Overview
The article "Master Zoning Compliance for Solar Farms: Key Steps to Success" serves as an essential guide for achieving zoning compliance in solar farm development. It underscores the critical need to comprehend local land use regulations, engage relevant stakeholders, and meticulously prepare documentation. These steps are vital for effectively navigating the intricate regulatory landscape, ultimately facilitating successful project approvals and implementation.
Introduction
Navigating the regulatory landscape for solar farms presents significant challenges, yet it is essential for successful project implementation. As the demand for renewable energy surges, understanding zoning compliance becomes paramount. The intricacies of local land use regulations, engagement with stakeholders, and the process of securing necessary permits create multiple layers of complexity. With solar energy gaining momentum, mastering these critical elements can lead to smoother approvals and a more sustainable future. This article explores the key components of zoning compliance for solar farms, providing insights and strategies to empower stakeholders in effectively overcoming the challenges ahead.
Understand Zoning Compliance Basics for Solar Farms
Zoning compliance for solar farms presents a significant challenge that necessitates a comprehensive understanding of local land use regulations governing the installation of energy systems. Key concepts to consider include:
- Zoning Districts: Familiarity with various zoning classifications—such as residential, commercial, and agricultural—is essential, as each classification comes with specific regulations regarding photovoltaic installations. Unique requirements within each district can greatly influence the feasibility of renewable energy initiatives.
- Permitted Uses: It is crucial to evaluate whether renewable energy farms are considered an allowed use within the desired zoning district. In some cases, a specific use permit may be necessary, which could involve additional scrutiny and community hearings.
- Setback and Height Restrictions: Understanding regional regulations pertaining to minimum distances from property lines and maximum heights for renewable installations is vital. Adhering to these limitations helps prevent potential legal disputes and project delays.
- Environmental Considerations: Awareness of ecological regulations that may impact installation is imperative, including land use limitations for agricultural purposes and protections for local wildlife habitats. Recent regulations on zoning compliance for solar farms in 2025 underscore the importance of these factors as the sector continues to grow. For instance, the installation of 1.1 GW of residential photovoltaic systems in Q4 2024 reflects a 1% quarter-over-quarter increase, highlighting the rising demand for renewable power solutions.
Comprehending zoning districts is crucial for successful project execution, as it directly affects site selection and timelines. Expert insights reinforce the need for effective navigation of these regulations. Andrew Blake notes that the transition to renewable power is not only inevitable but also increasingly economical, making compliance even more critical as the market evolves. Successful examples of zoning compliance for solar farms illustrate that proactive engagement with community regulations can lead to smoother project approvals and implementation. By mastering the fundamentals of zoning compliance for solar farms, you will be better equipped to navigate the regulatory landscape and ensure the successful execution of renewable energy projects. Furthermore, readers are encouraged to customize their subscription preferences to receive pertinent information about renewables, thereby enhancing their engagement with this critical topic.
Assess Local Zoning Regulations and Requirements
To effectively evaluate regional zoning rules and prerequisites for photovoltaic farms, it is essential to follow these steps:
-
Research Local Ordinances: Begin by visiting your local government’s website or planning department to access zoning ordinances. Pay special attention to sections that specifically address renewable power systems. Thorough research is crucial; neglecting this step can lead to significant consequences, as approximately 20% of projects face rejection due to zoning compliance for solar farms.
-
Identify Key Regulations: Focus on critical regulations that pertain to:
- Permitted uses for solar farms
- Setback requirements
- Height restrictions
- Special provisions for solar energy systems.
-
Consult with Local Authorities: Engage with local planning officials to clarify any ambiguous regulations and confirm your understanding of the requirements. This step is vital for ensuring zoning compliance for solar farms.
-
Review Community Plans: Examine comprehensive plans or renewable policies that may influence zoning decisions. These documents often detail community objectives related to renewable energy, providing context for your initiative. As noted by Gomez and Morley, model ordinances exist to assist communities in regulating utility-scale photovoltaic plants, which can be advantageous in this review process.
