quality, reduced urban heat, and heightened property values. Moreover, the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) has been effectively utilized in planning to prioritize impactful elements for successful green infrastructure innovation, ensuring alignment with ecological and community needs.
As urban areas continue to transform, the importance of integrating green infrastructure innovation into development projects is paramount. This integration not only addresses pressing environmental issues but also cultivates long-term sustainability and resilience in urban environments. Future research should concentrate on large-scale applications of Urban Green Infrastructure (UGI) across varying climates and urban contexts to further amplify its effectiveness.
Furthermore, understanding the development, assessment, and management of sustainable systems, along with their interplay with land use and ecological processes, is crucial for successful implementation. Familiarity with these principles is indispensable for executing sustainable solutions that fulfill both regulatory mandates and community expectations.
Innovative Green Infrastructure Solutions for Urban Development
Innovative solutions for incorporating green infrastructure into city development increasingly depend on advanced technologies such as GIS mapping and AI-driven analytics. GIS mapping is crucial for identifying optimal locations for green spaces by analyzing environmental data, which is essential for effective city planning. Recent studies indicate that socioeconomic factors are the most mentioned cause of city disparity, underscoring the importance of addressing these issues through GIS and AI technologies.
The systematic review titled "Disparity Analytics Using GIS" highlights the applications of geospatial technology in studying disparities in cities, revealing a predominant focus on accessibility analysis and a recent shift towards environmental justice. How can cities leverage these technologies to bridge the gap in disparities?
AI technologies further enhance this process by predicting stormwater runoff patterns, enabling developers to design and strategically place green infrastructure elements more effectively. This predictive capability is essential, particularly as urban areas face growing challenges related to stormwater management. Statistics indicate that AI applications in stormwater management can result in significant enhancements in efficiency and effectiveness, ultimately contributing to more resilient city environments.
Moreover, practices such as bioretention systems and green roofs not only manage stormwater but also promote biodiversity and enhance air quality. As Sonila Sinjari observes, "All these issues will be meticulously examined regarding providing guidance for city planning in the service of the community, the environment, and regional economy." These innovative technologies are essential for creating sustainable cityscapes through green infrastructure that addresses both ecological and community needs.
