Overview
The article focuses on the importance of local zoning compliance in the development of wind farms, emphasizing that adherence to local regulations is crucial for securing permits and fostering community support. It supports this by detailing how understanding zoning laws can prevent project delays and legal challenges, while also highlighting effective strategies for community engagement and regulatory navigation to ensure successful energy initiatives.
Introduction
In the evolving landscape of renewable energy, wind farm development stands at the forefront of sustainable initiatives. However, the path to successful project execution is fraught with challenges, particularly concerning local zoning compliance. This critical aspect not only dictates where wind farms can be established but also influences the overall viability of these projects.
As developers grapple with an intricate web of local, state, and federal regulations, understanding the nuances of zoning ordinances becomes paramount. Engaging with communities and navigating the regulatory framework effectively can mean the difference between project success and costly delays.
With the stakes higher than ever, the importance of local zoning compliance is increasingly recognized as a cornerstone for fostering renewable energy advancements.
The Importance of Local Zoning Compliance in Wind Farm Development
Local zoning compliance for wind farms is crucial for energy farm developments, ensuring conformity to municipal regulations and land use policies. This compliance is not just a formality; it is critical for securing necessary permits and mitigating potential legal challenges. Developers need to thoroughly understand local zoning compliance for wind farms, which outlines permissible locations, specifies height restrictions, and governs proximity to residential areas.
Engaging with local zoning compliance for wind farms early in the planning process can significantly enhance execution and cultivate community support. Moreover, recent updates suggest that effective local zoning compliance for wind farms is increasingly acknowledged as a crucial element in the success of renewable initiatives. Non-compliance can result in project delays, financial penalties, or outright denials, underscoring the significance of this area for developers.
According to Joe Lynn Schroeder from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, understanding local zoning compliance for wind farms is essential to navigating the complexities of renewable resource development. Her insights reflect a growing consensus in the industry on the importance of local zoning in fostering sustainable initiatives. As renewable power sources continue to grow, local zoning compliance for wind farms will certainly remain a central concern for developers in relation to initiative viability.
Moreover, it is essential to recognize that power purchase agreements (PPAs) for turbine initiatives generally have terms spanning from 10 to 25 years, emphasizing the long-term aspect of these developments and their dependence on local zoning compliance for wind farms. The U.S. Department of the Interior's Minerals Management Service plays a crucial role in reviewing offshore wind-energy development proposals, further emphasizing the regulatory landscape that developers must navigate. Furthermore, incorporating wind power into the U.S. power grid requires tackling reliability issues, as shown in the case study on grid integration of wind power, which highlights the practical implications of zoning adherence on feasibility and reliability in the power mix.
Navigating Regulatory Frameworks for Wind Energy Projects
Wind energy projects must comply with local zoning compliance for wind farms, in addition to a complex array of regulations at local, state, and federal levels. The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) and local planning commissions play pivotal roles in establishing local zoning compliance for wind farms. Developers are encouraged to conduct comprehensive research to identify relevant regulations concerning local zoning compliance for wind farms, as well as land use, environmental protection, and public safety.
As of 2023, with cumulative global land-based capacity reaching 1,021 GW and a remarkable increase in electricity generation from this source by 243,580 GWh or 134% from 2014 to 2023, adherence to these regulatory standards is more critical than ever. This growth highlights the broadening scope of wind initiatives, especially as distributed wind applications are now set up in all 50 states. Hiring legal advisors with knowledge in energy initiatives can greatly simplify adherence efforts and elucidate the effects of different regulations.
Moreover, remaining updated on the latest regulatory changes for 2024 is crucial for ensuring ongoing local zoning compliance for wind farms. Joseph Womble notes the importance of this diligence:
Analyses of achieving 100% carbon-free electricity by 2035 indicate that annual installation rates of renewables must nearly double those seen in 2023.