-
Document Findings: Maintain a detailed record of all relevant regulations and requirements. This documentation will serve as a vital reference throughout the development process. It's also important to note that photovoltaic panels installed for on-site use on Clean and Green land are exempt from rollback tax penalties, incentivizing compliance and sustainable practices. Furthermore, after construction, land not utilized for grid-scale solar power can be reenrolled in the Clean and Green program, allowing on-site power use without rollback tax penalties. This emphasizes the significance of comprehending zoning compliance for solar farms. By thoroughly evaluating regional zoning regulations, you can ensure that your photovoltaic farm endeavor meets zoning compliance for solar farms and is strategically positioned for success. For instance, the Cumberland County Solar Energy Systems Model Ordinance serves as a useful framework for municipalities, aiding them in adjusting regulations to fit community contexts effectively.
Engage Stakeholders and Address Conflicting Interests
To effectively engage stakeholders and address conflicting interests in solar energy initiatives, it is crucial to follow these essential steps:
- Identify Stakeholders: Begin by compiling a comprehensive list of all relevant stakeholders, which includes local residents, government officials, environmental groups, and potential investors.
- Communicate Early and Often: Initiate dialogue with stakeholders from the outset. Clearly articulate the advantages of the energy farm, such as job creation and environmental sustainability, while addressing any concerns they may have. Notably, research indicates that a significant proportion of renewable energy initiatives face community resistance, underscoring the necessity for proactive involvement.
- Host Community Meetings: Organize public forums to present your project and solicit feedback. These meetings not only foster community involvement but also allow stakeholders to express their opinions openly.
- Address Concerns: Proactively tackle conflicting interests by demonstrating how the solar farm can positively impact the community, including potential decreases in utility costs and contributions to regional job markets. As emphasized by IRENA, prioritizing inclusivity in the renewable energy sector promotes a more equitable future for all.
- Build Partnerships: Collaborate with local organizations and community leaders to enhance support for your initiative. Their endorsements can significantly influence public perception and acceptance of the energy farm. For instance, the Renewable Energy Independent Power Producer Procurement Programme in South Africa has generated approximately 69,554 job-years, illustrating the positive impact of community participation in renewable energy initiatives.
By emphasizing stakeholder interaction and proactively addressing community issues, you can cultivate a supportive atmosphere that enhances the success of your photovoltaic farm endeavor. Integrating a holistic framework for policy-making that considers technological, social, economic, and environmental priorities will further strengthen your approach.
