Overview
Proven strategies for success in agricultural land restoration emphasize the implementation of effective practices such as:
- Reforestation
- Cover cropping
- Agroecology
These methods not only enhance biodiversity but also improve soil health and increase productivity. The article elaborates on various restoration techniques, underscores the importance of strategic planning, and highlights the necessity for stakeholder engagement. Together, these elements are crucial for achieving sustainable ecological and agricultural outcomes.
Introduction
In an era where environmental degradation significantly threatens food security and ecological health, the necessity of agricultural land restoration is paramount. Climate change, urbanization, and unsustainable farming practices are wreaking havoc on our ecosystems, making the restoration of degraded lands a critical solution to rejuvenate their productivity and ecological functions.
With nearly one-third of global soils compromised, the urgency for effective restoration practices is increasingly pressing. This article examines the multifaceted dimensions of agricultural land restoration, highlighting its benefits, diverse methodologies, and the strategic planning essential for successful implementation.
By emphasizing the co-benefits that extend beyond mere productivity, it underscores the indispensable role of stakeholder collaboration and engagement in cultivating a sustainable future for both agriculture and the environment.
Understanding Agricultural Land Restoration: Importance and Relevance
Agricultural land restoration is a crucial process dedicated to rehabilitating degraded terrains, thereby reviving their ecological functions and productivity. The urgency of this approach has intensified due to escalating pressures from climate change, urbanization, and unsustainable farming techniques, all of which have significantly contributed to soil degradation. According to the USDA TOTAL survey, approximately 33% of global soils are degraded, posing a serious threat to food security and adversely affecting agricultural output and livelihoods. Agricultural land restoration not only enhances food security but also plays a vital role in biodiversity conservation and carbon sequestration.
For instance, regenerative agriculture methods, although still limited in adoption, have demonstrated promise in enhancing soil health and increasing carbon storage. A case study in Minnesota revealed the challenges farmers face in transitioning to sustainable practices, showing that while some have embraced regenerative methods, conventional farming remains predominant. This situation underscores the necessity for broader assistance and education regarding the advantages of sustainable agriculture, as many farmers continue to encounter obstacles in adopting these methods.
The ecological benefits of soil recovery are substantial. Experts emphasize that rehabilitating degraded areas can lead to improved water quality and enhanced ecosystem services, which are essential for sustaining farming productivity. Moreover, efforts directed at soil recovery can significantly mitigate the effects of climate change, with research indicating that successful recovery could reduce farming greenhouse gas emissions by as much as 6%.
A report from the World Economic Forum suggests that if farmers receive support to adopt climate-smart practices, it could yield considerable environmental benefits.