Additionally, the case study titled 'A Decade of Wind Growth Across the US (2014-2023)' illustrates how states like Texas, Oklahoma, Iowa, Kansas, and Illinois have successfully navigated regulatory frameworks to achieve substantial growth in wind capacity.
This highlights not only the regulatory landscape but also the pressing need for effective navigation of these frameworks to achieve local zoning compliance for wind farms and meet ambitious carbon reduction targets.
Best Practices for Ensuring Land Compliance in Wind Energy Projects
To attain local zoning compliance for wind farms in renewable energy initiatives, developers must prioritize comprehensive land surveys and evaluations to identify any zoning conflicts or limitations. Engaging with local authorities and initiating public outreach are essential strategies to mitigate community concerns from the outset. As William Daly, the planning and development director of Wyoming County, emphasizes,
Establishing a robust dialogue with stakeholders early in the process can significantly enhance project acceptance.
Clear communication with landowners is crucial for securing necessary agreements and easements, thereby fostering a collaborative environment. Furthermore, meticulous documentation of all compliance-related activities not only supports the permitting process but also serves as concrete evidence of adherence to regulatory standards. Anticipatory planning for wind-energy development should be coordinated with regulatory reviews to improve decision quality.
The financial implications of local zoning compliance for wind farms are significant; for instance, approximately $32 million per year of lost revenue from Kansas' lifetime exemption could have been allocated to rural school districts, highlighting the importance of proper land regulation. Additionally, case studies such as 'Navigational Tools for Wind Project Development' illustrate strategies for successfully navigating the permitting process, including understanding ROW processes and engaging in NEPA compliance. By applying these best practices, developers can simplify the route toward successful execution in the energy sector.
Conducting Effective Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs)
Conducting comprehensive Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) is essential for identifying the potential environmental consequences of wind farm initiatives, including impacts on wildlife, air quality, and local ecosystems. Effective communication and coordination among stakeholders are crucial in designing these impact studies. Engaging qualified environmental consultants is essential for ensuring adherence to the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) and relevant state regulations.
Recent developments highlight the necessity for a centralized repository for data gathered from EIAs and post-construction monitoring, which can significantly inform planning decisions. Furthermore, incorporating community input throughout the EIA process not only addresses local concerns but also fosters transparency and trust among stakeholders. Presenting EIA findings to the community and other stakeholders can enhance support for the initiative, ultimately streamlining compliance and permitting efforts.
As noted by Philip J. K. McGowan,
We also would like to thank R. Cox for contacting different companies and asking for data,
underscoring the importance of collaborative data-sharing efforts. Furthermore, floating turbines can presently function in water depths up to 300 m and possess the capability to attain depths of up to 700 m, which is crucial for future energy initiatives. Moreover, case studies such as 'Measuring Responses of Marine Mammals to Wind Farm Construction' reveal that traditional before-after-control-impact (BACI) designs have limitations.
The proposed gradient design allows for improved assessment of spatial impacts, emphasizing the critical need for enhanced data collection techniques and its implications for future spatial planning decisions.
