Introduction
Effective land resource planning and management is essential in today's rapidly changing environmental landscape, where the balance between development and conservation is more critical than ever. This article delves into the fundamental principles that underpin this complex process, exploring key components such as:
- Land use planning
- Natural resource management
- Stakeholder engagement
With the backdrop of global initiatives like the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework, the importance of strategic land management becomes increasingly evident. As professionals navigate the intricate legal and regulatory frameworks, they must also embrace innovative technologies and sustainable practices to foster long-term ecological health.
By integrating community engagement strategies, land resource management can evolve to meet both developmental objectives and the needs of local populations, ensuring that future generations inherit a balanced and thriving environment.
Fundamentals of Land Resource Planning and Management
Land resource planning is a crucial process that systematically evaluates and manages territory to strike a balance between developmental needs and environmental conservation. Essential concepts include:
-
Territory Use Planning: This involves a comprehensive assessment of space to ascertain its optimal applications, considering social, economic, and environmental factors.
The process of land resource planning encompasses zoning regulations, terrain capability assessments, and the identification of areas designated for conservation. For instance, the area of cropland in Africa increased by a third between 2003 and 2019, illustrating significant changes in land use that necessitate careful planning.
-
Natural Asset Management: Emphasizing the sustainable management of natural assets, this aspect focuses on efficient usage while minimizing environmental impacts.
It necessitates a profound understanding of ecosystems, availability of materials, and the consequences of human activities on the environment.
-
Stakeholder Engagement: Successful resource planning hinges on the collaboration among diverse stakeholders, including local communities, governmental bodies, and private developers. Involving these groups guarantees that diverse viewpoints are included in decision-making processes, improving the overall effectiveness of management strategies.
-
Regulatory Frameworks: A thorough understanding of the local, state, and federal regulations governing property use is vital. Familiarity with these legal frameworks enables professionals to navigate compliance requirements effectively during property acquisition and development projects.
In light of recent developments, such as the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework, which aims to conserve at least 30% of terrestrial and marine areas by 2030, land resource planning has become even more imperative. This framework not only tackles biodiversity decline but also mobilizes substantial funding aimed at enhancing land resource planning for sustainable resource use. The '30×30' target specifically emphasizes the need for land resource planning to protect critical ecosystems, reinforcing the importance of integrating conservation goals into usage strategies.
As Bergmann and Holmberg observed in their study, > Terrain in Motion <, land resource planning is essential for promoting ecological health while accommodating growth. Furthermore, the National Land Cover Database (NLCD), developed by the U.S. Geological Survey, acts as an essential tool that offers updated coverage data for informed decision-making in territory policy. By mastering these fundamental principles, professionals can devise effective territory governance strategies that align with sustainability goals while fulfilling project objectives.
Sustainable Practices in Land Resource Management
Incorporating sustainable practices into environmental management is vital for encouraging ecological balance and supporting long-term viability. Key strategies include:
- Ecosystem-Based Management: This comprehensive approach evaluates entire ecosystems rather than isolating individual resources. By prioritizing biodiversity and ecological integrity, it evaluates the interrelations among various uses of terrain and their cumulative effects on the environment. Recent findings from Marzloff et al. (2016) suggest a less than 5% likelihood of transitioning to a barren ecosystem dominated by long-spined sea urchins when target levels of southern rock lobster biomass are maintained, underscoring the necessity of comprehensive oversight.
- Land resource planning: Effective strategies for land use are pivotal for minimizing environmental degradation. This practice advocates for the preservation of green spaces, the protection of wetlands, and the implementation of smart growth principles to mitigate urban sprawl. The successful implementation of these strategies can significantly improve the sustainability of resource use through effective land resource planning, as demonstrated by various planning initiatives across the globe.
- Conservation Techniques: Techniques such as reforestation, habitat restoration, and the establishment of protected areas are crucial for safeguarding biodiversity and natural habitats. These practices not only help counteract the adverse effects of development but also ensure ecosystem resilience. Ongoing research in biodiversity and human dimensions highlights the need for developing effective ecosystem-level reference points, as noted in the case study titled "Biodiversity and Human Dimensions Research," which tracks critical aspects of ecosystems that may be overlooked by other indicators.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in the planning process is essential for promoting stewardship and aligning resource practices with community values and needs. Community input can lead to more effective and widely accepted usage strategies, enhancing overall project success rates.