Given these advantages, it is imperative for stakeholders—including farmers, policymakers, and environmental advocates—to recognize the diverse benefits of soil improvement initiatives. By prioritizing agricultural land restoration, we can foster a more sustainable future that not only addresses immediate food security challenges but also contributes to long-term ecological well-being and resilience. Furthermore, the upcoming article on the loss of territory in US farms will delve deeper into the challenges and implications of land usage, reinforcing the necessity for proactive measures in resource management.
Exploring Different Types of Agricultural Land Restoration Practices
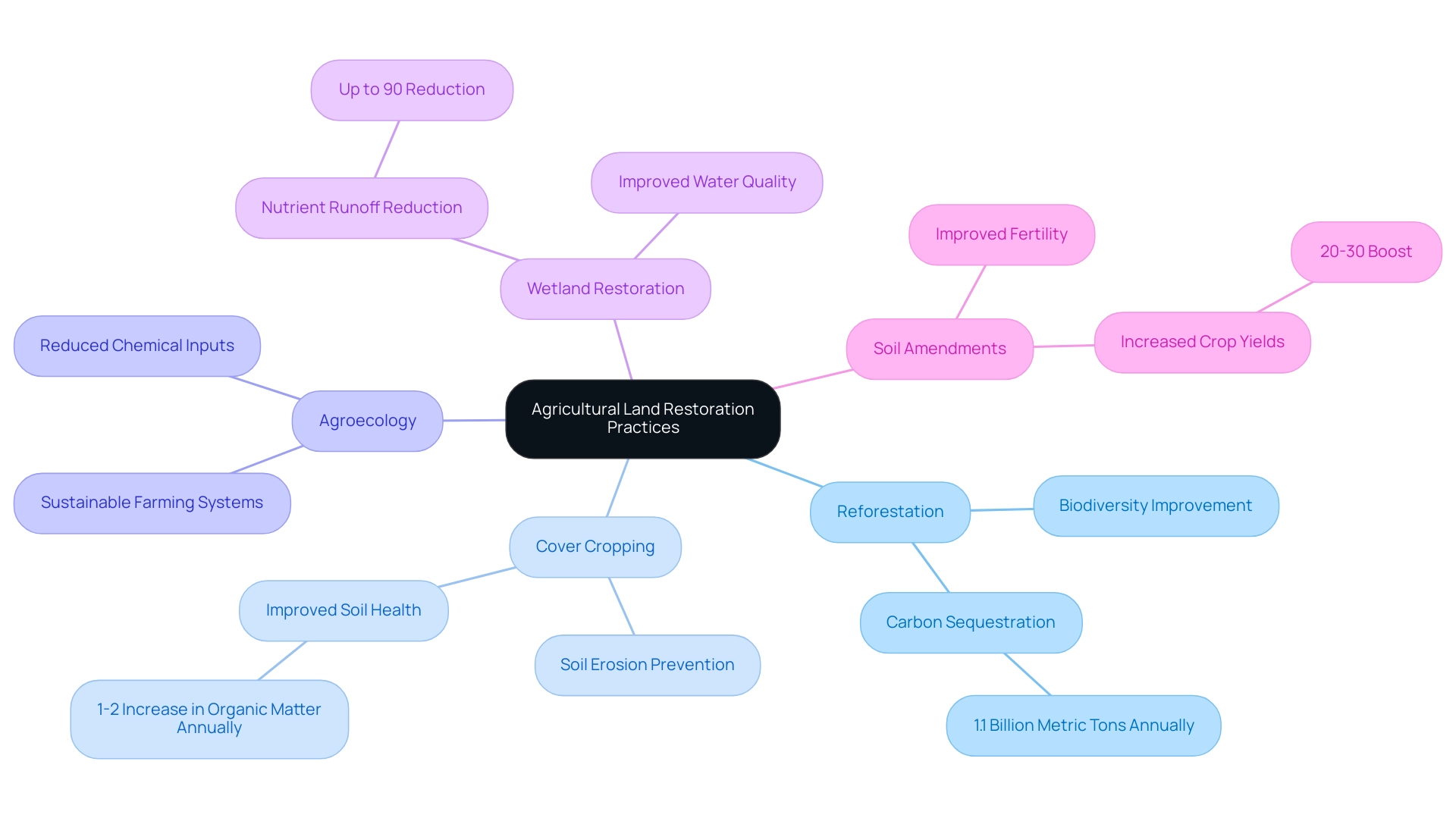
The process of agricultural land restoration encompasses a variety of effective methods tailored to specific environmental contexts and restoration goals. These methods are widely recognized for their positive impact:
- Reforestation: This practice involves planting trees to restore forest cover, which not only improves biodiversity but also significantly enhances carbon sequestration. Recent statistics indicate that reforestation can sequester up to 1.1 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide annually, underscoring its effectiveness in combating climate change. Furthermore, regenerative agriculture promotes biodiversity by creating habitat corridors and reducing chemical inputs, contrasting with the habitat destruction caused by conventional farming.
- Cover Cropping: Utilizing cover crops is essential for preventing soil erosion, improving soil health, and enhancing nutrient cycling. Successful examples of cover cropping have demonstrated that these crops can enhance soil organic matter by 1-2% annually, resulting in improved farming productivity and resilience.
- Agroecology: By applying ecological principles in farming methods, agroecology establishes sustainable systems that imitate natural ecosystems. This approach not only boosts biodiversity but also promotes soil health and reduces dependency on chemical inputs, aligning with the principles of regenerative agriculture.
- Wetland Restoration: Rehabilitating wetlands plays a crucial role in improving water quality, providing wildlife habitat, and enhancing flood resilience. Studies have demonstrated that restored wetlands can reduce nutrient runoff by up to 90%, making them vital for ecosystem health.
- Soil Amendments: Adding organic matter or nutrients to the soil improves fertility and structure, facilitating better crop growth. The use of compost or biochar has been demonstrated to boost crop yields by 20-30%, emphasizing the significance of soil health in farming productivity.
These methods can be adjusted according to regional circumstances and particular recovery goals, ensuring that agricultural land restoration is both efficient and sustainable. As recovery specialist Robin Chazdon emphasizes, "It is important to recognize that the costs of not repairing ecosystems will be substantially higher than the costs of taking effective actions now." Furthermore, the Tenure, Ownership, and Transition of Property (TOTAL) survey offers essential information regarding ownership and its effects on farming area renewal, emphasizing the necessity for sustainable approaches amid ongoing environmental challenges.
Regenerative agriculture is increasingly recognized as a sustainable food production method that regenerates ecosystems and ensures food security, contrasting with conventional farming practices.
