Overview
This article addresses the critical steps essential for ensuring compliance in hydraulic fracturing. It underscores the importance of conducting thorough environmental analyses and adhering to regulatory standards. The significant environmental impacts of fracking, including water contamination and air quality degradation, are highlighted, showcasing the pressing challenges faced by operators.
Best practices for operators are outlined, emphasizing the necessity of:
- Baseline evaluations
- Chemical disclosure
- Stakeholder engagement
These measures are aimed at mitigating ecological risks while ensuring compliance with regulations. By implementing these strategies, operators can effectively navigate the complexities of hydraulic fracturing and contribute to a more sustainable energy future.
Introduction
Hydraulic fracturing is a pivotal technique that unlocks vast reserves of oil and natural gas, fundamentally transforming the energy landscape. However, this transformation is not without significant environmental repercussions. As energy demand surges, it becomes paramount to understand the intricate balance between resource extraction and ecological preservation.
What challenges arise when navigating the complex regulatory frameworks surrounding hydraulic fracturing? How can operators ensure compliance while minimizing environmental impacts?
This article delves into the essential steps for conducting a thorough hydraulic fracturing environmental analysis, equipping stakeholders with the knowledge to effectively address both compliance and sustainability in this critical industry.
Define Hydraulic Fracturing and Its Purpose
Hydraulic stimulation, commonly known as hydraulic extraction, serves as a pivotal method for extracting oil and natural gas from deep subterranean rock formations, particularly shale. This process entails injecting a high-pressure mixture of water, sand, and chemicals into the rock, creating fractures that facilitate the free flow of hydrocarbons to the well. The primary objective of water-based rock breaking is to enhance resource retrieval, thereby increasing energy output to meet the surging energy demands.
