Overview
Microgrid energy storage solutions significantly enhance resilience and sustainability compared to traditional energy storage systems, which are primarily centralized and reliant on fossil fuels. Microgrids can seamlessly integrate renewable sources and operate independently during outages. In contrast, traditional systems, although cost-effective and built on established technologies, lack the adaptability and environmental advantages that microgrid solutions offer.
Introduction
As the world transitions to a more sustainable energy future, the debate surrounding microgrid energy storage versus traditional energy storage systems has gained significant relevance. Microgrids, capable of harnessing renewable resources and functioning independently from the main grid, offer a compelling alternative to conventional centralized systems that frequently depend on fossil fuels. This article explores the intricate details of both approaches, examining their respective advantages and disadvantages, as well as the scenarios in which each excels.
With rapid technological advancements transforming the energy storage landscape, grasping these options is essential for making informed decisions that meet modern energy demands and align with environmental objectives.
Understanding Microgrid Energy Storage and Traditional Energy Storage
Microgrid power reserves represent localized networks capable of operating autonomously or in conjunction with the primary grid. These systems typically integrate renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, and utilize advanced battery technologies, which are part of microgrid energy storage solutions, to store excess power for future utilization. In contrast, traditional power retention frameworks are predominantly centralized, relying on conventional energy sources like fossil fuels to generate and store electricity. Such conventional setups often include large-scale battery installations or pumped hydro facilities, designed to enhance grid stability and meet peak demand. The key distinction lies in the operational flexibility and sustainability offered by microgrid energy storage solutions, which enhance power resilience and reduce reliance on centralized power generation.
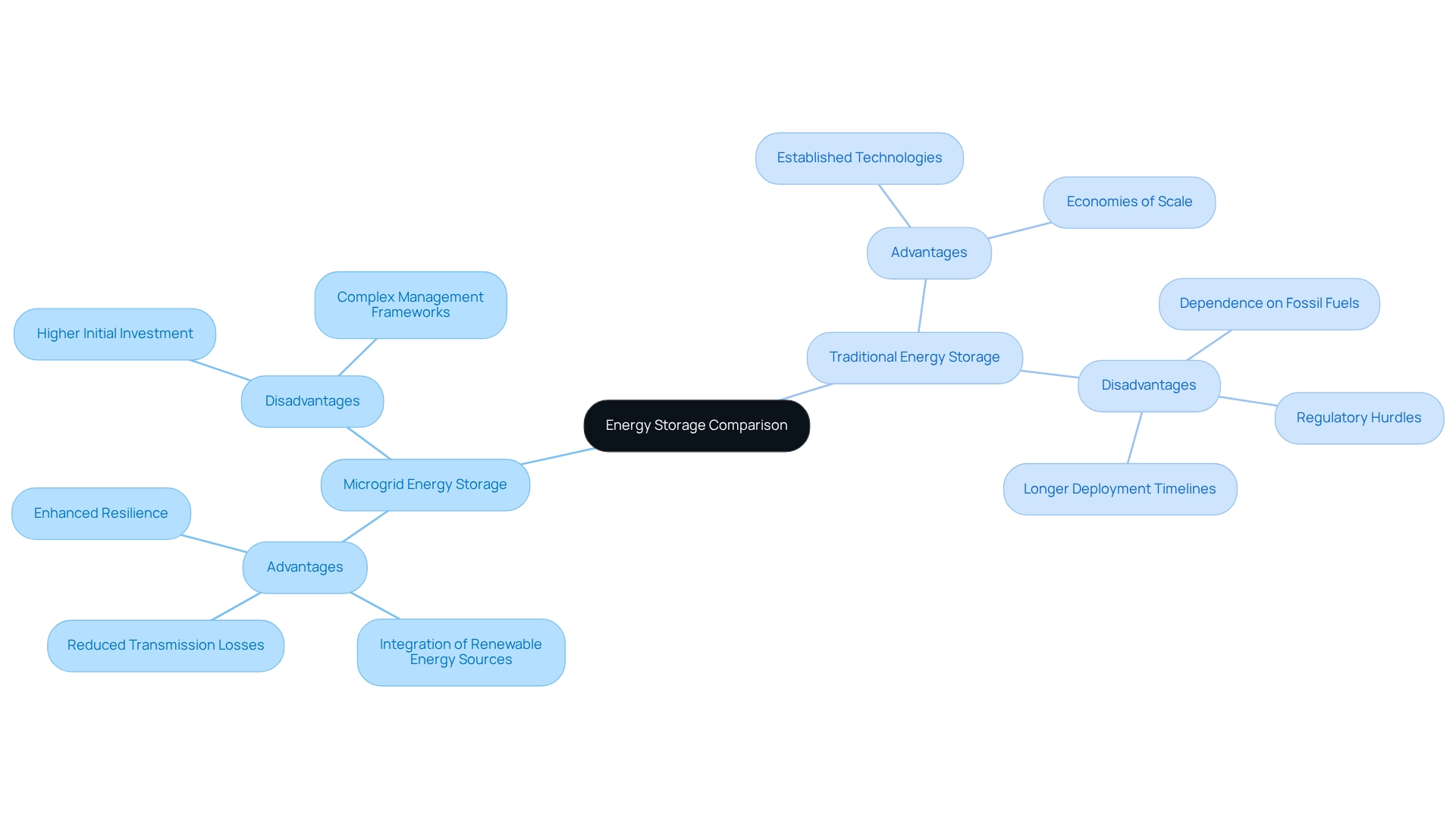
Comparing Advantages and Disadvantages of Microgrid and Traditional Energy Storage
Microgrid energy storage solutions offer significant advantages, including:
- Enhanced resilience
- The ability to integrate renewable energy sources
- Reduced transmission losses through localized generation
They can function independently during grid outages, ensuring critical power supply to essential services. However, these systems may necessitate higher initial investments and complex management frameworks.
