Introduction
The effective management and acquisition of land for transmission lines is a multifaceted endeavor that plays a crucial role in the development of energy infrastructure. As the demand for renewable energy sources surges, understanding the complexities of transmission line land services becomes increasingly vital. This article delves into the fundamental components of these services, highlighting the importance of:
- Meticulous land assessments
- Regulatory compliance
- Community engagement
It examines the strategic acquisition and management of right-of-way (ROW), the integration of advanced technologies such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS), and the necessity of addressing regulatory and environmental considerations. Furthermore, it explores future trends and challenges that will shape the landscape of transmission line land services, underscoring the need for adaptability and innovation in a rapidly evolving industry. Through a comprehensive analysis, this article aims to illuminate the critical aspects that influence the success of transmission projects in a world striving for sustainable energy solutions.
Fundamentals of Transmission Line Land Services
Transmission line land services encompass a comprehensive suite of activities crucial for the effective management and acquisition of space required for the installation and maintenance of transmission lines. These transmission line land services extend beyond basic site identification and encompass meticulous use assessments and evaluations of property ownership and rights. A comprehensive grasp of essential elements like easements and encroachments, together with pertinent use regulations, is crucial for the successful implementation of these endeavors.
As noted by experts in the field, the importance of these elements cannot be overstated; they directly influence timelines and cost efficiency. For instance, recent studies have highlighted that in Krakow alone, 105 expropriation decisions were issued, significantly limiting the use of real properties and demonstrating the complexities involved. To mitigate risks associated with land acquisition and avoid delays, consultants emphasize the necessity of thorough research and strategic planning.
This proactive method is crucial in navigating the complex environment of delivery initiatives, ensuring adherence to regulations while effectively managing stakeholder expectations. Furthermore, as Thomas O. Jackson stated, the NIEHS determined that while EMF exposure cannot be ruled as entirely safe, the scientific evidence of health risks is 'insufficient to warrant aggressive regulatory concern.' This viewpoint emphasizes the significance of tackling health risks in relation to power lines.
Furthermore, the study details potential research avenues for carbon emission accounting in the power grid sector, which could offer valuable insights into the environmental effects of infrastructure projects. A pertinent case study is the exploration of property expropriation in China, which reveals how governance outcomes can significantly affect acquisition processes and quality of governance in peri-urban areas.
Right-of-Way Acquisition and Management in Transmission Projects
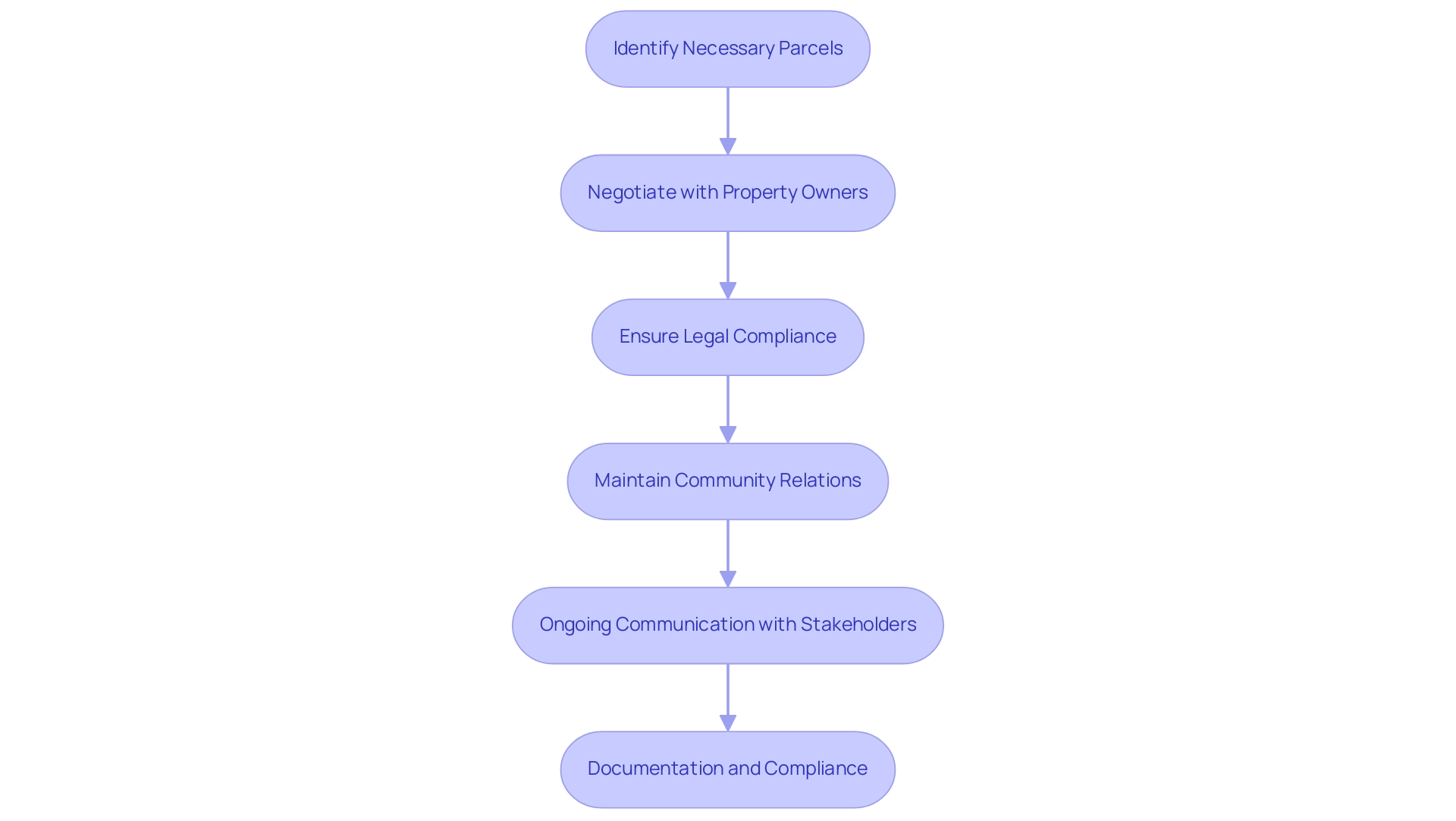