Recent estimates reveal that fracking constitutes nearly half of the total U.S. crude oil production and two-thirds of marketed natural gas production, highlighting its critical role in the energy sector. The fluid injection market was valued at USD 18.88 billion in 2024, underscoring its substantial economic impact. Moreover, modern water-based extraction and horizontal boring techniques can reduce the drilling zone's surface footprint by up to 90 percent, illustrating their efficiency.
Barry Russell, President and CEO of IPAA, asserts, "America’s energy producers are the backbone of our nation’s security and economic growth," which emphasizes the importance of high-pressure extraction within the broader context of energy production and national security. The market is anticipated to exhibit a CAGR of 5.77% during the forecast period, indicating sustained relevance and growth in the industry.
Nevertheless, it is essential to consider the ecological challenges associated with hydraulic extraction, including methane emissions and water pollution, within the framework of hydraulic fracturing environmental analysis, which are crucial for understanding the regulatory landscape and public sentiment. Comprehending this process is vital for evaluating its ecological impacts and understanding the hydraulic fracturing environmental analysis and regulatory obligations.
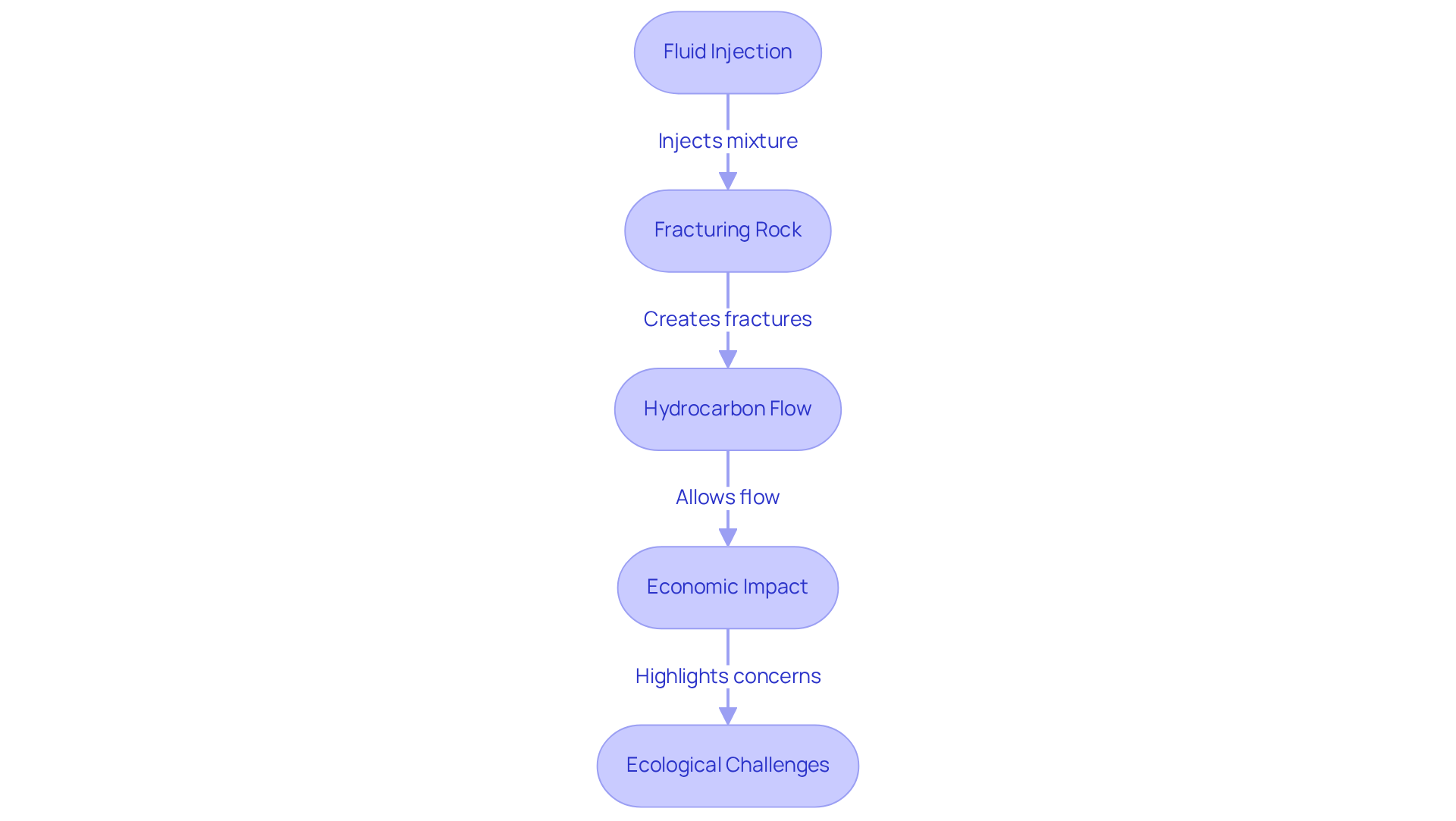
Examine Environmental Impacts of Hydraulic Fracturing
Hydraulic fracturing presents several significant environmental challenges that warrant serious attention:
-
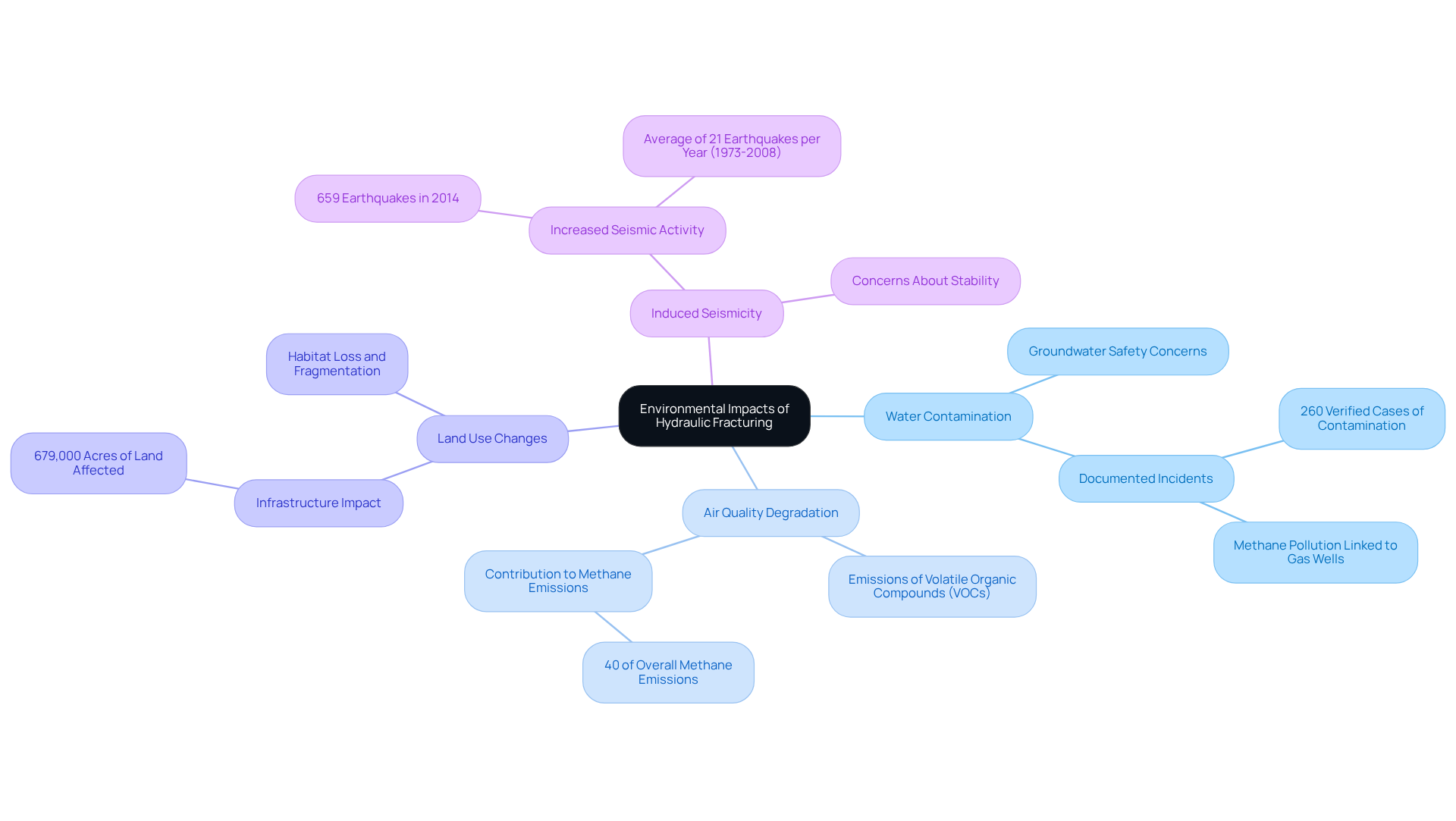