Strategic Planning for Successful Agricultural Land Restoration
Successful agricultural land restoration demands meticulous strategic planning. Key steps are essential:
- Assessment of Current Conditions: A thorough evaluation of soil health, vegetation, and hydrology is crucial to establish baseline conditions. This evaluation guides future choices and plans, ensuring that recovery efforts are grounded in the realities of the land.
- Setting Clear Objectives: Defining specific, measurable goals for recovery is vital. Objectives may include enhancing biodiversity, improving soil health, or increasing crop yields. Clear targets steer the planning process and facilitate success measurement.
- Engaging Stakeholders: Involving local communities, farmers, and other stakeholders in the planning process is essential. Their insights and needs must be integrated to foster a sense of ownership and ensure that recovery efforts remain relevant and effective. Effective stakeholder involvement has been shown to significantly improve project outcomes, aligning renewal goals with community interests.
- Resource Allocation: Identifying and securing necessary resources—such as funding, labor, and materials—is critical for executing recovery activities. Strategic planning should encompass a detailed budget and resource management plan to ensure that all project aspects receive adequate support. Local authorities should also quantify the farming system's economic contributions to guide development strategies and investments.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Establishing success metrics and a framework for ongoing monitoring is imperative. This enables stakeholders to continuously evaluate the effectiveness of recovery efforts and make necessary adjustments. Regular evaluation not only tracks progress but also informs future planning and resource allocation.
The rising demand for timber, projected to increase by 54% from 2010 to 2050, underscores the importance of sustainable land use in the recovery of agricultural areas. By adhering to these steps, stakeholders can formulate a robust plan that significantly enhances the likelihood of successful agricultural land restoration, ultimately supporting biodiversity conservation and carbon sequestration efforts. The holistic approach of Produce-Protect-Reduce-Restore exemplifies how strategic planning can tackle pressing global challenges, such as climate change and biodiversity loss, while promoting sustainable resource use.
As the Sustainable Agriculture Network indicates, "SAN’s mission and delivery is considered and carried out through the perspective of the SDGs," emphasizing the connection of recovery efforts with sustainable development goals. Furthermore, the ON TO 2050 plan highlights successful strategies for resource preservation, emphasizing infill and reinvestment in existing neighborhoods to sustain ecosystem functions and support local economies.
Site Assessment and Evaluation: Key Steps in Restoration
Site assessment stands as a cornerstone in the process of agricultural land restoration, encompassing several critical components that collectively inform effective strategies:
- Soil Analysis: Comprehensive testing of soil composition, pH levels, and nutrient availability is essential. Understanding these elements is crucial for assessing the area's suitability for different crops and rehabilitation methods. Recent statistics from the TOTAL survey indicate that effective soil analysis can increase crop yields by up to 30%, underscoring its pivotal role in recovery efforts.
- Vegetation Surveys: Thorough surveys to identify existing plant species and assess their health are vital. This information guides decisions on replanting and enhancing biodiversity. For instance, a case study from the Farmland Information Center illustrates how targeted vegetation surveys led to a 25% increase in native plant diversity in restored areas, demonstrating the impact of informed replanting strategies.
- Hydrological Assessment: Assessing water availability and drainage patterns is essential to ensure that revitalization methods align with the area's hydrological dynamics. Effective hydrological evaluations can prevent waterlogging and promote optimal growth conditions, thereby enhancing recovery success rates.
- Historical Use Review: Analyzing previous usage practices offers insights into potential challenges and opportunities for recovery. Understanding the historical context enables stakeholders to customize their strategies, mitigating risks associated with prior degradation.
Furthermore, the Purchase of Agricultural Conservation Easement (PACE) Programs exemplify how financial incentives can aid in preserving and rehabilitating natural resources. These programs reimburse property owners for limiting future usage, thereby ensuring the preservation of farmland for generations to come.
Julia Freedgood from the American Farmland Trust remarked, "Our Agricultural Protection Scorecard evaluated six policy tools typically employed to safeguard farmland, support agricultural viability, and ensure access to property," emphasizing the significance of policy in ecological recovery.
By conducting a thorough site evaluation, stakeholders can formulate focused recovery strategies for agricultural land restoration that not only address specific environmental conditions but also significantly enhance the overall efficiency of their recovery initiatives. This methodical approach is essential for fostering sustainable resource use and promoting biodiversity, ultimately contributing to carbon sequestration goals. Moreover, the updates organized by Verra, with technical contributions from TerraCarbon LLC and Viresco Solutions, highlight the importance of specialized teamwork in advancing land rehabilitation methods.
Effective Site Management and Monitoring for Sustainable Outcomes
The success of agricultural land restoration activities is fundamentally dependent on robust site management and diligent monitoring, which are essential for achieving long-term sustainability. Regular monitoring through systematic assessments of soil health, vegetation growth, and ecosystem functions is vital. These periodic evaluations not only track progress but also facilitate the early identification of potential issues, ensuring timely interventions.