Acquiring and managing right-of-way (ROW) for transmission line land services encompasses a series of critical steps that require both strategic planning and effective execution. Initially, it is essential to identify the necessary parcels, followed by conducting thorough negotiations with property owners to secure easements. This process demands a robust understanding of legal frameworks, as regulatory compliance is paramount in ensuring successful project implementation.
As Dr. Varun Chhachhar states, "to preserve basic freedom of individual and to maintain the dignity and personality, a Constitution should be permeated with Constitutionalism; that is, it should have in-built restrictions on powers." Moreover, maintaining positive community relations is vital; it fosters trust and facilitates smoother negotiations. Experts recommend proactive engagement with landowners early in the process regarding transmission line land services to mitigate disputes and enhance cooperation.
Effective ROW management also includes transmission line land services, ongoing communication with stakeholders, meticulous documentation of agreements, and adherence to evolving regulatory requirements. Recent recommendations advocate for employing mediators in disputes and utilizing the same agents for both appraisal and acquisition to streamline the process. Statistics indicate that there are diverse approaches to ROW acquisition across 36 states, reflecting the complexity and variability of this undertaking.
The importance of stakeholder communication cannot be overstated, as successful negotiations hinge on understanding and addressing the concerns of landowners and the community alike.
Leveraging Technology in Transmission Line Land Services
Technology is integral to the efficiency and effectiveness of transmission line land services, with Geographic Information Systems (GIS) at the forefront. GIS facilitates precise mapping and comprehensive analysis of property parcels, which is crucial for identifying potential challenges in acquisition processes. This capability is especially vital in light of the recent backlog of renewable interconnection applications, estimated at five years, which has been exacerbated by decarbonization efforts.
The U.S. Department of Energy projects that grid capacity will need to double regionally and quadruple inter-regionally in the coming decades. In this context, GIS aids stakeholders in navigating complexities related to the National Interest Electric Transmission Corridor (NIETC), including:
- Jurisdictional considerations
- Siting
- Property issues
- Compliance
- The provision of transmission line land services
The case study titled 'Decarbonization and Renewable Interconnection Backlog' exemplifies how GIS is applied to understand these grid challenges effectively.
Furthermore, GIS addresses engineering challenges posed by America's diverse terrain, helping to identify areas prone to costly geological issues such as earthquakes and floods. The incorporation of AI-powered title research tools significantly accelerates the verification of property ownership and encumbrances. By streamlining these processes, these technologies enhance accuracy and significantly decrease the time needed for completion.
