Overview
Proven strategies for success in renewable integration with storage begin with the adoption of advanced resource management systems. Engaging stakeholders early is crucial, as is utilizing hybrid systems. Furthermore, investing in research and development, along with leveraging financial incentives, plays a significant role. These strategies not only enhance operational efficiency and project feasibility but also position utilities as leaders in the transition to a sustainable energy future. They effectively address the technical and regulatory challenges associated with renewable integration. By implementing these strategies, organizations can navigate the complexities of the energy landscape with confidence.
Introduction
In the quest for a sustainable energy future, the integration of renewable resources with advanced storage systems stands as both a pivotal challenge and a significant opportunity. As the world confronts the urgent necessity to reduce carbon emissions and bolster energy security, it becomes imperative to understand how to effectively incorporate solar, wind, and other renewable sources into existing infrastructures.
With 2025 marking a crucial turning point, innovations in energy storage technologies—such as lithium-ion batteries and pumped hydro systems—are reshaping the energy landscape. These advancements enable utilities to capture excess energy and optimize resource utilization.
However, this transition is fraught with hurdles, including:
- Regulatory complexities
- Infrastructure limitations
- Public acceptance
By delving into the latest strategies, technologies, and policies, stakeholders can effectively navigate these challenges and harness the full potential of renewable energy integration, paving the way for a cleaner, more resilient energy system.
Understanding Renewable Energy Integration and Storage Systems
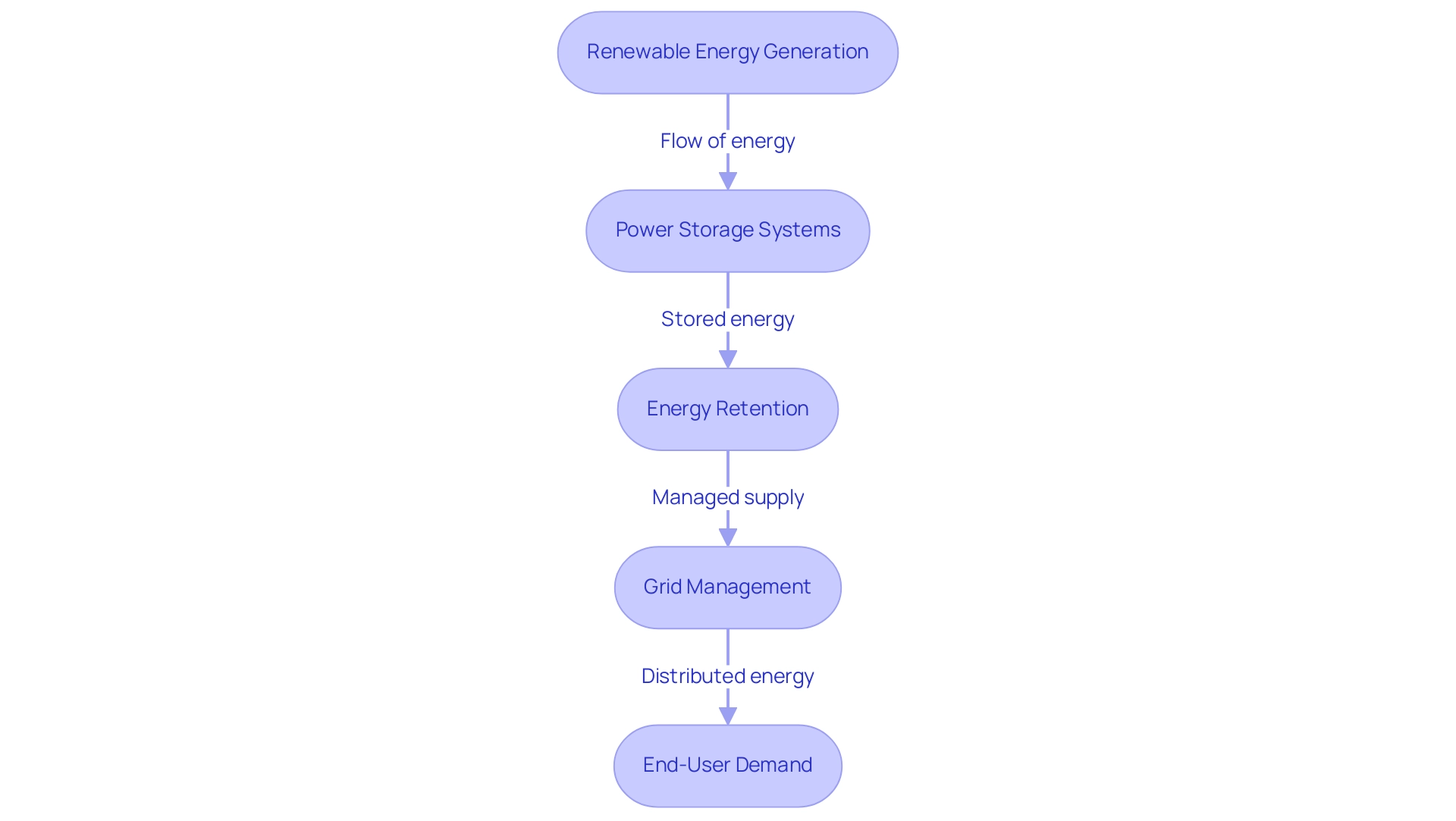
Sustainable power integration is paramount as it seamlessly incorporates alternative sources, such as solar and wind, into existing power infrastructures. By 2025, the significance of holding systems has become increasingly evident; they capture surplus power generated during peak production times for later use during high demand. This capability enhances grid reliability and optimizes the use of sustainable resources, making power systems more resilient and efficient.
Recent advancements in power retention technologies, including lithium-ion batteries and pumped hydro systems, have transformed the landscape of renewable integration with storage in sustainable power. For instance, U.S. hydropower production is expected to increase by 6% in 2024, indicating a growing reliance on reservoir solutions to balance supply and demand efficiently. The interaction among production, retention, and usage is crucial for achieving sustainable power management, enabling utilities to balance fluctuating green generation with consumer demands.
