Overview
Local economic evaluations for gas extraction are crucial in understanding the economic impacts of gas production on nearby communities. These evaluations focus on:
- Job creation
- Regional business growth
- Tax revenues
- Infrastructure development
By employing methodologies such as input-output analysis and cost-benefit analysis, stakeholders can grasp the financial implications of gas extraction. This understanding is essential for guiding informed decision-making, maximizing benefits, and addressing potential adverse effects.
The complexities of land acquisition, including legal and regulatory challenges, further emphasize the need for comprehensive evaluations. Stakeholders must navigate these intricacies to ensure that gas extraction contributes positively to local economies. The methodologies mentioned not only clarify the economic landscape but also empower communities to advocate for their interests effectively.
Ultimately, local economic evaluations serve as a vital tool for stakeholders, providing insights that drive strategic decisions. By understanding the financial ramifications, communities can better position themselves to harness the benefits of gas production while mitigating any negative impacts.
Introduction
Local economic evaluations for gas extraction represent a crucial connection between energy production and community welfare, illuminating how drilling activities can transform local economies. By exploring methodologies that assess job creation, tax revenues, and infrastructure development, stakeholders can reveal both the advantages and potential challenges of gas extraction initiatives. As communities confront the implications of these projects, a critical question emerges: how can local economic evaluations be optimized to promote sustainable growth while addressing environmental and social challenges?