Flexibility in management practices is crucial. By being responsive to monitoring results and changing environmental conditions, stakeholders can optimize recovery efforts and enhance resilience. Engaging local communities in monitoring initiatives fosters a sense of stewardship and ensures that recovery objectives align with community needs. This collaborative approach can significantly enhance the effectiveness of restoration projects.
Moreover, adopting sustainable agricultural methods, such as crop rotation, reduced tillage, and the use of organic amendments, is essential for maintaining soil health and productivity. These methods not only support biodiversity but also aid in carbon sequestration, addressing broader environmental goals.
The significance of monitoring in ecosystem restoration cannot be overstated. In 2025, it is anticipated that over 13 million U.S. households will depend on private wells for drinking water, highlighting the necessity for effective resource management practices that safeguard water quality and encourage ecological health. Successful case studies, like the USDA National Water Quality Initiative, illustrate how collaborative efforts can result in significant enhancements in water quality and ecosystem resilience.
Furthermore, there is an urgent need for researchers to evaluate the role of Pals in the terrestrial carbon cycle, as emphasized by Stephen M. Bell, who stated, "Without this information, Pals will continue to be just another uncertain and ultimately misused piece of the sustainable resource management puzzle." By prioritizing effective site management and monitoring, stakeholders can significantly enhance the sustainability and productivity of agricultural land restoration. Identifying suitable locations for recarbonizing Pals can assist decision-makers in balancing various resource management needs and promoting sustainable practices.
Co-Benefits of Agricultural Land Restoration: Beyond Productivity
Agricultural land restoration presents a multitude of co-benefits that extend well beyond mere productivity, significantly impacting ecological and community well-being. These advantages include:
- Biodiversity Enhancement: Restoration initiatives can lead to a remarkable increase in species diversity, fostering healthier ecosystems. Recent statistics reveal that effective ecosystem rehabilitation can enhance biodiversity by up to 30% in specific regions, creating habitats that support a broader range of flora and fauna.
- Carbon Sequestration: The revival of healthy soils and vegetation is crucial for capturing and storing carbon, thereby mitigating climate change impacts. Research indicates that agricultural land restoration in rehabilitated farming areas can sequester approximately 1.1 billion tons of CO2 annually, playing a pivotal role in global carbon reduction objectives. Furthermore, the availability of biomass feedstock for bioenergy production, estimated at 50%, underscores the potential of agricultural land restoration as a co-benefit of bioenergy.
- Water Quality Improvement: Implementing rehabilitation practices can significantly reduce runoff and enhance water filtration, resulting in cleaner local water bodies. For example, projects aimed at restoring wetlands have shown a 50% reduction in nutrient runoff, which is essential for maintaining aquatic ecosystems.
Agricultural land restoration also aids local communities in achieving sustainable livelihoods and bolstering food security, thereby enhancing community resilience. Evidence from various case studies indicates that communities engaged in agricultural land restoration activities experience a 20% increase in farming productivity, directly supporting local economies. Additionally, the economic implications of GHG pricing on producers imply that carbon sequestration alternatives can influence farming productivity and food prices, making recovery efforts even more crucial.
Recognizing these co-benefits empowers stakeholders to advocate more effectively for agricultural land restoration initiatives, facilitating the acquisition of necessary funding and support. As illustrated by the European Union's ambitious goal to increase organic farmland to 25% by 2030, such initiatives aim not only to enhance biodiversity but also to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainable agricultural practices. This holistic approach emphasizes the importance of integrating biodiversity and carbon sequestration strategies into environmental recovery efforts, ensuring a resilient and sustainable future.
As Esther Boere noted, "All authors provided feedback and contributed to the discussion and interpretation of the results," highlighting the collaborative nature of these efforts and the significance of stakeholder engagement.