- Innovative Technologies: The use of advanced technologies, such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and artificial intelligence in property evaluations, significantly enhances the efficiency and precision of resource oversight. These tools facilitate comprehensive data collection, analysis, and visualization, empowering professionals to make informed decisions regarding usage.
As J.B.H. noted in the original draft, collaboration among experts is essential in the field, and by embedding these sustainable practices into resource frameworks, professionals can harmonize developmental objectives with environmental stewardship, ultimately leading to more resilient and sustainable ecosystems.
Integrating Technology in Land Resource Management
Integrating advanced technologies into land resource planning can greatly simplify processes and produce better results. The following key technologies play a pivotal role:
-
Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS technology enables the mapping and analysis of use patterns, environmental features, and zoning regulations.
By offering a visual representation of complex data, GIS enhances land resource planning and supports decision-making. As noted by Zabidullaeva Ranokhan Kenesbaevna,
By leveraging spatial data and analytical tools, GIS enhances decision-making processes, supports sustainable resource use practices, and contributes to the conservation and sustainable development of natural resources on a global scale.
Moreover, numerous open-source GIS data sources, such as the USGS National Map and OpenStreetMap, provide valuable information on property parcels, infrastructure, and environmental factors, which can further support investors in their land resource planning and decision-making.
-
AI-Powered Tools: Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications are transforming title research and property assessments through automation and predictive analytics. These tools not only enhance efficiency but also improve accuracy, ultimately reducing the time required for project completion. Recent statistics indicate that AI applications can streamline assessments by providing data insights that were previously difficult to analyze, with some studies showing efficiency improvements of up to 30% in project timelines.
-
Remote Sensing: Utilizing satellite or aerial imagery, remote sensing technology enables the gathering of data regarding terrain conditions and changes over time. This approach is instrumental in monitoring environmental changes, assessing usage, and planning targeted conservation efforts, which are essential components of effective land resource planning, offering a comprehensive view of dynamics. Unmanned aerial vehicles offer high-resolution imagery of terrain and facilitate detailed inspections and surveys.
Their capability to swiftly and precisely evaluate extensive or distant regions renders them an essential resource in contemporary territory oversight methods.
-
Data Handling Systems: Implementing robust data handling systems improves the organization and accessibility of information concerning usage, titles, and stakeholder engagement. By centralizing data, these systems encourage collaboration and informed decision-making, ultimately supporting effective land resource planning and territory management.
Additionally, GIS software tools are evolving to provide more value and efficient functionality, with advancements in data analysis, visualization, and sharing now being cloud-based and integrating with other software for real-time data. Adopting these technologies enables professionals to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of spatial asset oversight, resulting in better project outcomes and promoting sustainability.
Navigating Legal and Regulatory Challenges
Navigating the complex legal and regulatory challenges in land resource planning necessitates a comprehensive understanding of applicable laws and the implementation of effective compliance strategies. Key considerations include:
-
Understanding Regulatory Frameworks: It is essential to familiarize yourself with the local, state, and federal regulations that govern use, zoning, and environmental protection.
Mastery of this regulatory landscape is crucial for land resource planning, ensuring compliance and preempting potential legal issues. Identifying the permits required for land development is a critical step in the land resource planning process. Understanding application processes and engaging with regulatory bodies at the outset can significantly streamline approvals.
For example, organizations that have effectively navigated permitting processes have demonstrated enhanced project timelines and reduced delays, showcasing the importance of early engagement.
-
Conducting thorough environmental assessments is often mandated by law for projects impacting sensitive ecosystems as part of land resource planning. These assessments are vital in identifying potential environmental impacts and formulating effective mitigation strategies as part of land resource planning, ensuring that projects comply with environmental regulations.
-
Negotiating with Stakeholders: Proficient negotiation skills are essential for managing the diverse interests of stakeholders involved in land resource planning, including government agencies, landowners, and local residents. Building and maintaining positive relationships with these parties can facilitate smoother project execution and enhance community support.
