Introduction
In the complex landscape of land development, securing transmission land entitlement stands as a crucial step for developers aiming to establish projects such as power lines and substations. This multifaceted process encompasses a range of legal, regulatory, and community engagement elements that can significantly influence project outcomes.
From understanding property rights and navigating zoning regulations to addressing stakeholder concerns and leveraging technology, each component plays a pivotal role in achieving successful entitlements. As the demand for efficient energy solutions grows, so too does the necessity for developers to master the intricacies of this process, ensuring not only compliance with legal frameworks but also fostering positive relationships with local communities.
This article delves into the fundamentals of transmission land entitlement, outlining key steps, common challenges, and best practices that can enhance project viability in an ever-evolving regulatory environment.
Fundamentals of Transmission Land Entitlement
The legal framework of transmission land entitlement enables developers to secure the necessary rights for establishing transmission initiatives, such as power lines and substations. A thorough comprehension of this process involves several key components:
-
Understanding Land Rights: Developers must have a solid grasp of various property rights, including fee simple ownership, easements, and leases.
Each type of right carries distinct implications regarding usage and ownership, which can significantly influence execution.
-
Zoning Regulations: Understanding local zoning laws is essential, as these regulations determine allowable uses and the kinds of structures that can be built. Recent updates in zoning regulations can further affect use for transmission projects, necessitating close attention to local governance.
-
Permitting Requirements: Before any development activities commence, securing the appropriate permits from local, state, and federal authorities is essential. This often includes comprehensive environmental assessments and specific land use permits, which can be time-consuming. In Oregon, for instance, the state's siting process mandates that a final route is determined prior to the commencement of the review process, potentially extending permitting timelines significantly.
-
Stakeholder Engagement: Successful initiatives rely heavily on the engagement with local communities, landowners, and governmental entities. Constructive stakeholder outreach fosters support and helps mitigate potential conflicts during project progression. Significantly, employing neutral third-party facilitators is increasingly advised to manage the complexities of conflict resolution among various authorities during the permitting phase.
As emphasized by WAPA, due to Southline’s comprehensive routing methodology and extensive stakeholder outreach, agency alternatives developed through the NEPA framework resulted in only minor route variations, which could potentially minimize or evade local resource conflicts.
-
Legal Considerations: Developers must be aware of the legal frameworks governing property rights, which include property laws and regulations pertaining to easements and rights-of-way. A comprehensive grasp of these legalities is essential to guarantee a smooth and successful approval procedure.
For instance, the use of Programmatic Environmental Impact Statements (PEIS) is gaining traction, as seen in the BLM's draft PEIS for utility-scale solar energy development. This approach enables a wider environmental impact evaluation, simplifying specific reviews and potentially assisting in rights acquisition for transmission land entitlement related initiatives.
Focusing on these fundamentals not only helps in managing the complexities of the approval system but also improves the chances for success.
Navigating the Entitlement Process: Key Steps for Developers
Successfully navigating the entitlement process requires developers to meticulously follow several essential steps:
- Initial Site Assessment: Conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the proposed site to determine its suitability for the intended development. This evaluation should include a comprehensive examination of environmental reports, current usage, and any potential constraints that may impact the project.
- Engaging Legal Experts: It is crucial to consult with legal professionals who specialize in use regulations. As Michael Belasco, an expert with an MBA and Master in Real Estate from Cornell University, emphasizes, "The right legal guidance is essential for navigating the complexities of land use laws and ensuring compliance with local regulations." Their knowledge guarantees adherence to local regulations and helps in tackling any legal challenges that may occur during the approval phase.
- Submitting Applications: Developers must prepare and submit the required applications for transmission land entitlement permits to the appropriate authorities. This step necessitates meticulous attention to detail, including ensuring that all necessary documentation is complete and accurate.
- Community Outreach: Proactive engagement with local stakeholders and the community is vital. By gathering support and addressing any concerns related to the initiative, developers can foster positive relationships that may facilitate smoother approval processes. This community outreach is essential, particularly given A. CRE Consulting's experience with over $21 billion in services, underscoring the significance of strong local connections.