Water Contamination: The use of various chemicals in drilling fluids raises critical concerns regarding groundwater safety. Documented incidents of spills, leaks, and improper wastewater disposal have led to severe water quality issues. Research in Pennsylvania has uncovered methane pollution in drinking water linked to proximity to gas wells, emphasizing the importance of a hydraulic fracturing environmental analysis, with at least 260 verified cases of private well contamination. This underscores the inherent dangers associated with such operations.
-
Air Quality Degradation: Emissions from hydraulic fracturing activities contribute to air pollution, releasing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other harmful pollutants. The energy industry, particularly through hydraulic fracturing environmental analysis, has emerged as a major contributor to air pollution, accounting for nearly 40% of overall methane emissions from human activities. These emissions significantly impact local air quality, exacerbating respiratory issues and other health problems in nearby communities. Stricter regulations are necessary to mitigate these effects.
-
Land Use Changes: The construction of well pads, access roads, and pipelines transforms landscapes, disrupting local ecosystems and wildlife habitats. The hydraulic fracturing environmental analysis reveals that since 2005, hydraulic fracturing infrastructure has directly impacted at least 679,000 acres of land, resulting in habitat loss and fragmentation that jeopardizes biodiversity.
-
Induced Seismicity: The injection of wastewater into deep wells has been linked to increased seismic activity in various regions. In 2014, the U.S. experienced 659 earthquakes associated with fracking, a substantial increase compared to an average of just 21 earthquakes per year from 1973 to 2008. This raises significant concerns regarding the stability of surrounding areas and the potential for larger seismic events.
Understanding these effects is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations through hydraulic fracturing environmental analysis. Ongoing monitoring and innovative approaches are essential to address the environmental challenges posed by shale extraction.