-
Staying Informed: The legal environment concerning territory asset oversight is in a state of constant flux.
Professionals must commit to staying informed about changes in laws and regulations through ongoing education and professional development. This proactive approach can aid in navigating recent legal challenges effectively, especially in land resource planning. By proactively addressing these legal and regulatory aspects, professionals can mitigate risks and ensure a more efficient project implementation process. For instance, organizations that adopt a formal compliance charter can save an average of $520,000, highlighting the financial benefits of rigorous compliance strategies.
Furthermore, with only 18% of organizations currently employing automated processes for reporting and IT risk data collection, there is a significant opportunity for enhancement in compliance practices across the sector. This statistic highlights the necessity for enhanced automation in compliance tracking, which can result in more effective project oversight. As noted by Ayush Saxena, a senior security and compliance writer, understanding the latest trends and emerging technologies is essential in developing relevant and actionable compliance insights.
Additionally, the Stats system's yearly authorization activity reports provide valuable data that allows stakeholders to track the authorization status and effectiveness of RCRA rules, further illustrating the importance of detailed reporting in enhancing compliance tracking.
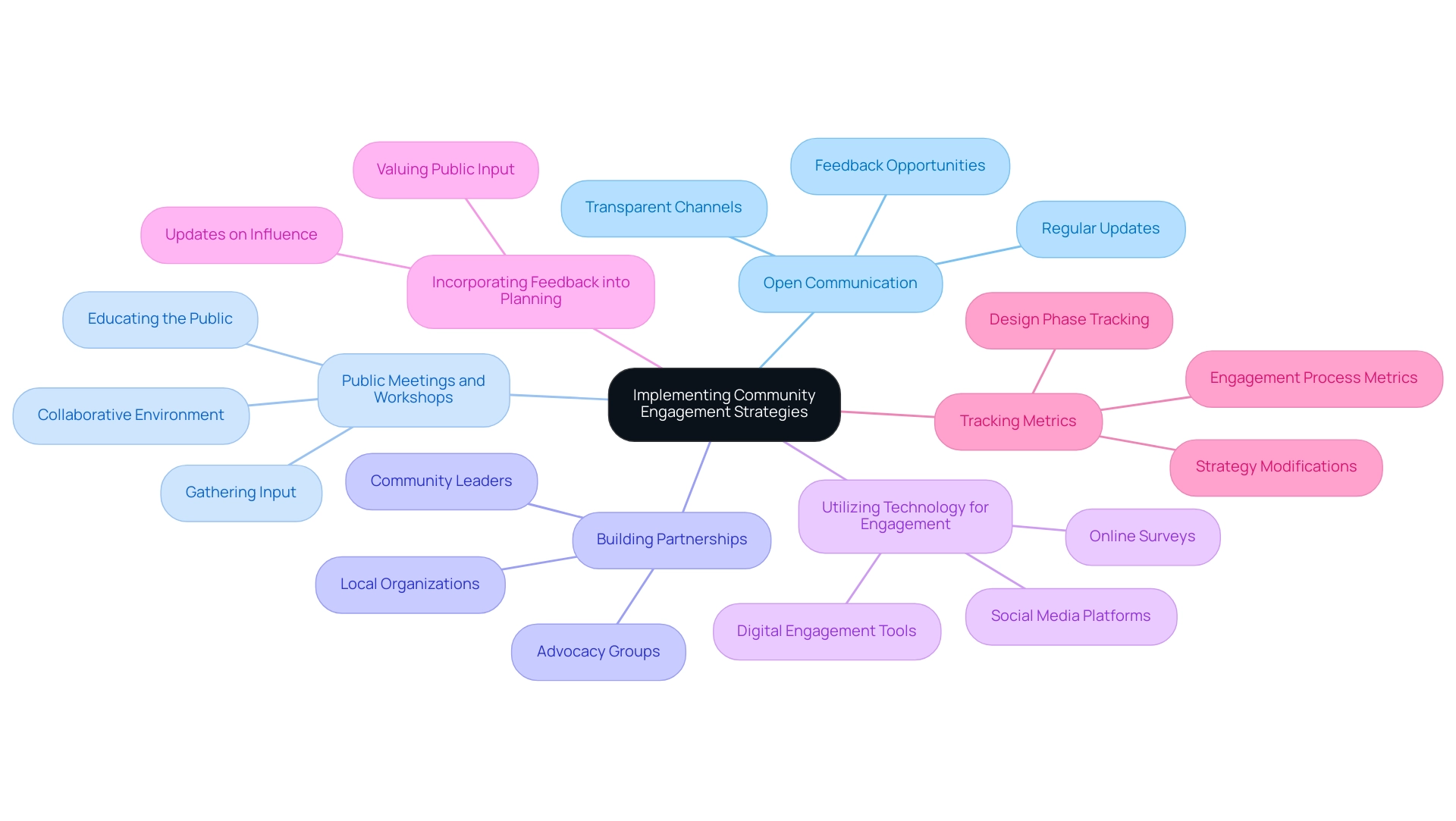
Implementing Community Engagement Strategies
Implementing effective public engagement strategies is crucial for enhancing the success of land resource planning projects. Key strategies include:
- Establishing Open Communication: Creating channels for transparent communication with members of the public is essential. Regular updates and opportunities for feedback not only foster trust but also promote inclusivity, allowing residents to feel invested in the process.
- Public Meetings and Workshops: Organizing public meetings and workshops serves to educate the public about project objectives while gathering valuable input. Such forums encourage active participation and provide a platform for residents to express their concerns and ideas, forging a collaborative environment.
- Building Partnerships: Collaborating with local organizations, advocacy groups, and leaders can significantly enhance outreach efforts and foster local support. These partnerships often result in stronger support for project objectives and increased involvement from various segments of the population.
- Utilizing Technology for Engagement: Leveraging technology, including online surveys and social media platforms, allows for reaching a broader audience and gathering a wider range of perspectives. Digital engagement tools facilitate participation and feedback from members who may be unable to attend in-person events, ensuring inclusivity in the engagement process.