Prepare Necessary Documentation and Obtain Permits
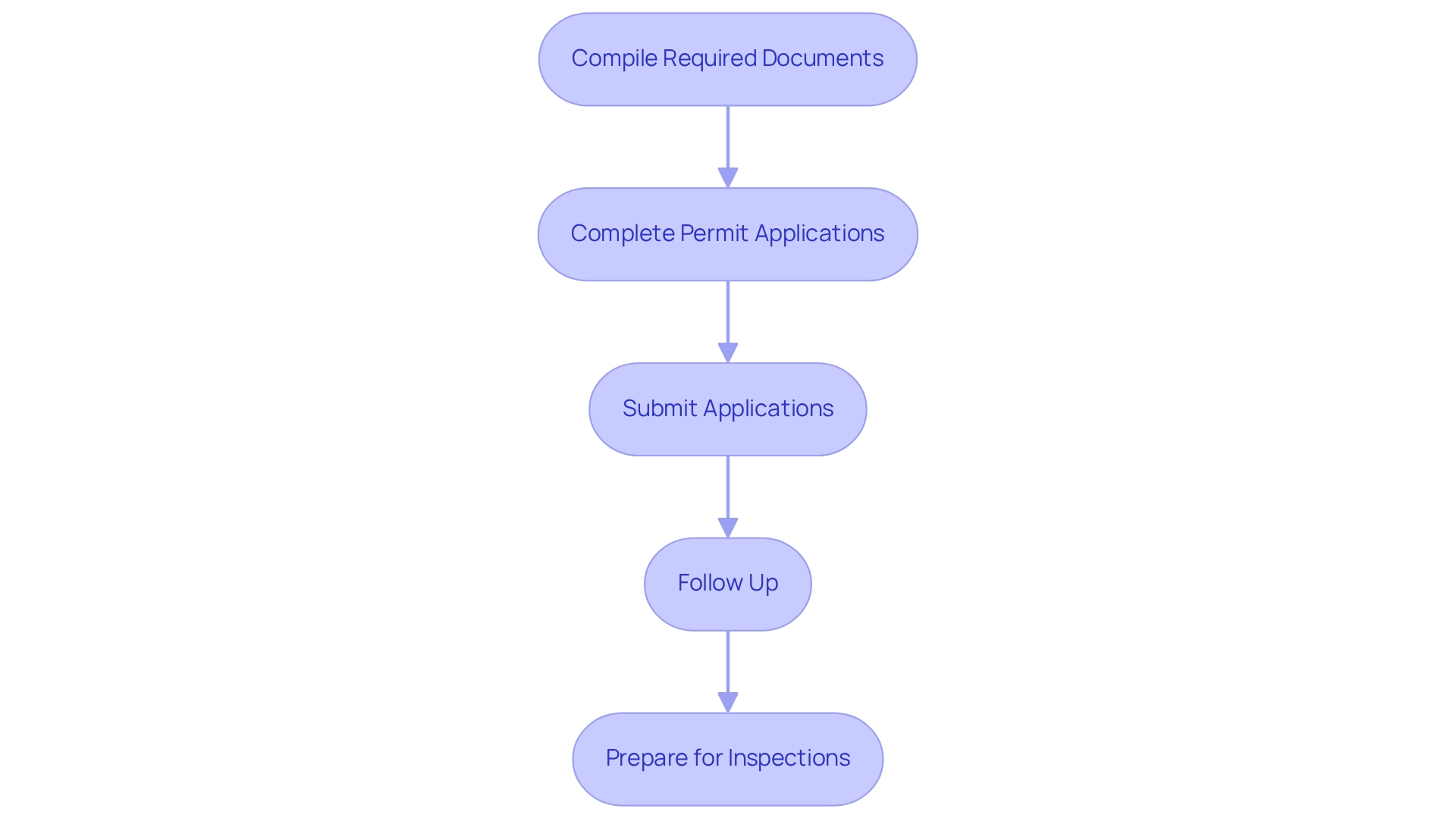
To effectively prepare the necessary documentation and secure permits for your solar farm, it is essential to adhere to the following steps:
-
Compile Required Documents: Assemble all essential documentation, which typically includes:
- Detailed site plans and comprehensive project descriptions.
- Environmental impact assessments to evaluate potential effects.
- Proof of stakeholder engagement to demonstrate community involvement.
- Financial documents that validate project viability and funding.
-
Complete Permit Applications: Accurately fill out all required permit applications. Common permits you may need include:
- Building permits to ensure structural compliance.
- Special use permits, if your project requires deviations from zoning laws.
- Environmental permits to address ecological considerations.
-
Submit Applications: Deliver your completed applications to the appropriate regional authorities. Adhering to submission deadlines and providing any additional information they may request is crucial.
-
Follow Up: After submission, proactively follow up with the permitting office to monitor the status of your applications. Address any questions or concerns they may have to facilitate the review process.
-
Prepare for Inspections: Be prepared for inspections by local authorities. Ensure that your project adheres to all safety regulations and zoning compliance for solar farms before these inspections to prevent delays.
By carefully preparing documentation and obtaining the necessary permits, you can simplify the approval process for your renewable energy farm, focusing on zoning compliance for solar farms. The solar industry is projected to add over 375 GWdc by 2035, with a high case scenario envisioning a 24% increase in total solar installations through 2034, translating to an additional 118 GWdc of capacity. This emphasizes the significance of effective permit acquisition in addressing increasing power requirements. However, challenges such as interconnection delays and an anticipated average annual contraction of 1% over the next decade due to market saturation may impact project timelines, making thorough preparation even more critical. As Preston Lyons aptly states, 'Adopting the hardware for solar energy is the first step towards a greener future.' Including successful case studies of permit acquisition can further illustrate effective strategies in navigating this complex process.
Conclusion
Successfully navigating the regulatory landscape for solar farms is essential for advancing renewable energy projects. Understanding the nuances of zoning compliance—ranging from local land use regulations to stakeholder engagement—establishes a solid foundation for effective project implementation. Key concepts such as zoning districts, permitted uses, and environmental considerations must be thoroughly understood to prevent potential setbacks that could impede project progress.