Define Local Economic Evaluations in Gas Extraction
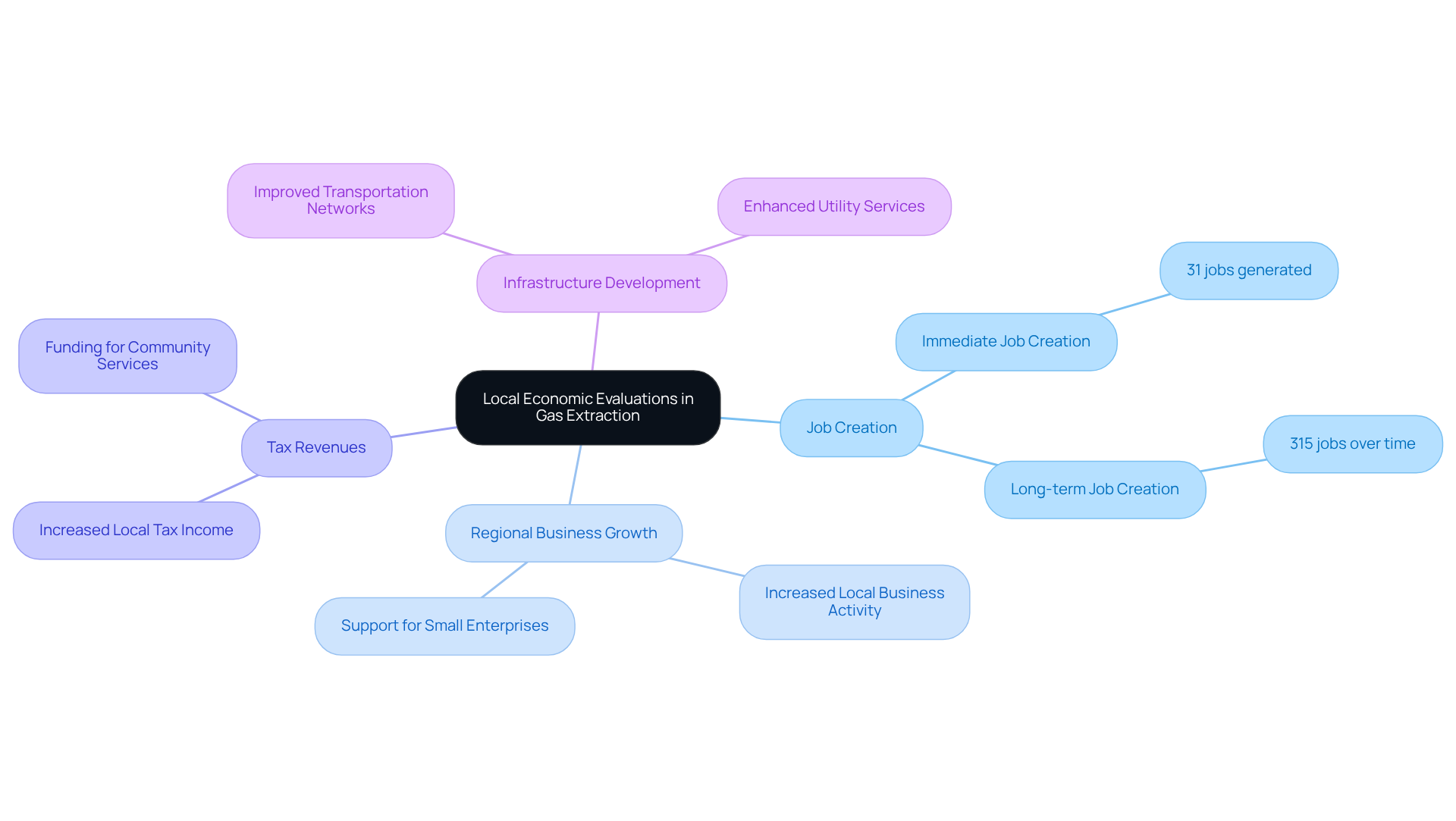
Local economic evaluations for gas extraction are critical assessments of the economic impacts that gas production activities exert on nearby communities. These evaluations focus on key elements such as:
- Job creation
- Regional business growth
- Tax revenues
- Infrastructure development
Notably, studies indicate that an increase in drilling can immediately generate 31 jobs and 315 jobs over time, underscoring the substantial employment benefits associated with gas production projects. By analyzing these factors, stakeholders gain insights into how local economic evaluations for gas extraction influence community financial health and present challenges. This understanding is vital for informed decision-making regarding project development and community engagement, ensuring that local economic evaluations for gas extraction are conducted to maximize benefits while mitigating any adverse effects on regional economies.
Furthermore, economists assert that the oil and gas sector significantly impacts regional labor markets, particularly in rural areas, where it serves as a cornerstone of economic activity. Therefore, local economic evaluations for gas extraction are essential for fostering sustainable growth and addressing community challenges.
Explore Methodologies for Economic Evaluations
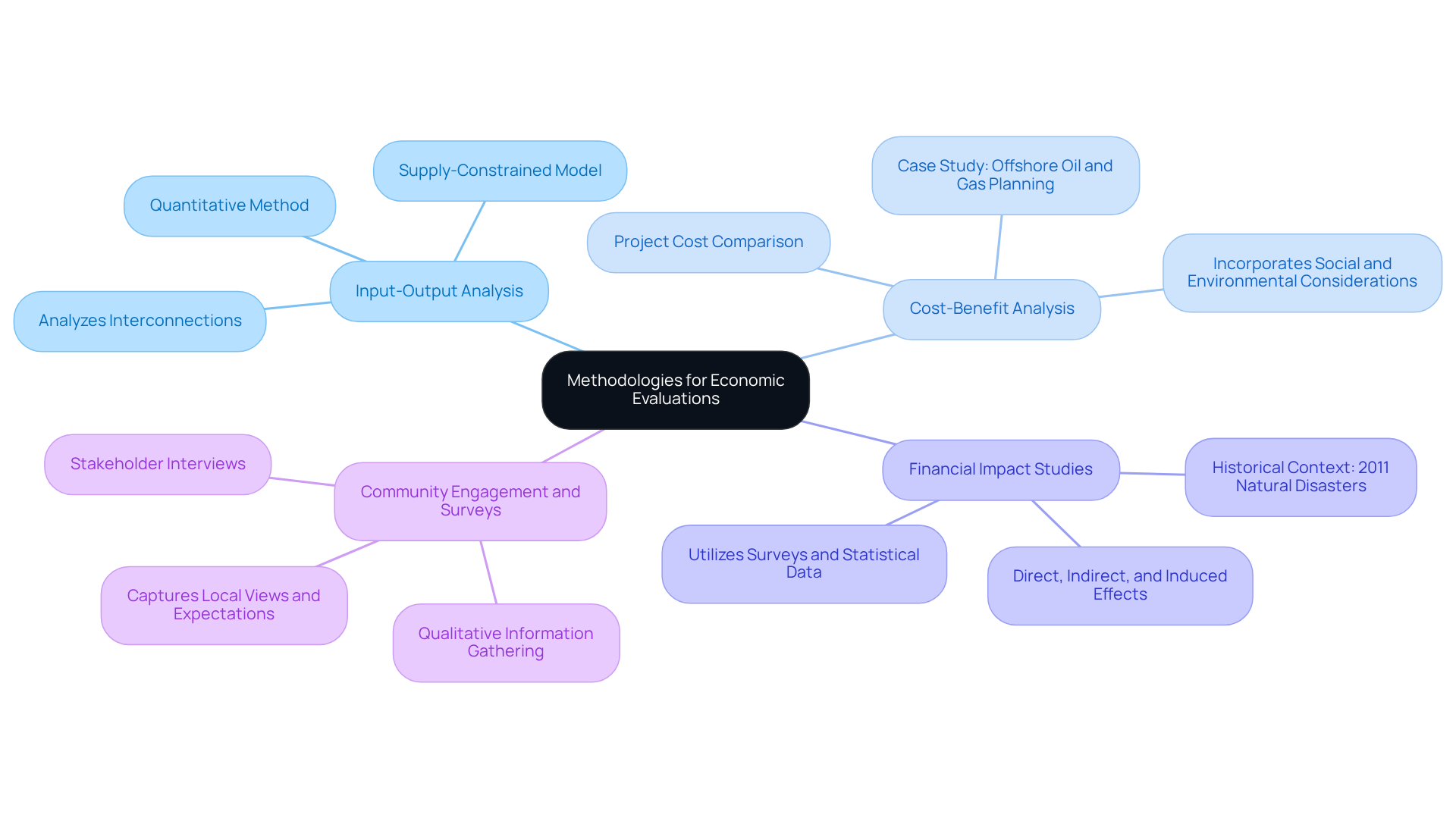
A variety of methodologies are essential for conducting local economic evaluations for gas extraction. These methodologies include:
-
