Overview
The article presents a compelling overview of the critical steps necessary for the implementation and management of community-based smart grids. These systems integrate renewable energy sources and advanced technologies, significantly enhancing local energy management.
- Structured planning is paramount.
- Active community engagement is crucial.
- Addressing challenges such as regulatory compliance and cybersecurity is essential to ensure the successful deployment and operation of these sustainable energy systems.
By focusing on these elements, communities can effectively harness the benefits of smart grids, paving the way for a more sustainable energy future.
Introduction
Community-based smart grids are transforming local energy systems by integrating renewable energy sources with advanced technologies, significantly enhancing power distribution and consumption. These innovative networks promise not only substantial cost savings and improved energy efficiency but also empower communities to take control of their energy resources.
However, the journey toward implementing these smart grids is fraught with challenges, including regulatory hurdles and technological integration.
How can communities effectively navigate these complexities to harness the full potential of smart grid technology and foster a sustainable energy future?
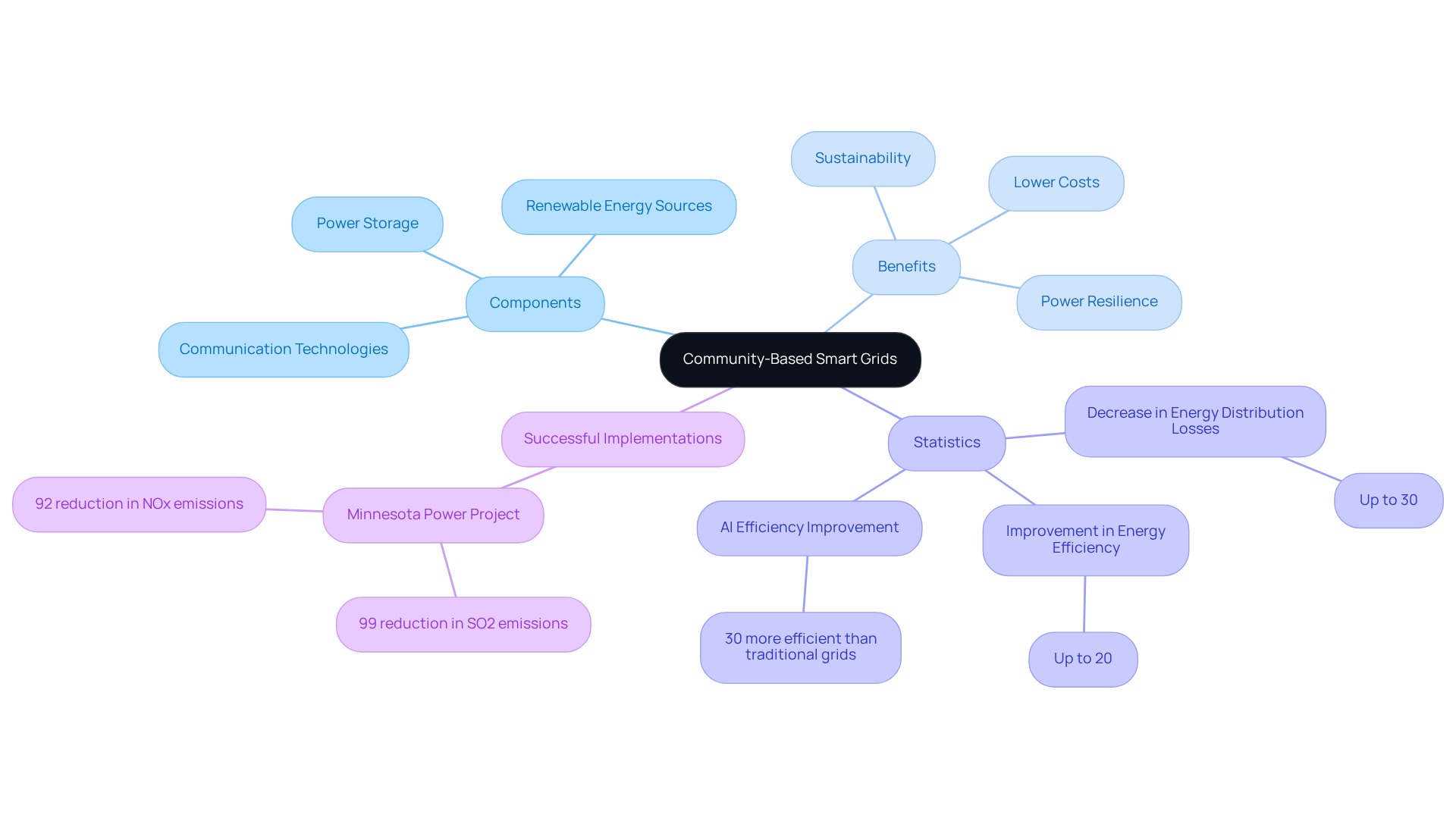
Define Community-Based Smart Grids and Their Importance
Community-based smart grids represent a pivotal advancement in localized power systems, integrating renewable energy sources, power storage, and cutting-edge communication technologies to optimize power distribution and consumption within communities. These networks are designed to bolster power resilience, lower costs, and promote sustainable practices. Their importance lies in empowering local communities to manage their energy resources with community-based smart grids, reduce reliance on centralized systems, and foster collaboration among residents.
By facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources, community-based smart grids not only support environmental sustainability but also enhance autonomy, making them an essential component of modern infrastructure. Notably, statistics indicate that these systems can decrease energy distribution losses by up to 30% while improving overall energy efficiency by as much as 20%. Moreover, AI-enabled smart grids can operate 30% more efficiently than traditional grids, underscoring their potential for superior performance.
Successful implementations across the United States, such as the Minnesota Power project, which achieved a remarkable 99% reduction in sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions, illustrate the tangible benefits of these systems. They offer improved reliability and reduced operational costs. As communities increasingly adopt community-based smart grids, they not only enhance their power resilience but also pave the way for sustainable resource management.
Explore Key Technologies Driving Community-Based Smart Grids
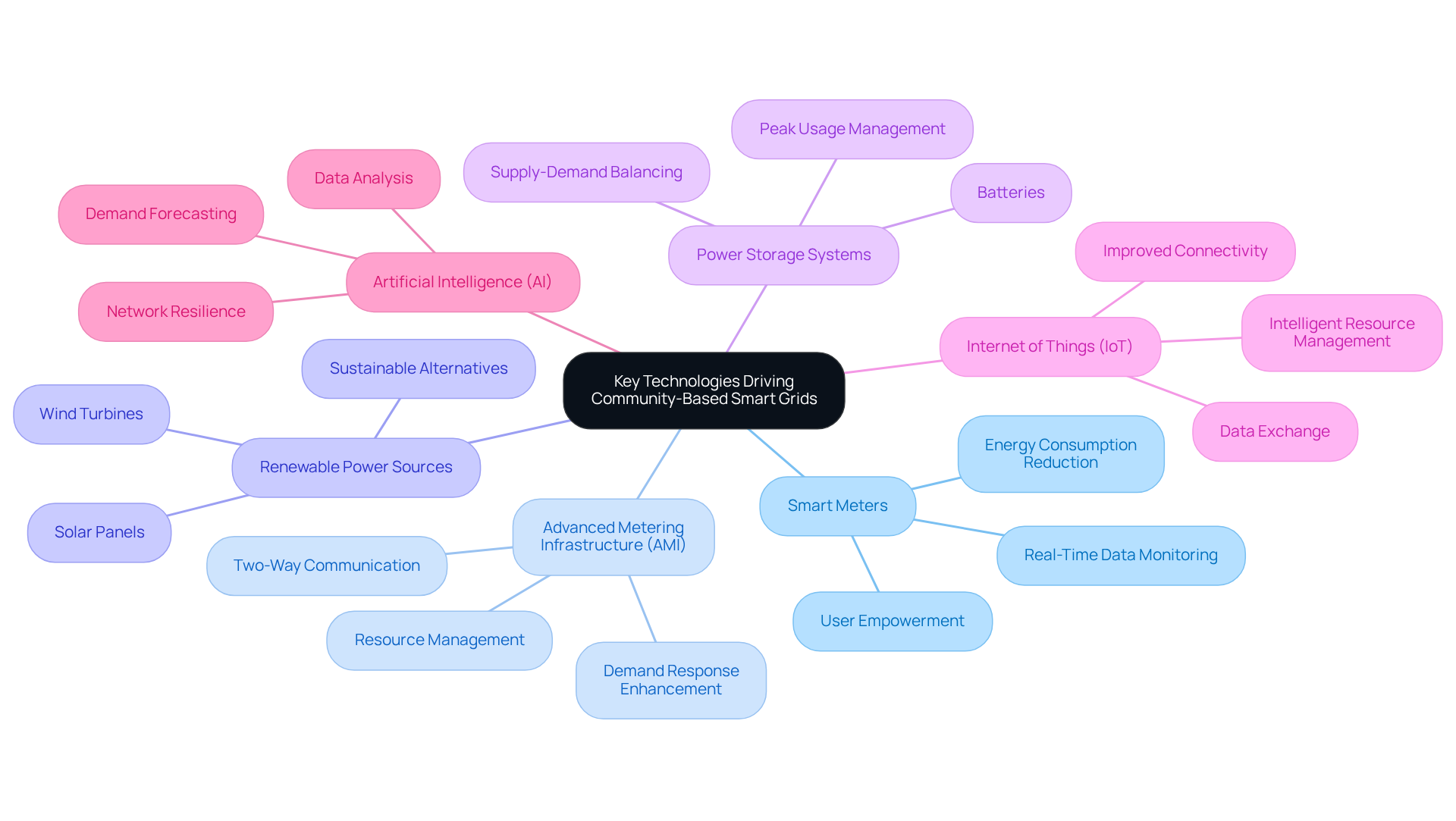
Key technologies driving community-based smart grids play a crucial role in shaping the future of energy management. Consider the following advancements:
-
Smart Meters: These devices provide real-time data on power consumption, empowering users to monitor and manage their usage effectively.
-
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI): This system facilitates two-way communication between utilities and consumers, enhancing demand response and resource management.
-
Renewable Power Sources: The integration of solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable technologies into the network offers sustainable power alternatives, addressing the growing need for eco-friendly energy solutions.
-
Power Storage Systems: Batteries and other storage solutions play a crucial role in balancing supply and demand, ensuring a dependable power supply even during peak usage times.
-
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices significantly improve connectivity and data exchange throughout the network, enabling more intelligent resource management and operational effectiveness.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms analyze data to enhance power distribution, forecast demand, and fortify network resilience against disruptions.
These technologies not only address the complexities of modern energy needs but also pave the way for the implementation of community-based smart grids, fostering a more sustainable and efficient energy landscape. Are you ready to embrace these innovations in your community?
Implement Community-Based Smart Grids: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing community-based smart grids requires a structured approach that caters to the unique needs of each community. Begin by evaluating community requirements through surveys and direct engagement with residents to ascertain their power needs and preferences. This foundational step sets the stage for defining clear goals and objectives for community-based smart grids, such as reducing energy costs, increasing renewable energy usage, or enhancing grid reliability.
Next, develop a comprehensive plan that outlines timelines, budgets, and resource allocation. This plan is crucial for ensuring that all stakeholders are aligned and aware of the project's scope. Engage stakeholders effectively by collaborating with local authorities, utility firms, and community groups to garner support and resources essential for the success of community-based smart grids.
Selecting appropriate technologies is critical; it involves choosing solutions that align with the community's goals and infrastructure capabilities. Following this, conduct pilot testing to implement a trial project, allowing for the assessment of technologies and processes before full-scale deployment.