The outcome is not only enhanced operational efficiencies but also significant cost savings for clients, thereby reinforcing the critical role of technological advancements in contemporary acquisition strategies. As Barbara Shields aptly notes,
Because of this online access to geographic data, GTC employees are beginning to think more spatially than they once did and applying corporate data in new ways.
Regulatory and Environmental Considerations in Land Services
In the domain of transmission line land services, a thorough grasp of regulatory and environmental factors is crucial for successful execution. Compliance with local, state, and federal regulations often necessitates conducting Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA) and securing the required permits. Recent statistics show that initiatives with an EIS developed between 2010 and 2020, while comprising only 3.5% of total undertakings, represented a significant 26% of domestic cable miles.
This underscores the critical nature of these assessments in shaping outcomes. Experts emphasize that engaging with regulatory agencies early in the planning process is crucial for identifying potential challenges and mitigating risks associated with non-compliance. As highlighted by environmental authorities, nurturing robust relationships with stakeholders not only promotes smoother implementation but also improves transparency concerning ratings and methodologies.
The Commission has emphasized that the benefits of enhanced clarity in rating systems surpass any drawbacks, enabling market participants to make more informed and economic decisions. Furthermore, Vistra correctly observes that, in addition to sunrise/sunset times, solar heating also fluctuates throughout the days of the year and the hours of the day, emphasizing the necessity for a nuanced approach to environmental assessments.
Thus, the integration of EIAs is not merely a regulatory hurdle but a fundamental component that supports sustainable land development and transmission line land services compliance. Furthermore, Prysmian warns against mandatory AAR execution without a comprehensive assessment of conductor ratings, highlighting the necessity for thorough consideration of all factors involved. Case studies, like those assessed under the Regulatory Flexibility Act, show that thorough evaluation can result in compliance outcomes that do not notably impact small entities, further highlighting the significance of regulatory diligence in project implementation.
Future Trends and Challenges in Transmission Line Land Services
The path of delivery system services is increasingly influenced by the global shift towards renewable energy sources and the rising demand for sustainable infrastructure. By 2032, the power line sector is projected to reach a remarkable USD 158.62 billion, underscoring the urgency for transmission line land services to evolve in tandem with this growth. However, this transformation is not without its challenges.
The integration of new technologies, such as:
- Lattice Towers
- Monopole Towers
- Guyed Towers
and the need to navigate shifting regulatory frameworks pose significant hurdles. Experts highlight the importance of staying attuned to key industry trends, such as the proliferation of community solar projects and the expansion of electric vehicle infrastructure. A consultant emphasizes that adaptability will be vital, stating that organizations should invest in both training and technology that align with these future demands.
Moreover, improvements in energy storage systems and grid modernization, as demonstrated in the case study titled 'Future Trends in Transmission and Interconnection,' will boost the efficiency and reliability of the infrastructure. As Salasar recently showcased by securing a contract worth INR 238.65 crore (USD 32 million) from Power Grid for constructing transmission lines and substations in Arunachal Pradesh, innovative approaches are essential for enhancing operational efficiency. Looking ahead to 2024 and beyond, flexibility and innovation will be paramount in ensuring that transmission line land services continue to meet the evolving needs of the industry, particularly in overcoming the challenges of integrating renewable energy infrastructure.
Conclusion
The management and acquisition of land for transmission lines is a critical component of developing robust energy infrastructure, particularly as the global demand for renewable energy escalates. This article has highlighted the essential elements of transmission line land services, including:
- Thorough land assessments
- The importance of regulatory compliance
- The need for effective community engagement
Each of these facets plays a significant role in ensuring the timely and cost-effective execution of transmission projects.
The strategic acquisition and management of right-of-way (ROW) is fundamental to project success, necessitating strong negotiation skills and a deep understanding of legal frameworks. The incorporation of advanced technologies, such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS), has proven invaluable in streamlining the land acquisition process, thereby enhancing efficiency and reducing project timelines. Furthermore, the necessity of conducting Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA) underscores the importance of adhering to regulatory and environmental standards, which are vital for sustainable project development.
Looking to the future, the landscape of transmission line land services will undoubtedly continue to evolve in response to emerging technologies and the pressing need for sustainable infrastructure. The challenges associated with this transformation require adaptability and innovation, ensuring that land services can effectively support the industry's growth. As the sector progresses toward a more sustainable future, the insights gleaned from this comprehensive analysis will be instrumental in navigating the complexities that lie ahead, ultimately leading to successful energy solutions that benefit communities and the environment alike.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are transmission line land services?