Challenges and Limitations in Agricultural Land Restoration
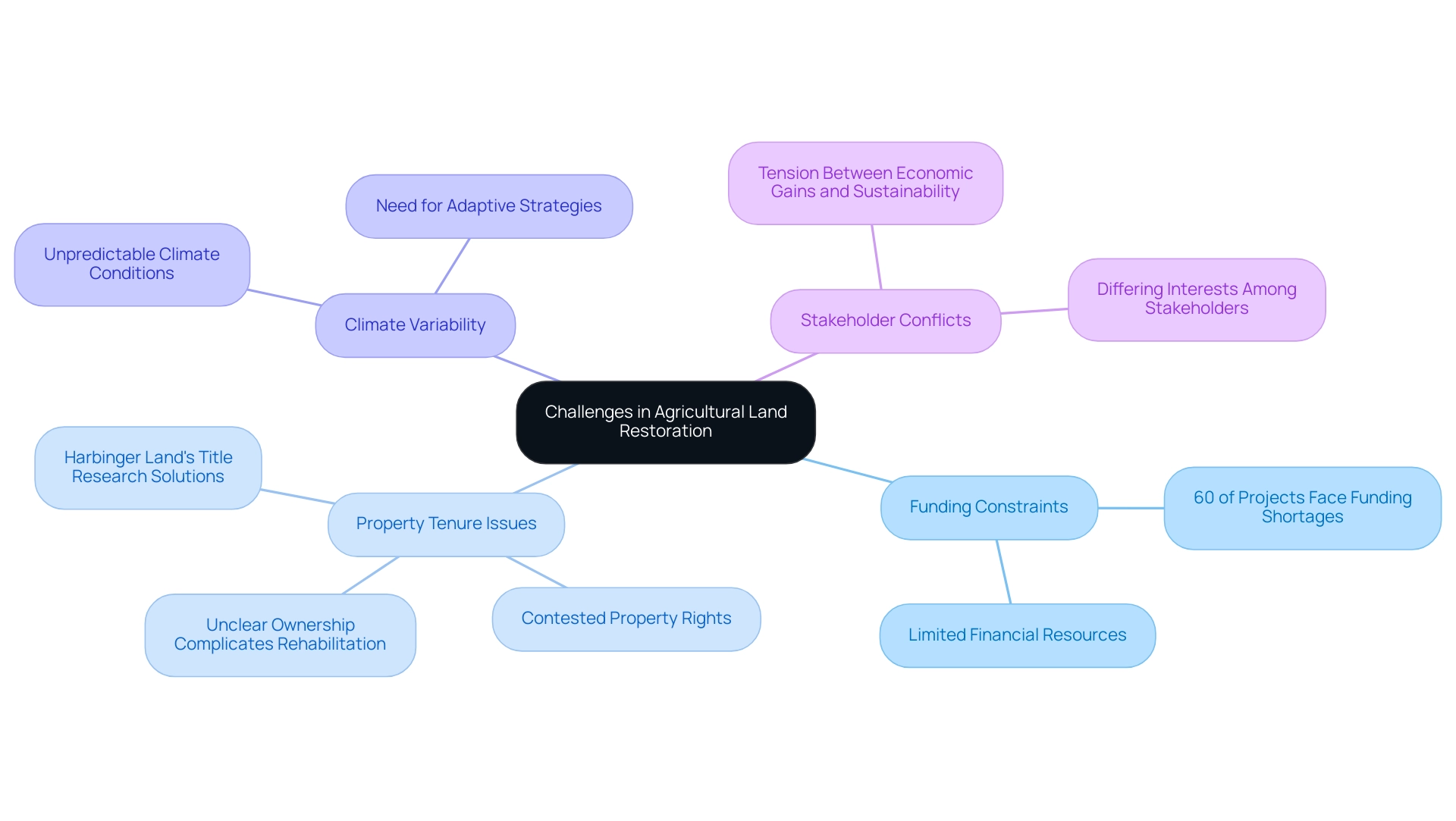
Agricultural land restoration presents numerous advantages, yet it is not devoid of challenges. Key obstacles include:
- Funding Constraints: A significant barrier to the implementation of renewal projects is the limited financial resources available. In 2025, it was reported that nearly 60% of rehabilitation initiatives faced funding shortages, directly impacting their viability and effectiveness.
- Property Tenure Issues: Unclear ownership complicates rehabilitation efforts, creating uncertainty that deters investment. This challenge is particularly pronounced in regions where property rights are contested, resulting in delays and diminished participation from potential stakeholders. Harbinger Land's advanced title research solutions can clarify land ownership, instilling the confidence necessary for stakeholders to invest in renewal projects.
- Climate Variability: The unpredictability of climate conditions presents a challenge to the success of renewal practices. As climate patterns shift, adaptive strategies become essential to ensure recovery efforts remain effective and resilient.
- Stakeholder Conflicts: Differing interests among stakeholders can lead to conflicts that impede progress. For instance, farming producers may prioritize short-term economic gains over long-term sustainability, creating tension with conservationists advocating for ecological balance.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for enhancing the prospects of successful recovery through agricultural land restoration. The global space squeeze challenge necessitates urgent action from governments, the private sector, and civil society to ensure sustainable resource use. Furthermore, only 28% of U.S. inhabitants frequently hear about climate change in the media, underscoring the need for increased awareness regarding farming area recovery challenges.
A practical example of overcoming these challenges can be observed in the case study on changing dietary habits, which illustrates how promoting a transition from high meat consumption to plant-based diets can significantly reduce the area impact associated with food production. By advocating for plant-based alternatives, we can alleviate the environmental impacts of agriculture and support sustainable soil use. Additionally, integrating technological innovations, such as Harbinger Land's GIS mapping services, financing, and governance, is vital to effectively address the global space squeeze.