In contrast, traditional power retention methods benefit from:
- Established technologies
- Economies of scale
This makes them more cost-effective for large-scale applications. Yet, they often lack the adaptability and sustainability that microgrid energy storage solutions offer, as they typically depend on fossil fuels and centralized generation. Furthermore, conventional frameworks may face regulatory hurdles and longer deployment timelines compared to the more versatile microgrid energy storage solutions.
As we navigate the evolving energy landscape, the choice between these options becomes increasingly crucial for stakeholders.
Evaluating Applications: When to Choose Microgrid vs. Traditional Energy Storage
Microgrid energy storage solutions provide significant advantages in scenarios where power resilience is crucial, such as in isolated communities, military installations, or disaster-prone regions. These networks provide reliable power during outages, fostering local autonomy in energy generation. In contrast, conventional power retention systems are often better suited for large-scale applications, such as utility-scale power retention projects that require substantial capacity and cost-effectiveness. They excel in balancing supply and demand on the grid and facilitating large-scale integration of renewable resources. Ultimately, the choice between microgrid and conventional power preservation depends on factors like project size, location, regulatory considerations, and specific power requirements.
Technological Innovations in Energy Storage Solutions
Recent advancements in power storage technologies are revolutionizing microgrid energy storage solutions. Innovations such as solid-state and flow batteries are leading the way, delivering greater power densities and extended lifespans that enhance the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of microgrid energy storage solutions. The integration of AI and machine learning into power management systems is particularly noteworthy, as it optimizes resource usage and enables predictive maintenance, significantly improving the reliability of these systems. Furthermore, traditional power storage solutions are also progressing, benefiting from enhanced grid management software and improved battery recycling processes that foster sustainability.
For instance, the optimization model utilized by Advanced Microgrid Solutions (AMS) incorporates approximately 600,000 variables, which boosts the efficiency of microgrid operations by allowing for more precise management of power resources. This model not only reduces electric bills but also fulfills utility capacity obligations, adding redundancy to the electrical power grid without necessitating additional generation capacity. Andrew Martinez, a member of the Data Science and Optimization Team at AMS, remarked, "During this 40-minute recording, featuring AMS, we focus on how AMS integrates Gurobi into their software solutions." This integration of cutting-edge technology underscores the transformative potential of these innovations in the power sector.
As these technologies advance, microgrid energy storage solutions are set to play a vital role in the future framework of power preservation, impacting both microgrid and traditional applications. Overall, while advanced energy storage solutions present substantial benefits, traditional systems are also evolving, underscoring the necessity for continuous innovation in this field.
Conclusion
The evolving discourse surrounding microgrid energy storage and traditional energy storage systems highlights the substantial transformations within the energy landscape. Microgrids offer a sustainable and flexible alternative, leveraging renewable resources to deliver autonomous energy solutions that bolster resilience, especially in vulnerable regions. Their capability to function independently from the main grid during outages renders them essential in specific scenarios, despite potential challenges related to initial investments and operational complexity.
In contrast, traditional energy storage systems maintain a critical role, particularly in large-scale applications where established technologies and cost-effectiveness are crucial. Their capacity to balance supply and demand on the grid remains vital, even as they face regulatory hurdles and an ongoing reliance on fossil fuels.
As technological innovations continue to arise, both microgrid and traditional systems are advancing, enhancing efficiency and sustainability within the energy sector. The integration of cutting-edge storage technologies and AI-driven management systems is transforming operational capabilities, ensuring that both approaches can adapt to the evolving energy demands of the future.
Ultimately, the decision between microgrid and traditional energy storage systems depends on specific project requirements, including size, location, and energy needs. Embracing these advancements is essential for facilitating the transition toward a more sustainable energy future, where both microgrids and traditional systems can coexist and complement each other in addressing diverse energy challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are microgrid power reserves?
Microgrid power reserves are localized networks that can operate independently or in conjunction with the primary grid, integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
How do microgrids utilize energy storage?
Microgrids utilize advanced battery technologies to store excess power generated from renewable sources for future use.
What is the main difference between microgrid energy storage solutions and traditional power retention frameworks?
The main difference is that microgrid energy storage solutions offer greater operational flexibility and sustainability, while traditional frameworks are predominantly centralized and rely on conventional energy sources like fossil fuels.
What types of energy sources do traditional power retention frameworks use?
Traditional power retention frameworks primarily use conventional energy sources such as fossil fuels to generate and store electricity.
How do traditional setups enhance grid stability?
Traditional setups enhance grid stability through large-scale battery installations or pumped hydro facilities designed to meet peak demand.
What benefits do microgrid energy storage solutions provide?
Microgrid energy storage solutions enhance power resilience and reduce reliance on centralized power generation.
List of Sources
- Technological Innovations in Energy Storage Solutions
- Advanced Microgrid Solutions: Reducing Customer Electric Bills - Gurobi Optimization (https://gurobi.com/case_studies/advanced-microgrid-solutions)