Input-Output Analysis: This quantitative method analyzes the interconnections among different industries, quantifying how changes in gas production activities affect local output, employment, and income levels. Notably, the supply-constrained input-output model effectively analyzes sudden output reductions in specific sectors, offering a nuanced understanding of financial impacts.
-
Cost-Benefit Analysis: This approach compares the total projected costs of a gas removal project with its anticipated advantages, allowing stakeholders to evaluate the project's overall financial viability. A relevant case study is the "Cost-Benefit Analysis in Offshore Oil and Gas Planning," illustrating how methodologies have evolved to incorporate broader social and environmental considerations.
-
Financial Impact Studies: Utilizing surveys and statistical data, these studies assess the direct, indirect, and induced financial effects of gas removal on nearby communities, providing a comprehensive understanding of its implications. Historical data, such as the financial losses from natural disasters in 2011 amounting to nearly $55 billion, offers context for the financial assessments being discussed.
-
Community Engagement and Surveys: Gathering qualitative information through community surveys and stakeholder interviews enhances the evaluation process by capturing local views and expectations concerning gas removal. This qualitative insight is vital for comprehending the wider social implications of financial activities.
By applying these methodologies, stakeholders can gain a thorough comprehension of the financial impacts of gas removal projects, which is essential for local economic evaluations for gas extraction, thereby enabling informed decision-making. As Irving Fisher observed, "The surplus can only be generated by an increase in efficiency," underscoring the significance of these assessments in optimizing resource use.
