Introduction
The rapid evolution of energy storage technology has ushered in a new era of possibilities for sustainable energy solutions. As the demand for efficient and reliable power sources continues to grow, the strategic placement of battery storage facilities becomes increasingly vital.
Identifying suitable locations for these facilities involves a multifaceted approach that considers:
- Energy needs
- Infrastructure proximity
- Environmental impacts
- Community engagement
This article delves into the essential steps and considerations for successfully establishing battery storage sites, including:
- Navigating the complexities of land acquisition
- Conducting thorough environmental assessments
- Securing financing
- Implementing projects effectively
By understanding these critical components, stakeholders can contribute to the advancement of energy infrastructure that not only meets current demands but also supports a sustainable future.
Identifying Suitable Locations for Battery Storage Facilities
To identify optimal locations for battery reserve facilities, adhere to the following structured approach:
-
Evaluate Power Requirements: Start by examining regional power demands to determine the necessary capacity for the battery holding facility. Understanding these requirements is crucial for ensuring that the facility can meet the expected power load.
- Proximity to Infrastructure: Prioritize sites that are situated close to existing electrical infrastructure, such as substations and transmission lines. This proximity minimizes the costs and complexities associated with interconnection, facilitating a smoother integration into the power grid.
-
Land Use Compatibility: Verify that the land is appropriately zoned for energy storage. Review local land use regulations to ensure that the intended use aligns with community development plans and zoning laws.
-
Ecological Considerations: Conduct thorough assessments to evaluate potential impacts on local ecosystems. This step is essential for compliance with ecological regulations and for identifying any mitigation measures that may be necessary.
- Community Factors: Engage with local stakeholders early in the site selection process to address community acceptance and anticipate potential opposition. Building relationships with the community can foster support and reduce resistance.
-
GIS Mapping Tools: Utilize Geographic Information System (GIS) mapping tools to visualize potential sites and analyze spatial data. These tools are invaluable for identifying optimal locations based on multiple criteria, including environmental impact, accessibility, and infrastructure proximity.
-
Site Visits: Conduct physical site visits to assess the land's characteristics, including accessibility, topography, and existing infrastructure. This hands-on evaluation is critical for verifying the feasibility of the selected locations.
-
Hazmat Data Utilization: Incorporate data from the Hazmat Incident Report Search Tool, which was last updated on March 19, 2024. This tool enables users to query data from the DOT Hazardous Materials Incident Report Form, offering vital insights for understanding regulatory compliance and safety measures in the context of battery facility locations. Employing this data improves the safety of hazardous materials transportation, a crucial factor in site selection for development.
By methodically adhering to these steps, you can successfully pinpoint locations that meet both operational needs and regulatory requirements for battery storage facility land acquisition while guaranteeing the secure transportation of hazardous materials.
Navigating Legal and Community Engagement in Land Acquisition
Navigating the legal and community engagement aspects of land acquisition for energy projects requires a strategic approach that encompasses several critical steps:
- Conduct Title Research: Leverage AI-powered title research software to accurately verify land ownership and identify any encumbrances or liens that may affect the property. This ensures clarity and reduces future legal disputes.
- Understand Local Regulations: Acquaint yourself with local zoning laws, land use regulations, and permitting processes that could impact your endeavor. This knowledge is essential for compliance and to avoid legal challenges. As highlighted by the FTC, "If you have lost money to a clean power scam involving fraud, discrimination, or other unfair, deceptive, or abusive practices, federal and state agencies can help," underscoring the importance of legal diligence.
- Develop Lease Agreements: When leasing land, collaborate with legal experts to create comprehensive lease agreements. These documents should protect your interests while adhering to local legal requirements, minimizing potential risks.
- Community Engagement: Early and proactive communication with local communities is essential. Inform them about the initiative and address any concerns they might have. Public meetings or informational sessions can foster transparency and build trust. The statistic from EnergySage indicates that 7.15 kilowatts is sufficient power to satisfy all the energy requirements for an average home in Austin, Texas, illustrating the critical role energy initiatives play in local communities.