- Incorporating Feedback into Planning: Demonstrating that public input is valued by integrating it into planning decisions can significantly bolster trust and support for projects. Providing updates on how public input has influenced planning outcomes not only maintains engagement but also reinforces the importance of public participation in the process.
- Tracking Metrics: It is vital to track metrics during the design phase and throughout the engagement process. This permits strategy modifications based on public feedback and the effectiveness of engagement efforts, ensuring that the process remains responsive to public needs.
One notable case study exemplifying the effectiveness of these strategies is the research conducted in Zurich, focusing on cycling safety. By involving local residents to gather data, the project led to enhanced safety measures and improved urban planning for cyclists. As Thomas aptly noted, "It changed the relationship with the city."
Thus, prioritizing public involvement allows professionals to create more inclusive and successful land resource planning strategies that genuinely reflect the needs and values of the population. Notably, Maptionnaire was among the Top-50 Teams in the Lee Kuan Yew Global Business Plan Competition, underscoring the importance of effective community engagement in achieving successful outcomes.
Conclusion
Effective land resource planning and management is not merely a necessity but a fundamental pillar for achieving a harmonious balance between development and environmental conservation. The principles outlined in this article emphasize the essential components that contribute to successful land management strategies. From the critical importance of land use planning and natural resource management to the necessity of engaging stakeholders, each element plays a pivotal role in fostering sustainable practices.
The integration of innovative technologies such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and artificial intelligence enhances the efficiency and accuracy of land assessments, while a thorough understanding of legal and regulatory frameworks ensures compliance and mitigates risks. Furthermore, community engagement strategies underscore the value of local input, ultimately leading to more accepted and effective land use initiatives.
In conclusion, as global initiatives like the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework highlight the urgency of protecting our natural ecosystems, the call for strategic land management becomes increasingly pressing. By embracing sustainable practices, utilizing advanced technologies, and prioritizing community involvement, professionals can not only meet developmental goals but also contribute to the preservation of the environment for future generations. The path forward is clear: a commitment to integrated and informed land resource management is essential for cultivating resilient ecosystems and thriving communities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is land resource planning?