The incorporation of power conservation systems has proven advantageous in numerous projects nationwide. Successful initiatives have demonstrated that renewable integration with storage can lead to significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and enhanced power security. However, challenges remain, particularly in navigating regulatory landscapes and addressing the financial implications of new technologies.
For example, the Biden administration's implementation of tariffs on solar components has raised installation expenses, potentially impeding the expansion of the solar market and affecting the financial feasibility of sustainable projects.
Expert perspectives underscore the importance of resource retention in renewable power integration. Carolyn Amon, a research leader at the Deloitte Research Center for Energy and Industrials, emphasizes that "the incorporation of renewable integration with storage is vital for decarbonization strategies and achieving a sustainable power future." Industry leaders advocate for the establishment of statutory standards to enhance monitoring and verification of carbon removal techniques, further supporting the implementation of technologies for carbon retention.
As the power sector evolves, the demand for innovative solutions to incorporate sustainable resources efficiently will only grow, making resource retention a critical component of future power strategies.
In summary, while the integration of sustainable resources offers numerous advantages, including reduced dependence on fossil fuels and improved grid stability, it also presents challenges that require careful consideration. Continuous advancements in power retention systems will be crucial in overcoming these obstacles, ensuring a sustainable and resilient future for resources.
Exploring Different Energy Storage Technologies for Renewables
Energy preservation methods are pivotal in facilitating the integration of renewables with storage solutions, essential for incorporating renewable energy sources. The following key technologies are currently shaping this landscape:
- Battery Storage: Dominating the market, lithium-ion batteries are recognized for their high efficiency and rapid response capabilities. With a projected battery capacity of 20 gigawatts in the United States for 2023, these systems are ideally suited for short-term applications, scalable from residential setups to utility-level deployments.
- Pumped Hydro Reservoirs: As a conventional and highly effective method, pumped hydro systems utilize surplus power to elevate water to higher reservoirs. This stored water can be released to generate electricity during peak demand, making it particularly effective for [large-scale power storage solutions](https://harbingerland.com).
- Thermal Energy Storage: This technology captures energy in the form of heat, which can later be converted into electricity or utilized for heating purposes. It is especially advantageous in solar thermal applications, where energy can be stored during peak sunlight hours for use when generation is low.
- Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES): CAES systems operate by compressing air in subterranean caverns, storing energy that can be released to drive turbines when electricity is needed. This method is gaining traction as a viable option for large-scale power storage.