Navigate Regulatory Framework and Compliance Requirements
The regulatory framework governing the extraction of natural gas through high-pressure fluid injection is intricate and varies widely across jurisdictions, making a comprehensive understanding essential for compliance. Key components include:
-
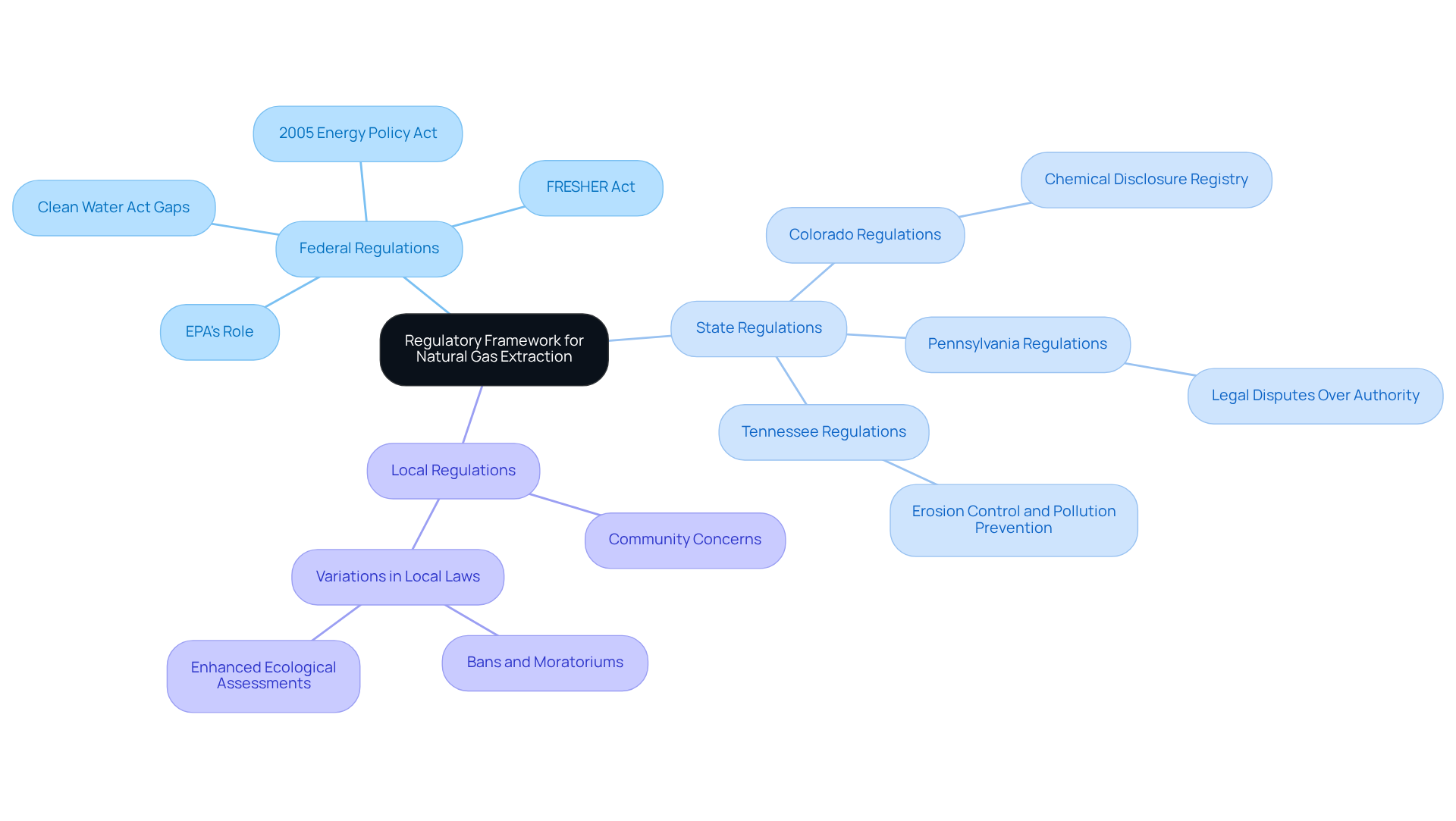
Federal Regulations: The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is pivotal in overseeing aspects of fluid extraction, particularly concerning water quality under the Safe Drinking Water Act. However, the 2005 Energy Policy Act excluded high-pressure extraction from several federal regulations, resulting in significant oversight gaps. As of 2025, the EPA continues to enforce regulations aimed at safeguarding water resources, but primary regulatory authority lies at the state level. Notably, the FRESHER Act has been introduced to address a loophole in the Clean Water Act that exempts the oil and gas industry from permitting requirements for industrial stormwater runoff. Additionally, a 2012 NRDC report underscored that the Clean Water Act regulatory program lacks comprehensiveness and has outdated discharge standards.