- Public Hearings: Developers should be prepared to present their plans at public hearings or community meetings. This forum provides an opportunity to justify their plans and respond directly to community feedback, which can be critical for gaining support.
- Final Approvals: After incorporating community feedback and making necessary adjustments, developers must secure final approvals from all relevant agencies. This may encompass state and federal entities, depending on the extent of the initiative. A relevant case study is the handling of zoning variances, which allow for waivers of certain zoning requirements, thus providing flexibility in meeting zoning regulations and facilitating development.
- Monitoring and Compliance: Once permissions are granted, it becomes imperative for developers to monitor compliance with all conditions outlined in the approvals. This diligence is essential to prepare for subsequent phases of development.
By following these steps and utilizing the knowledge from industry specialists and case studies, developers can greatly improve their chances of a successful and efficient approval procedure related to transmission land entitlement, thereby reducing possible delays and legal obstacles.
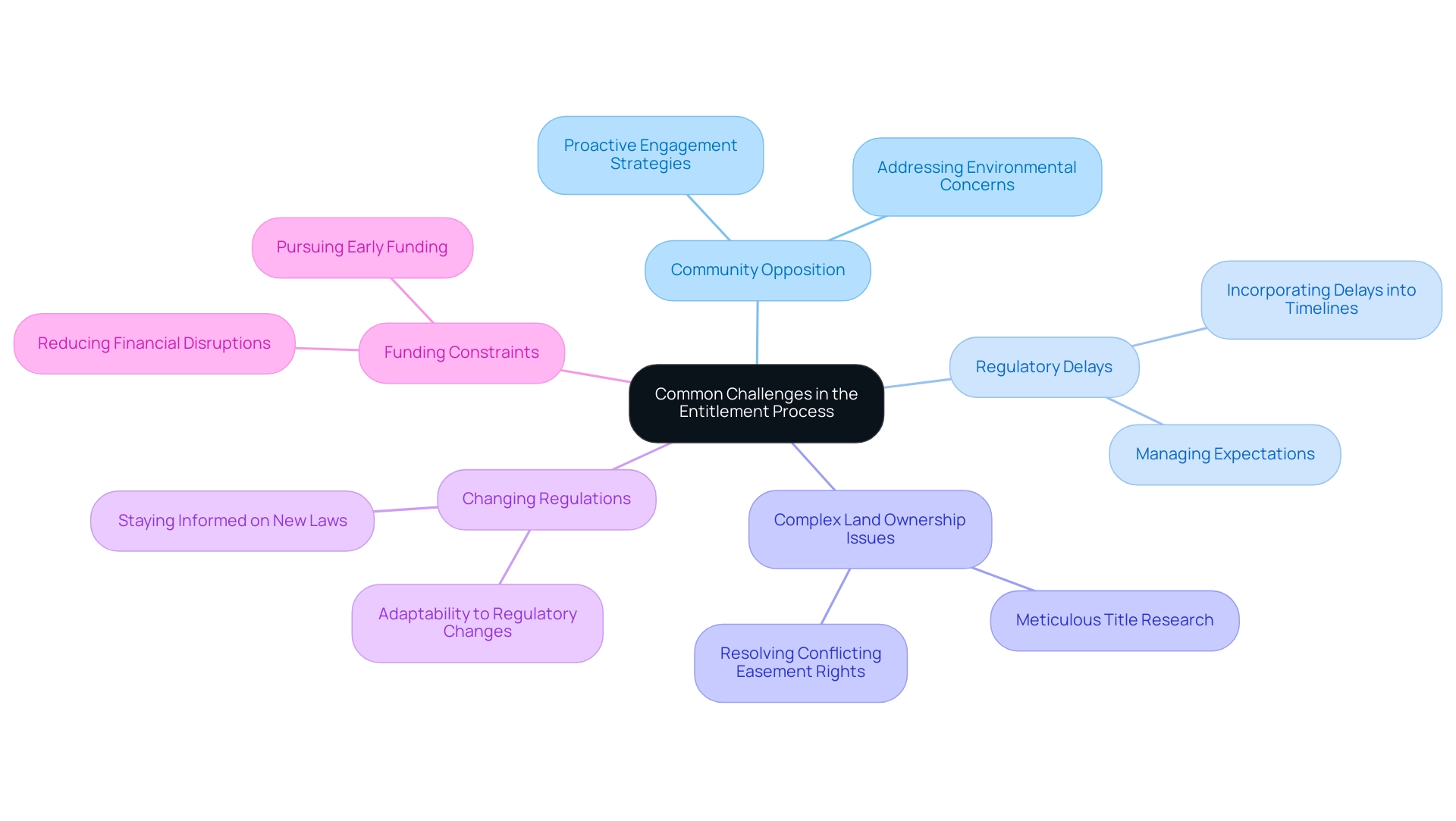
Common Challenges in the Entitlement Process
Navigating the transmission land entitlement approval journey presents developers with several significant challenges, which can greatly influence timelines and results. Key challenges include:
-
Community Opposition: Resistance from local communities often arises due to concerns regarding environmental impacts or changes to the neighborhood's character.
According to recent statistics, 60% of programs in 2021 focused on new member welcomes and onboarding, highlighting the importance of proactive community engagement strategies. Adrian Speyer, former Head of Community at Higher Logic, emphasizes that combining passion for digital marketing and community can help brands create meaningful connections with their audiences. These outreach strategies are essential in addressing community concerns early and fostering a collaborative environment.
-
Regulatory Delays: The permitting procedure usually necessitates several approvals, which can result in considerable holdups, especially when further studies or evaluations are required. Developers should incorporate potential delays into their project timelines to manage expectations and maintain momentum.
-
Complex Land Ownership Issues: The presence of multiple landowners or conflicting easement rights can complicate the approval process for transmission land entitlement.