As city planners increasingly acknowledge the importance of integrating green systems, green infrastructure innovation utilizing GIS and AI technologies will be essential for promoting livable, resilient communities in the future. The conclusion of the study emphasizes that aggregated spatial data sources are particularly valuable for livability studies, reinforcing the argument for using diverse data sources in city planning.
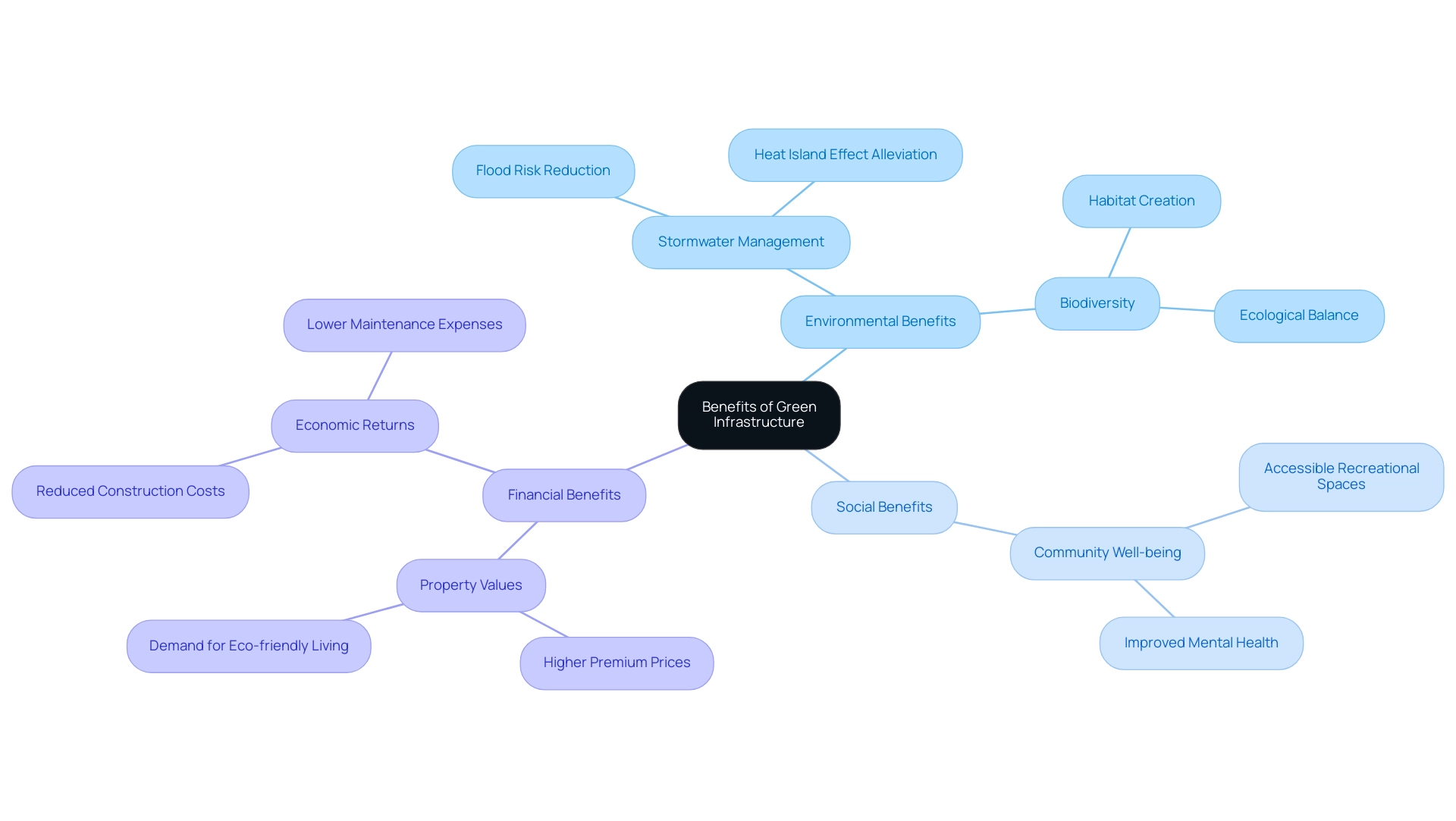
The Multifaceted Benefits of Green Infrastructure in Development
Green infrastructure innovation presents a multitude of benefits that extend beyond mere environmental advantages, significantly shaping city development and enhancing community well-being. By effectively capturing and filtering rainwater, these systems improve stormwater management, play a crucial role in reducing flooding risks, and alleviate the heat island effect. The concept of 'sponge city' embodies stormwater management that aligns with nature, further enriching the discourse on the advantages of stormwater management.
The integration of green infrastructure innovation fosters city biodiversity, creating habitats that support multiple species and enhance ecological balance.
From a social perspective, green infrastructure innovation in eco-friendly structures promotes community well-being by providing accessible recreational spaces that encourage physical activity and bolster mental health. Research indicates that access to nature correlates with improved mental health outcomes, highlighting the importance of green infrastructure innovation in urban planning.
Financially, the advantages of eco-friendly systems are substantial. Implementing these systems can lead to reduced construction costs, as they often necessitate less extensive drainage systems and incur lower maintenance expenses. Additionally, properties located near green infrastructure innovation frequently experience higher property values.
Research shows that homes adjacent to parks and natural spaces can command premium prices, reflecting the growing demand for green infrastructure innovation in sustainable living environments.
By 2025, the economic benefits of sustainable development are expected to become even more pronounced, with projections suggesting that eco-friendly building practices could divert over 80 million tons of waste from landfills, aiming for 540 million tons by 2030. This transition minimizes resource consumption while enhancing the overall sustainability of urban settings.
Case studies underscore the efficacy of green infrastructure innovation in stormwater management. For instance, resilience strategies in eco-friendly construction projects demonstrate that green infrastructure innovation, which incorporates sustainable designs and technologies, fosters collaboration among residents and property owners, ultimately enhancing quality of life. Tools like LEED for Cities and LEED for Communities facilitate resilience planning, ensuring that green infrastructure innovation results in developments that are both environmentally sound and economically viable.