-
State Regulations: Each state has crafted its own regulations governing hydraulic fracturing, often incorporating stringent requirements for chemical disclosure, wastewater management, and baseline water quality assessments. For example, states like Colorado mandate detailed chemical disclosure registries, while others, such as Pennsylvania, are embroiled in legal disputes over the balance of state versus municipal regulatory authority. Recent case studies highlight the challenges municipalities face when state laws limit local authority, particularly in managing wastewater from drilling. It is also noteworthy that 91 percent of America's oil and natural gas wells are developed by independent producers, influencing the regulatory landscape.
-
Local Regulations: Municipal authorities may impose additional limitations or mandates on drilling activities, reflecting community concerns about ecological impacts. These regulations can vary significantly, with some municipalities enacting bans or moratoriums on drilling, while others may require enhanced ecological assessments before granting permission. Legal experts have observed that these local regulations can result in a patchwork of compliance requirements that operators must navigate.
-
Operators must traverse a multifaceted permitting process that is part of the hydraulic fracturing environmental analysis before initiating fracking activities. This process typically involves obtaining various permits, which may require public consultation and a hydraulic fracturing environmental analysis. For instance, Tennessee regulations necessitate an action plan for erosion control and pollution prevention as part of the permitting process. Moreover, the EPA's air pollution standards for natural gas drilling, effective since January 2015, mandate that new and modified wells capture escaping emissions, further complicating the compliance landscape. Adhering to these requirements is vital to mitigate legal risks and ensure ecological protection.
Understanding and navigating this regulatory environment is crucial for operators to ensure compliance and minimize potential legal issues associated with drilling projects.
Implement Best Practices for Environmental Analysis
To effectively conduct environmental analyses in hydraulic fracturing, operators must adhere to several best practices:
-
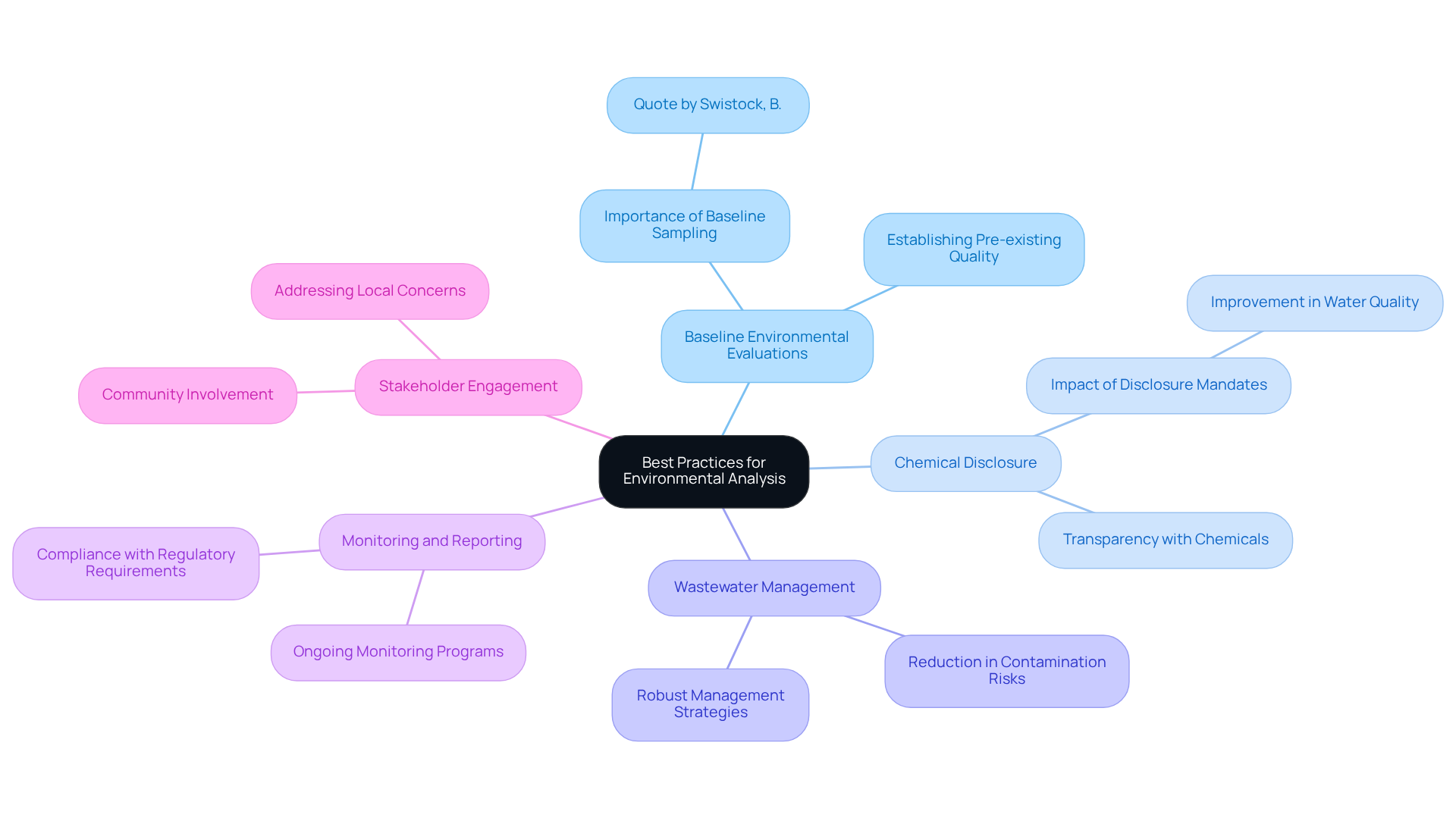
Baseline Environmental Evaluations: Comprehensive evaluations of air, water, and soil quality should be performed before initiating hydraulic fracturing activities. Establishing a baseline is crucial for future comparisons and for identifying potential impacts on local resources. As noted by Swistock, B., "Baseline sampling, although not mandated by law, is prudent to establish the pre-existing quality of the groundwater."
-
Chemical Disclosure: Operators must ensure transparent disclosure of the chemicals utilized in hydraulic fracturing fluids to both regulatory agencies and the public. This practice fosters trust and accountability, as evidenced by the increase in publicly disclosed ingredients from approximately 0% to 95% between 2010 and 2019. The study on the "Impact of Disclosure Mandates on Fracking Pollution" highlights significant improvements in water quality following these mandates.