Assess Impacts on Land Acquisition Strategies
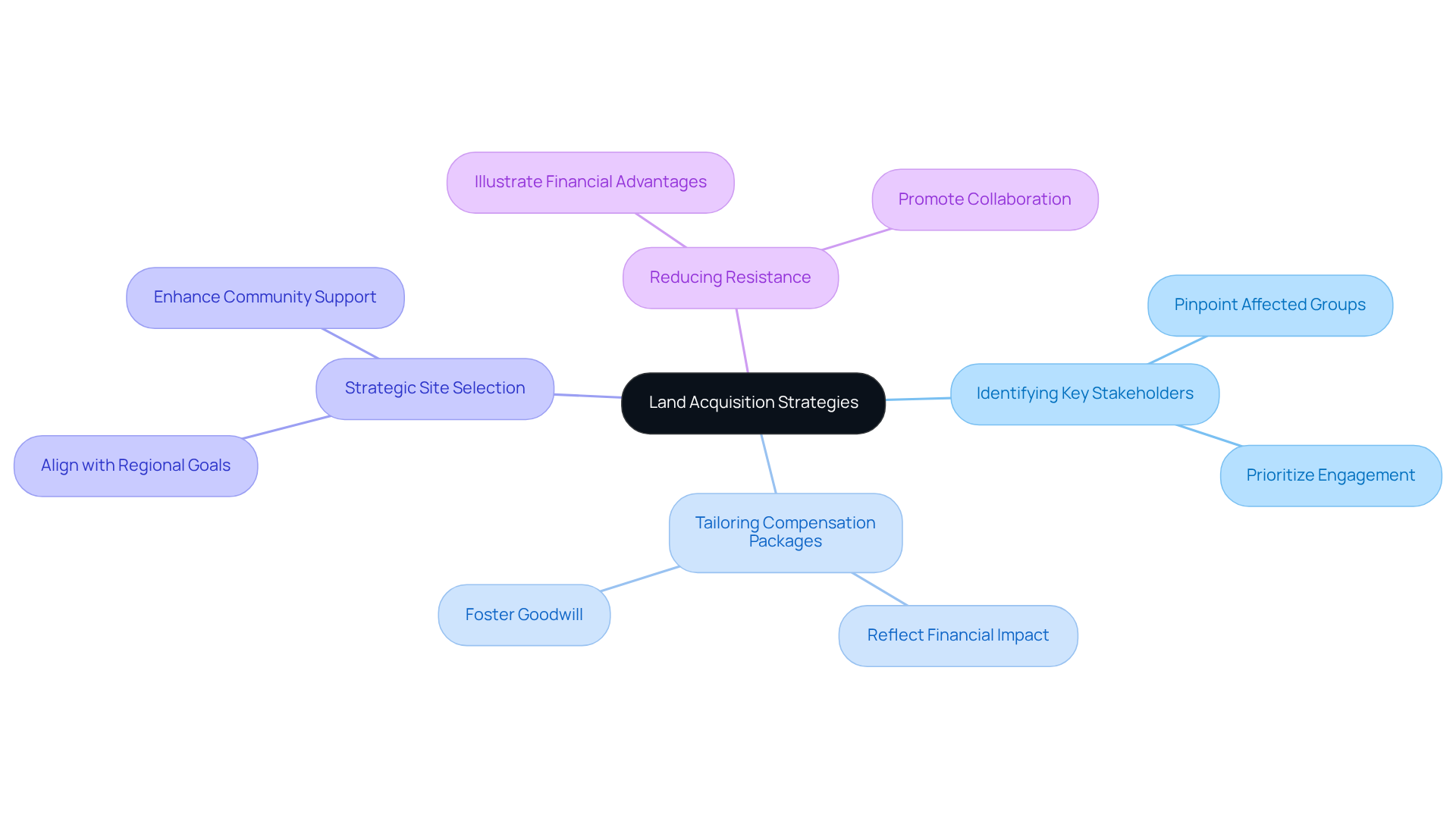
Local economic evaluations are crucial in shaping land acquisition strategies for gas extraction projects, influencing several key areas:
-
Identifying Key Stakeholders: Economic evaluations help pinpoint stakeholders most affected by gas extraction activities. This allows project developers to prioritize engagement with these groups during the land acquisition process.
