Overview
Flood risk assessments for solar farms are essential for evaluating potential inundation hazards and ensuring the sustainability of photovoltaic installations. The article emphasizes that these assessments are crucial for compliance with regulatory standards, safeguarding investments, and guiding strategic site selection, thereby highlighting their role in mitigating financial and operational risks associated with flooding.
Introduction
In the quest for sustainable energy solutions, solar farms are emerging as a beacon of hope. However, their development is not without challenges, particularly when it comes to flood risks that can jeopardize both construction and operations.
Flood risk assessments play a critical role in identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring the longevity of these renewable energy projects. By analyzing historical data, geographical features, and climate patterns, stakeholders can make informed decisions that mitigate potential flooding impacts.
As the industry evolves, understanding the implications of these assessments becomes increasingly vital, not just for compliance and investment protection, but also for fostering community resilience in the face of changing environmental conditions.
This article delves into the significance of flood risk assessments in solar farm development, exploring methodologies, case studies, and future trends that underscore their indispensable role in shaping a sustainable energy future.
Introduction to Flood Risk Assessments in Solar Farm Development
Flood risk assessments for solar farms act as methodical analyses that determine the probability of inundation in specified regions, especially concentrating on their effects on the establishment and functioning of photovoltaic plants. These evaluations take into account several important elements, including:
- Historical water data
- Topography
- Soil conditions
- Prevailing climate patterns
Given that photovoltaic farms are often located in extensive areas prone to environmental changes, conducting flood risk assessments for solar farms emerges as a fundamental necessity.
The United States Geological Survey (USGS) has been instrumental in this area, operating its system of stream gages for over a century, providing valuable data that informs these assessments. Weather events, such as snowstorms and hurricanes, significantly impact energy production; for instance, low sunlight levels and snow accumulation during snowstorms can drastically reduce energy output, while hurricanes can bring heavy rainfall and unexpectedly low wind speeds that further complicate operations. Real-world examples demonstrate that failure to consider these factors can lead to operational challenges, necessitating a robust approach to flood risk assessments for solar farms.
Furthermore, a recent case study titled 'Wildfire Impact on Photovoltaic Farms,' conducted in collaboration with Sandia, highlights the effects of wildfires on energy generation, particularly noting data limitations due to the lack of maintenance logs during extreme weather events. Nicole, a field specialist, highlighted the significance of this research, stating, 'We’re extending the approach into wildfires to examine their performance impacts on energy generation in greater detail.' This indicates an evolving understanding of how various environmental factors can collectively influence farm sustainability and operational viability.
Why Flood Risk Assessments Are Essential for Solar Power Stations
Flood risk assessments for solar farms are essential for evaluating flood potential, fulfilling several vital roles. They are essential for compliance with legal and regulatory standards, which are increasingly stringent as environmental concerns take center stage. With a baseline anticipated annual damage (EAD) of €1.1 million to €1.6 million estimated for the near future and the end of the century, the financial stakes of ignoring inundation hazards are considerable.
Moreover, these assessments play a vital role in safeguarding investments by proactively identifying threats that could lead to costly damages or project delays. Insights from the study on inundation hazards in Dresden, Germany, highlight the potential for a four-fold increase in future water-related dangers due to climate and socioeconomic changes. However, adaptation measures proposed in the study could mitigate this threat by up to 60%, showcasing the value of thorough evaluations.
Furthermore, it is essential to comprehend the legal obligations for inundation vulnerability evaluations in energy projects, ensuring adherence and protecting investments. Comprehending water-related hazards is also crucial for strategic site selection, directing developers to choose areas that reduce susceptibility to inundation and thus improving long-term operational efficiency. As environmental specialist Julio Garrote highlights in his bibliometric review, the importance of thorough flood risk assessments for solar farms and evaluations of flooding potential cannot be overstated, especially concerning renewable energy initiatives such as photovoltaic power facilities.
For further insights, readers are encouraged to explore the dedicated information section available to learn more about MDPI and its contributions to this field.