Implementing Community Engagement Strategies for Successful Compliance
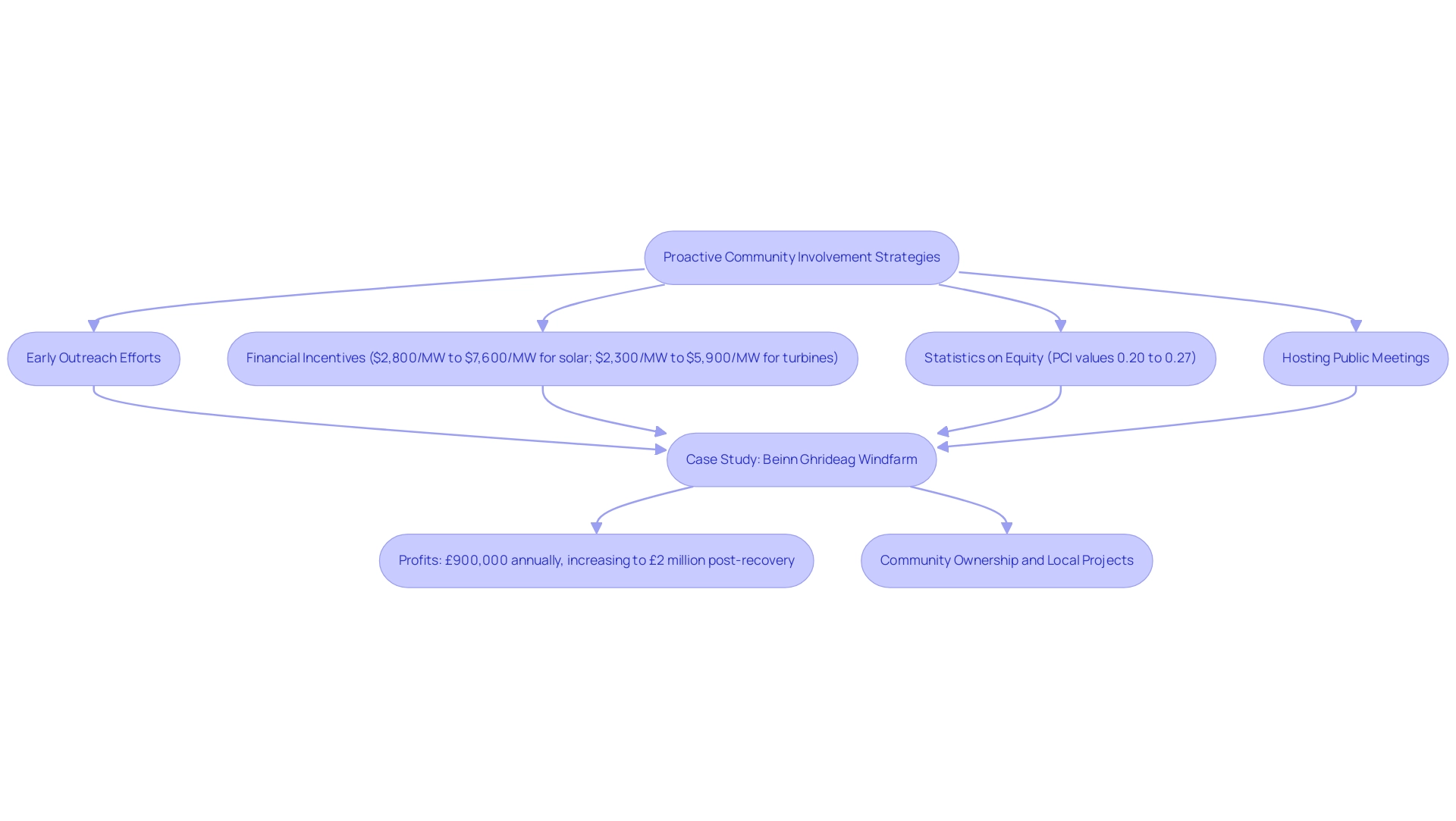
Proactive community involvement strategies are essential for achieving local zoning compliance for wind farms and the successful development of energy farm initiatives. Early outreach efforts that offer clear, accessible information about the initiative’s benefits and potential impacts can significantly influence public perception. For example, community benefit agreements for solar initiatives vary from $2,800/MW to $7,600/MW each year, whereas for turbines, they generally span from $2,300/MW to $5,900/MW annually, highlighting the financial incentives that can be utilized to foster community backing.
Additionally, statistics on distributional justice statements indicate PCI values ranging from 0.20 to 0.27, highlighting the importance of equity in community engagement efforts. Hosting public meetings and informational sessions encourages open dialogue, allowing developers to address community concerns directly. As one resident aptly noted,
they strongly support small scale communities' wind power.