-
Tailoring Compensation Packages: Insights from financial assessments guide the creation of compensation packages that accurately reflect the financial impact on nearby communities. This approach fosters goodwill and facilitates smoother negotiations, addressing the common concern that compensation is often limited and inconsistent.
-
Strategic Site Selection: A thorough understanding of the financial landscape aids in identifying locations that not only meet operational needs but also align with regional development goals. Such alignment can significantly enhance community support for the project, as stakeholders recognize the potential for mutual benefits.
-
Reducing Resistance: By clearly illustrating the potential financial advantages of gas extraction, stakeholders can effectively address community concerns and resistance. This proactive approach promotes a more collaborative land acquisition process, ultimately leading to improved project outcomes.
Incorporating these considerations into land acquisition strategies not only increases the likelihood of successful project execution but also strengthens community relations, which are essential for long-term sustainability in local economic evaluations for gas extraction.
Integrate Regulatory and Environmental Factors
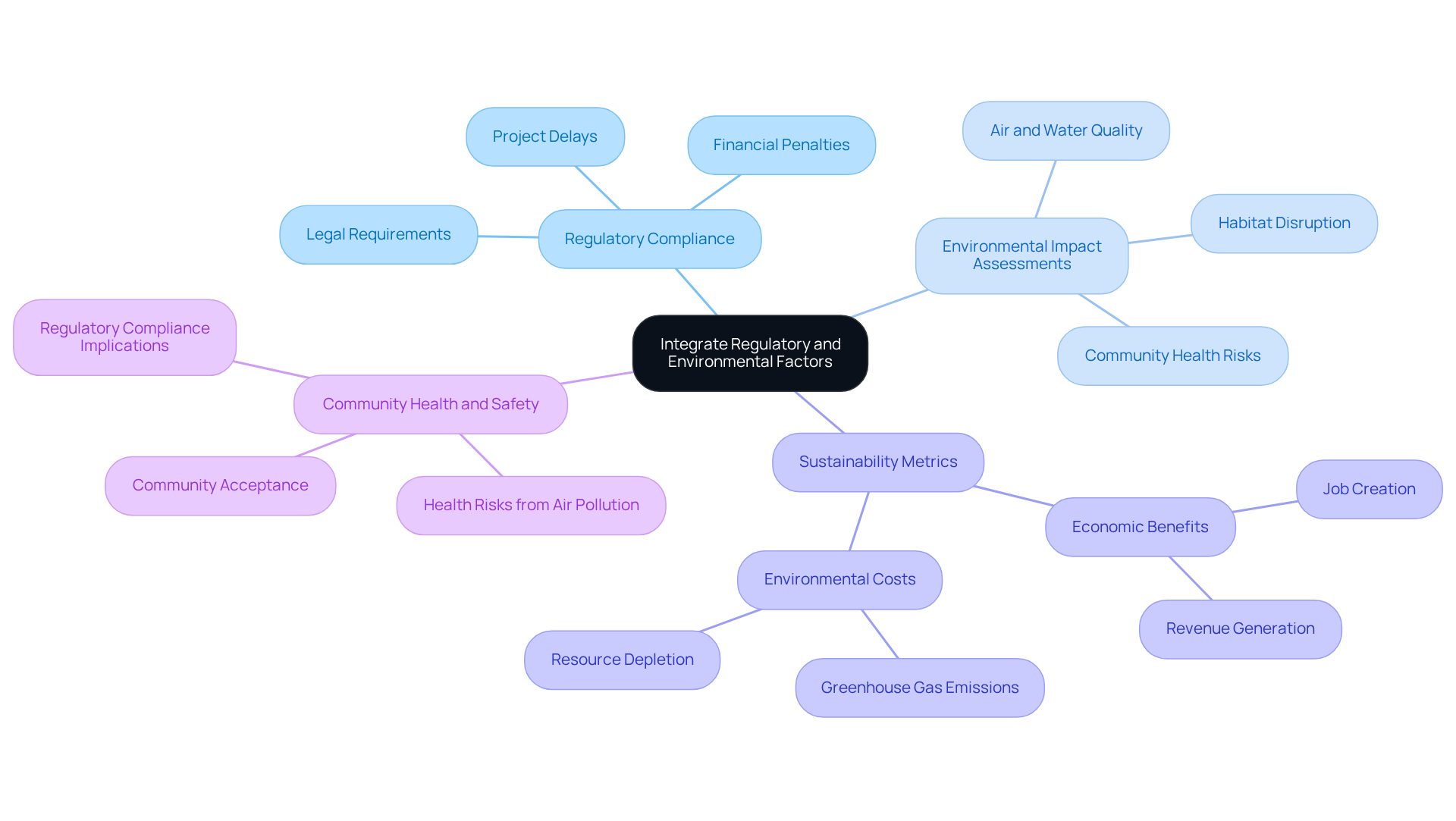
Incorporating regulatory and environmental elements into regional financial assessments is essential for a comprehensive understanding of gas production initiatives. This necessity arises from several key considerations:
-
Regulatory Compliance: A thorough grasp of local, state, and federal regulations is vital for ensuring that gas removal activities meet legal requirements. Noncompliance can lead to substantial financial penalties and project delays, ultimately jeopardizing overall viability and financial assessments.
-
Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs): Conducting EIAs is crucial for identifying potential environmental risks associated with gas extraction. These evaluations empower stakeholders to proactively address issues concerning air and water quality, habitat disruption, and community health—factors that are critical to informed financial assessments and land acquisition strategies. For instance, the EPA has identified over 1,000 chemical additives used in hydraulic fracturing, underscoring the urgent need for improved management to prevent environmental contamination.
-
Sustainability Metrics: Including sustainability metrics in financial assessments provides a more nuanced perspective on project effects. This approach not only highlights economic benefits, such as job creation and revenue generation, but also emphasizes environmental costs, including greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. For example, in 2022, burning natural gas for energy accounted for approximately 35% of total U.S. energy-related CO2 emissions, illustrating the critical need for careful consideration of environmental impacts. Furthermore, methane emissions from natural gas and petroleum systems represented about 33% of total U.S. methane emissions in 2021, further emphasizing the environmental costs associated with gas production.