- Flywheel Energy Storage: Flywheels store energy as kinetic force, allowing for quick bursts of power. This innovation is particularly beneficial for grid stabilization, providing instant assistance during fluctuations in power supply and demand.
Each of these technologies presents unique benefits and challenges, with the choice often influenced by project-specific factors such as scale, duration, and cost considerations. As the global capacity for installed Battery Power Systems (BESS) surpassed 50 GWh in 2023, the growing reliance on renewable integration with storage underscores their importance in advancing toward a sustainable energy future. Notably, companies like AES Corporation are at the forefront of this evolution, pioneering solutions that exemplify renewable integration with storage, thus facilitating the clean power transition.
Their innovative approaches highlight the effective incorporation of power retention technologies in practical applications.
Laura Wood, Senior Press Manager, underscores the significance of this market, stating, "The 'Advanced Energy Storage Systems Market Report 2025' report has been added to ResearchAndMarkets.com's offering." This statement emphasizes the increasing focus on power retention options, aligning with Harbinger Land's commitment to delivering prompt and precise services tailored to client needs.
Challenges in Integrating Renewable Energy with Storage Solutions
Integrating renewable energy with storage solutions in 2025 presents significant challenges that must be navigated to ensure a successful transition to cleaner energy sources.
- Intermittency of Renewable Sources: The inherent variability of solar and wind power creates mismatches between supply and demand. In 2025, studies indicate that intermittency problems continue to impact around 30% of sustainable power generation, complicating efforts to maintain a stable supply. As Piotr Bojek, lead author of the IEA’s annual Renewables market report, states, "this edition provides forecasts for the deployment of sustainable technologies in electricity, transport, and heat to 2030, while also exploring key challenges facing the industry and identifying barriers that are preventing faster growth."
- Infrastructure Limitations: Current grid systems are not sufficiently prepared to handle the growing influx of sustainable energy and related systems. Upgrading these infrastructures is essential, with estimates suggesting that an investment of over $100 billion will be necessary to modernize the grid to effectively support renewable integration with storage.
- Regulatory Barriers: The implementation of collection systems is often obstructed by intricate regulatory structures. In 2025, unclear policies regarding interconnection and compensation for service provision remain a significant obstacle, with many stakeholders advocating for streamlined regulations to facilitate faster deployment.
- Economic Viability: The significant initial expenses linked to advanced systems present an obstacle, especially for smaller initiatives and local governments with limited budgets. Innovative financing solutions are critical, as evidenced by recent projects that have successfully reduced payback periods through strategic partnerships, such as integrating Bitcoin mining with solar initiatives, which cut payback times from 8.1 years to just 3.5 years. Additionally, tools like Astra Canyon Group's IFS ERP solutions can streamline procurement and project timelines, making it easier for stakeholders to manage costs and resources effectively.
- Public Acceptance: Community concerns regarding the environmental effect and safety of holding methods can hinder project execution. Engaging with local stakeholders and addressing their concerns is vital for fostering public support and ensuring the successful implementation of solutions.
To effectively tackle these challenges, collaboration among stakeholders, innovative financing mechanisms, and supportive policies are essential. Successful projects that have addressed intermittency challenges, such as those featured in recent case studies on technological innovations in sustainable sources, demonstrate the potential for federal funding and industry partnerships to accelerate the commercialization of advanced storage technologies. This highlights the role of renewable integration with storage as a key factor in positioning them as significant players in the future power landscape.
