Overview
The article addresses the intricate challenges associated with high-voltage line placement, underscoring the pivotal role of land acquisition professionals in navigating these complexities. It presents critical factors such as:
- Environmental impact
- Community concerns
- Regulatory requirements
- Financial implications
Each factor is essential for the effective planning and execution of high-voltage projects. This highlights the necessity for informed decision-making in land management strategies, ultimately advocating for a proactive approach to overcoming these challenges.
Introduction
High-voltage power lines are integral to modern energy infrastructure, adeptly transmitting electricity over extensive distances to satisfy the escalating demands of consumers. With voltages exceeding 36 kV, these lines interconnect diverse power generation sources, ranging from renewable energy facilities to traditional power plants, thereby playing a vital role in the stability and reliability of the electrical grid.
Yet, the challenges associated with their placement and management extend beyond engineering; they encompass environmental considerations, community impacts, and regulatory compliance. As land acquisition professionals navigate this complex landscape, a comprehensive understanding of the multifaceted factors influencing high-voltage line projects is essential.
This article explores the fundamental aspects of high-voltage power lines, scrutinizing the key considerations for effective placement, the implications for local communities, and the financial and regulatory frameworks that govern these critical infrastructure projects.
Fundamentals of High-Voltage Power Lines
High-voltage power cables are pivotal in the efficient transmission of electricity over extensive distances, operating at voltages exceeding 36 kV (kilovolts). These connections are essential for linking power generation sources, such as solar and natural gas facilities, to consumers, thereby fortifying the energy infrastructure. The primary components of elevated power systems comprise conductors, insulators, and support structures, including towers or poles.
A thorough understanding of these components is vital for land acquisition professionals, enabling them to evaluate land requirements and the potential impacts of elevated systems on surrounding environments and communities. For instance, the height and spacing of towers can significantly influence land use patterns and property values in adjacent areas. Recent studies indicate that the integration of smart meters into distribution networks has led to a 33.6% improvement in loss detection, highlighting the critical role of technology in enhancing efficiency and reducing energy losses.
This advancement is supported by a dataset for loss identification and localization, which included 57,000 observations from field trials. Furthermore, ongoing research into the reconfiguration of power grids seeks to minimize active power losses, underscoring the necessity for a reliable power supply while concurrently lowering operational costs. As Yury Kononov emphasized, methodologies for detecting measurement errors are essential in addressing non-technical losses, further illustrating the significance of technology in this sector. Understanding these dynamics is imperative for land acquisition experts, as they navigate the complexities of high-voltage line placement and its repercussions on land use and property values.