-
Community Health and Safety: Evaluating the potential health and safety impacts of gas extraction on nearby communities is essential. Research indicates that residents near unconventional gas well sites face heightened health risks from air pollution, influencing both community acceptance and regulatory compliance. Understanding these implications is vital for fostering positive relationships with community stakeholders and ensuring project sustainability.
By integrating these regulatory and environmental factors, stakeholders can ensure that their local economic evaluations are not only thorough but also aligned with best practices in sustainability and compliance. This holistic approach ultimately supports more responsible and informed decision-making in gas extraction projects.
Conclusion
Local economic evaluations for gas extraction are essential for understanding the economic ramifications of gas production on surrounding communities. These assessments illuminate the potential for job creation and regional business growth, while also highlighting the importance of infrastructure development and tax revenue generation. By thoroughly analyzing these elements, stakeholders can make informed decisions that maximize benefits and address the challenges arising from gas extraction activities.
This article underscores several key methodologies crucial for conducting effective local economic evaluations. Techniques such as:
- Input-output analysis
- Cost-benefit analysis
- Financial impact studies
- Community engagement surveys
provide a comprehensive framework for assessing the economic influences of gas extraction. By integrating these methodologies, stakeholders gain insights into the financial impacts of gas removal projects, ensuring local economies are supported and community concerns are addressed.
Ultimately, the significance of local economic evaluations extends beyond mere financial metrics; they foster sustainable growth and community engagement. By incorporating regulatory and environmental considerations into these evaluations, stakeholders can navigate the complexities of gas extraction with a holistic approach that prioritizes both economic benefits and community well-being. As gas extraction continues to shape local economies, embracing these evaluations is crucial for ensuring responsible development that respects both the environment and the communities affected.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are local economic evaluations in gas extraction?