However, the shocking scale of the EDF wind farm highlights issues regarding local zoning compliance for wind farms and the lack of consultation. This sentiment underscores the importance of meaningful consultation before major developments and suggests that developers should prioritize local zoning compliance for wind farms, along with transparency and responsiveness in their outreach efforts. Collaborating with local organizations and influencers can further enhance support.
The Beinn Ghrideag Windfarm exemplifies this approach; it is owned by community councils and supported by a Scottish Government loan, and this 9 MW wind farm was developed with local zoning compliance for wind farms despite initial planning objections, generating £900,000 annually in profits, which will increase to £2 million post-recovery of initial costs, funding local projects like woodland creation and energy efficiency initiatives. This case illustrates how effective community engagement can lead to successful financial outcomes and local benefits. Recent recommendations from LBNL suggest leveraging federal clean-energy tax credits to incentivize shared decision-making and profit-sharing arrangements with host communities.
By nurturing positive connections and guaranteeing extensive public engagement, developers can not only diminish opposition but also improve adherence to local regulations.
Monitoring and Reporting Compliance: Best Practices for Developers
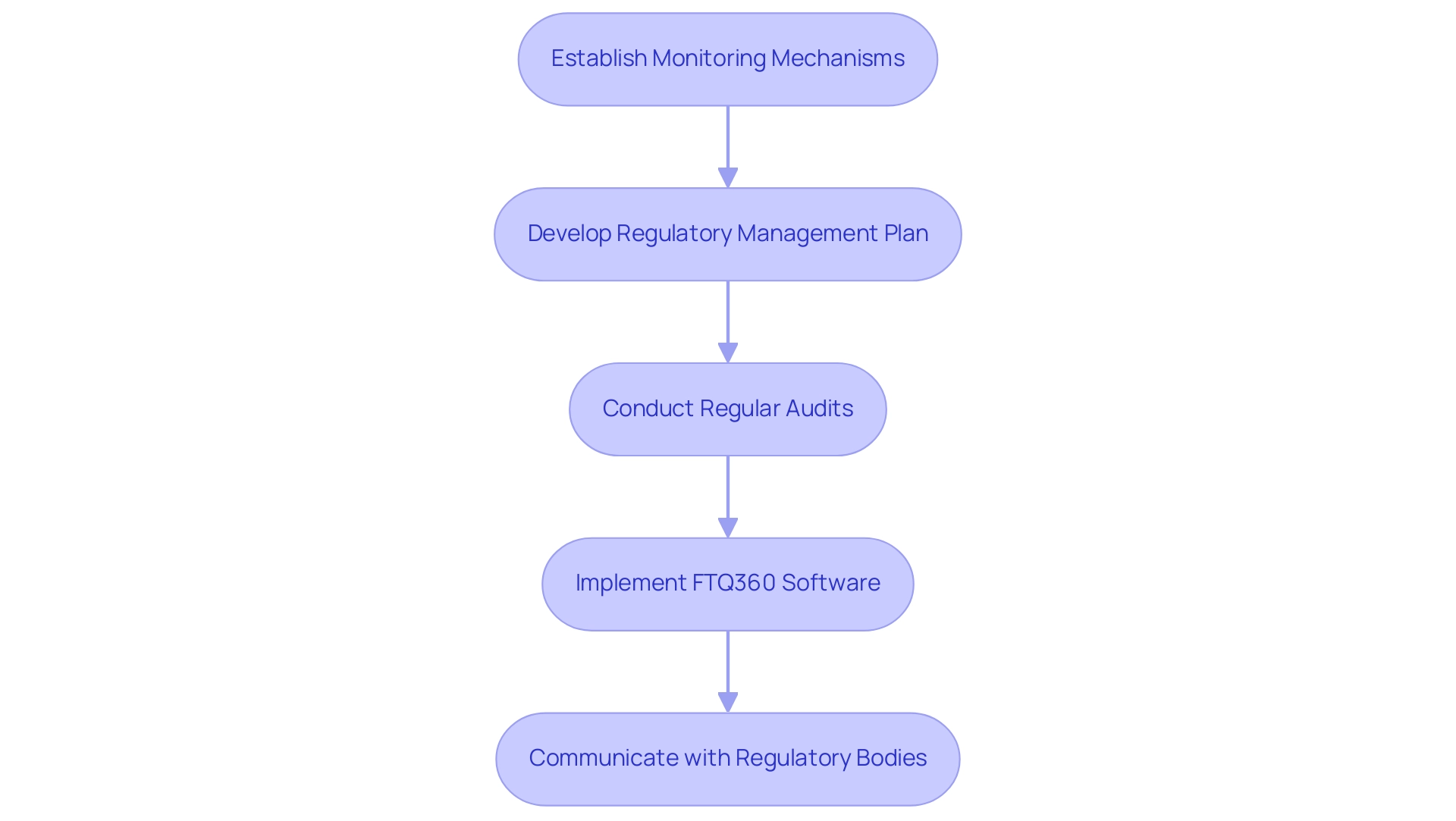
Once a wind farm becomes operational, it is imperative for developers to establish robust monitoring and reporting mechanisms to ensure local zoning compliance for wind farms and adherence to environmental regulations. Effective navigation of zoning controls, which dictate land use types and include specific permitting restrictions, is essential for achieving local zoning compliance for wind farms. A well-defined regulatory management plan is essential; it should clearly outline monitoring responsibilities and establish reporting timelines.
Regular audits and evaluations can proactively recognize potential adherence issues before they escalate, thereby mitigating risks. The implementation of comprehensive solutions like FTQ360 Quality Management Software significantly enhances the visibility of compliance requirements and inspection processes, ensuring that endeavors meet regulatory standards. FTQ360 streamlines the tracking and examination of inspection data, offering insights that assist in minimizing risks linked to non-compliance in renewable initiatives.