-
Wastewater Management: Developing and implementing robust wastewater management strategies, including recycling and proper disposal methods, is essential. Efficient management reduces contamination risks and adheres to best practices in resource stewardship. Research indicates that operators reported using fewer hazardous chemicals and experienced fewer spills after implementing better wastewater management practices.
-
Monitoring and Reporting: Establishing ongoing monitoring programs to track ecological impacts throughout and after fracking operations ensures compliance with regulatory requirements and allows for timely responses to any identified issues.
-
Stakeholder Engagement: Actively engaging with local communities and stakeholders to address concerns and incorporate their feedback into operational practices is crucial. This engagement maintains a positive relationship with the public and enhances the overall effectiveness of ecological strategies.
By adhering to these best practices, operators can significantly improve their environmental stewardship and ensure compliance with regulatory frameworks through a comprehensive hydraulic fracturing environmental analysis, ultimately leading to better outcomes for both the industry and the communities affected.
Conclusion
Hydraulic fracturing is integral to the extraction of oil and natural gas; however, it presents substantial environmental challenges that demand urgent attention. A comprehensive understanding of hydraulic fracturing's intricacies—including its objectives, economic ramifications, and ecological impacts—is vital for stakeholders within the energy sector. By acknowledging the necessity of thorough environmental analyses and adherence to regulatory frameworks, operators can adeptly navigate the complexities of this industry while prioritizing ecological stewardship.
This article delineates the principal environmental impacts of hydraulic fracturing, including:
- Water contamination
- Air quality degradation
- Land use changes
- Induced seismicity
Each factor highlights the imperative for operators to execute rigorous environmental assessments and comply with both federal and state regulations. Furthermore, the discussion underscores best practices such as:
- Baseline evaluations
- Chemical disclosure
- Effective wastewater management
- Stakeholder engagement
All of which are essential for minimizing ecological footprints and ensuring compliance with evolving regulatory standards.
Ultimately, the future of hydraulic fracturing depends on the industry's capacity to harmonize energy production with environmental protection. By committing to best practices and fostering transparent operations, energy producers can cultivate public trust and contribute to sustainable resource management. As energy demand continues to escalate, it is crucial for all stakeholders to prioritize environmental considerations, ensuring that hydraulic fracturing not only satisfies energy needs but also protects the planet for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is hydraulic fracturing and its purpose?