Local economic evaluations in gas extraction are assessments of the economic impacts that gas production activities have on nearby communities, focusing on aspects such as job creation, regional business growth, tax revenues, and infrastructure development.
How many jobs can gas drilling create?
Studies indicate that an increase in drilling can immediately generate 31 jobs and 315 jobs over time, highlighting the significant employment benefits associated with gas production projects.
Why are local economic evaluations important?
These evaluations are important because they provide insights into how gas extraction influences community financial health, helping stakeholders make informed decisions regarding project development and community engagement while maximizing benefits and mitigating adverse effects.
What impact does the oil and gas sector have on regional labor markets?
The oil and gas sector significantly impacts regional labor markets, especially in rural areas, where it serves as a cornerstone of economic activity.
How do local economic evaluations contribute to community challenges?
Local economic evaluations help address community challenges by fostering sustainable growth and understanding the economic implications of gas extraction activities on local economies.
List of Sources
- Define Local Economic Evaluations in Gas Extraction
- The regional economic impact of oil and gas extraction in Texas (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0301421515300768)
- 30 of the Most Impactful Climate Change Quotes - Curious Earth (https://curious.earth/blog/climate-change-quotes)
- The local economic impacts of the oil and gas industry: Boom, bust and resilience to shocks (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0140988321001900)
- 32 Quotes on Why Canada's Oil & Gas Emissions Cap Doesn't Make Sense (https://canadaaction.ca/quotes-why-emissions-cap-oil-gas-not-good-for-canada-world)
- Quotable Fracking Quotes (https://conservationcouncil.ca/quotable-fracking-quotes)
- Explore Methodologies for Economic Evaluations
- Assessing the suitability of input–output analysis for enhancing our understanding of potential economic effects of Peak Oil (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0360544208001746)
- 30 Best Irving Fisher Quotes With Image | Bookey (https://bookey.app/quote-author/irving-fisher)
- From investment to net benefits: A review of guidelines and methodologies for cost–benefit analysis in the electricity sector (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2214629625001331)
- Cost-Benefit Analysis in Offshore Oil and Gas Planning (https://policyintegrity.org/publications/detail/cost-benefit-analysis-in-offshore-oil-and-gas-planning)
- John Maynard Keynes - Wikiquote (https://en.wikiquote.org/wiki/John_Maynard_Keynes)
- Assess Impacts on Land Acquisition Strategies
- Oil & Natural Gas Contribution to U.S. Economy Fact Sheet (https://api.org/news-policy-and-issues/taxes/oil-and-natural-gas-contribution-to-us-economy-fact-sheet)
- Revenues and Disbursements from Oil and Natural Gas Leases on Onshore Federal Lands (https://congress.gov/crs-product/R46537)
- Good fences make good neighbors: Stakeholder perspectives on the local benefits and burdens of large-scale solar energy development in the United States (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2214629623004358)
- Natural Gas Fuels Jobs: Factsheet (https://empoweringamerica.org/natural-gas-fuels-jobs-factsheet-national)
- “Shale gas development will bring local economic benefits”. An analysis of central Appalachian landowners' lived experience and situated knowledge of extractivism (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016718524001118)
- Integrate Regulatory and Environmental Factors
- Environmental Impacts of Natural Gas (https://ucs.org/resources/environmental-impacts-natural-gas)
- Data and Statistics Overview (https://phmsa.dot.gov/data-and-statistics/pipeline/data-and-statistics-overview)
- Natural gas and the environment - U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) (https://eia.gov/energyexplained/natural-gas/natural-gas-and-the-environment.php)
- Topic: Oil and gas industry emissions worldwide (https://statista.com/topics/10956/oil-and-gas-industry-emissions-worldwide)
- Tracking the Cost of Complying with Government Regulation (https://nber.org/digest/20232/tracking-cost-complying-government-regulation)