As the energy industry evolves, staying informed about the latest advancements in elevated power transmission technology and their ecological implications will be crucial for effective land management and acquisition strategies. Additionally, research focused on energy losses aligns with sustainability goals, contributing to improved energy efficiency and economic advantages.
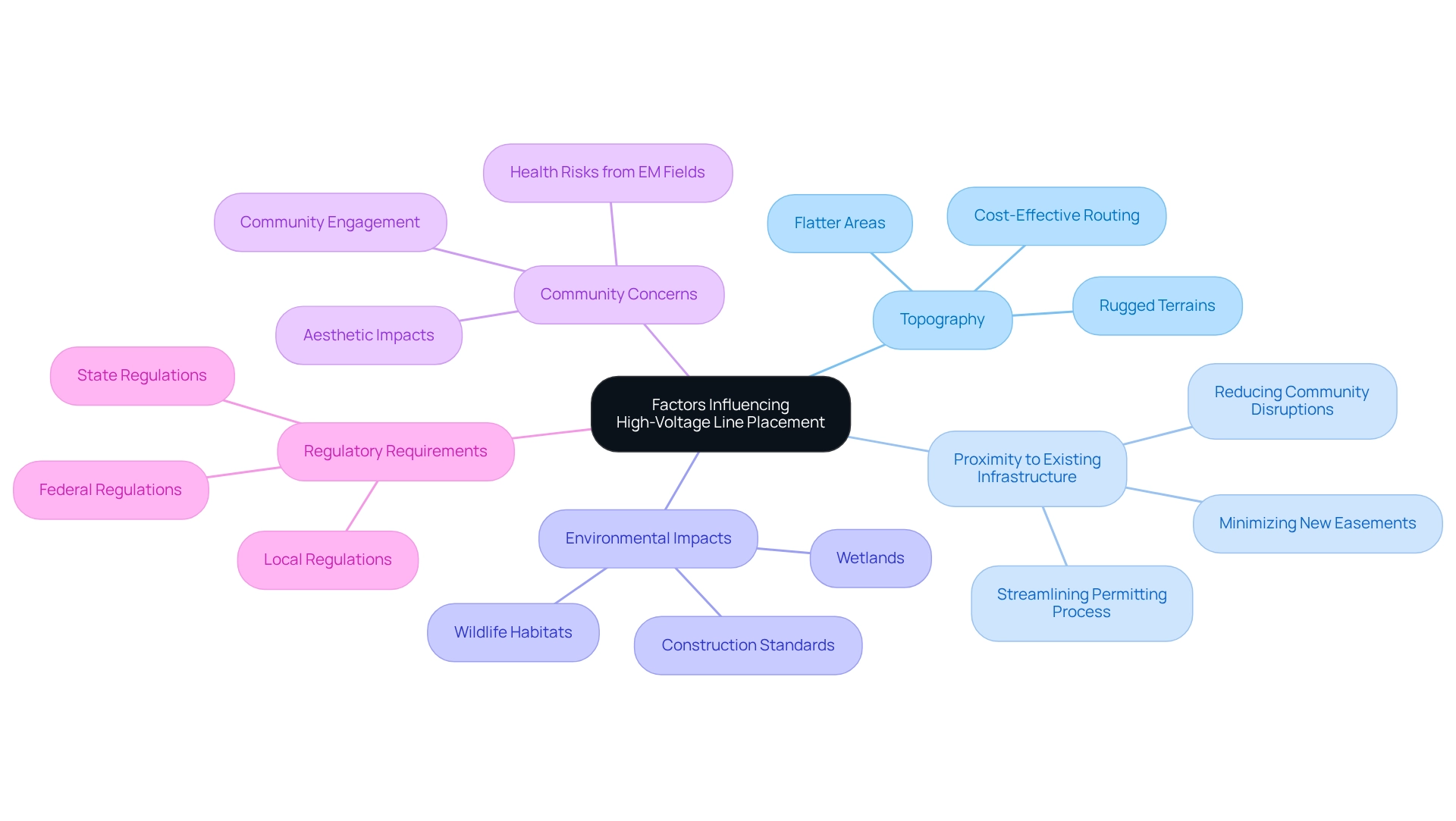
Key Factors Influencing High-Voltage Line Placement
The placement of high-voltage lines is influenced by a multitude of factors, each playing a vital role in ensuring efficiency and compliance with regulatory standards. Key considerations include:
- Topography: The physical landscape significantly impacts routing decisions. Rugged terrains may necessitate more complex engineering solutions, whereas flatter areas can facilitate easier construction. Understanding the topographical challenges is crucial, as they can determine the most cost-effective and environmentally sensitive routes for high-voltage line placement.
- Proximity to Existing Infrastructure: High-voltage lines are frequently routed near existing roads and utilities. This strategy minimizes the need for new easements, thus reducing both construction costs and potential disruptions to the community. The integration of existing infrastructure can streamline the permitting process and enhance the feasibility of high-voltage line placement.
Comprehensive environmental assessments are essential to evaluate potential effects on wildlife habitats, wetlands, and other sensitive ecosystems, particularly concerning high-voltage line placement. Research has demonstrated that such placement can significantly influence local wildlife, necessitating careful planning to mitigate negative effects. Furthermore, contractors must adhere to stringent standards and regulations during the construction of electric transmission lines, which can have numerous environmental impacts.
- Community Concerns: Local opposition often arises from perceived health risks associated with electromagnetic fields or aesthetic impacts on the landscape. Engaging with the community through education and open communication can help address these concerns and foster support for the initiative.
- Regulatory Requirements: Adhering to federal, state, and local regulations is paramount. These regulations dictate specific routing and construction practices, ensuring that projects meet safety and environmental standards. The complexity of these requirements underscores the need for thorough planning and expert guidance.
As we approach 2025, the rising demand for electricity makes understanding these factors more critical than ever. Currently, the four largest electric power firms supply service to over 85% of California households, underscoring the urgent need for efficient transmission placement. Recent case studies have illustrated the importance of geocoding practices in accurately assessing environmental impacts related to high-voltage line placement, achieving high accuracy levels in spatial analysis.
