Introduction
In the intricate realm of oil and gas operations, the concept of right-of-way (ROW) acquisition stands as a cornerstone for the successful development of infrastructure necessary for resource extraction and transportation. This multifaceted process encompasses a range of legal, regulatory, and negotiation challenges that require a deep understanding of key definitions and methodologies. As the demand for land acquisition grows, particularly in regions like the Eagle Ford and Bakken basins, stakeholders must navigate an evolving landscape shaped by new regulations and community dynamics.
From comprehending easements and condemnation to employing strategic negotiation techniques, mastering the intricacies of ROW acquisition is essential for ensuring compliance and fostering positive relationships with landowners. This article delves into the critical elements of ROW acquisition, offering insights that are pivotal for industry professionals aiming to enhance their operational effectiveness and community engagement.
Understanding Oil and Gas Right-of-Way: Key Definitions and Concepts
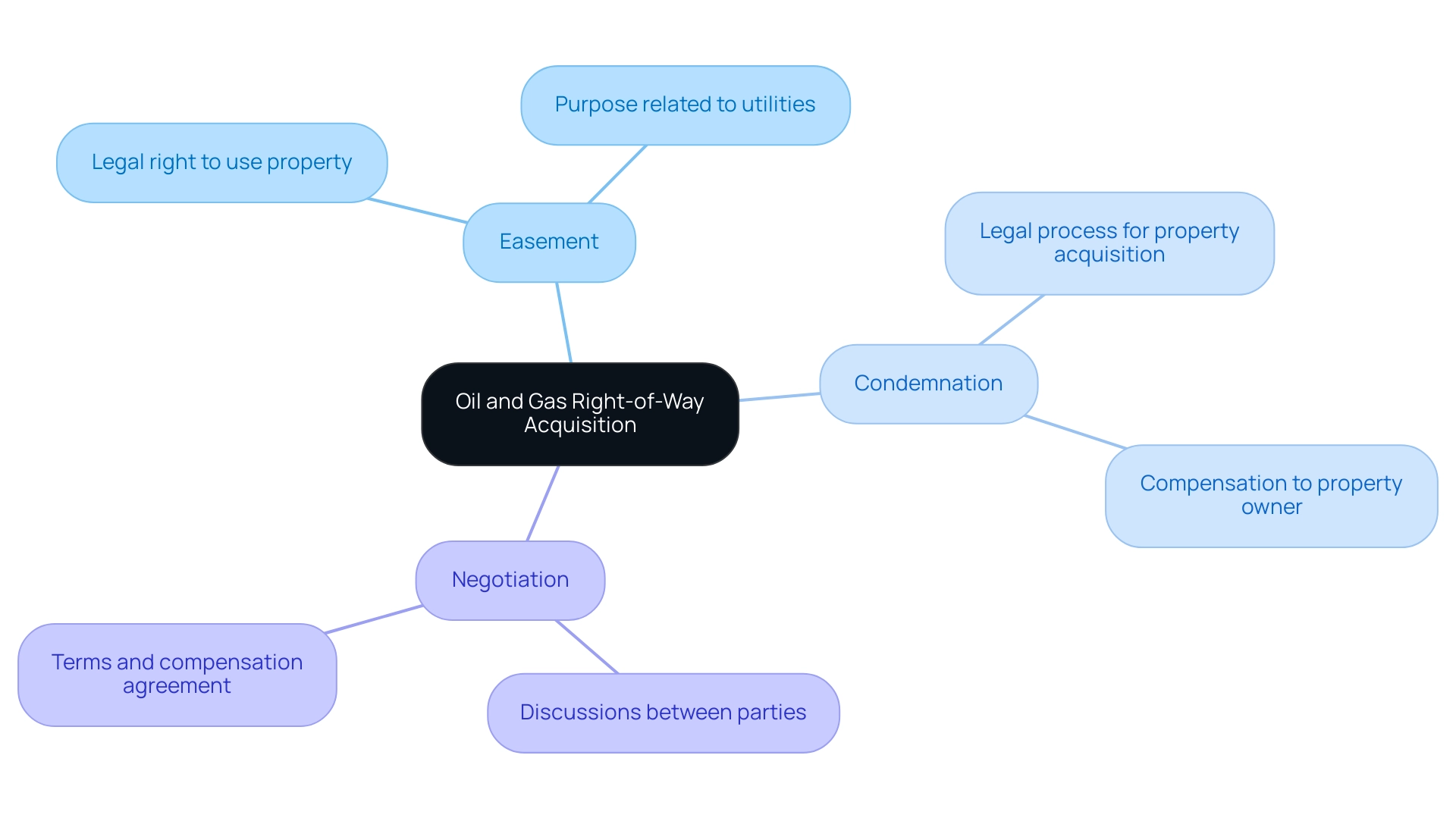
In the oil and gas sector, oil and gas right-of-way acquisition signifies the legal permission to cross property owned by another entity, which is a vital component for building and maintaining pipelines and other necessary infrastructure. Grasping the following essential concepts is crucial for effective management and negotiation in property procurement:
- Easement: This denotes the legal right granted to use another person's property for a specific purpose, which often relates to utilities and access for oil and gas operations.