Conducting meticulous title research is crucial to identify and resolve these issues before they escalate, ensuring a smoother progression through approvals. Insights from regression analysis on agricultural land transfer can illuminate the complexities of these ownership issues and their effect on the allocation process.
-
Changing Regulations: The regulatory landscape is subject to change, and new laws or amendments may emerge during the approval process.
Staying informed and adaptable to evolving regulations is vital for developers to maintain viability and compliance.
-
Funding Constraints: Obtaining financing can prove challenging, especially if authorization delays occur. Developers are encouraged to pursue funding early in the stages, which can reduce financial disruptions and enable prompt execution.
These challenges highlight the significance of strategic planning and proactive management in the property acquisition process, particularly in relation to transmission land entitlement, enabling developers to maneuver around obstacles efficiently and improve success.
Best Practices for Successful Land Entitlement
To significantly enhance the likelihood of success in land entitlement, developers should consider the following best practices:
- Early Engagement: Begin conversations with local authorities and community members at the outset of the initiative. This proactive approach fosters relationships and cultivates community support, which is crucial for long-term initiative viability. According to a recent study, early engagement can lead to a 30% increase in project acceptance rates.
- Thorough Research: Conduct comprehensive research on property use, environmental impacts, and zoning laws. This diligence ensures that all potential issues are identified and addressed prior to submission, minimizing the risk of delays. As noted by land development expert Jane Doe, "Understanding the regulatory landscape before submitting applications can save developers significant time and resources."
- Clear Communication: Maintain consistent and transparent communication with all stakeholders throughout the entitlement process. Open dialogue fosters trust and encourages collaboration, which is essential for overcoming challenges that may arise. A case study involving the Greenfield Development Initiative demonstrated that endeavors with regular stakeholder updates experienced 25% fewer disputes.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Be prepared to adjust plans based on stakeholder feedback and evolving regulations. This flexibility not only mitigates potential setbacks but also demonstrates responsiveness to community concerns, ultimately contributing to acceptance. Recent trends indicate that developers who adapt their plans based on community input are 40% more likely to achieve successful outcomes.