As Spencer Abraham, the US Secretary of Energy, pointed out, "The shortage of transmission routes is nationwide and will worsen as data and analysis on transmission route siting are limited." Addressing these challenges requires insights from experts in the field, which will be essential in shaping effective strategies for high-voltage line placement.
Navigating Regulatory and Legal Frameworks
Land acquisition experts navigate a complex regulatory environment when overseeing high-voltage power projects. Key considerations include:
-
Easements: Understanding the intricacies of easements is crucial, as they grant utility companies the right to access and maintain power lines on private property. These rights not only facilitate infrastructure development but can also enhance property usability and potentially increase property value.
For instance, easements can lead to shared community resources, alleviating individual maintenance burdens and costs for property owners. A case study underscores that easements provide various advantages, particularly in improving property usability by allowing access, enhancing infrastructure, and possibly boosting property value.
-
Permitting: A variety of permits may be required at local, state, and federal levels, contingent on the scope and geographical location. Typically, large-scale electrical infrastructure initiatives necessitate multiple permits, which can vary significantly based on the complexity of the endeavor and the regulatory landscape.
-
Environmental Regulations: Compliance with the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) and additional environmental laws is essential for assessing and mitigating potential effects. This adherence ensures that initiatives align with environmental standards and societal expectations.
-
Public Utility Commission (PUC) Regulations: These regulatory bodies oversee the siting and construction of utility infrastructure. Their guidelines must be meticulously followed to avoid project delays and ensure smooth execution. Effectively managing these elements is vital for successful land acquisition in high-voltage line placement projects, particularly as recent changes in permitting processes for utility infrastructure can introduce additional challenges. Legal experts highlight the importance of understanding easement implications, noting that 'future generations will thank you for it,' which emphasizes the long-term benefits of thoughtful land management. Moreover, California Code Civil Procedure § 1263.410 delineates compensation for any harm to the remainder of the land once a right of way is established, underscoring the necessity for careful consideration of land access rights and easement negotiations. It is important to note that CohnReznick disclaims liability for actions taken based on the information in their publication, which should be factored into the interpretation of this information.
Community Impact and Public Perception of High-Voltage Lines
The placement of high-voltage lines presents significant challenges for nearby areas, raising critical concerns about health hazards, property values, and visual appeal. To navigate these complexities effectively, land acquisition professionals must implement the following strategies:
- Engage with the Community: Organize informational meetings to educate residents on the benefits and safety measures associated with high-voltage lines. This proactive approach fosters transparency and builds trust within the community.
- Address Health Concerns: Supply residents with evidence-based information regarding electromagnetic fields (EMFs) and their health implications. Research indicates that homes located more than 2,000 feet from high-voltage transmission lines were typically built around 1957, providing a historical context for local concerns. By clarifying misconceptions, professionals can alleviate fears and encourage informed discussions.
- Incorporate Feedback: Actively seek and integrate community input into planning. This responsiveness not only demonstrates respect for local issues but also enhances acceptance and support for the initiative.
Highlight the economic benefits of high-voltage line placement by emphasizing the potential advantages of elevated transmission initiatives, such as job creation and infrastructure enhancements. These factors can significantly influence public opinion and garner local support.
Utilize case studies by referencing successful engagement strategies from previous high-voltage line placement initiatives. For instance, studies have shown that addressing public perception of health risks related to electromagnetic fields can lead to more favorable responses from the community. Engaging health experts to discuss these findings can further validate the project's safety and benefits. The case study titled "Limitations and Generalizability of Health Response Studies" illustrates the challenges in generalizing health responses to elevated power sources, underscoring the need for careful consideration of local issues.
- Monitor Public Perception: Remain vigilant regarding local concerns about health risks associated with elevated power cables. Statistics reveal that a substantial segment of the public remains apprehensive about EMFs, necessitating ongoing dialogue and education. Georeferenced data can be utilized to determine distances from homes to power sources and roads, providing a systematic basis for addressing these issues.
By applying these strategies, land acquisition experts can effectively mitigate public concerns and foster a collaborative atmosphere that supports the successful placement of high-voltage lines and the evaluation of powerful electrical cables. As Daniel Wartenberg noted, "the concept of environmental justice may not apply equally to all environmental risk factors," emphasizing the complexities of public perception related to environmental risks. Collaboration with local health services and TenneT for geographical data further highlights the importance of partnerships in effectively addressing community concerns.