- Stakeholder Collaboration: Engage with local governments, environmental organizations, and community groups to garner support and mitigate opposition. Establishing these alliances can significantly improve acceptance of the initiative. The case study of Tionna Richardson showcases how effective community involvement in solar energy initiatives can inspire others and demonstrate the tangible benefits of such endeavors.
- Mitigation Strategies: Prepare effective mitigation strategies to address any potential environmental impacts and community concerns. Demonstrating a commitment to responsible development can enhance your initiative's reputation and acceptance.
- Documentation: Maintain meticulous records of all communications, agreements, and regulatory approvals. This documentation is crucial for ensuring compliance and facilitating future negotiations.
By systematically addressing these legal and community engagement aspects, you can secure the necessary land rights for battery storage facility land acquisition while fostering positive relationships with stakeholders. This method not only improves the chances of success for the initiative but also aids in the sustainable growth of infrastructure.
Conducting Environmental Impact Assessments
Carrying out an Impact Assessment (EIA) is a vital procedure that ensures the implications of energy projects, especially concerning battery storage facility land acquisition, are thoroughly evaluated. According to Carl Grainger, Chair of the Credentials Committee, "The adoption of the credentials report at this meeting should not be interpreted as support for the political situation in Venezuela," emphasizing the importance of context in assessments. The following steps outline an effective approach to conducting an EIA:
- Define the Scope: Establish a clear scope for the assessment, detailing the specific components of nature to be investigated, such as air quality, water resources, and biodiversity.
- Gather Baseline Data: Accumulate baseline data to understand the current conditions of the proposed site. This may involve field surveys, data gathering from local agencies, and a review of existing studies pertinent to the area.
- Identify Potential Impacts: Evaluate the possible ecological impacts of the proposed battery storage facility land acquisition, focusing on how it may affect land, water, air quality, and local ecosystems.
- Consult with Experts: Collaborate with ecological consultants and specialists who can provide valuable insights and recommendations, drawing on their expertise in the field.
- Prepare the EIA Report: Compile the findings into a comprehensive EIA report that details potential impacts, mitigation measures, and compliance with relevant regulations. This report should also reflect the findings from discussions held by the Informal Working Group on Area-based Management Tools, which met from March 27-29, 2019, to address similar objectives. Additionally, the report must include key components as outlined in the case study titled "Contents of an EIA Report," which necessitates a description of the planned activity, results of scoping, baseline assessments, potential impacts, and public consultation processes.
- Public Review: Distribute the EIA report to stakeholders and the public, inviting feedback and addressing any concerns raised during this review process to foster transparency and trust.
- Implement Mitigation Measures: Develop and execute strategies to mitigate identified environmental impacts, ensuring ongoing compliance with regulatory requirements and enhancing community acceptance of the initiative.
By following these organized steps and including collaborative responsibilities discussed by states parties, you can carry out an EIA that not only safeguards the environment but also enhances the initiative's credibility and acceptance within the community.
Securing Financing and Investment for the Project
Securing financing for your battery storage facility land acquisition requires a strategic approach. Here are essential steps to guide you:
- Develop a Comprehensive Business Plan: Craft a thorough business plan that outlines the scope, financial projections, and potential return on investment (ROI). A well-articulated plan is crucial for attracting investors and demonstrating the initiative's viability.
- Identify Funding Sources: Investigate various funding options, including government grants, private investors, venture capital, and bank loans. It is essential to research programs specifically tailored to renewable energy and battery storage to maximize your funding opportunities.
- Prepare Financial Models: Construct robust financial models that demonstrate the profitability of the endeavor, focusing on potential revenue streams and cost savings. Transparent financial forecasts will alleviate investor concerns and demonstrate the financial soundness of the initiative.
- Engage with Investors: Actively present your business plan and financial models to potential investors. Highlight the initiative's benefits, particularly its alignment with sustainability goals, to resonate with investors prioritizing environmental impact.
- Negotiate Terms: Collaborate with investors to negotiate favorable conditions that align with your objectives. Ensuring adequate funding while maintaining flexibility in the agreement is paramount for success.
- Utilize Incentives: Take advantage of available tax benefits and credits for renewable initiatives. These financial incentives significantly enhance the attractiveness of your proposal, making it a more compelling investment opportunity.