Transmission line land services involve a comprehensive suite of activities necessary for managing and acquiring space for the installation and maintenance of transmission lines, including site identification, property ownership assessments, and understanding easements and encroachments.
Why are easements and encroachments important in transmission line land services?
Easements and encroachments are crucial as they directly influence project timelines and cost efficiency. A thorough understanding of these elements helps ensure successful project implementation.
What challenges are associated with land acquisition for transmission lines?
Challenges include navigating complex regulations, mitigating risks related to land acquisition, and addressing potential delays. Recent studies have shown that expropriation decisions can significantly limit the use of real properties.
How can risks associated with land acquisition be mitigated?
Risks can be mitigated through thorough research, strategic planning, and proactive engagement with stakeholders to manage expectations and avoid disputes.
What role does community relations play in transmission line land services?
Maintaining positive community relations is vital as it fosters trust and facilitates smoother negotiations with landowners, which is essential for successful project execution.
What steps are involved in acquiring and managing right-of-way (ROW) for transmission lines?
The process includes identifying necessary parcels, negotiating easements with property owners, ensuring regulatory compliance, ongoing communication with stakeholders, and meticulous documentation of agreements.
What are some recommendations for effective ROW management?
Recommendations include proactive engagement with landowners, employing mediators in disputes, and utilizing the same agents for both appraisal and acquisition to streamline the process.
How does stakeholder communication impact ROW acquisition?
Effective stakeholder communication is crucial as successful negotiations depend on understanding and addressing the concerns of landowners and the community, thus enhancing cooperation.
List of Sources
- Fundamentals of Transmission Line Land Services
- Study on Land Compensation for High-Voltage Transmission Lines in Power Grid Based on Easement (https://researchgate.net/publication/341652383_Study_on_Land_Compensation_for_High-Voltage_Transmission_Lines_in_Power_Grid_Based_on_Easement)
- m.economictimes.com (https://m.economictimes.com/industry/services/property-/-cstruction/landowners-compensation-doubled-in-power-projects/articleshow/111147311.cms)
- (PDF) The Effects of Electric Transmission Lines on Property Values: A Literature Review (https://researchgate.net/publication/228631703_The_Effects_of_Electric_Transmission_Lines_on_Property_Values_A_Literature_Review)
- Right-of-Way Acquisition and Management in Transmission Projects
- (PDF) Barriers and Recommendations for Right-of-Way Acquisition Process (https://researchgate.net/publication/370429456_Barriers_and_Recommendations_for_Right-of-Way_Acquisition_Process)
- (PDF) Right-of-Way Acquisition and Property Condemnation: A Comparison of U.S. State Laws (https://researchgate.net/publication/237403257_Right-of-Way_Acquisition_and_Property_Condemnation_A_Comparison_of_US_State_Laws)
- Leveraging Technology in Transmission Line Land Services
- Transmission GIS: Fueling Innovation (https://esri.com/en-us/industries/blog/articles/transmission-gis-fueling-innovation)
- Using GIS for Efficient Transmission Line Siting (https://power-grid.com/news/using-gis-for-efficient-transmission-line-siting)
- Using GIS for Renewable Energy Projects, Transmission Lines, and More (https://icf.com/insights/environment/gis-renewable-energy-transmission-lines)
- The Power of GIS for Electric Transmission Planners and Operators Webinar (https://mediaspace.esri.com/media/t/1_9b4vsixl/244549092)
- Regulatory and Environmental Considerations in Land Services
- Evidence-based recommendations for overcoming barriers to federal transmission permitting - Niskanen Center (https://niskanencenter.org/evidence-based-recommendations-for-overcoming-barriers-to-federal-transmission-permitting)
- Managing Transmission Line Ratings (https://federalregister.gov/documents/2022/01/13/2021-27735/managing-transmission-line-ratings)
- Managing Transmission Line Ratings (https://federalregister.gov/documents/2022/05/25/2022-11233/managing-transmission-line-ratings)
- Future Trends and Challenges in Transmission Line Land Services
- Transmission Line Market Size, Share & Growth Report [2032] (https://fortunebusinessinsights.com/transmission-line-market-106347)
- Transmission Line Market Size, Growth, Trends, Report 2034 (https://marketresearchfuture.com/reports/transmission-line-market-23298)
- Optimizing Renewable Energy Transmission and Interconnection with LandGate (https://landgate.com/news/how-renewable-energy-developers-can-navigate-transmission-and-interconnection-challenges)