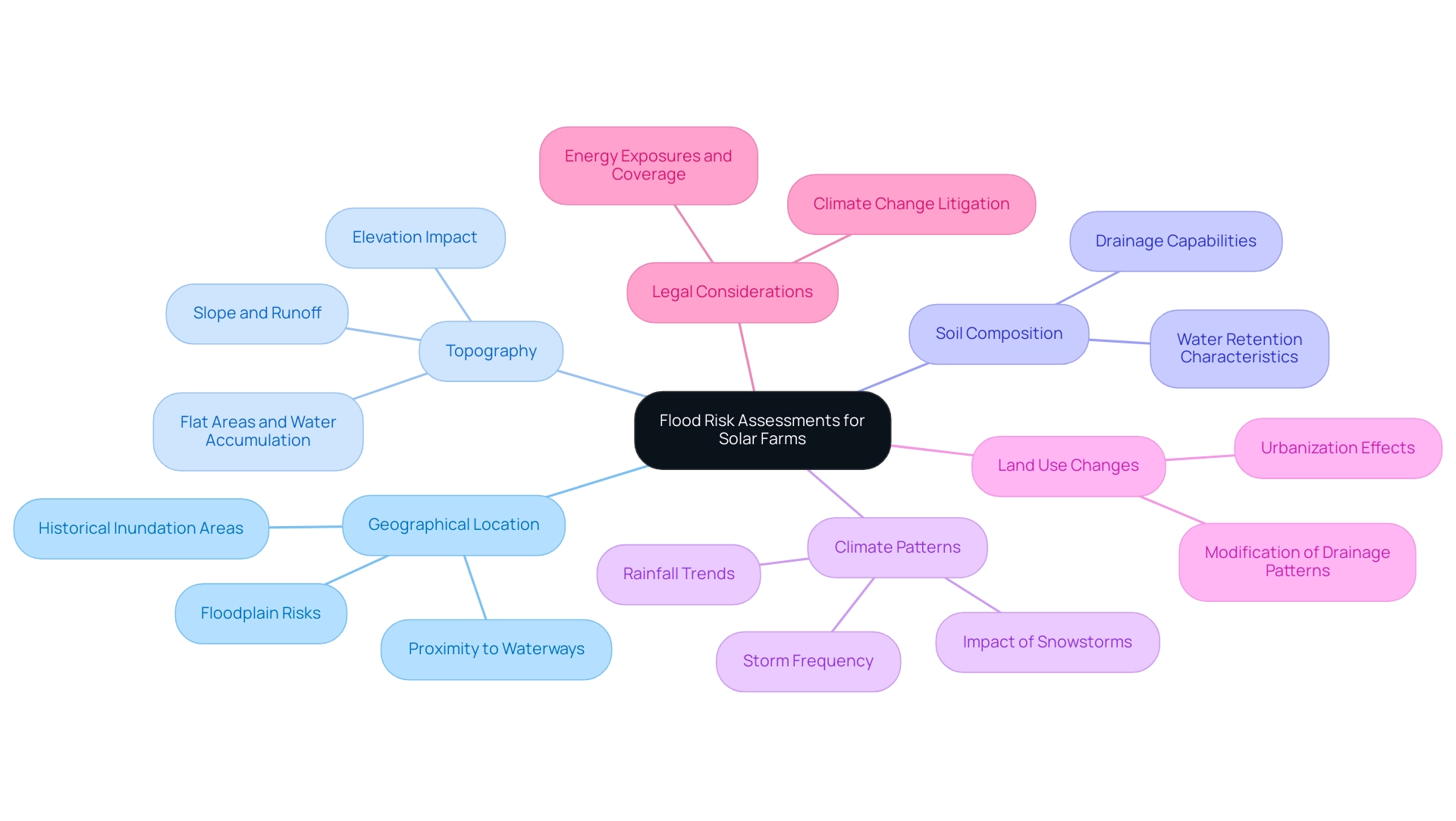
Key Factors Influencing Flood Risk Assessments for Solar Farms
Flood risk assessments for solar farms are influenced by a variety of critical factors that must be thoroughly understood to ensure the resilience of these projects. Key considerations include:
-
Geographical Location: The closeness to waterways, floodplains, and historical inundation areas plays a significant role in determining hazard levels.