- Condemnation: This is the legal process through which governmental or authorized entities obtain private property for public utility, typically accompanied by compensation to the property owner.
- Negotiation: This entails discussions between property owners and project developers aimed at reaching a mutual agreement on the terms and compensation associated with the oil and gas right-of-way acquisition.
The recent implementation of the Environmental Justice Law in New Jersey illustrates how regulatory changes can affect oil and gas right-of-way acquisition in the property procurement process within the sector. This law signifies an important advancement in environmental regulation, highlighting the necessity for adherence in property procurement procedures. Furthermore, assessors are encouraged to obtain reference texts to better understand pipeline terminology and operations, which can enhance their effectiveness in negotiations.
Recent statistics indicate that in the first three quarters of 2024, buying interest in the Eagle Ford and Bakken basins reached approximately US$7.7 billion, highlighting the significance of understanding these terms as demand for land procurement intensifies. As noted by industry experts,
To have an impact on the delivery or operation of a pipeline, it’s vital to eliminate the intra- and inter-company barriers, including those in the areas of communications, culture and technology.
Thus, a comprehensive grasp of these definitions not only facilitates clearer communication but also enhances the negotiation process during oil and gas right-of-way acquisition efforts.
Step-by-Step Guide to Right-of-Way Acquisition in Oil and Gas
- Preliminary Planning: The initial step in the right-of-way (ROW) procurement process involves a thorough assessment of project requirements. This includes determining the specific width and location necessary for the ROW, which is crucial for ensuring both operational efficiency and regulatory compliance. Companies must prioritize capital discipline while leveraging technology to optimize productivity and minimize costs. In fact, historical data shows that the Trend Factor was 3.080 in 1993 and prior, highlighting the importance of maintaining strict financial oversight in acquisition processes.
- Landowner Identification: Identifying all landowners impacted by the proposed ROW is essential. This step ensures that no stakeholders are overlooked and that all relevant parties are engaged in the negotiation process.
- Title Research: Conducting comprehensive title research is vital to verify land ownership and uncover any existing encumbrances. This step not only aids in avoiding legal complications but also provides clarity on the rights and limitations associated with the land.
- Initial Contact: Initiating communication with landowners is a critical juncture. During this phase, it is important to discuss the objectives of the venture and gauge landowner interest in negotiations. A respectful and informative approach can foster goodwill and facilitate smoother discussions.
- Negotiation: Engaging in negotiations requires a strategic approach to address terms, compensation, and any concerns raised by landowners. As mentioned by Le, Caldas, and Gibson, utilizing statistical techniques to examine the impacts of various factors on ROW procurement can improve negotiation results. Their insights underscore the importance of understanding the factors influencing landowner decisions, which can be pivotal in formulating effective negotiation strategies.
- Drafting Agreements: Once terms are agreed upon, preparing legal documents that clearly outline the ROW agreement's terms is essential. These documents must be precise to avoid ambiguities that could lead to disputes later.