Land resource planning is a systematic process that evaluates and manages territory to balance developmental needs with environmental conservation.
What are the key concepts of land resource planning?
The key concepts include Territory Use Planning, Natural Asset Management, Stakeholder Engagement, and Regulatory Frameworks.
What does Territory Use Planning involve?
Territory Use Planning involves assessing space for its optimal applications, considering social, economic, and environmental factors, including zoning regulations and terrain capability assessments.
How has land use changed in Africa?
The area of cropland in Africa increased by a third between 2003 and 2019, indicating significant changes that require careful land resource planning.
What is Natural Asset Management?
Natural Asset Management focuses on the sustainable management of natural resources, emphasizing efficient usage while minimizing environmental impacts.
Why is Stakeholder Engagement important in land resource planning?
Stakeholder Engagement is crucial as it involves collaboration among local communities, governmental bodies, and private developers, ensuring diverse perspectives are included in decision-making.
What role do Regulatory Frameworks play in land resource planning?
Regulatory Frameworks provide the legal guidelines that govern property use, helping professionals navigate compliance during property acquisition and development.
What is the significance of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework?
This framework aims to conserve at least 30% of terrestrial and marine areas by 2030, emphasizing the need for land resource planning to protect critical ecosystems.
How does ecosystem-based management contribute to sustainable practices?
Ecosystem-Based Management evaluates entire ecosystems, prioritizing biodiversity and ecological integrity, and assesses the cumulative effects of various terrain uses on the environment.
What are some conservation techniques mentioned in the article?
Conservation techniques include reforestation, habitat restoration, and establishing protected areas to safeguard biodiversity and natural habitats.
Why is community involvement important in land resource planning?
Community involvement promotes stewardship and aligns resource practices with local values and needs, leading to more effective and accepted usage strategies.
How do innovative technologies enhance resource oversight?
Technologies like Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and artificial intelligence improve the efficiency and precision of property evaluations, enabling informed decision-making.
List of Sources
- Fundamentals of Land Resource Planning and Management
- The emerging global crisis of land use | 02 The state of the world’s land resources (https://chathamhouse.org/2023/11/emerging-global-crisis-land-use/02-state-worlds-land-resources)
- ers.usda.gov (https://ers.usda.gov/about-ers/partnerships/strengthening-statistics-through-the-icars/land-use-and-land-cover-estimates-for-the-united-states)
- Sustainable Practices in Land Resource Management
- A performance measure framework for ecosystem-based management (https://academic.oup.com/icesjms/advance-article/doi/10.1093/icesjms/fsae164/7906164)
- AFS Publications (https://afspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/mcf2.10285)
- Marine ecosystem-based management: challenges remain, yet solutions exist, and progress is occurring - npj Ocean Sustainability (https://nature.com/articles/s44183-024-00041-1)
- Integrating Technology in Land Resource Management
- communitylands.com (https://communitylands.com/communitychronicle/the-role-of-geographic-information-systems-(gis)-in-land-investments)
- id.land (https://id.land/blog/gis-applications-real-world-use-cases-examples)
- Unlocking the Power of GIS for Land Management (https://landgate.com/news/everything-you-need-to-know-about-gis)
- THE USE OF GIS TECHNOLOGIES IN THE MANAGEMENT AND MONITORING OF LAND RESOURCES (https://researchgate.net/publication/378984827_THE_USE_OF_GIS_TECHNOLOGIES_IN_THE_MANAGEMENT_AND_MONITORING_OF_LAND_RESOURCES)
- Navigating Legal and Regulatory Challenges
- 100+ Compliance Statistics You Should Know (https://sprinto.com/blog/compliance-statistics)
- epa.gov (https://epa.gov/rcra/state-authorization-tracking-system-stats)
- Implementing Community Engagement Strategies
- How to Measure Community Engagement and Its Impact with KPIs (https://maptionnaire.com/blog/measure-community-engagement-impact-with-metrics)
- nar.realtor (https://nar.realtor/on-common-ground/the-importance-of-community-engagement-in-zoning-reform)