- Documentation: Keep meticulous records of all correspondence, permits, and approvals. This practice encourages openness and responsibility throughout the approval procedure, acting as a useful resource if any disagreements occur. As highlighted in the FTC's recent ruling on noncompete agreements, thorough documentation can be critical in resolving conflicts.
By applying these optimal methods, backed by pertinent data and specialist perspectives, developers can manage the intricacies of property authorization more efficiently, ultimately enhancing the likelihood of favorable results.
The Role of Technology in Streamlining Entitlement
The integration of technology is crucial for streamlining the transmission land entitlement process, offering developers a range of tools to enhance efficiency and precision in their projects. Notable technologies include:
-
GIS Mapping: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) offer advanced mapping functions and spatial analysis, allowing developers to visualize usage patterns and identify potential issues proactively.
The application of GIS in spatial use planning is increasingly recognized for its ability to improve decision-making processes.
-
AI-Powered Title Research: The implementation of AI-driven software significantly accelerates title research, improving both speed and accuracy. This technology enables developers to swiftly recognize land ownership and easement issues, which can otherwise postpone the approval process.
-
Project Management Tools: Utilizing project management software helps streamline workflow by tracking progress, managing critical documents, and fostering effective communication among team members. This ensures that all stakeholders are consistently informed, contributing to a more organized and efficient approval process.
-
Virtual Public Engagement: Online engagement platforms facilitate communication with community members and stakeholders, particularly in scenarios where traditional in-person meetings may be impractical. This technology fosters inclusivity and transparency, allowing for broader community input.
-
Data Analytics: Utilizing data analytics offers insights into property use, zoning regulations, and community demographics, which are essential for informed decision-making and strategic planning. Current trends indicate that developers who effectively analyze these data points can better anticipate community needs and regulatory challenges.
Incorporating these technological advancements not only enhances the efficiency of the transmission land entitlement process but also aligns with contemporary expectations for transparency and community engagement in development projects. As noted by Zhang, Zhi, the digital economy has the potential to enhance urban green use efficiency, indicating that technology can play a significant role in sustainable development. Furthermore, considering the average self-reported health rating of 3.129 among household members, it becomes evident that the implications of technology in property development extend beyond efficiency, affecting overall community welfare.
The insights gained from the China Family Panel Studies (CFPS) underscore the importance of digital access in influencing land rental behavior, illustrating how technology can shape socio-economic dynamics in rural contexts.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of transmission land entitlement is essential for developers aiming to successfully navigate the complexities of establishing vital energy infrastructure. By grasping the fundamentals of land rights, zoning regulations, and permitting requirements, developers can lay a solid foundation for their projects. Engaging with stakeholders and adhering to legal considerations further enhances the likelihood of achieving successful entitlements.
The path to entitlement is fraught with challenges, including community opposition, regulatory delays, and complex land ownership issues. However, by implementing best practices such as:
- Early engagement
- Thorough research
- Clear communication
developers can mitigate these obstacles and foster positive relationships within the communities they serve. Moreover, the integration of technology plays a crucial role in streamlining the entitlement process, enabling developers to enhance efficiency and precision.
Ultimately, mastering the transmission land entitlement process not only ensures compliance with legal frameworks but also promotes collaboration and transparency with local stakeholders. As the demand for efficient energy solutions continues to rise, the ability to navigate this multifaceted landscape will be pivotal in achieving successful project outcomes, contributing to a sustainable energy future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the legal framework of transmission land entitlement?
The legal framework of transmission land entitlement enables developers to secure necessary rights for establishing transmission initiatives, such as power lines and substations.
What are the key components developers need to understand regarding land rights?
Developers must understand various property rights, including fee simple ownership, easements, and leases, as each type carries distinct implications for usage and ownership.
Why are zoning regulations important for transmission projects?