As Ed Caldeira highlights, for the sector to keep supplying clean, renewable power from turbine installations, managers must establish effective QAQC programs. Additionally, fostering open communication with regulatory bodies and stakeholders post-approval not only promotes transparency but also helps cultivate favorable relationships, which can facilitate future endeavors. The renewable power sector experienced a significant rise in capacity, with 113 GW introduced in 2020 compared to 59 GW in 2019, highlighting the necessity of adherence as more initiatives become operational.
By adhering to these best practices in compliance monitoring, wind energy projects can navigate the complexities of regulatory requirements, ensuring local zoning compliance for wind farms while contributing to sustainable energy goals.
Conclusion
The successful development of wind farms hinges significantly on local zoning compliance, which serves as a critical foundation for project viability. Understanding and adhering to zoning ordinances not only facilitates the securing of necessary permits but also mitigates potential legal challenges that could derail project timelines. Engaging early with local authorities and communities fosters support and can lead to more streamlined project execution, reflecting the growing recognition of compliance as a vital component of renewable energy initiatives.
As the landscape of wind energy continues to evolve, developers must navigate a complex regulatory framework that encompasses local, state, and federal regulations. The importance of staying informed about these regulations cannot be overstated, especially given the ambitious goals for carbon reduction and the increasing demand for renewable energy solutions. By implementing best practices, such as:
- Conducting thorough land assessments
- Engaging in effective community outreach
developers can enhance their chances of success while building trust with stakeholders.
Incorporating comprehensive Environmental Impact Assessments and robust monitoring systems further solidifies compliance efforts, ensuring that wind projects not only meet regulatory standards but also address environmental and community concerns. Ultimately, the interplay between local zoning compliance and successful wind energy development will remain a focal point as the sector strives to meet growing energy demands sustainably. By prioritizing compliance and community engagement, developers can pave the way for a more resilient and environmentally friendly energy future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is local zoning compliance important for wind farms?
Local zoning compliance is crucial for wind farms as it ensures conformity to municipal regulations and land use policies, secures necessary permits, and mitigates potential legal challenges.