Proven Strategies for Effective Renewable Integration
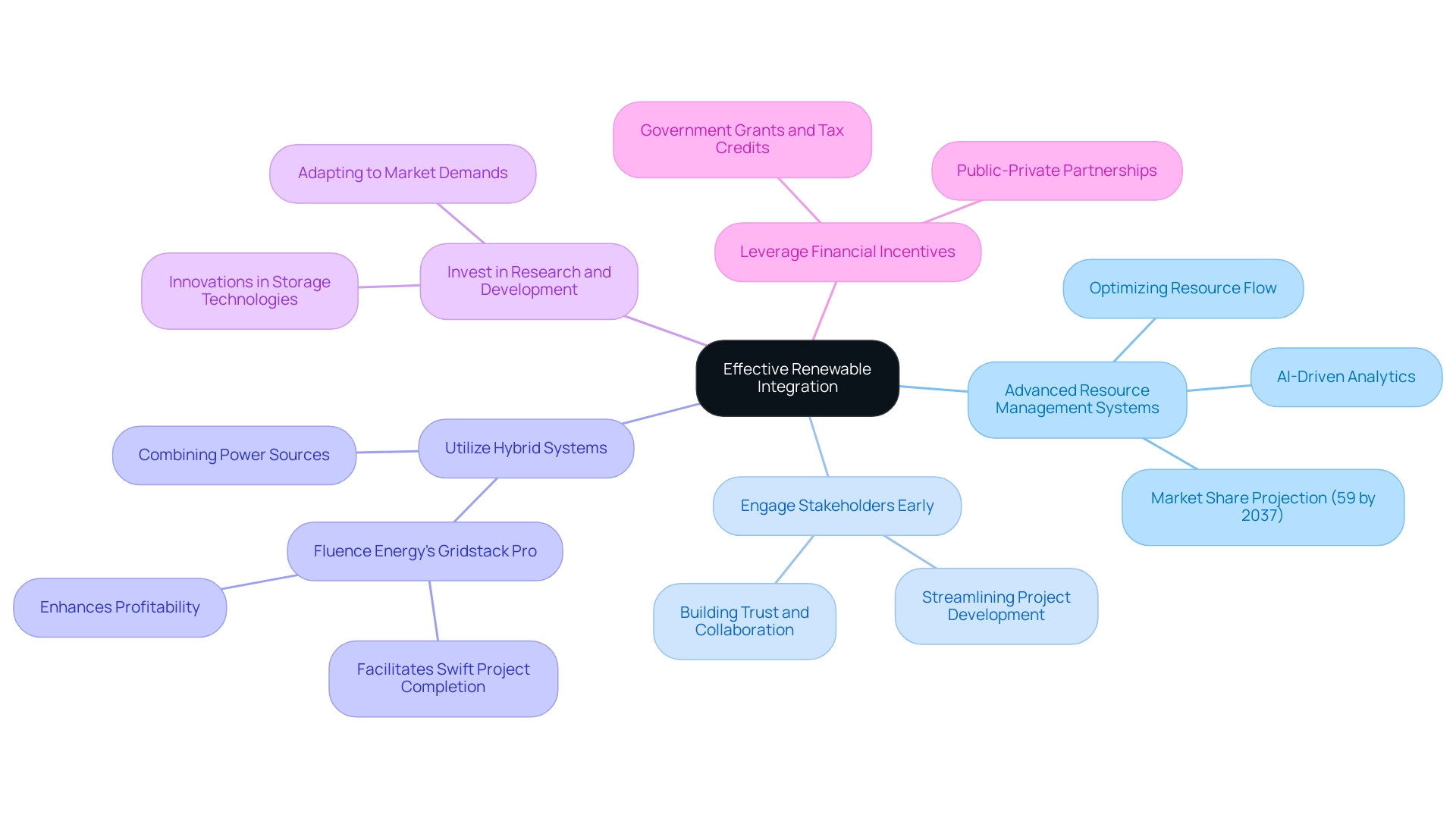
To achieve effective renewable integration, consider the following strategies:
- Adopt Advanced Resource Management Systems: Implementing advanced resource management systems is essential for optimizing resource flow and enhancing decision-making. By utilizing advanced grid systems and AI-driven analytics, utilities can significantly enhance operational efficiency. In 2037, the commercial segment of this market is projected to capture approximately 59% of the total share, underscoring the growing reliance on these systems.
- Engage Stakeholders Early: Early engagement with stakeholders—including local communities, regulators, and industry partners—can streamline project development and proactively address concerns. Effective stakeholder engagement strategies are crucial for building trust and collaboration, which are vital for the long-term success of renewable initiatives.
- Utilize Hybrid Systems: Implementing hybrid systems that combine various power sources and techniques for resource management enhances reliability and efficiency. This method not only supports a more robust power infrastructure but also aligns with the latest advancements in power retention solutions. For instance, Fluence Energy's Gridstack Pro, unveiled in October 2023, facilitates quicker revenue generation by managing complex utility-scale projects, illustrating the benefits of innovative hybrid systems.