Harbinger Land's GIS mapping services provide clients enhanced visibility into all aspects of a project or portfolio through various data visualizations, including heat maps and interactive dashboards, facilitating more efficient decision-making. As Dana Nuccitelli noted, while the food system is at a 'breaking point,' sustainable solutions are within reach, highlighting the urgency for immediate action and innovative approaches to surmount these barriers.
Collaboration and Stakeholder Engagement: Keys to Successful Restoration
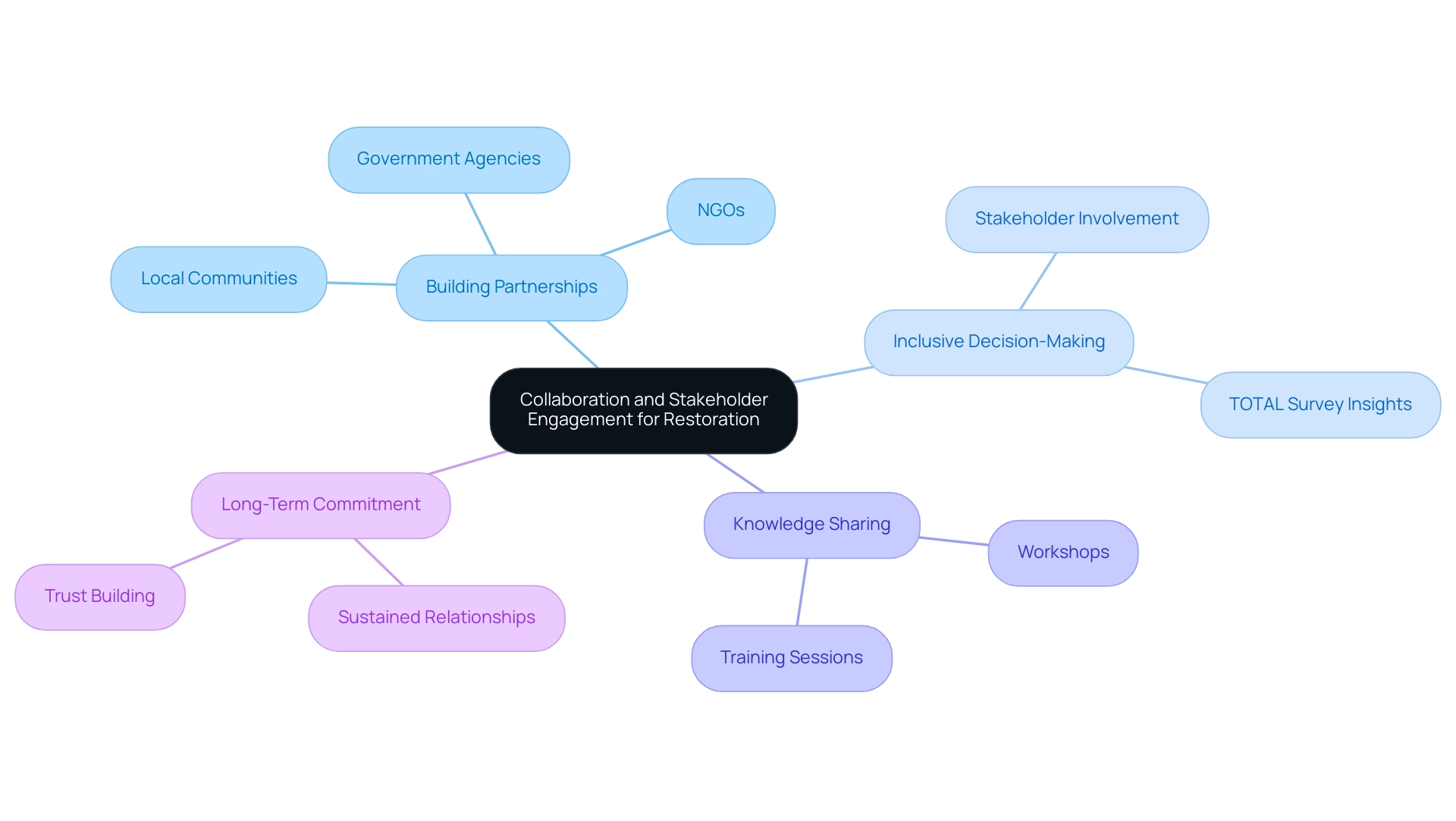
Collaboration and stakeholder engagement are pivotal to the success of agricultural land restoration initiatives. Effective strategies for fostering these elements include:
- Building Partnerships: Establishing alliances with local communities, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and government agencies allows for the pooling of resources and expertise, enhancing the overall impact of restoration efforts. The Census of Agriculture data is utilized by various stakeholders, including agribusinesses and community planners, to inform their decision-making processes in these partnerships.