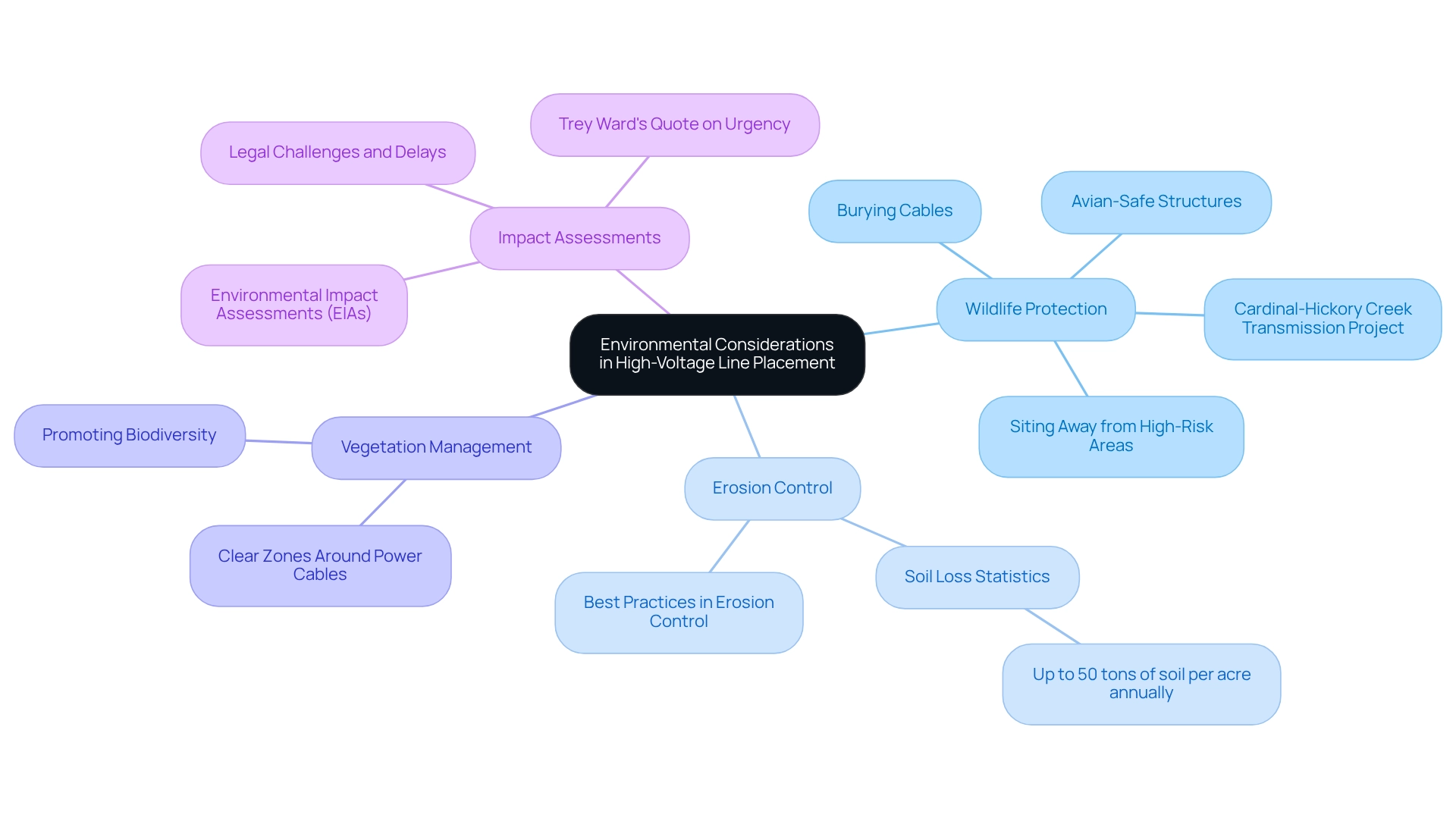
Environmental Considerations in High-Voltage Line Placement
When planning high-voltage line placements, addressing several key environmental considerations is crucial.