Once the pilot phase is successful, proceed with full-scale implementation of the intelligent network throughout the community. This phase should include adequate training and assistance for users, ensuring seamless integration into daily life. Finally, establish a system for ongoing monitoring and evaluation to continuously observe performance and gather user feedback, making necessary adjustments and enhancements as needed.
Navigate Challenges in Community-Based Smart Grid Management
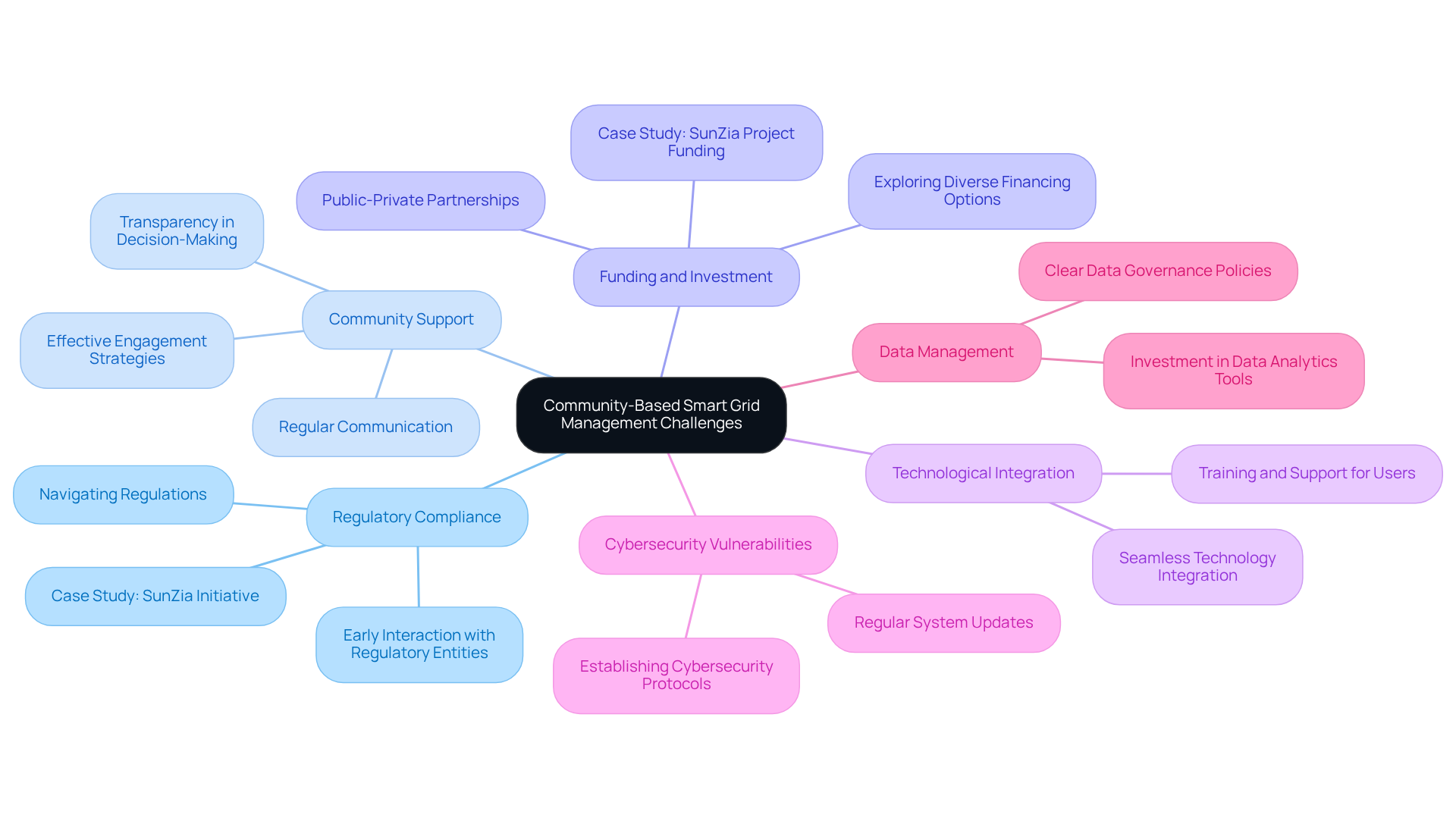
Managing community-based smart grids involves a unique set of challenges that require strategic approaches for successful implementation and operation.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Navigating the intricate landscape of local, state, and federal regulations is essential. Awareness of legal obligations and early interaction with regulatory entities can alleviate potential challenges and enhance execution. For instance, the SunZia initiative faced various regulatory hurdles, addressed through meticulous planning and coordination.