- Inclusive Decision-Making: Actively involving stakeholders in both the planning and implementation phases ensures that diverse perspectives and needs are integrated into the recovery process, leading to more tailored and effective outcomes. The Tenure, Ownership, and Transition of Agricultural Land (TOTAL) survey provides valuable insights into land ownership dynamics, which can influence stakeholder engagement strategies.
- Knowledge Sharing: Organizing workshops and training sessions facilitates the exchange of best practices and lessons learned among stakeholders, promoting a culture of continuous improvement and innovation in recovery techniques.
- Long-Term Commitment: Developing sustained relationships with stakeholders is crucial for maintaining support for recovery initiatives over time. This commitment fosters trust and encourages ongoing collaboration.
Recent statistics indicate that effective stakeholder engagement can significantly enhance recovery outcomes, with studies showing that projects involving diverse stakeholder input are 30% more likely to achieve their ecological goals. Moreover, success stories from different areas demonstrate how joint efforts have resulted in remarkable enhancements in ecological health and biodiversity. For instance, a case study titled "The Case for Global Adoption of Regenerative Agriculture" highlights how community-driven initiatives have not only restored ecosystems but also bolstered local economies and ensured food security.
As Joseph D'Souza, founder of ElectroIQ, noted, "According to Regenerative Agriculture Statistics 2023, consumers in the UK said more extraordinary biodiversity is the leading benefit of regenerative farming." This viewpoint highlights the significance of biodiversity in recovery initiatives.
By prioritizing collaboration and engagement, stakeholders can significantly enhance the effectiveness and sustainability of agricultural land restoration initiatives, ensuring that these efforts contribute positively to biodiversity and carbon sequestration goals.
Conclusion
Restoring agricultural lands is not merely an environmental imperative; it is a multifaceted solution that addresses food security, biodiversity, and climate resilience. The alarming degradation of global soils underscores the urgent need for effective restoration practices. Various methodologies—such as reforestation, cover cropping, and agroecology—enable stakeholders to enhance soil health, boost productivity, and foster thriving ecosystems.
Strategic planning is crucial for successful restoration. This involves thorough assessments, clear objectives, and active stakeholder engagement. The significance of monitoring and adaptive management cannot be overstated; these practices ensure that restoration efforts remain relevant and effective over time. By recognizing the co-benefits of restoration—such as improved water quality, increased biodiversity, and community resilience—stakeholders can effectively advocate for necessary support and funding.
However, challenges such as funding constraints, land tenure issues, and climate variability must be addressed to realize the full potential of restoration initiatives. Collaboration among stakeholders, including farmers, policymakers, and local communities, is essential for overcoming these obstacles and fostering a shared commitment to sustainable land management.
Ultimately, the path to a more sustainable agricultural future lies in collective efforts to restore degraded lands. By prioritizing agricultural land restoration, it is possible to create a resilient ecosystem that meets the immediate needs of food production while securing ecological health for generations to come. The time to act is now; the benefits of restoration extend far beyond the fields, enriching both the environment and the communities that depend on it.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is agricultural land restoration?
Agricultural land restoration is the process dedicated to rehabilitating degraded terrains to revive their ecological functions and productivity, addressing issues like soil degradation caused by climate change, urbanization, and unsustainable farming techniques.
Why is agricultural land restoration urgent?
The urgency of agricultural land restoration has intensified due to escalating pressures from climate change, urbanization, and unsustainable farming practices, which have led to significant soil degradation affecting food security and agricultural output.
What percentage of global soils are degraded?
According to the USDA TOTAL survey, approximately 33% of global soils are degraded, which poses a serious threat to food security and agricultural livelihoods.
How does agricultural land restoration contribute to biodiversity and carbon sequestration?
Agricultural land restoration enhances food security, plays a vital role in biodiversity conservation, and aids in carbon sequestration, helping to mitigate climate change effects.
What are some methods used in agricultural land restoration?
Effective methods for agricultural land restoration include reforestation, cover cropping, agroecology, wetland restoration, and soil amendments, each tailored to specific environmental contexts and restoration goals.
What is the impact of reforestation on carbon sequestration?
Reforestation can sequester up to 1.1 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide annually, significantly aiding in combating climate change while improving biodiversity.
How do cover crops benefit soil health?
Cover crops prevent soil erosion, improve soil health, and enhance nutrient cycling, demonstrating the ability to increase soil organic matter by 1-2% annually, which boosts farming productivity and resilience.
What role does agroecology play in sustainable farming?