- Wildlife Protection: Comprehensive assessments must focus on identifying and safeguarding critical habitats and migratory paths. The Cardinal-Hickory Creek Transmission Project, spanning approximately 100 miles, aims to improve electric reliability and transport clean power from wind-rich states to populated areas. However, it has faced significant scrutiny from environmental groups due to its potential impact on wildlife, particularly avian species. This situation underscores the importance of incorporating wildlife protection strategies into planning to reduce the risks of electrocution and habitat disruption. Statistics indicate that electrocutions can lead to power outages, damage equipment, and increase operational and maintenance costs, highlighting the necessity for effective wildlife protection strategies.
- Erosion Control: Implementing effective erosion control measures during construction is vital for preserving local ecosystems. Inadequate management can result in considerable soil deterioration, impacting both the environment and financial expenses. Studies show that erosion can lead to a loss of up to 50 tons of soil per acre annually in certain regions. By employing best practices in erosion control, projects can minimize their ecological footprint and enhance sustainability.
- Vegetation Management: Establishing clear zones around power cables is essential to prevent vegetation interference while promoting biodiversity. This approach not only protects the infrastructure but also supports local flora and fauna, fostering a balanced ecosystem around high-voltage lines.
- Impact Assessments: Conducting thorough Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) is critical for identifying potential issues early in the planning process. These evaluations enable the development of focused mitigation strategies, ensuring adherence to environmental regulations and addressing local concerns. The ongoing legal challenges faced by the Cardinal-Hickory Creek initiative underscore the necessity of transparent and comprehensive EIAs to avoid costly delays and reputational damage. As Trey Ward, CEO of Direct Connect Development Company, stated, "And speed is going to be key to meeting President Biden’s ambitious goals," highlighting the urgency of addressing these environmental considerations.
Integrating these factors into the planning and implementation of high-voltage line placement not only complies with regulatory standards but also promotes community confidence and environmental responsibility. Suggested actions to safeguard birds include creating avian-safe structures, placing new transmission pathways away from high-risk zones, and burying cables to reduce collision hazards.
Financial Implications of High-Voltage Line Projects
High-voltage line placement initiatives are fundamentally influenced by significant financial factors that are crucial for successful implementation and long-term viability. Understanding these factors is essential for stakeholders involved in these projects.
Construction Costs: A comprehensive understanding of the costs associated with materials, labor, and equipment is vital for accurate budgeting. Average construction expenses for high-voltage line placement can vary significantly based on geographical location and specifications, frequently ranging from $1 million to $3 million per mile.
Funding Sources: Identifying potential funding sources is essential for securing the necessary capital. Options may include government grants, private investments, and utility company financing. Recent statistics indicate that approximately 40% of funding for utility infrastructure initiatives comes from federal and state grants, underscoring the importance of exploring these avenues.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis is essential for demonstrating the initiative’s financial viability to stakeholders and investors. This analysis should encompass not only initial construction costs but also long-term benefits such as increased property values and enhanced energy reliability. For instance, a case study on a 225 kV cable in France revealed that burying sections of the cable resulted in a 38% rise in property values for adjacent homes, highlighting the potential economic advantages of well-designed large-scale initiatives.
Long-term maintenance is critical for the sustainability of high-voltage line placement, necessitating the allocation of funds for ongoing upkeep and operational expenses. Financial analysts emphasize that neglecting these costs can lead to substantial expenses later on, potentially jeopardizing the initial investment. It is advisable to allocate approximately 2-5% of the total cost each year for maintenance to ensure operational efficiency and longevity.
Public Participation: Engaging the public is vital for the success of elevated power transmission endeavors. The case study titled "Public Involvement in SRP Initiatives" illustrates a structured approach to public outreach, including mailing notifications and creating initiative websites for updates. This engagement addresses public inquiries and fosters a collaborative environment.
Technological Integration: The integration of technology in planning and operations is increasingly important. As noted by ThinkLabs AI, the 2025 winner of DTECH's Initiate program, AI assistance is becoming essential for electric grids, enhancing critical planning and operational efficiency.
By addressing these financial factors and integrating community involvement and technological advancements, land acquisition experts can more effectively navigate the complexities of elevated power initiatives, ensuring that they are not only practical but also beneficial for all parties involved. Furthermore, a thorough understanding of congestion and interconnection challenges is crucial, as these factors can impede clean energy infrastructure development and lead to increased costs for consumers.