- Closing the Deal: Finalizing the agreements entails ensuring that all parties have signed the necessary documents. This step solidifies the commitment of both the company and the landowners, paving the way for project advancement.
- Post-Purchase Management: Following the purchase, it is essential to sustain ongoing communication with landowners. This not only helps manage any obligations related to the ROW but also builds trust and fosters positive relationships, which are beneficial for future projects.
In light of recent developments, such as the introduction of a new tectonic map for the Vendian–Lower Paleozoic structural stage of the Lena–Tunguska petroleum province, understanding the spatial and morphological characteristics of major structures can also inform ROW planning. Additionally, the Level of Value Adjustment for Personal Property case study illustrates how actual values for personal property must be adjusted to align with the level of value applicable for real property, ensuring consistency in property valuation across different types of assets. Successful negotiations in oil and gas right-of-way acquisition depend on clarity, respect, and strategic engagement, ultimately resulting in higher success rates and more efficient procurement processes.
Navigating Legal and Regulatory Frameworks for Right-of-Way Acquisition
Navigating the complex legal landscape for oil and gas right-of-way acquisition necessitates a thorough understanding of various regulatory frameworks at the federal, state, and local levels. Key considerations include:
- Federal Regulations: It is imperative to familiarize yourself with essential laws such as the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA), which outlines the requirements for environmental assessments and ensures that potential impacts are evaluated prior to implementation. Compliance with NEPA remains crucial for oil and gas right-of-way acquisition, especially in pipeline developments, where adherence to these regulations is closely monitored. In fact, the yearly burden hours for compliance total 47,338, emphasizing the considerable effort needed to fulfill these legal obligations.
- State Regulations: Each state has distinct statutes governing use of property and ROW acquisition, necessitating diligent research to understand specific legal requirements. For instance, holders of existing solar or wind energy rights prior to July 1, 2024, may request to apply new annual rent and fee structures or continue with previous methodologies. This variability in state laws can significantly affect negotiations related to oil and gas right-of-way acquisition, as different jurisdictions may impose different requirements and processes.
- Permitting: Securing the necessary permits from pertinent authorities is a vital step before initiating any construction activities. This process often involves multiple agencies, each with its own requirements and timelines.
- Compliance: It is essential to ensure that all agreements align with applicable laws to mitigate potential legal risks and disputes. The Bureau of Land Management (BLM) emphasizes this need, stating, > The BLM is a multiple-use agency, and solar and wind energy development is one of the many uses for which the BLM manages the public lands. Moreover, the BLM possesses the authority to issue an immediate temporary suspension of activities if a grant holder violates the terms of their grant, which can significantly influence project planning. Such suspensions can occur orally or in writing, and the BLM is required to respond to requests for permission to resume activities within five business days. By maintaining compliance and proactively addressing regulatory requirements, entities can navigate the oil and gas right-of-way acquisition process more effectively. With 75 participants giving feedback on these processes and a total of 3,116 annual responses, the landscape of ROW procurement remains dynamic and complex.
Valuation and Compensation in Right-of-Way Acquisition
Valuing property for oil and gas right-of-way acquisition is a critical process that employs various methodologies to ascertain fair compensation. The Market Approach is widely utilized, wherein property is compared to similar assets that have recently sold, allowing for an informed determination of fair market value. Meanwhile, the Income Approach evaluates the projected income that the property could generate, offering a view on its economic potential.
Lastly, the Cost Approach estimates the costs associated with acquiring and preparing the site for its intended use. Each of these methodologies plays a vital role in ensuring that compensation aligns with the fair market value of the property, including any potential damages incurred during the purchasing process. It is imperative to document all agreements meticulously to foster transparency and fairness in the valuation process.
According to the International Right of Way Association (IRWA), 'the legal and equitable title to property needed for the construction, operation, maintenance, or protection of a public highway system' underscores the need for careful valuation. Furthermore, understanding current compensation trends in oil and gas right-of-way acquisition agreements is pivotal, as it influences how fair market value is determined and ensures that landowners receive equitable compensation reflective of their property’s true worth. Notably, researchers have identified 22 barriers to smooth ROW procurement, highlighting the challenges faced in the valuation process.