- Invest in Research and Development: Ongoing investment in research and development is crucial for overcoming obstacles to clean energy integration. Innovations in storage technologies and renewable integration with storage methods will drive performance improvements and ensure that utilities can adapt to evolving market demands.
- Leverage Financial Incentives: Utilizing financial incentives such as government grants, tax credits, and public-private partnerships can alleviate costs and stimulate investment in sustainable projects. These incentives play a crucial role in making sustainable power initiatives more financially viable and appealing to stakeholders.
As Laura Wood, Senior Press Manager, pointed out, the 'Advanced Energy Storage Systems Market Report 2025' highlights the essential role of advanced power management systems in facilitating renewable integration with storage. By implementing these strategies, utilities can not only enhance the feasibility of sustainable integration but also contribute to a more eco-friendly future, positioning themselves as leaders in the transition to cleaner power solutions.
The Role of Policy and Regulation in Renewable Integration
Policies and regulations are crucial in shaping the environment for sustainable resource integration, influencing both the pace and success of adoption. Key considerations include:
- Supportive Legislation: Governments can enact laws that significantly promote sustainable power adoption. For instance, portfolio standards and feed-in tariffs have proven effective in incentivizing investment and development in sustainable technologies. In 2024, the demand for sustainable energy surged, reflecting the positive impact of such legislative measures. As Carolyn Amon, a research leader in power, utilities, and renewables, noted, "Demand growth is a rising tide that lifts all boats, and it especially elevated the sustainable ones in 2024."
- Streamlined Permitting Processes: Simplifying the permitting process for facilities and renewable projects is essential for accelerating deployment and reducing costs. Efficient permitting can lead to faster project initiation, which is crucial in a rapidly evolving energy market. Statistics indicate that projects with streamlined permitting processes experience up to a 30% reduction in time to completion, enhancing overall project viability.
- Incentives for Innovation: Financial incentives for research and development are vital in driving advancements in technology and integration methods. The Inflation Reduction Act has catalyzed over $100 billion in new private sector investments in the solar and energy sectors, showcasing how supportive legislation can foster innovation and growth. This act is projected to result in a 48% increase in solar deployment over the next decade, significantly impacting job creation and CO2 emissions offsets.
- Interconnection Standards: Establishing clear interconnection standards for storage systems is critical to ensuring seamless integration into the grid. These standards help mitigate technical challenges and enhance the reliability of sustainable power sources, facilitating a smoother transition to a more sustainable infrastructure.
- Public Engagement: Policies that promote public involvement in resource planning can significantly boost community backing and approval of sustainable initiatives. Involving stakeholders early in the process promotes transparency and establishes trust, which is crucial for the successful execution of sustainable initiatives.
- Market Challenges: Recent developments, such as the Biden administration's imposition of aggressive tariffs on Chinese solar components and electric vehicles in 2024, may increase installation costs while potentially boosting domestic manufacturing. This context is essential for grasping the present environment of sustainable power integration.
By promoting a supportive regulatory framework, stakeholders can enable the successful incorporation of renewable integration with storage and alternative power sources, ultimately aiding in a cleaner and more sustainable future. Moreover, credits generated from sustainable-powered methods represent 84% of CDR credit purchases, highlighting the effectiveness of sustainable initiatives.
Future Trends in Energy Storage and Renewable Integration
The future environment of power retention and renewable integration is on the cusp of substantial transformation, highlighted by several key advancements:
- Emergence of Solid-State Batteries: Solid-state batteries are at the forefront of advancements in power retention, offering significantly higher density levels and enhanced safety features. Although challenges related to stability and production scalability persist, industry experts assert that with increasing investment, these batteries could reach commercial viability by 2030. This positions them as potential game-changers across various applications, particularly in the electric vehicle market. For instance, projections indicate that EVs could attain ranges exceeding 600 miles on a single charge, effectively alleviating range anxiety and making electric travel more feasible for long-distance journeys.
- Integration of AI and Machine Learning: The incorporation of AI and machine learning in resource management is becoming increasingly essential. These technologies enable advanced analytics that optimize power usage, enhance predictive maintenance for storage systems, and improve overall operational efficiency, especially in the context of renewable integration with storage. This not only drives down costs but also bolsters reliability.