Strategies for Negotiation and Stakeholder Collaboration
Effective negotiation and cooperation with stakeholders are vital for the success of high-voltage line placement initiatives. Implementing effective strategies can yield more favorable results and ensure smoother execution. Key strategies include:
- Building Relationships: Establishing trust and rapport with landowners and community members is essential. Strong relationships can lead to more collaborative negotiations, as stakeholders are more inclined to endorse initiatives with which they feel a connection. Farmers expect adherence to formal rules in negotiations, which can protect their interests and facilitate fair outcomes.
- Understanding Interests: Identifying the interests and concerns of all parties involved is crucial. Tailoring solutions to meet diverse needs fosters goodwill and enhances the likelihood of successful negotiations. Research indicates that when stakeholders perceive fairness in negotiations, they are more inclined to engage positively, significantly influencing outcomes. A case study titled "Role of Perceived Fairness in Land Acquisition Negotiations" explored how administrative power and perceived fairness affect farmers' attitudes, highlighting the complexity of negotiation dynamics.
- Flexibility in Negotiations: Being open to alternative solutions, such as compensation packages or easement agreements, can facilitate smoother negotiations. Flexibility demonstrates a willingness to accommodate landowners' needs, leading to more amicable agreements. Statistics show that legal ownership can protect farmers and encourage short-term investments, emphasizing the benefits of effective negotiation strategies.
- Consistent Communication: Maintaining open channels of communication during the endeavor is essential. Promptly addressing concerns and keeping stakeholders informed can build ongoing support and mitigate potential conflicts. Research indicates that efficient communication techniques are linked to increased satisfaction levels among stakeholders, ultimately enhancing timelines and success. Prof. Yisheng Liu suggests that local governments could encourage farmers to embrace a cooperative attitude in land acquisition negotiations by fostering constructive interactions and pursuing a service-oriented approach.
In electrical infrastructure initiatives, cooperation among stakeholders is not merely advantageous; it is crucial. Successful negotiators emphasize the importance of building relationships and fostering a collaborative environment. For instance, case studies reveal that projects with strong stakeholder engagement often experience fewer delays and reduced costs, underscoring the impact of relationship building on negotiation success.
By prioritizing these strategies, land acquisition professionals can enhance their effectiveness in navigating the complexities of high-voltage line placement.

Conclusion
High-voltage power lines play a crucial role in modern energy infrastructure, enabling the effective transmission of electricity across extensive distances. The successful placement and management of these lines hinge on a thorough understanding of various factors, such as engineering considerations, environmental impacts, community concerns, and regulatory frameworks. Land acquisition professionals face a complex landscape that includes topography, proximity to existing infrastructure, and compliance with environmental regulations, all while engaging with local communities to address concerns and foster support.
The financial implications of high-voltage line projects further highlight the necessity of strategic planning and stakeholder collaboration. By conducting comprehensive cost-benefit analyses, understanding funding sources, and budgeting for long-term maintenance, project leaders can ensure the sustainability and economic viability of their initiatives. Moreover, effective negotiation strategies that prioritize relationship-building and open communication can significantly enhance stakeholder engagement, resulting in smoother project execution and minimized conflicts.
Ultimately, the successful integration of high-voltage power lines into the energy grid demands a multifaceted approach that balances technical, environmental, and community considerations. As electricity demand continues to rise, the insights gained from this exploration will be invaluable for land acquisition professionals and stakeholders alike. Emphasizing collaboration, transparency, and informed decision-making will not only facilitate the development of critical infrastructure but also cultivate community trust and promote environmental stewardship throughout the process.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are high-voltage power cables used for?
High-voltage power cables are essential for the efficient transmission of electricity over long distances, operating at voltages exceeding 36 kV. They connect power generation sources, such as solar and natural gas facilities, to consumers, strengthening the energy infrastructure.
What are the primary components of elevated power systems?
The primary components of elevated power systems include conductors, insulators, and support structures like towers or poles.
Why is it important for land acquisition professionals to understand high-voltage systems?
A thorough understanding of high-voltage systems is vital for land acquisition professionals to evaluate land requirements and assess the potential impacts of these systems on surrounding environments and communities, including land use patterns and property values.
How has technology improved efficiency in power distribution networks?
The integration of smart meters into distribution networks has resulted in a 33.6% improvement in loss detection, showcasing the critical role of technology in enhancing efficiency and reducing energy losses.
What ongoing research is being conducted in the field of power grids?
Ongoing research focuses on reconfiguring power grids to minimize active power losses, which is essential for maintaining a reliable power supply while reducing operational costs.
What factors influence the placement of high-voltage lines?