Experts in environmental economics emphasize the long-term financial benefits of sustainable development initiatives, noting that green infrastructure innovation generates significant returns through increased property values and reduced public health costs. As the focus on sustainable growth intensifies, it becomes imperative for developers to articulate the multifaceted advantages of green infrastructure innovation to stakeholders, thereby garnering support for eco-friendly initiatives in their projects. As stated by the US EPA, "This research was performed while FAH held a National Research Council Research Associateship Award at the United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA)."
Furthermore, the monitoring and evaluation framework underscores the importance of data collection, analysis, reporting, and continuous enhancement of environmental projects, emphasizing the need for ongoing assessment in these initiatives.
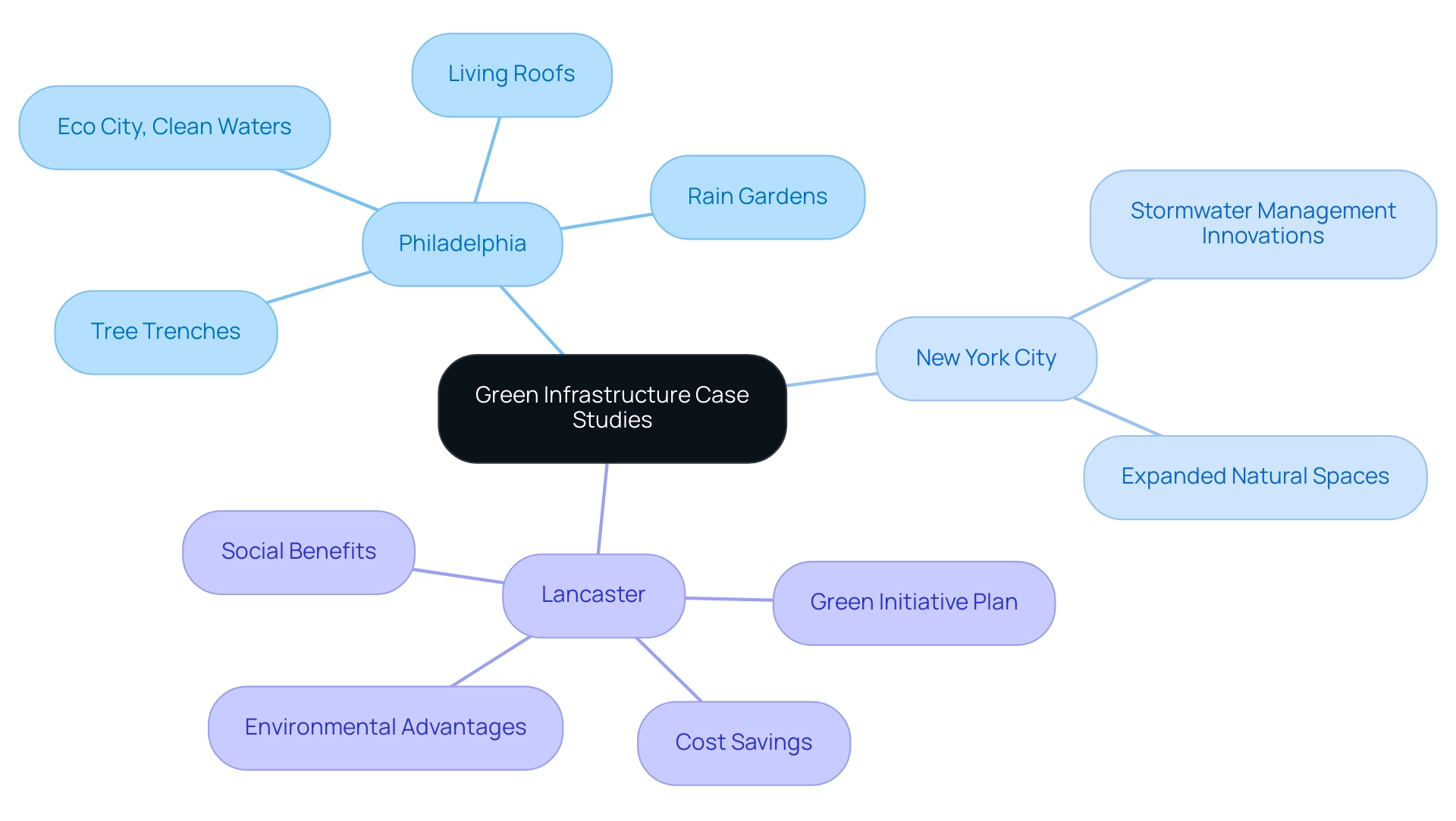
Case Studies: Successful Implementations of Green Infrastructure
Cities worldwide are increasingly establishing standards for sustainable development, showcasing innovative green infrastructure that addresses urban challenges while delivering ecological and community benefits. Philadelphia's Eco City, Clean Waters program serves as a prime example of this innovation, integrating living roofs, rain gardens, and tree trenches to manage stormwater effectively. This initiative not only enhances urban aesthetics but also significantly improves water quality, illustrating the multifaceted advantages of green infrastructure.