Projects situated near these areas face heightened vulnerability to flooding events.
-
Topography: The elevation and slope of the landscape are crucial in assessing how water flows during heavy rainfall.
Steep slopes may worsen runoff, leading to heightened chances of inundation, while flat areas may be more prone to water accumulation.
-
Soil Composition: Different soil types have varying drainage capabilities and water retention characteristics, directly impacting how much water can be absorbed and how quickly it can drain away.
This is an essential factor for predicting potential flooding.
-
Climate Patterns: Analyzing regional climate trends is vital for forecasting future flood risks.
As Thushara Gunda, a senior researcher on environmental impacts, states,
Trying to understand how future climate conditions could impact our national energy infrastructure is exactly what we need to be doing if we want our renewable energy sector to be resilient under a changing climate.
Comprehending changes in rainfall patterns or heightened storm frequency is essential for precise evaluations. Notably, snowstorms have the highest effect on electricity production, followed by hurricanes and other storms, underscoring the importance of these assessments in relation to energy production.
-
Land Use Changes: Nearby developments can significantly modify water drainage patterns, potentially elevating the chances of inundation.
Urbanization and changes in land use must be meticulously evaluated to ensure that renewable energy projects are not adversely affected by these factors.
-
Legal Considerations: Recent developments in climate change litigation are also influencing energy exposures and coverage.
Grasping these legal elements is crucial for a thorough evaluation of water-related hazards, as they may influence the overall viability and coverage of energy initiatives.
By comprehensively analyzing these elements, including the projected renewable energy capacity from sunlight and wind by 2035, where these sources could account for over 50% of energy capacity in many U.S. states, developers can utilize flood risk assessments for solar farms to make informed decisions that enhance the resilience of renewable energy projects against flooding, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable energy future.
Methodologies for Conducting Effective Flood Risk Assessments
Efficient evaluations involving flood risk assessments for solar farms necessitate a range of approaches that significantly inform planning and decision-making. Among the most significant are:
-
Hydrological Modeling: Utilizing advanced software to simulate water flow across various scenarios helps identify potential inundation areas.
Recent advancements in hydrological modeling techniques enable more precise assessments of inundation hazards, considering factors like climate change and land use effects.
-
GIS Mapping: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) play a crucial role in visualizing hazard data.
Harbinger Land's GIS mapping services improve comprehension of spatial relationships and historical flood patterns, rendering it an invaluable resource in flood assessment. This technology allows for the integration of diverse datasets, facilitating strategic planning by highlighting vulnerable areas and informing site selection for solar farms, which is essential for conducting flood risk assessments for solar farms and ultimately supporting efficient land rights acquisition decisions. The application of GIS modeling not only simplifies the site selection procedure but also results in considerable time and cost reductions for clients by decreasing the intricacy of negotiations and ensuring that the right-of-way acquisitions are grounded on precise evaluations.
-
Field Surveys: Conducting on-site evaluations is essential for gathering empirical data on factors such as soil conditions, vegetation, and existing drainage systems. These surveys enhance modeling efforts by offering real-world insights that can improve assessments.
-
Historical Analysis: By examining previous inundation events and their effects on comparable projects, developers can foresee future risks. This retrospective approach allows for a more nuanced understanding of flood dynamics and community vulnerabilities.
-
Stakeholder Consultation: Engaging local authorities and community members is vital for gathering insights on historical flooding issues and potential mitigation measures. This collaborative approach ensures that the evaluations take into account local knowledge and priorities, ultimately enhancing community resilience against flooding.