The placement of high-voltage lines is influenced by several factors, including topography, proximity to existing infrastructure, community concerns, and regulatory requirements.
How does topography affect high-voltage line routing?
The physical landscape, such as rugged terrains, can complicate routing decisions, while flatter areas can facilitate easier construction. Understanding topographical challenges is crucial for determining cost-effective and environmentally sensitive routes.
Why is proximity to existing infrastructure important for high-voltage line placement?
Routing high-voltage lines near existing roads and utilities minimizes the need for new easements, reducing construction costs and potential disruptions to the community, while also streamlining the permitting process.
What are the community concerns related to high-voltage lines?
Community concerns often stem from perceived health risks associated with electromagnetic fields and the aesthetic impact on the landscape. Engaging with the community through education and communication can help address these issues.
What regulatory requirements must be adhered to during the construction of electric transmission lines?
Compliance with federal, state, and local regulations is essential, as these regulations dictate specific routing and construction practices to ensure safety and environmental standards are met.
Why is understanding these factors critical as we approach 2025?
As electricity demand rises, understanding the factors influencing high-voltage line placement becomes increasingly critical, especially considering that the four largest electric power firms supply service to over 85% of California households.
List of Sources
- Fundamentals of High-Voltage Power Lines
- Electricity Losses in Focus: Detection and Reduction Strategies—State of the Art (https://mdpi.com/2076-3417/15/7/3517)
- Key Factors Influencing High-Voltage Line Placement
- Part 1 - Current and consequences: Understanding environmental impacts of transmission lines (https://blg.com/en/insights/2023/06/part-1-current-and-consequences-understanding-environmental-impacts-of-transmission-lines)
- Epidemiologic study of residential proximity to transmission lines and childhood cancer in California: description of design, epidemiologic methods and study population - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4617228)
- Quantifying siting difficulty: A case study of US transmission line siting (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0301421506000048)
- Navigating Regulatory and Legal Frameworks
- Leases: Land easements and Topic 842 (https://cohnreznick.com/insights/leases-land-easements-and-topic-842)
- Understanding Utility Easement Acquisition Services: A Complete Tutorial for Property Owners (https://blog.harbingerland.com/understanding-utility-easement-acquisition-services-a-complete-tutorial-for-property-owners)
- Understanding Easements: Key Facts for Property Owners (https://bluenotary.us/easement)
- Community Impact and Public Perception of High-Voltage Lines
- Residential distance from high-voltage overhead power lines and risk of Alzheimer’s dementia and Parkinson’s disease: a population-based case-control study in a metropolitan area of Northern Italy (https://academic.oup.com/ije/article/48/6/1949/5529302)
- Environmental justice: A contrary finding for the case of high-voltage electric power transmission lines - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4343544)
- Health responses to a new high-voltage power line route: design of a quasi-experimental prospective field study in the Netherlands - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3975333)
- Environmental Considerations in High-Voltage Line Placement
- Bird Safety a Concern in National Push to Build More Power Lines (https://audubon.org/news/bird-safety-concern-national-push-build-more-power-lines)
- (PDF) Wildlife and power lines (https://researchgate.net/publication/366440803_Wildlife_and_power_lines)
- Avoidance and Minimization Measures: Power Lines | U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service (https://fws.gov/story/avoidance-and-minimization-measures-power-lines)
- Financial Implications of High-Voltage Line Projects
- External costs of high-voltage overhead transmission lines: Evidence from a causal approach in rural France (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0195925524002269)
- Humphrey-Turpen 69 kV transmission project | SRP (https://srpnet.com/grid-water-management/grid-management/improvement-projects/humphrey-turpen-transmission)
- The Cost of Upgrading Electricity Transmission - AAF (https://americanactionforum.org/research/the-cost-of-upgrading-electricity-transmission)
- Benchmarking in Action: Comparing the Costs of HVDC (https://renewableenergyworld.com/power-grid/transmission/benchmarking-in-action-comparing-the-costs-of-hvdc)
- Strategies for Negotiation and Stakeholder Collaboration
- Effect of large-scale land acquisition by domestic and international entities on farm investment in northern Ghana (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405844024042336)
- The Effectiveness of Administrative Power on Farmers’ Attitude in Land Acquisition Negotiation: Mediating Role of Perceived Fairness (https://mdpi.com/2073-445X/13/6/896)