- Growth of Decentralized Energy Systems: The rise of microgrids and distributed resources is fundamentally reshaping the energy landscape. This transition not only enhances resilience against outages but also fosters local autonomy in power management, empowering communities to effectively harness and control their resources.
- Heightened Attention to Sustainability: As ecological concerns intensify, there is an escalating focus on sustainable materials and practices within power reserve technologies. This trend underscores a broader commitment to minimizing carbon footprints and advocating for eco-friendly solutions within the power sector.
- Policy Evolution: Regulatory frameworks are adapting to keep pace with technological advancements and market dynamics. This evolution is vital for facilitating renewable integration with storage and ensuring that policies remain aligned with the innovative energy storage landscape.
These trends collectively herald a dynamic and promising future for renewable integration with storage, presenting both challenges and opportunities for stakeholders in the energy sector. Furthermore, the establishment of a fully integrated solid-state cell and battery manufacturing facility by an Indian company, with the potential to scale up to 5 GWh, underscores the growing investment and interest in solid-state battery technology, reinforcing the narrative of industry evolution.
Conclusion
The integration of renewable energy with advanced storage systems transcends mere technical challenge; it embodies a crucial pathway toward a sustainable energy future. By harnessing innovations in energy storage technologies—such as lithium-ion batteries and pumped hydro systems—the energy sector can effectively capture excess renewable energy and bolster grid reliability. This transformation is imperative as the world increasingly strives to reduce carbon emissions and enhance energy security.
Yet, the journey toward effective renewable integration is laden with challenges, including regulatory complexities, infrastructure limitations, and public acceptance issues. Addressing these hurdles necessitates strategic collaboration among stakeholders, innovative financing solutions, and supportive policies that cultivate a growth-conducive environment. By adopting proven strategies and leveraging technological advancements, utilities can enhance operational efficiency and contribute to a more resilient energy infrastructure.
Looking ahead, emerging trends such as solid-state batteries, AI integration, and decentralized energy systems are poised to reshape the landscape of energy storage and renewable integration. These advancements not only present opportunities for innovation but also underscore the significance of sustainable practices within the energy sector. As policies evolve to support these transformations, the prospect of a cleaner, more sustainable energy future becomes increasingly achievable. The time to act is now; the integration of renewables with storage solutions is the key to realizing a greener and more resilient energy system for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is sustainable power integration important?
Sustainable power integration is crucial because it incorporates alternative energy sources like solar and wind into existing power infrastructures, enhancing grid reliability and optimizing the use of sustainable resources.
What role do holding systems play in power management?
Holding systems capture surplus power generated during peak production times for later use during high demand, which improves grid reliability and makes power systems more resilient and efficient.
What advancements have been made in power retention technologies?
Recent advancements include lithium-ion batteries and pumped hydro systems, which have transformed renewable integration by enabling efficient storage solutions to balance supply and demand.
What is the expected trend for U.S. hydropower production in 2024?
U.S. hydropower production is expected to increase by 6% in 2024, indicating a growing reliance on reservoir solutions for balancing supply and demand.
What are the benefits of renewable integration with storage?
It leads to significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, enhanced power security, and improved grid stability while reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
What challenges does the renewable integration with storage face?
Challenges include navigating regulatory landscapes and addressing financial implications, such as increased installation costs due to tariffs on solar components.
How do experts view the importance of resource retention in renewable power integration?
Experts, including Carolyn Amon from Deloitte, emphasize that incorporating renewable integration with storage is vital for decarbonization strategies and achieving a sustainable power future.
What are the key technologies shaping energy preservation methods?
Key technologies include: 1. Battery Storage: Dominated by lithium-ion batteries for high efficiency and rapid response. 2. Pumped Hydro Reservoirs: Utilize surplus power to generate electricity during peak demand. 3. Thermal Energy Storage: Captures energy as heat for later conversion or heating. 4. Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES): Stores energy by compressing air in caverns. 5. Flywheel Energy Storage: Stores energy as kinetic force for quick power bursts.
What factors influence the choice of energy storage technology?
The choice is influenced by project-specific factors such as scale, duration, and cost considerations.
What is the current trend in Battery Power Systems (BESS) capacity?