Incorporating methodologies such as the Systems Theoretic Process Analysis (STAMP) aids in identifying hazards arising from unsafe control actions, highlighting the significance of human factors and organizational structures in evaluating potential dangers. As mentioned by Ernest Hiong Yew Moa Yun Ii Go, "there is a pressing need for enhancement in safety and management, particularly in contexts involving grid-scale renewable energy systems." Additionally, the guidance document describes danger as the likelihood that one or more occurrences will surpass a certain water level within a defined timeframe of years, emphasizing the essential nature of these evaluations.
By combining these approaches and knowledge, the evaluations can more effectively tackle community resilience and the intricacies of water-related challenges in renewable energy projects, such as flood risk assessments for solar farms.
Implications of Flood Risk Assessments on Solar Farm Planning and Development
Flood risk assessments for solar farms are crucial for influencing the planning and development of photovoltaic installations. By directing site selection towards locations with reduced water hazards, flood risk assessments for solar farms assist in securing the long-term sustainability of solar facilities. The novel incorporation of inundation and erosion vulnerability indices into the decision-making process is vital, as it enables a more comprehensive assessment of potential locations.
For instance, mitigation strategies such as:
- Elevated installation designs
- Enhanced drainage systems
can be implemented to bolster project resilience against flooding. The challenges encountered in 2022, when severe flooding in Bangladesh displaced millions and rendered many previously suitable locations for renewable energy projects too hazardous, underscore the critical importance of conducting flood risk assessments for solar farms in site selection processes. Furthermore, the 2021 inundations in China interrupted the supply chain for photovoltaic panels, resulting in delays in the development of new renewable energy projects, further emphasizing the effects of flooding on energy initiatives.
Ignoring thorough flood risk assessments for solar farms can result in:
- Non-compliance with regulatory standards
- Exposure to possible legal consequences
- Increased susceptibility to inundation
As Elif N. Ayhan stated, 'The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.' This, in turn, threatens the overall success and sustainability of renewable energy initiatives.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications of Flood Risk Assessments in Solar Farms
Numerous case studies demonstrate the successful execution of inundation hazard evaluations in renewable energy facility development:
- Case Study 1: A renewable energy farm initiative in California carried out thorough evaluations of inundation vulnerabilities that revealed previously unrecognized low-lying regions. This critical information prompted the elevation of photovoltaic panels, significantly mitigating potential damage from floodwaters. This corresponds with discoveries from the top 20 referenced documents in hazard assessments, which highlight the significance of comprehensive evaluations in project planning.
- Case Study 2: In Texas, a renewable energy project harnessed the power of GIS mapping to pinpoint flood-prone regions. This strategic approach to site selection not only avoided high-risk zones but also resulted in substantial cost savings and increased project reliability. Such methodologies reflect the expanding body of research on effective inundation management strategies.
- Case Study 3: Working with local governments in Florida, an energy developer conducted historical analyses that highlighted the importance of community involvement in managing water-related hazards. This initiative fostered enhanced local support and led to smoother project approval processes. Furthermore, incorporating pollinator strategies into the design can additionally decrease project expenses and improve system efficiency by reducing surrounding temperatures, demonstrating how environmental factors relate to water management evaluations. As noted by Gerald Robinson from the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, 'Stormwater and floodwater have entered electrical pull boxes in the array field and then flowed downhill to the electrical switchgear and inverters.' This emphasizes the essential requirement for thorough flood risk assessments for solar farms to safeguard infrastructure and ensure the sustainability of renewable energy initiatives. These examples highlight the vital importance of comprehensive evaluations, such as flood risk assessments for solar farms, in guaranteeing the success and sustainability of solar energy initiatives.
Future Trends in Flood Risk Assessments for Renewable Energy Developments
Upcoming patterns in evaluating hazards for renewable energy projects are set to progress considerably, propelled by technological innovations and changing regulatory environments. Key areas of focus include:
- The incorporation of AI-driven analysis into flood hazard modeling is poised to enhance flood risk assessments for solar farms, enabling the precise forecasting of potential flood scenarios.
These technologies will play an essential part in improving evaluations of potential issues. Significantly, recent studies suggest that future threats may surpass five times the historical dangers in specific areas, including southern Africa and the Mediterranean basin, emphasizing the need for enhanced methodologies.