- Establish Partnerships: Consider forming strategic alliances with established power companies or technology providers. Collaborations can strengthen your position, enhance credibility, and provide access to additional resources and expertise.
By systematically adhering to these steps, you can effectively obtain the necessary funding for the battery storage facility land acquisition to bring your initiative to fruition, aligning with the current trends in renewable resource investment. As noted by the Independent High-Level Expert Group on Climate Finance, "Sound regulations and public policies, strengthened institutions and greatly expanded international support are the keys to unlock private financing for clean energy in EMDEs at scale." With USD 136 billion of Green, Social, Sustainability, and Sustainability-Linked (GSSS) bonds issued by EMDEs in 2022, utilizing these insights will position your endeavor for success.
Additionally, improving data availability is crucial for attracting investors, as evidenced by initiatives like the Global Emerging Markets Risk Database, which help mitigate perceived risks associated with EMDE investments.
Implementing the Project and Monitoring Progress
Implementing a battery storage facility land acquisition initiative requires meticulous planning and ongoing monitoring to ensure success. Follow these essential steps:
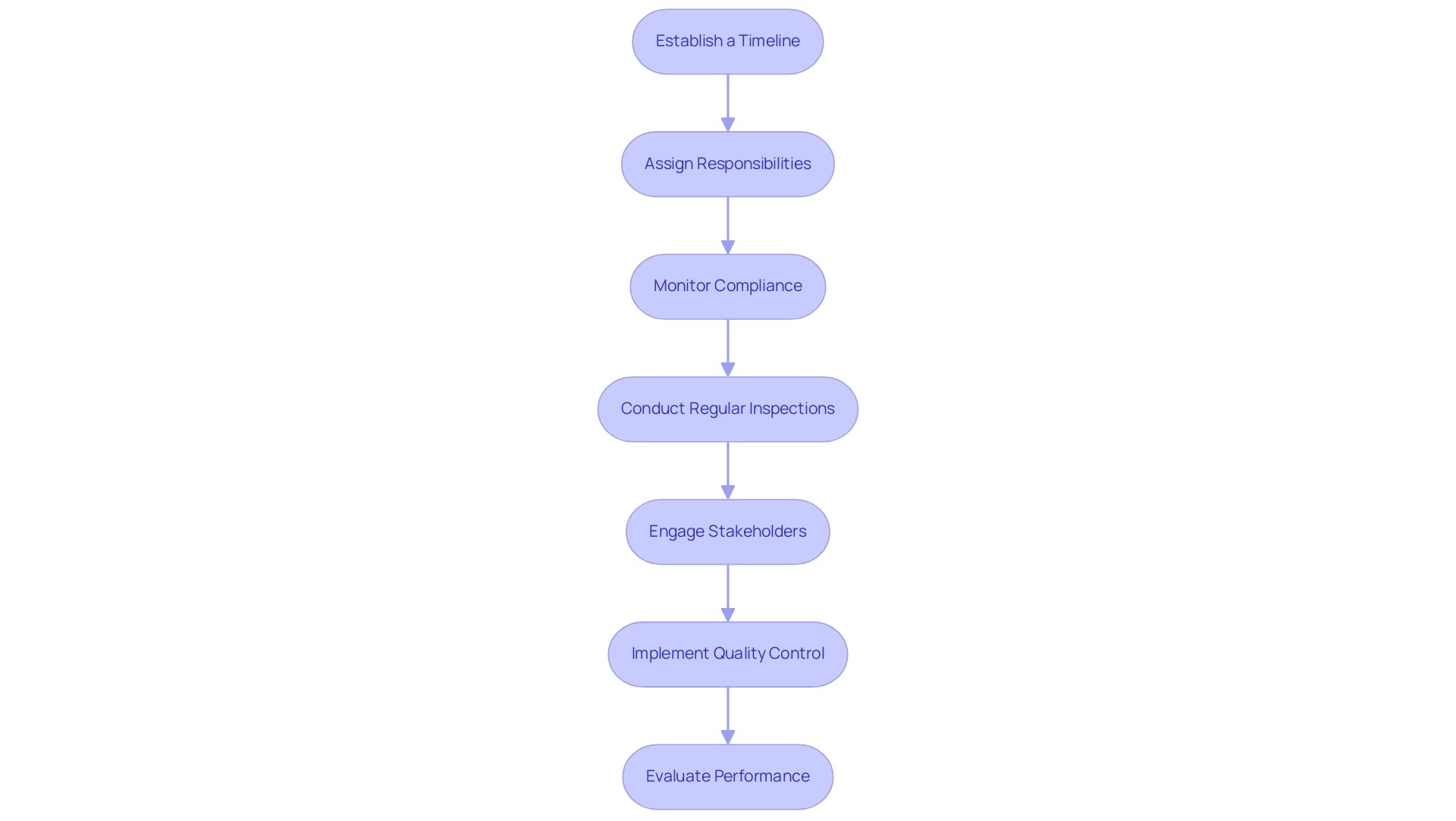
- Establish a Timeline: Create a comprehensive timeline that delineates key milestones and deadlines for each phase. This not only aids in tracking progress but also facilitates adherence to regulatory frameworks and project objectives.