Engaging with stakeholders early in the process is equally critical. By fostering open communication and addressing community concerns, project developers can build trust and support, which are vital for overcoming opposition. Proactive outreach and collaboration with local organizations can further enhance community acceptance and facilitate smoother project approvals.
Moreover, meticulous preparation of necessary documentation and permits is vital to streamline the approval process. As the solar industry continues to expand, efficient permit acquisition becomes increasingly crucial to meet the growing energy demands. By mastering the intricacies of zoning compliance and engaging effectively with stakeholders, solar energy projects can not only achieve successful implementation but also contribute to a sustainable future. Embracing these strategies is essential for harnessing the full potential of solar energy and driving the transition to a greener economy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is zoning compliance for solar farms?
Zoning compliance for solar farms refers to the adherence to local land use regulations that govern the installation of energy systems, ensuring that projects meet specific requirements based on zoning classifications.
Why are zoning districts important for solar farm installations?
Zoning districts, such as residential, commercial, and agricultural, have specific regulations that can significantly influence the feasibility of renewable energy initiatives, making familiarity with these classifications essential for successful project execution.
What are permitted uses in the context of solar farms?
Permitted uses determine whether renewable energy farms are allowed within a specific zoning district. In some cases, a specific use permit may be needed, which could involve additional scrutiny and community hearings.
What are setback and height restrictions for solar installations?
Setback restrictions refer to the minimum distances that renewable installations must maintain from property lines, while height restrictions dictate the maximum allowable heights. Understanding these regulations is vital to prevent legal disputes and project delays.
What environmental considerations must be taken into account for solar farm installations?
Environmental considerations include awareness of ecological regulations that may impact land use, such as limitations for agricultural purposes and protections for local wildlife habitats, which are crucial for compliance.
How does the growth of renewable energy impact zoning compliance?
The increasing demand for renewable power solutions, as evidenced by the installation of residential photovoltaic systems, underscores the importance of understanding zoning compliance as the sector continues to evolve.
What role does expert insight play in navigating zoning regulations for solar farms?
Expert insights highlight the need for effective navigation of zoning regulations, emphasizing that compliance is critical as the transition to renewable power becomes more economical and widespread.
How can proactive engagement with community regulations benefit solar farm projects?
Proactive engagement with community regulations can lead to smoother project approvals and implementation, facilitating the successful execution of renewable energy projects.
List of Sources
- Understand Zoning Compliance Basics for Solar Farms
- Solar Industry Research Data – SEIA (https://seia.org/research-resources/solar-industry-research-data)
- 20 Quotes To Get You Inspired For a Renewable Future - Solstice (https://solstice.us/solstice-blog/20-quotes-for-a-renewable-future)
- Quotes About Solar Power: 50 Picks to Light Up Your Life - Lumify Energy (https://lumifyenergy.com/blog/quotes-about-solar-power)
- Assess Local Zoning Regulations and Requirements
- Regulating Utility-Scale Solar Projects on Agricultural Land (https://kleinmanenergy.upenn.edu/research/publications/regulating-utility-scale-solar-projects-on-agricultural-land)
- pa.gov (https://pa.gov/agencies/dep/residents/solar-energy-resource-hub/local-government.html)
- Developers (https://pa.gov/agencies/dep/residents/solar-energy-resource-hub/developers.html)
- Engage Stakeholders and Address Conflicting Interests
- Renewable energy and jobs: Annual review 2023 (https://irena.org/Digital-Report/Renewable-energy-and-jobs-Annual-review-2023)
- Prepare Necessary Documentation and Obtain Permits
- Solar Market Insight Report 2024 Year in Review – SEIA (https://seia.org/research-resources/solar-market-insight-report-2024-year-in-review)
- Solar Permit Guide: Requirements & Permitting Checklist (https://permitflow.com/blog/solar-permit)
- Solar Market Insight Report 2023 Year in Review – SEIA (https://seia.org/research-resources/solar-market-insight-report-2023-year-review)