-
Integrated Evaluations: There is an increasing acknowledgment of the significance of merging water hazard evaluations with environmental impact analyses.
This holistic approach ensures that all facets of project feasibility are considered, leading to more sustainable outcomes. As highlighted by Renaud et al., environmental factors such as salinity intrusion in areas like the Mekong Delta must be taken into account to comprehend their effects on evaluations for renewable energy initiatives.
-
Increased Regulatory Focus: With climate resilience becoming a priority, we anticipate stricter regulations regarding sustainability in project planning.
This change will require that developers embrace more stringent flood risk assessments for solar farms to satisfy changing compliance standards.
-
Community Involvement: Involving local stakeholders in the evaluation process is gaining traction.
This collaboration not only addresses community concerns but also enriches project planning with local knowledge, fostering better acceptance and support for renewable energy initiatives.
-
Data-Driven Decision Making: The use of large-scale data analysis is transforming the processes of evaluating inundation hazards.
By utilizing extensive datasets, developers can improve decision-making concerning site selection and project design, thereby optimizing environmental and economic results. Additionally, the continuous reduction in ESL return periods further highlights the urgency of flood risk assessments for solar farms, which require advanced technological applications in water-related prediction.
Integrating these trends will ultimately lead to more resilient and responsible energy development. Additionally, insights from the case study on uncertainty in drought and flood risk projections illustrate the complexities involved in such assessments, emphasizing the need for incorporating diverse environmental factors to avoid underestimating future risks.
Conclusion
Understanding the critical role of flood risk assessments in solar farm development is essential for ensuring the sustainability and operational viability of these renewable energy projects. By systematically evaluating historical data, geographical features, and climate patterns, stakeholders can identify vulnerabilities that pose risks to both construction and ongoing operations. The integration of advanced methodologies such as hydrological modeling and GIS mapping into these assessments enhances the accuracy of flood predictions, ultimately guiding strategic site selection and investment protection.
The implications of effective flood risk assessments extend beyond compliance with regulatory standards; they are instrumental in fostering community resilience and safeguarding investments against potentially costly damages. Real-world case studies highlight the positive impacts of thorough evaluations, showcasing how informed decision-making can mitigate risks and enhance the reliability of solar energy initiatives. As the energy landscape evolves, the importance of these assessments will only grow, particularly in the face of climate change and increasing environmental uncertainties.
In conclusion, prioritizing flood risk assessments is not merely an operational necessity but a strategic imperative for the future of solar energy. By embracing innovative technologies and methodologies, the industry can navigate the complexities of environmental challenges, ensuring that solar farms not only contribute to a sustainable energy future but also thrive in the face of changing climate conditions. The commitment to comprehensive flood risk evaluations will ultimately empower stakeholders to build resilient energy infrastructures that benefit both the environment and the communities they serve.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a flood risk assessment for solar farms?
A flood risk assessment for solar farms is a methodical analysis that determines the probability of flooding in specific areas and evaluates its effects on the establishment and operation of photovoltaic plants.
What factors are considered in flood risk assessments for solar farms?
Key factors include historical water data, topography, soil conditions, and prevailing climate patterns.
Why are flood risk assessments important for solar farms?
They are essential for evaluating flood potential, ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory standards, safeguarding investments, identifying threats that could lead to costly damages or project delays, and aiding in strategic site selection.
How do environmental changes affect flood risk assessments for solar farms?
Photovoltaic farms are often located in extensive areas prone to environmental changes, making it crucial to conduct flood risk assessments to address potential future water-related dangers.
What role does the United States Geological Survey (USGS) play in flood risk assessments?
The USGS has provided valuable historical water data through its system of stream gages for over a century, which informs flood risk assessments for solar farms.
What are some real-world impacts of weather events on solar farm operations?
Weather events like snowstorms can reduce energy output due to low sunlight levels and snow accumulation, while hurricanes can bring heavy rainfall and low wind speeds that complicate operations.