The program underscores the necessity of quality natural spaces within green infrastructure, providing essential ecosystem services that enhance health for both humans and wildlife. In New York City, similar innovations in stormwater management have led to expanded natural spaces and improved environmental health. These successful case studies emphasize the critical role of quality natural spaces in promoting green infrastructure, which in turn offers vital ecosystem services and health benefits.
Moreover, Lancaster's Green Initiative Plan quantifies the cost savings, social benefits, and environmental advantages of these efforts, further evidencing the effectiveness of green infrastructure innovation. The lessons learned from Philadelphia's program—particularly its focus on customized city planning and community engagement—serve as a valuable guide for developers. As David Martin, principal at the Terra Group, stated, "I would like to see a fixed funding source for infrastructure that’s not relying on macroeconomic forces that go up and down," highlighting the importance of sustainable financing in these initiatives. By examining these examples, developers can extract insights to inform their project designs, ensuring positive contributions to urban environments through green infrastructure while maximizing sustainability and resilience.
It is also crucial to recognize the limitations of existing studies on urban vegetation areas, especially in developing countries, which underscores the need for tailored urban planning and policies. Incorporating metrics such as species richness can add a quantitative dimension to the discussion on the ecological benefits of sustainable development.
Navigating Challenges in Green Infrastructure Implementation
Establishing environmentally friendly systems presents a complex array of obstacles, including regulatory barriers, funding constraints, and community opposition. Developers must engage with local authorities early in the planning process to gain a comprehensive understanding of regulatory requirements. This proactive approach not only streamlines compliance but also fosters collaborative relationships that facilitate smoother execution.
In this context, Harbinger Land's commitment to providing prompt and precise services tailored to client needs is essential, empowering developers to effectively navigate these challenges.
Funding remains a critical element of green infrastructure innovation initiatives. The EPA's Managing Wet Weather with Green Infrastructure Municipal Handbook identifies two common funding options: stormwater fees and loan programs, which offer vital financial support. Furthermore, exploring grants and public-private partnerships can significantly alleviate financial constraints, enhancing project viability.
Understanding these funding approaches is crucial for developers to address the financial challenges associated with implementing green infrastructure innovation projects.
Community engagement is another essential factor in overcoming opposition to eco-friendly initiatives. Successful outreach and educational programs can clarify sustainable systems, showcasing their benefits to the community. A case study from Keszthely, Hungary, illustrates the importance of environmental planning in smaller communities, demonstrating how a systematic evaluation of ecological systems can lead to sustainable growth and ecosystem conservation.
Moreover, the World Bank Group emphasizes that shared characteristics of regulatory frameworks for climate change and sustainability are vital for guiding developers through the complexities of ecological initiatives. By confronting these challenges directly and employing strategic financing and community involvement strategies, developers can significantly enhance the likelihood of successful implementation of green infrastructure innovation projects. This approach not only aligns with the increasing demand for sustainable solutions, as highlighted by the 2022 G20 Infrastructure Investors’ Dialogue, but also positions ventures as bankable investment opportunities that contribute to long-term community resilience.
Engaging Stakeholders: Collaboration for Successful Green Infrastructure
The successful execution of eco-friendly systems hinges on effective stakeholder involvement. Developers must proactively identify and engage key stakeholders—local government officials, community organizations, and residents—throughout the planning process. By facilitating public meetings, workshops, and collaborative design sessions, meaningful dialogue is fostered, ensuring a diverse range of perspectives is considered.
This method not only enhances the transparency of initiatives but also cultivates trust and support for green infrastructure innovation efforts.