- Assign Responsibilities: Clearly define roles and responsibilities within your team. Ensuring that each member understands their specific tasks and expectations is crucial for maintaining accountability and fostering collaboration.
- Monitor Compliance: Regularly assess compliance with regulatory requirements and environmental standards throughout the construction process. This diligence is crucial as it aligns with broader objectives for sustainable resource development and contributes to achieving energy-related Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). As highlighted by Gabriela Elizondo Azuela, Manager of the Energy Management Assistance Program (ESMAP), monitoring SDG 7 is essential for ensuring that energy initiatives achieve their intended goals.
- Conduct Regular Inspections: Implement a schedule for frequent site inspections to evaluate progress. These inspections help identify potential issues early, allowing for timely interventions that minimize delays and additional costs.
- Engage Stakeholders: Maintain transparent communication with all stakeholders. Regular updates on progress status and proactive engagement can address concerns promptly, enhancing trust and collaboration among all parties involved.
- Implement Quality Control: Establish stringent quality control measures to ensure that all construction activities meet the required specifications and standards. This not only safeguards the initiative's integrity but also bolsters its long-term operational performance.
- Evaluate Performance: Upon completion of the initiative, conduct a thorough evaluation of the facility's performance against initial projections. Collecting feedback from stakeholders is crucial to guide future initiatives and enhance implementation strategies.
By adhering to these steps, you can effectively manage your battery storage facility land acquisition initiative and ensure its success through diligent monitoring and proactive stakeholder engagement. The investment of over $5 billion by LCRA TSC in transmission projects highlights the significant financial commitment required for successful power initiatives. Furthermore, as highlighted in the case study titled "Policy Responses to Energy Challenges," an ambitious energy transition, supported by robust policy responses, can foster sustainable growth and job creation, aligning with broader economic objectives.
Conclusion
The establishment of battery storage facilities is a critical component in advancing sustainable energy solutions. By following a structured approach that includes:
- Assessing energy needs
- Ensuring proximity to infrastructure
- Engaging with the community
stakeholders can identify suitable locations that align with both operational requirements and regulatory frameworks.
Navigating the complexities of land acquisition and securing financing are equally important. Conducting thorough title research, understanding local regulations, and fostering community engagement can mitigate potential challenges. A well-prepared business plan and robust financial models can attract investors, ensuring that projects are not only viable but also sustainable in the long term.
Environmental impact assessments play a pivotal role in safeguarding ecosystems while also enhancing project credibility. By involving experts and maintaining transparency with stakeholders, projects can address concerns effectively and implement necessary mitigation strategies.
Finally, the successful implementation of battery storage facilities hinges on meticulous planning and ongoing monitoring. Establishing clear timelines, assigning responsibilities, and conducting regular inspections are essential for maintaining compliance and achieving project objectives. As the demand for efficient energy solutions continues to grow, the strategic development of battery storage infrastructure will be vital in supporting a sustainable and resilient energy future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the first step in identifying optimal locations for battery reserve facilities?