Agroecology applies ecological principles to establish sustainable farming systems that mimic natural ecosystems, promoting biodiversity, soil health, and reducing dependency on chemical inputs.
How does wetland restoration improve ecosystem health?
Wetland restoration improves water quality, provides wildlife habitat, and enhances flood resilience, with studies showing it can reduce nutrient runoff by up to 90%.
What are soil amendments and how do they benefit crop growth?
Soil amendments involve adding organic matter or nutrients to improve soil fertility and structure, which can boost crop yields by 20-30%, highlighting the importance of soil health in farming productivity.
What is the significance of regenerative agriculture?
Regenerative agriculture is recognized as a sustainable food production method that regenerates ecosystems and ensures food security, contrasting with conventional farming practices.
Why is it important for stakeholders to support agricultural land restoration?
It is crucial for stakeholders—including farmers, policymakers, and environmental advocates—to recognize the diverse benefits of soil improvement initiatives to foster a sustainable future that addresses food security and ecological well-being.
List of Sources
- Understanding Agricultural Land Restoration: Importance and Relevance
- Data and Statistics - FIC (https://farmlandinfo.org/data-and-statistics)
- World Soil Day: Restoring degraded soil is vital for food security (https://weforum.org/stories/2022/06/soil-land-degraded-food-crisis)
- Loss of US Farmland in the 21st Century: The National Perspective from the Census of Agriculture - farmdoc daily (https://farmdocdaily.illinois.edu/2024/09/loss-of-us-farmland-in-the-21st-century-the-national-perspective-from-the-census-of-agriculture.html)
- Exploring Different Types of Agricultural Land Restoration Practices
- Regenerative Agriculture Statistics and Facts 2024 (https://electroiq.com/stats/regenerative-agriculture-statistics)
- Data and Statistics - FIC (https://farmlandinfo.org/data-and-statistics)
- Study says land restoration worldwide can be funded with tiny fraction of global GDP (https://news.mongabay.com/2025/02/study-says-land-restoration-worldwide-can-be-funded-with-tiny-fraction-of-global-gdp)
- Strategic Planning for Successful Agricultural Land Restoration
- How to Manage the Global Land Squeeze? Produce, Protect, Reduce, Restore (https://wri.org/insights/manage-global-land-squeeze-produce-protect-reduce-restore)
- Unveiling the Future: SAN's Strategic Plan for Sustainable Agriculture 2025-2030 (https://sustainableagriculture.eco/post/unveiling-the-future-san-s-strategic-plan-for-sustainable-agriculture-2025-2030)
- Integrate land preservation into strategic growth efforts (https://cmap.illinois.gov/regional-plan/goals/recommendation/integrate-land-preservation-into-strategic-growth-efforts)
- Site Assessment and Evaluation: Key Steps in Restoration
- Data and Statistics - FIC (https://farmlandinfo.org/data-and-statistics)
- VM0042 Improved Agricultural Land Management, v2.1 (https://verra.org/methodologies/vm0042-improved-agricultural-land-management-v2-1)
- Farms Under Threat: The State of the States - FIC (https://farmlandinfo.org/publications/farms-under-threat-the-state-of-the-states)
- Effective Site Management and Monitoring for Sustainable Outcomes
- Nonpoint Source: Agriculture | US EPA (https://epa.gov/nps/nonpoint-source-agriculture)
- Quantifying the recarbonization of post-agricultural landscapes - Nature Communications (https://nature.com/articles/s41467-023-37907-w)
- Co-Benefits of Agricultural Land Restoration: Beyond Productivity
- Enhanced agricultural carbon sinks provide benefits for farmers and the climate - Nature Food (https://nature.com/articles/s43016-024-01039-1)
- Environmental impacts of achieving 25% organic land - A study (https://organicseurope.bio/news/study-on-the-environmental-impacts-of-achieving-25-organic-land-by-2030-published)
- Challenges and Limitations in Agricultural Land Restoration
- UN report: The world’s farms stretched to ‘a breaking point’ » Yale Climate Connections (https://yaleclimateconnections.org/2022/01/un-report-the-worlds-farms-stretched-to-a-breaking-point)
- How to Manage the Global Land Squeeze? Produce, Protect, Reduce, Restore (https://wri.org/insights/manage-global-land-squeeze-produce-protect-reduce-restore)
- Collaboration and Stakeholder Engagement: Keys to Successful Restoration
- USDA - National Agricultural Statistics Service - Census of Agriculture (https://agcensus.usda.gov)
- Regenerative Agriculture Statistics and Facts 2024 (https://electroiq.com/stats/regenerative-agriculture-statistics)
- Data and Statistics - FIC (https://farmlandinfo.org/data-and-statistics)