What recent research highlights the effects of wildfires on solar farms?
A case study titled 'Wildfire Impact on Photovoltaic Farms,' conducted in collaboration with Sandia, examines how wildfires can affect energy generation and the limitations of data due to lack of maintenance logs during extreme weather.
What are the financial implications of ignoring flood risks for solar farms?
Ignoring inundation hazards can lead to significant financial stakes, with an estimated anticipated annual damage ranging from €1.1 million to €1.6 million in the near future.
How can adaptation measures mitigate flood risks for solar farms?
Proposed adaptation measures could potentially reduce the threat of future water-related dangers by up to 60%, highlighting the importance of thorough evaluations.
Why is understanding legal obligations for inundation vulnerability evaluations important?
It ensures adherence to regulations, protects investments, and aids in strategic site selection to improve long-term operational efficiency for energy projects.
List of Sources
- Introduction to Flood Risk Assessments in Solar Farm Development
- Comprehensive Flood Risk Assessment: State of the Practice (https://mdpi.com/2306-5338/10/2/46)
- Sandia uncovers hidden factors that affect solar farms during severe weather (https://sandia.gov/labnews/2021/08/27/sandia-uncovers-hidden-factors-that-affect-solar-farms-during-severe-weather)
- Why Flood Risk Assessments Are Essential for Solar Power Stations
- Projecting Flood Risk Dynamics for Effective Long‐Term Adaptation (https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2022EF003258)
- Flood Risk Analysis and Assessment, Applications and Uncertainties: A Bibliometric Review (https://mdpi.com/2073-4441/12/7/2050)
- Large-scale energy storage system: safety and risk assessment - Sustainable Energy Research (https://sustainenergyres.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s40807-023-00082-z)
- Key Factors Influencing Flood Risk Assessments for Solar Farms
- Sandia uncovers hidden factors that affect solar farms during severe weather (https://sandia.gov/labnews/2021/08/27/sandia-uncovers-hidden-factors-that-affect-solar-farms-during-severe-weather)
- Including flood, erosion hazards in solar project site selection (https://pv-magazine.com/2023/08/07/including-flood-erosion-hazards-in-solar-project-site-selection)
- The importance of flood risk assessments and their impact on solar farm insurance (https://miller-insurance.com/articles/news-and-insights/parametric-solutions-why-broker-specialisation-matters-in-parametric-insurance)
- A Decade of Growth in Solar and Wind Power: Trends Across the U.S. | Climate Central (https://climatecentral.org/report/solar-and-wind-power-2024)
- Methodologies for Conducting Effective Flood Risk Assessments
- Comprehensive Flood Risk Assessment: State of the Practice (https://mdpi.com/2306-5338/10/2/46)
- Large-scale energy storage system: safety and risk assessment - Sustainable Energy Research (https://sustainenergyres.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s40807-023-00082-z)
- Implications of Flood Risk Assessments on Solar Farm Planning and Development
- Exploring flood and erosion risk indices for optimal solar PV site selection and assessing the influence of topographic resolution (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0960148123009709)
- How Floods Impact the Development of Renewable Technologies and the Green Shift (https://linkedin.com/pulse/how-floods-impact-development-renewable-technologies-green)
- Case Studies: Real-World Applications of Flood Risk Assessments in Solar Farms
- Flood Risk Analysis and Assessment, Applications and Uncertainties: A Bibliometric Review (https://mdpi.com/2073-4441/12/7/2050)
- Preventing and Mitigating Flood Damage to Solar Photovoltaic Systems (https://energy.gov/femp/preventing-and-mitigating-flood-damage-solar-photovoltaic-systems)
- Future Trends in Flood Risk Assessments for Renewable Energy Developments
- ipcc.ch (https://ipcc.ch/srocc/chapter/chapter-4-sea-level-rise-and-implications-for-low-lying-islands-coasts-and-communities)
- Amplified Drought and Flood Risk Under Future Socioeconomic and Climatic Change (https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1029/2021EF002295)