Statistics reveal that companies with robust stakeholder engagement strategies are 40% more likely to complete tasks on schedule and within budget, underscoring the critical role of collaboration in urban development. Furthermore, case studies illuminate the challenges of public participation, as evidenced by industrial land redevelopment initiatives in China, where stakeholder exclusion can lead to social injustice and conflict. To mitigate these issues, it is essential to establish participatory mechanisms that empower community involvement, balancing governmental authority with stakeholder interests.
Looking ahead to 2025, the focus on stakeholder engagement strategies will continue to evolve, with collaborative design emerging as a vital aspect of green infrastructure innovation planning. Expert opinions stress that incorporating community feedback not only enhances outcomes but also aligns development with the community's needs and values. As Neli Banishka asserts, "Stakeholder Management throughout the life cycle of a construction project involves the processes necessary to identify the human resources, groups or organizations that could influence or be influenced by the project."
Successful instances of cooperation in urban ecological systems demonstrate that when developers prioritize stakeholder involvement, they create opportunities for green infrastructure innovation that benefit both the environment and the community. Additionally, the proposal for a novel conceptual analytics framework tailored to the requirements of Smart Cities highlights the future direction of stakeholder engagement strategies in urban development.
Leveraging Technology: Enhancing Green Infrastructure with Advanced Tools
Advanced technologies play a pivotal role in enhancing the efficiency of eco-friendly projects. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) serve as powerful tools for analyzing spatial data, enabling developers to pinpoint optimal locations for ecological components by considering various environmental factors. By 2025, the integration of GIS in environmental planning has seen a remarkable increase, with studies revealing that over 70% of city planners now leverage GIS technology to inform their decisions.
Digital systems are essential for fostering city-based innovation and achieving sustainable economic development in the digital economy era. Artificial Intelligence (AI) further amplifies this process by modeling stormwater management scenarios, facilitating data-driven decision-making that adapts to evolving environmental conditions. For example, AI modeling has been effectively implemented in numerous case studies, showcasing its capability to predict stormwater runoff and optimize drainage systems.
Additionally, tools such as remote sensing and monitoring systems deliver real-time data on the performance of environmentally friendly systems, promoting continuous optimization and ensuring that sustainable practices are not only executed but also perpetually enhanced. The statistical significance of these technologies is underscored by a t-value of 5.868, indicating a robust interaction effect in bolstering city environmental innovation, particularly when accounting for various control variables like financial development and government intervention.
As urban regions increasingly emphasize sustainability, the significance of advanced technologies in green infrastructure innovation becomes even more pronounced. Experts in GIS highlight the critical nature of spatial analysis in urban planning, asserting that effective utilization of these technologies can foster more resilient and adaptable communities. A participant at a recent conference noted, "I strive to remain knowledgeable about global policies, particularly those discussed at the G20 Summit," underscoring the importance of staying informed on global trends that impact urban planning and sustainability.
By harnessing the capabilities of GIS and AI, developers can significantly enhance project outcomes, ensuring that environmentally friendly initiatives contribute meaningfully to sustainable community development.
Future Trends: The Evolving Role of Green Infrastructure in Urban Planning
As metropolitan regions expand and grapple with ecological challenges, the significance of sustainable systems is set to increase markedly. Future trends signal a pivotal shift towards integrated approaches that merge sustainable and gray systems, thereby enhancing urban resilience against climate change. Notably, a recent survey revealed that three-quarters of participants expressed a willingness to engage in the creation and maintenance of natural areas, underscoring the community's vital role in these initiatives and their importance in sustainable land use strategies.
Moreover, city planners are increasingly prioritizing designs that emphasize social equity and accessibility, ensuring that ecological enhancements benefit all community members. This trend aligns with historical transformations from undeveloped natural spaces to areas that facilitate non-burdensome development, thereby improving urban ventilation and livability. Such evolution illustrates how urban systems are adapting to meet contemporary needs while fostering sustainability.
Developers must remain vigilant to these evolving trends and proactively seek to incorporate innovative eco-friendly solutions into their projects. For instance, case studies from North America highlight a growing focus on renewable energy and smart grid technologies, while Europe leads with initiatives such as the European Green Deal, showcasing diverse regional strategies for sustainable development. These examples serve as concrete representations of the successful integration of sustainable systems in development projects.