Furthermore, taking into account the economic possibilities, cities such as Nome, AK, and Mercer Island, WA, provide average salaries for property procurement positions that surpass the national average, giving context for compensation patterns in the sector.
Engaging Stakeholders: Best Practices for Community Relations in Right-of-Way Acquisition
Effective stakeholder engagement is crucial for fostering positive community relations and ensuring success in oil and gas right-of-way acquisition. Applying several best practices can significantly enhance this engagement:
- Transparent Communication: Keeping stakeholders informed about developments and timelines is vital. Regular updates can help build trust and mitigate misunderstandings.
- Address Concerns: Actively listening to and addressing concerns raised by landowners and community members demonstrates respect and commitment to their needs. This approach is essential, as the study demonstrates that communities surrounding gas and oil operations are highly socioeconomically vulnerable due to declining agricultural and fish catches, thus negatively affecting their livelihoods. Targeted initiatives by public and private entities are needed to enhance livelihood resilience among affected households.
- Community Meetings: Hosting public meetings provides an opportunity to discuss the initiative and gather feedback directly from the community. Such engagement allows for a two-way dialogue that can lead to more informed decision-making.
- Collaboration: Partnering with local organizations not only builds trust but also showcases a commitment to enhancing community welfare. Collaborating with these groups can facilitate the sharing of resources and expertise, ultimately benefiting all parties involved.
- Follow-Up: Maintaining ongoing communication post-acquisition is crucial to ensure continued positive relations and address any emerging issues that may arise. Proactive follow-ups help in managing expectations and demonstrating accountability.
Incorporating real-world examples, such as the case study titled 'Local content in Tanzania: Are local suppliers motivated to improve?', illustrates the motivations of local suppliers in the extractive industries and emphasizes the importance of community engagement. By adhering to these best practices, stakeholders in the oil and gas sector can significantly improve their community engagement efforts related to oil and gas right-of-way acquisition, positively impacting both project outcomes and local livelihoods.
Conclusion
Mastering the complexities of right-of-way (ROW) acquisition is indispensable for professionals in the oil and gas industry. As outlined, understanding key concepts such as:
- Easements
- Condemnation
- Strategic negotiation techniques
is crucial for effective land acquisition. With the increasing demand for land in resource-rich areas, stakeholders must navigate the intricate legal and regulatory frameworks that govern ROWs, ensuring compliance with federal and state laws while also maintaining positive relationships with landowners.
The step-by-step guide provided emphasizes the importance of:
- Thorough planning
- Effective communication
- Diligent research throughout the acquisition process.
By prioritizing transparency and actively engaging stakeholders, companies can foster goodwill within communities, ultimately leading to more efficient negotiations and successful project outcomes. The valuation methodologies highlighted further reinforce the need for fair compensation practices that reflect the true worth of the land.
In conclusion, the intricacies of ROW acquisition demand a multifaceted approach that combines legal knowledge, negotiation skills, and community engagement. By embracing these practices, industry professionals can not only enhance operational effectiveness but also contribute to sustainable and respectful development within the communities they engage. As the landscape of oil and gas continues to evolve, the ability to adeptly navigate these challenges will be paramount for future success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is oil and gas right-of-way acquisition?
Oil and gas right-of-way acquisition refers to the legal permission to cross property owned by another entity, which is essential for constructing and maintaining pipelines and other infrastructure.
What is an easement in the context of oil and gas operations?
An easement is the legal right granted to use another person’s property for a specific purpose, often related to utilities and access for oil and gas operations.
What does condemnation mean in property procurement?
Condemnation is the legal process through which governmental or authorized entities obtain private property for public utility, typically involving compensation to the property owner.
How does negotiation play a role in right-of-way acquisition?
Negotiation involves discussions between property owners and project developers to reach a mutual agreement on the terms and compensation related to the oil and gas right-of-way acquisition.
How has the Environmental Justice Law in New Jersey affected oil and gas right-of-way acquisition?
The Environmental Justice Law represents a significant advancement in environmental regulation, emphasizing the need for compliance in property procurement procedures within the oil and gas sector.