The first step is to evaluate power requirements by examining regional power demands to determine the necessary capacity for the battery holding facility.
Why is proximity to existing electrical infrastructure important when selecting a site?
Proximity to existing electrical infrastructure, such as substations and transmission lines, minimizes costs and complexities associated with interconnection, facilitating smoother integration into the power grid.
How can land use compatibility impact the site selection process?
It is essential to verify that the land is appropriately zoned for energy storage and to review local land use regulations to ensure alignment with community development plans and zoning laws.
What ecological considerations should be taken into account during site selection?
Conduct thorough assessments to evaluate potential impacts on local ecosystems to comply with ecological regulations and identify necessary mitigation measures.
How can GIS mapping tools assist in identifying optimal locations for battery facilities?
GIS mapping tools help visualize potential sites and analyze spatial data, which is invaluable for identifying optimal locations based on criteria like environmental impact, accessibility, and infrastructure proximity.
Why are site visits important in the site selection process?
Physical site visits allow for assessing the land's characteristics, including accessibility, topography, and existing infrastructure, which is critical for verifying the feasibility of selected locations.
What role does Hazmat data play in the site selection for battery facilities?
Incorporating data from the Hazmat Incident Report Search Tool helps understand regulatory compliance and safety measures, improving the safety of hazardous materials transportation in the context of site selection.
What is the importance of conducting title research in the land acquisition process?
Title research verifies land ownership and identifies any encumbrances or liens, ensuring clarity and reducing the likelihood of future legal disputes.
How does community engagement influence the success of land acquisition for energy projects?
Early and proactive communication with local communities helps address concerns, fosters transparency, and builds trust, which can enhance acceptance of the initiative.
What steps should be taken to conduct an Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)?
Steps include defining the scope, gathering baseline data, identifying potential impacts, consulting with experts, preparing the EIA report, conducting public review, and implementing mitigation measures.
What should a comprehensive business plan include for securing financing for a battery storage facility?
It should outline the scope, financial projections, and potential return on investment (ROI) to attract investors and demonstrate the initiative's viability.
How can one identify funding sources for battery storage facility projects?
Investigate various funding options, including government grants, private investors, venture capital, and bank loans, particularly those tailored to renewable energy and battery storage.
What is the significance of monitoring compliance during the implementation of a battery storage facility?
Regular assessments of compliance with regulatory requirements and environmental standards are crucial for aligning with sustainable resource development objectives.
What strategies can enhance stakeholder engagement during the implementation process?
Maintaining transparent communication, providing regular updates on progress, and proactively addressing concerns can enhance trust and collaboration among all parties involved.
List of Sources
- Identifying Suitable Locations for Battery Storage Facilities
- Incident Statistics (https://phmsa.dot.gov/hazmat-program-management-data-and-statistics/data-operations/incident-statistics)
- Navigating Legal and Community Engagement in Land Acquisition
- Homeowner’s Guide to Going Solar (https://energy.gov/eere/solar/homeowners-guide-going-solar)
- Conducting Environmental Impact Assessments
- Environmental Impact Assessment (https://bbnj-mgr.fas.harvard.edu/eias)
- Summary report 25 March – 5 April 2019 (https://enb.iisd.org/events/2nd-session-intergovernmental-conference-igc-conservation-and-sustainable-use-marine/summary)
- Securing Financing and Investment for the Project
- Executive summary – Scaling Up Private Finance for Clean Energy in Emerging and Developing Economies – Analysis - IEA (https://iea.org/reports/scaling-up-private-finance-for-clean-energy-in-emerging-and-developing-economies/executive-summary)
- CAEATFA REEL Contractor Information (https://treasurer.ca.gov/caeatfa/cheef/reel/contractor/index.asp)
- Implementing the Project and Monitoring Progress
- Tracking SDG 7 – The Energy Progress Report 2022 (https://worldbank.org/en/topic/energy/publication/tracking-sdg-7-the-energy-progress-report-2022)
- Electric Transmission - LCRA - Energy, Water, Community (https://lcra.org/energy/electric-transmission)