The global capacity for installed Battery Power Systems surpassed 50 GWh in 2023, highlighting the growing reliance on renewable integration with storage.
Who are some of the leaders in renewable integration with storage?
Companies like AES Corporation are pioneers in developing solutions that facilitate the clean power transition through effective incorporation of power retention technologies.
List of Sources
- Understanding Renewable Energy Integration and Storage Systems
- 2025 Renewable Energy Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/renewable-energy/renewable-energy-industry-outlook.html)
- US Clean Power Development Sees Record Progress, As Well As Stronger Headwinds (https://wri.org/insights/clean-energy-progress-united-states)
- Short-Term Energy Outlook - U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) (https://eia.gov/outlooks/steo/report/BTL/2023/02-genmix/article.php)
- Exploring Different Energy Storage Technologies for Renewables
- statista.com (https://statista.com/statistics/1441360/battery-storage-capacity-united-states-forecast)
- Advanced Energy Storage Systems Market Report 2025: ABB, LG Chem, Samsung SDI Co., General Electric Company, and Tesla Dominate the Competitive Landscape (https://globenewswire.com/news-release/2025/01/29/3017400/28124/en/Advanced-Energy-Storage-Systems-Market-Report-2025-ABB-LG-Chem-Samsung-SDI-Co-General-Electric-Company-and-Tesla-Dominate-the-Competitive-Landscape.html)
- Battery Market Outlook 2025-2030: Insights on Electric Vehicles, Energy Storage and Consumer Electronics Growth (https://globenewswire.com/news-release/2025/02/04/3020360/0/en/Battery-Market-Outlook-2025-2030-Insights-on-Electric-Vehicles-Energy-Storage-and-Consumer-Electronics-Growth.html)
- Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS): Market Growth and Deployment Trends (Latest Stats) (https://patentpc.com/blog/battery-energy-storage-systems-bess-market-growth-and-deployment-trends-latest-stats)
- 10 Energy Storage Companies to Know in 2025 (https://climateinsider.com/2025/01/21/10-energy-storage-companies-to-know-in-2025)
- Challenges in Integrating Renewable Energy with Storage Solutions
- Bitcoin Mining: The Key to Solving Renewable Energy Intermittency (https://mara.com/posts/bitcoin-mining-the-key-to-solving-renewable-energy-intermittency)
- Renewables - Energy System - IEA (https://iea.org/energy-system/renewables)
- 2025 Renewable Energy Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/renewable-energy/renewable-energy-industry-outlook.html)
- Renewable Energy Trends to Watch in 2025 (https://astracanyon.com/blog/renewable-energy-trends-to-watch-in-2025?hsLang=en)
- Proven Strategies for Effective Renewable Integration
- Advanced Energy Storage Systems Market Report 2025: ABB, LG Chem, Samsung SDI Co., General Electric Company, and Tesla Dominate the Competitive Landscape (https://globenewswire.com/news-release/2025/01/29/3017400/28124/en/Advanced-Energy-Storage-Systems-Market-Report-2025-ABB-LG-Chem-Samsung-SDI-Co-General-Electric-Company-and-Tesla-Dominate-the-Competitive-Landscape.html)
- 2025 Renewable Energy Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/renewable-energy/renewable-energy-industry-outlook.html)
- Energy Management Systems Market Size & Share, Growth Report 2037 (https://researchnester.com/reports/energy-management-systems-market/4860)
- The Role of Policy and Regulation in Renewable Integration
- 2025 Renewable Energy Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/renewable-energy/renewable-energy-industry-outlook.html)
- Impact of the Inflation Reduction Act – SEIA (https://seia.org/research-resources/impact-inflation-reduction-act)
- US Clean Power Development Sees Record Progress, As Well As Stronger Headwinds (https://wri.org/insights/clean-energy-progress-united-states)
- Future Trends in Energy Storage and Renewable Integration
- Advancements and Challenges in Solid-State Battery Technology: An In-Depth Review of Solid Electrolytes and Anode Innovations (https://mdpi.com/2313-0105/10/1/29)
- China and Korea to overtake Japan in commercialization of All-Solid... (https://evertiq.com/news/57009)
- Solid-state batteries: A new era for electric vehicles (https://whichev.net/2025/02/17/solid-state-batteries-a-new-era-for-electric-vehicles)