Why is it important for assessors to obtain reference texts in pipeline terminology?
Reference texts can enhance assessors' understanding of pipeline terminology and operations, improving their effectiveness in negotiations during right-of-way acquisition.
What recent statistics highlight the importance of land procurement in the oil and gas sector?
In the first three quarters of 2024, buying interest in the Eagle Ford and Bakken basins reached approximately US$7.7 billion, underscoring the significance of understanding right-of-way acquisition terms as demand for land procurement increases.
What are the initial steps in the right-of-way procurement process?
The initial steps include preliminary planning, landowner identification, title research, initial contact with landowners, and negotiation.
What is the significance of conducting title research during right-of-way acquisition?
Title research verifies land ownership and uncovers any existing encumbrances, helping to avoid legal complications and clarify rights and limitations associated with the land.
What should be included in the agreements drafted after negotiations?
The agreements must clearly outline the terms of the right-of-way acquisition to avoid ambiguities that could lead to disputes later.
What is the importance of post-purchase management in right-of-way acquisition?
Ongoing communication with landowners after the purchase helps manage obligations related to the right-of-way and fosters positive relationships for future projects.
List of Sources
- Understanding Oil and Gas Right-of-Way: Key Definitions and Concepts
- 2025 Oil and Gas Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/oil-and-gas/oil-and-gas-industry-outlook.html)
- Chapter 8 - Oil and Gas Pipeline | Assessors' Library (https://arl.colorado.gov/chapter-8-oil-and-gas-pipeline)
- Land Acquisition Consulting For Gas Pipeline | Right of Way (https://trccompanies.com/services/field-services-inspection/right-of-way-land-acquisition)
- Step-by-Step Guide to Right-of-Way Acquisition in Oil and Gas
- 2025 Oil and Gas Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/oil-and-gas/oil-and-gas-industry-outlook.html)
- Chapter 8 - Oil and Gas Pipeline | Assessors' Library (https://arl.colorado.gov/chapter-8-oil-and-gas-pipeline)
- Significant Factors Affecting Right-of-Way Acquisition Time in Highway Projects | Request PDF (https://researchgate.net/publication/269142178_Significant_Factors_Affecting_Right-of-Way_Acquisition_Time_in_Highway_Projects)
- Navigating Legal and Regulatory Frameworks for Right-of-Way Acquisition
- Rights-of-Way, Leasing, and Operations for Renewable Energy (https://federalregister.gov/documents/2024/05/01/2024-08099/rights-of-way-leasing-and-operations-for-renewable-energy)
- U.S.C. Title 30 - MINERAL LANDS AND MINING (https://govinfo.gov/content/pkg/USCODE-2011-title30/html/USCODE-2011-title30-chap3A.htm)
- 43 CFR Part 2800 -- Rights-of-Way Under the Federal Land Policy and Management Act (https://ecfr.gov/current/title-43/subtitle-B/chapter-II/subchapter-B/part-2800)
- Valuation and Compensation in Right-of-Way Acquisition
- Salary: Land Acquisition (December, 2024) United States (https://ziprecruiter.com/Salaries/Land-Acquisition-Salary)
- Right-of-Way Acquisition Explained - Vanguard Real Estate Solutions (https://vresolutions.com/right-of-way-acquisition)
- (PDF) Right-of-Way Acquisition Costs: Case Studies in Minnesota (https://researchgate.net/publication/340436029_Right-of-Way_Acquisition_Costs_Case_Studies_in_Minnesota)
- Engaging Stakeholders: Best Practices for Community Relations in Right-of-Way Acquisition
- How to Measure Community Engagement and Its Impact with KPIs (https://maptionnaire.com/blog/measure-community-engagement-impact-with-metrics)
- New Report Shows Commitment to Pipeline Safety, Community Engagement and Low-Carbon Future (https://api.org/news-policy-and-issues/news/2024/05/06/new-report-shows-commitment-to-pipeline-safety)
- The reality of local community participation in the natural gas sector in Southeastern Tanzania (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2214790X2030318X)