What factors do local zoning regulations for wind farms typically address?
Local zoning regulations outline permissible locations for wind farms, specify height restrictions, and govern the proximity of wind turbines to residential areas.
How can engaging with local zoning compliance early in the planning process benefit developers?
Early engagement with local zoning compliance can enhance project execution and cultivate community support, which is vital for the success of renewable initiatives.
What are the potential consequences of non-compliance with local zoning regulations for wind farms?
Non-compliance can lead to project delays, financial penalties, or outright denials, highlighting the significance of adhering to local zoning regulations.
Who emphasized the importance of understanding local zoning compliance for wind farms?
Joe Lynn Schroeder from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory emphasized that understanding local zoning compliance is essential for navigating the complexities of renewable resource development.
What role does the U.S. Department of the Interior's Minerals Management Service play in wind energy development?
The U.S. Department of the Interior's Minerals Management Service reviews offshore wind-energy development proposals, underscoring the regulatory landscape that developers must navigate.
How long do power purchase agreements (PPAs) for wind turbine initiatives typically last?
Power purchase agreements for turbine initiatives generally have terms spanning from 10 to 25 years.
What recent trends highlight the importance of local zoning compliance for wind farms?
The cumulative global land-based wind capacity reaching 1,021 GW and a significant increase in electricity generation from wind energy underscore the growing importance of local zoning compliance.
What should developers do to ensure adherence to local zoning compliance for wind farms?
Developers are encouraged to conduct comprehensive research on relevant regulations concerning local zoning compliance, land use, environmental protection, and public safety. Hiring legal advisors knowledgeable in energy initiatives can also simplify this process.
Why is it important for developers to stay updated on regulatory changes?
Staying updated on the latest regulatory changes is crucial for ensuring ongoing local zoning compliance, especially as achieving ambitious carbon reduction targets requires effective navigation of regulatory frameworks.
List of Sources
- The Importance of Local Zoning Compliance in Wind Farm Development
- nap.nationalacademies.org (https://nap.nationalacademies.org/read/11935/chapter/7)
- windexchange.energy.gov (https://windexchange.energy.gov/economic-development-guide)
- Navigating Regulatory Frameworks for Wind Energy Projects
- A Decade of Growth in Solar and Wind Power: Trends Across the U.S. | Climate Central (https://climatecentral.org/report/solar-and-wind-power-2024)
- US Clean Power Development Sees Record Progress, As Well As Stronger Headwinds (https://wri.org/insights/clean-energy-progress-united-states)
- Land-Based Wind Market Report (https://energy.gov/eere/wind/land-based-wind-market-report)
- Wind Market Reports: 2024 Edition (https://energy.gov/eere/wind/wind-market-reports-2024-edition)
- Best Practices for Ensuring Land Compliance in Wind Energy Projects
- windexchange.energy.gov (https://windexchange.energy.gov/economic-development-guide)
- stoel.com (https://stoel.com/insights/reports/the-law-of-wind/federal-land-issues-with-siting-and-permitting)
- nap.nationalacademies.org (https://nap.nationalacademies.org/read/11935/chapter/7)
- Conducting Effective Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs)
- aquaticbiosystems.biomedcentral.com (https://aquaticbiosystems.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/2046-9063-10-8)
- esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com (https://esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1890/ES14-00331.1)
- Implementing Community Engagement Strategies for Successful Compliance
- utilitydive.com (https://utilitydive.com/news/community-engagement-locals-renewable-energy-developers-berkeley-survey/726042)
- What makes local energy projects acceptable? Probing the connection between ownership structures and community acceptance (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301421522004761)
- Monitoring and Reporting Compliance: Best Practices for Developers
- windexchange.energy.gov (https://windexchange.energy.gov/small-wind-guidebook)
- QAQC for Wind Farm Construction Projects: Why it is Important (https://blog.ftq360.com/blog/qaqc-for-wind-farm-construction-projects)