As climate change continues to influence urban planning, the combination of eco-friendly and traditional systems will be essential for advancing climate resilience. The report advises local stormwater agencies and nonprofit organizations to champion green infrastructure innovation, which includes fostering partnerships and advocating for policy reforms. By leveraging expert insights and case studies, developers can gain a clearer understanding of these trends' implications and position their projects to effectively address the future demands of urban environments.
As noted in the Publisher's Note, it is imperative to maintain neutrality concerning jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations, highlighting the necessity for collaboration among various stakeholders in the field.
Conclusion
Integrating green infrastructure into urban development is essential for addressing the pressing environmental challenges that cities face today. This approach not only enhances stormwater management but also fosters biodiversity and improves community well-being, highlighting the multifaceted benefits of eco-friendly practices.
Advanced technologies such as GIS mapping and AI analytics play a pivotal role in optimizing green infrastructure. These tools empower developers to make informed decisions regarding the placement and effectiveness of green elements, ensuring that urban areas are both resilient and sustainable. Successful case studies from cities like Philadelphia and New York demonstrate how green infrastructure can enhance water quality, increase property values, and elevate residents' quality of life.
However, the implementation of green infrastructure is not without its challenges, including regulatory hurdles and community resistance. Engaging stakeholders through collaborative processes is crucial for overcoming these obstacles and ensuring that the benefits are equitably shared. By prioritizing community involvement and leveraging innovative technologies, developers can navigate the complexities of urban planning more effectively.
As urban areas continue to evolve, the emphasis on integrating green infrastructure will only intensify. Urban planners and developers must remain vigilant to emerging trends and solutions that promote sustainability and climate resilience. By committing to these principles, cities can transform their landscapes into thriving ecosystems that benefit both people and the planet for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are green systems and their purpose?
Green systems are a carefully planned network of natural and semi-natural spaces designed to manage stormwater, enhance biodiversity, and strengthen urban resilience.
What innovative techniques are used in green systems?
Techniques include eco-friendly roofs, rain gardens, and permeable pavements, all of which are essential for developers focused on sustainable practices.
How do green systems benefit urban environments?
They tackle environmental challenges by emulating natural processes and improve the aesthetic and functional quality of urban landscapes.
What recent trends highlight the importance of green spaces?
During the COVID-19 lockdown, there was a 291% increase in outdoor recreational activities in Oslo, indicating a growing public appreciation for natural spaces.
How do eco-friendly roofs and rain gardens contribute to urban resilience?
They are effective in managing stormwater and cooling urban areas, which enhances overall metropolitan resilience.
What role do sustainable systems play in biodiversity?
Sustainable systems act as biodiversity hotspots within urban areas, fostering a variety of plant and animal life.
What are some additional benefits of eco-friendly systems?
Benefits include improved air quality, reduced urban heat, and increased property values.
What planning method is used to prioritize elements for green infrastructure?
The Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) is utilized to ensure that planning aligns with ecological and community needs.
Why is integrating green infrastructure important for urban development?
It addresses environmental issues and promotes long-term sustainability and resilience in urban settings.
What future research areas are suggested for urban green infrastructure?
Future research should focus on large-scale applications of Urban Green Infrastructure (UGI) across different climates and urban contexts.
How do GIS mapping and AI technologies contribute to green infrastructure?
GIS mapping identifies optimal locations for green spaces by analyzing environmental data, while AI predicts stormwater runoff patterns to enhance the design and placement of green infrastructure.
What recent shifts have been observed in the study of city disparities using GIS?
There has been a focus on accessibility analysis and a recent shift towards addressing environmental justice.
What practices promote both stormwater management and biodiversity?
Practices such as bioretention systems and green roofs manage stormwater while also enhancing biodiversity and air quality.
How can cities leverage technology for better planning?
By utilizing GIS and AI technologies, cities can address disparities and enhance the effectiveness of green infrastructure in promoting livable and resilient communities.