-
Building and maintaining community support is vital for the success of community-based smart grids. Regular communication, transparency, and active involvement in decision-making processes foster trust and collaboration. Effective community engagement strategies have demonstrated significant improvements in acceptance and participation rates. As Tom Saager, Project Manager for SunZia West Converter Station, noted, "The collaboration among Pattern Energy, Hitachi Energy, and Quanta Services uniting to achieve a successful endeavor has been remarkable."
-
Funding and Investment: Securing sufficient financing for intelligent network initiatives can be challenging. Exploring diverse financing options—including grants, public-private partnerships, and community financing—is crucial to support implementation and sustainability. The SunZia project, for example, has successfully attracted significant investment, showcasing the potential for funding in large-scale renewable initiatives.
-
Technological Integration: The seamless integration of various technologies is paramount for operational efficiency. Careful planning and expertise are required to ensure compatibility. Investing in training and support for both staff and users can facilitate smoother transitions and enhance overall system performance.
-
Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities: With the reliance on digital technologies, intelligent networks are vulnerable to cyber threats. Establishing robust cybersecurity protocols and frequently refreshing systems are vital to protect against potential attacks and maintain the integrity of the network.
-
Data Management: The large volumes of information produced by intelligent networks can be overwhelming. Clear data governance policies and investment in advanced data analytics tools are critical for deriving actionable insights and making informed decisions.
By addressing these challenges with effective strategies, stakeholders can enhance the management and resilience of community-based smart grids, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable energy future.
Conclusion
Community-based smart grids signify a transformative approach to energy management, empowering local communities to harness renewable resources and optimize their energy consumption. By integrating advanced technologies, these systems not only enhance energy resilience but also promote sustainability while reducing reliance on centralized power sources.
Key technologies such as:
- Smart meters
- Renewable energy sources
- Artificial intelligence
are essential components driving the implementation of community-based smart grids. The article provides a step-by-step guide that offers insights into evaluating community needs, engaging stakeholders, and addressing challenges, including regulatory compliance and cybersecurity vulnerabilities. Successful case studies, such as the Minnesota Power project, illustrate the tangible benefits of adopting these innovative systems.
As communities increasingly embrace the potential of smart grids, the importance of strategic planning and active participation becomes evident. By fostering collaboration and investing in necessary technologies, communities can create resilient energy systems that meet current demands while paving the way for a sustainable future. Embracing community-based smart grids is not merely an energy solution; it is a crucial step towards empowering communities to take control of their energy resources and contribute to a greener planet.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are community-based smart grids?
Community-based smart grids are localized power systems that integrate renewable energy sources, power storage, and advanced communication technologies to optimize power distribution and consumption within communities.
Why are community-based smart grids important?
They empower local communities to manage their energy resources, reduce reliance on centralized systems, and promote collaboration among residents, while also enhancing power resilience and supporting sustainable practices.
How do community-based smart grids contribute to sustainability?
By facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources, community-based smart grids support environmental sustainability and enhance autonomy within communities.
What are the efficiency improvements associated with community-based smart grids?
These systems can decrease energy distribution losses by up to 30% and improve overall energy efficiency by as much as 20%. AI-enabled smart grids can operate 30% more efficiently than traditional grids.
Can you provide an example of successful implementation of a community-based smart grid?
The Minnesota Power project is a notable example, achieving a 99% reduction in sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions, showcasing the tangible benefits of community-based smart grids in improving reliability and reducing operational costs.