Hydraulic fracturing, also known as hydraulic stimulation, is a method used to extract oil and natural gas from deep rock formations, particularly shale. It involves injecting a high-pressure mixture of water, sand, and chemicals into the rock to create fractures that allow hydrocarbons to flow freely to the well.
How significant is hydraulic fracturing in U.S. energy production?
Hydraulic fracturing accounts for nearly half of the total U.S. crude oil production and two-thirds of marketed natural gas production, highlighting its critical role in the energy sector.
What is the economic impact of hydraulic fracturing?
The fluid injection market for hydraulic fracturing was valued at USD 18.88 billion in 2024, indicating its substantial economic impact.
How do modern techniques improve the efficiency of hydraulic fracturing?
Modern water-based extraction and horizontal boring techniques can reduce the drilling zone's surface footprint by up to 90 percent, demonstrating their efficiency.
What does Barry Russell say about the importance of hydraulic extraction?
Barry Russell, President and CEO of IPAA, states that "America’s energy producers are the backbone of our nation’s security and economic growth," emphasizing the importance of hydraulic extraction in energy production and national security.
What is the projected growth rate for the hydraulic fracturing market?
The hydraulic fracturing market is anticipated to exhibit a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.77% during the forecast period, indicating sustained relevance and growth in the industry.
What are some ecological challenges associated with hydraulic fracturing?
Ecological challenges related to hydraulic fracturing include methane emissions and water pollution, which are essential considerations for understanding its environmental impacts and regulatory obligations.
List of Sources
- Define Hydraulic Fracturing and Its Purpose
- Hydraulic fracturing accounts for about half of current U.S. crude oil production - U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) (https://eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=25372)
- Hydraulic Fracturing Market Size, Forecast | Statistics by 2032 (https://fortunebusinessinsights.com/industry-reports/hydraulic-fracturing-market-100419)
- Hydraulic Fracturing (https://api.org/news-policy-and-issues/hydraulic-fracturing)
- Hydraulic Fracturing (https://ipaa.org/fracking)
- Fracking in the United States (https://ballotpedia.org/Fracking_in_the_United_States)
- Examine Environmental Impacts of Hydraulic Fracturing
- A review of environmental issues caused by hydraulic fracturing of shale gas - Discover Applied Sciences (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42452-025-07122-x)
- Fracking by the Numbers (https://frontiergroup.org/resources/fracking-numbers-0)
- Environmental Implications of Shale Gas Hydraulic Fracturing: A Comprehensive Review on Water Contamination and Seismic Activity in the United States (https://mdpi.com/2073-4441/15/19/3334)
- 10 Quotes on the Heated Debate of Fracking's Impact on Global Warming (https://newsmax.com/fastfeatures/global-warming-fracking-climate-change-environment/2015/03/27/id/634941)
- 5 Quotes About Hydraulic Fracturing | Injury? Call DLP (https://dlplaw.com/5-quotes-about-hydraulic-fracturing)
- Navigate Regulatory Framework and Compliance Requirements
- Hydraulic Fracturing (https://ipaa.org/fracking)
- Fracking regulations (https://gem.wiki/Fracking_regulations)
- Hydraulic Fracturing: Critical for Energy Production, Jobs, and Economic Growth (https://heritage.org/environment/report/hydraulic-fracturing-critical-energy-production-jobs-and-economic-growth)
- 5 Quotes About Hydraulic Fracturing | Injury? Call DLP (https://dlplaw.com/5-quotes-about-hydraulic-fracturing)
- Quotable Fracking Quotes (https://conservationcouncil.ca/quotable-fracking-quotes)
- Implement Best Practices for Environmental Analysis
- Hydraulic Fracturing Chemical Disclosure Policy and Data Analysis: Metrics and Trends in Transparency - PubMed (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33657319)
- Hydraulic fracturing chemicals reporting: Analysis of available data and recommendations for policymakers (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0301421515301804)
- Guidelines for Voluntary Baseline Groundwater Quality Sampling in the Vicinity of Hydraulic Fracturing Operations (https://kgs.ku.edu/guidelines-voluntary-baseline-groundwater-quality-sampling-vicinity-hydraulic-fracturing-operations)
- Disclosure and Public Pressure Reduce Fracking-Related Pollution (https://nber.org/digest/20234/disclosure-and-public-pressure-reduce-fracking-related-pollution)
- Quotable Fracking Quotes (https://conservationcouncil.ca/quotable-fracking-quotes)