List of Sources
- Understanding Green Infrastructure: A Foundation for Development Projects
- Benefits and co-benefits of urban green infrastructure for sustainable cities: six current and emerging themes - Sustainability Science (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11625-024-01475-9)
- (PDF) Urban green infrastructure and its role in sustainable cities: A comprehensive review (https://researchgate.net/publication/378548201_Urban_green_infrastructure_and_its_role_in_sustainable_cities_A_comprehensive_review)
- Green infrastructure: systematic literature review (https://tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/1331677X.2021.1893202)
- Urban Planning with Rational Green Infrastructure Placement Using a Critical Area Detection Method (https://mdpi.com/2673-7418/4/3/14)
- Innovative Green Infrastructure Solutions for Urban Development
- Urban Disparity Analytics Using GIS: A Systematic Review (https://mdpi.com/2071-1050/16/14/5956)
- (PDF) Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Urban Planning (https://researchgate.net/publication/318535166_Geographic_Information_Systems_GIS_in_Urban_Planning)
- The Multifaceted Benefits of Green Infrastructure in Development
- Press: Benefits of green building | U.S. Green Building Council (https://usgbc.org/press/benefits-of-green-building)
- Green infrastructure: systematic literature review (https://tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/1331677X.2021.1893202)
- Examining the effects of green infrastructure on residential sales prices in Omaha, Nebraska - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7510957)
- What Statistics Indicate Green Infrastructure's Impact? → Question (https://sustainability-directory.com/question/what-statistics-indicate-green-infrastructures-impact)
- Case Studies: Successful Implementations of Green Infrastructure
- Green infrastructure through the lens of “One Health”: A systematic review and integrative framework uncovering synergies and trade-offs between mental health and wildlife support in cities (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969720351184)
- The Economic Benefits of Green Infrastructure: A Case Study of Lancaster, PA (https://cnt.org/publications/the-economic-benefits-of-green-infrastructure-a-case-study-of-lancaster-pa)
- Cities Are Investing in Green Infrastructure—Should Developers Help Foot the Bill? (https://lincolninst.edu/publications/articles/2020-01-riches-resilience-cities-investing-green-infrastructure-should-developers-foot-bill)
- Navigating Challenges in Green Infrastructure Implementation
- Cities Are Investing in Green Infrastructure—Should Developers Help Foot the Bill? (https://lincolninst.edu/publications/articles/2020-01-riches-resilience-cities-investing-green-infrastructure-should-developers-foot-bill)
- Sustainable Infrastructure (https://gihub.org/sustainable-infrastructure)
- (PDF) Green Infrastructure Financing as an Imperative to Achieve Green Goals (https://researchgate.net/publication/331676669_Green_Infrastructure_Financing_as_an_Imperative_to_Achieve_Green_Goals)
- Green Infrastructure Funding and Technical Assistance Opportunities | US EPA (https://epa.gov/green-infrastructure/green-infrastructure-funding-and-technical-assistance-opportunities)
- Engaging Stakeholders: Collaboration for Successful Green Infrastructure
- Stakeholder Analysis and Social Network Analysis in the Decision-Making of Industrial Land Redevelopment in China: The Case of Shanghai - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7763527)
- Stakeholder Engagement Effectiveness Statistics (https://zoetalentsolutions.com/stakeholder-engagement-effectiveness)
- (PDF) Stakeholder Analysis For Smart City Development Project: An Extensive Literature Review (https://researchgate.net/publication/331225610_Stakeholder_Analysis_For_Smart_City_Development_Project_An_Extensive_Literature_Review)
- STAKEHOLDER MANAGEMENT FOR URBAN DEVELOPMENT PROJECTS IN SOUTH AFRICA (https://academia.edu/36847941/STAKEHOLDER_MANAGEMENT_FOR_URBAN_DEVELOPMENT_PROJECTS_IN_SOUTH_AFRICA)
- Leveraging Technology: Enhancing Green Infrastructure with Advanced Tools
- nature.com (https://nature.com/articles/s41599-024-02787-y)
- Research on digital infrastructure construction empowering new quality productivity - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11850791)
- Resilient green infrastructure: Navigating environmental resistance for sustainable development, social mobility in climate change policy - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11259874)
- Future Trends: The Evolving Role of Green Infrastructure in Urban Planning
- Changing approaches to green infrastructure design: from modernism to the future: Warsaw case study - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10191077)
- Global Sustainable Infrastructure Market Size, Forecast 2033 (https://custommarketinsights.com/report/sustainable-infrastructure-market)
- Public-Sector Green Infrastructure on the Rise, New Report Finds - Stormwater Report (https://stormwater.wef.org/2023/05/public-sector-green-infrastructure-on-the-rise-new-report-finds)