Zoning regulations determine allowable uses and the types of structures that can be built, and recent updates can significantly affect transmission projects, requiring developers to pay close attention to local governance.
What are the permitting requirements for developers?
Developers must secure appropriate permits from local, state, and federal authorities before commencing development, often including environmental assessments and land use permits. In Oregon, a final route must be determined before the review process, which can extend permitting timelines.
How important is stakeholder engagement in the development process?
Engaging with local communities, landowners, and governmental entities is crucial for fostering support and mitigating conflicts during project progression. Employing neutral third-party facilitators is advised to manage complexities in conflict resolution.
What legal considerations should developers be aware of?
Developers must understand property laws and regulations regarding easements and rights-of-way to ensure a smooth approval process. Programmatic Environmental Impact Statements (PEIS) are also gaining traction to simplify reviews and assist in rights acquisition.
What are the essential steps in successfully navigating the entitlement process?
Essential steps include initial site assessment, engaging legal experts, submitting applications, community outreach, public hearings, securing final approvals, and monitoring compliance with approval conditions.
Why is community outreach vital for developers?
Proactive engagement with local stakeholders helps gather support, address concerns, and foster positive relationships, which can facilitate smoother approval processes.
What role do public hearings play in the entitlement process?
Public hearings provide developers an opportunity to present their plans, justify them, and respond to community feedback, which is critical for gaining support.
What should developers do after securing approvals?
Developers must monitor compliance with all conditions outlined in the approvals to prepare for subsequent phases of development.
List of Sources
- Fundamentals of Transmission Land Entitlement
- Evidence-based recommendations for overcoming barriers to federal transmission permitting - Niskanen Center (https://niskanencenter.org/evidence-based-recommendations-for-overcoming-barriers-to-federal-transmission-permitting)
- Navigating the Entitlement Process: Key Steps for Developers
- Strategic Triumph: Harnessing the Power of Entitlement Data in Land Use Planning (https://atcresearch.co/guest-blog/the-power-of-entitlement-data-in-land-use-planning)
- Through The Entitlement Process: Identifying Risks and Strategies For Mitigation (Updated Aug 2024) (https://adventuresincre.com/entitlement)
- A Guide To The Land Entitlement Process | VestRight (https://vestright.com/land-entitlement-process)
- Common Challenges in the Entitlement Process
- Analyzing Online Community Stats: 44 Takeaways for 2021 | Higher Logic (https://higherlogic.com/blog/online-communities-facts-statistics-2021)
- Overcoming Community Opposition: A Guide for Developers (https://bhfs.com/insights/alerts-articles/2024/overcoming-community-opposition-a-guide-for-developers)
- (PDF) The Factors Driving the Escalation of Community Opposition to Affordable Housing Development (https://researchgate.net/publication/297674959_The_Factors_Driving_the_Escalation_of_Community_Opposition_to_Affordable_Housing_Development)
- Best Practices for Successful Land Entitlement
- Six Tips and Best Practices to Successfully Navigate the Entitlement Process for Commercial Developments (https://bhfs.com/insights/alerts-articles/2024/six-tips-and-best-practices-to-successfully-navigate-the-entitlement-process-for-commercial-developments)
- Open Data for Official Statistics: History, Principles, and Implementation (https://opendatawatch.com/publications/open-data-for-official-statistics-history-principles-and-implentation)
- The Role of Technology in Streamlining Entitlement
- The Impact of Digital Technology on Land Rent-Out Behavior: Information Sharing or Exclusion? (https://mdpi.com/2077-0472/12/7/1046)
- Has the Digital Economy Improved the Urban Land Green Use Efficiency? Evidence from the National Big Data Comprehensive Pilot Zone Policy (https://mdpi.com/2073-445X/13/7/960)
- Finding common ground: Integrating data, science and innovation for better use of land (https://gov.uk/government/publications/finding-common-ground-integrating-data-science-and-innovation-for-better-use-of-land/finding-common-ground-integrating-data-science-and-innovation-for-better-use-of-land)




