Overview
Understanding wind energy regulatory compliance involves navigating a complex framework of federal, state, and local regulations that govern the development and operation of wind energy projects. The article emphasizes the importance of adhering to laws such as the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) and engaging with local authorities to ensure compliance, thereby facilitating successful project approvals and mitigating environmental impacts.
Introduction
The landscape of wind energy development is intricately woven with a myriad of regulatory frameworks that dictate the success and sustainability of projects. As the demand for renewable energy surges, stakeholders must navigate a complex array of federal, state, and local regulations that govern everything from environmental assessments to operational permits. Central to this endeavor is a robust understanding of compliance requirements, particularly those outlined in pivotal legislation such as the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) and the Clean Air Act.
This article delves into the foundational elements of wind energy regulatory compliance, exploring the critical roles of:
- Environmental assessments
- Community engagement
- Financial structures
- Ongoing compliance management
By examining these facets, developers can better position their projects for success in an evolving regulatory environment, ultimately contributing to the global ambition of expanding renewable energy capacity.
Foundations of Wind Energy Regulatory Compliance
Navigating wind energy regulatory compliance involves following a comprehensive set of laws and guidelines that oversee the development and operation of wind energy initiatives. Central to this framework is a thorough understanding of federal, state, and local regulations, which encompass zoning laws, environmental protection standards, and safety requirements. Stakeholders must pay particular attention to the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA), which plays a critical role in the regulatory landscape.
NEPA mandates a rigorous assessment of environmental impacts, thereby influencing the timelines and processes for approvals. Furthermore, the Clean Air Act and other relevant laws enforce crucial adherence measures that must be incorporated into planning and execution. To effectively mitigate risks and ensure the viability of initiatives from inception through operation, establishing a robust framework for wind energy regulatory compliance is indispensable.
This framework not only aligns with current regulatory requirements but also positions endeavors for success amidst evolving legal landscapes, including anticipated reforms aimed at expediting grid connection timelines for renewable initiatives. Significantly, WETO, in partnership with Innovation Fund Denmark, provided $2.1 million for a total of $4.2 million to support U.S.-Danish consortia working on common research goals to enhance floating offshore wind mooring and anchoring technologies and methods towards cost-effective commercialization and industry growth. Furthermore, the IEA's report highlights that global renewable capacity ambitions correspond to almost 8,000 GW by 2030, illustrating the significant challenges and ambition gaps that continue to impede faster renewable power expansion.
Navigating Regulatory Frameworks for Wind Energy Projects
Wind energy initiatives are subject to wind energy regulatory compliance, governed by a complex array of regulations that differ significantly across various jurisdictions. At the federal level, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) plays a pivotal role in establishing the regulatory framework for wind energy regulatory compliance initiatives. In 2024, wind energy regulatory compliance with FERC regulations is especially vital, as they outline essential requirements for approval, including:
- Detailed permit applications
- Comprehensive public hearings
- Thorough environmental assessments
Moreover, state public utility commissions impose additional requirements for wind energy regulatory compliance that can vary widely, necessitating developers to be well-acquainted with local ordinances.
The Sierra Club has emphasized the importance of eliminating barriers for demand response (DR) aggregators, asserting that "removing barriers to DR aggregators from participating in the market will increase the aggregate amount of DR available to the grid." This highlights the necessity for developers to effectively navigate the challenges of wind energy regulatory compliance. Engaging with local authorities during the initial planning stages is vital for achieving wind energy regulatory compliance; this proactive approach not only ensures compliance but also facilitates a smoother execution of the initiative, ultimately leading to successful approvals.
Recent publications, including ESV Energy Management, LLC's FR Document 2024-08990 and Venturi Asset Management, LLC's FR Document 2024-15295, illuminate the changing regulatory environment and provide insights into wind energy regulatory compliance and its consequences for renewable initiatives. Additionally, the case study of Solar Star 3, LLC, published on July 18, 2024, demonstrates successful navigation of wind energy regulatory compliance frameworks, serving as a practical example for developers aiming to secure project approvals.
Environmental Compliance and Community Engagement in Wind Energy
Environmental compliance in energy development necessitates rigorous Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) to systematically identify and mitigate potential impacts on wildlife, habitats, and local communities. Recent mandates have underscored the significance of conducting synoptic studies and establishing demonstrator sites to better understand interactions with various species and habitats, particularly in the context of offshore wind farms across Europe, where over 2,000 wind turbines have been installed in 69 operational sites. Engaging with communities throughout the development lifecycle is vital for addressing concerns and cultivating local support.
Effective strategies for community engagement may encompass:
- Public meetings
- Informational sessions
- Direct outreach initiatives aimed at local stakeholders
Compliance with the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) and relevant state-specific regulations is paramount to ensure wind energy regulatory compliance, allowing for thorough assessment and appropriate mitigation of all potential ecological impacts prior to project approval. As Helen Bailey noted, "The manuscript was drafted by HB and revised and finalized together with KB and PT."
Insights from case studies, including the one titled 'Use of EIA Data for Wildlife Management,' emphasize the significance of utilizing data from Environmental Impact Assessments and post-construction monitoring to guide planning decisions related to renewable developments and their impact on wildlife, especially black grouse. This case study emphasizes the need for a centralized repository for EIA data to facilitate better access for researchers and planners, enhancing the robustness of studies surrounding wildlife impacts. These measures together establish the foundation for sustainable power development while promoting community trust and environmental stewardship.
Financial Structures and Contracts in Wind Energy Compliance
Successful wind energy initiatives are underpinned by diverse financial structures such as:
- equity financing
- debt financing
- power purchase agreements (PPAs)
These mechanisms are not merely financial tools; they are essential components in navigating the complex landscape of wind energy regulatory compliance. Key contracts that developers must consider include:
- land leases
- interconnection agreements
- supply contracts
Each serving a critical role in ensuring integrity of the endeavor.
For example, the dairy farm in Yuma, Colorado, employs two 100-kilowatt Northern Power Systems wind turbines to offset high power demand, showcasing practical uses of wind power and the related financial frameworks. As the landscape evolves, recent trends indicate that wind energy regulatory compliance must be aligned with financial agreements to safeguard developers' interests and enhance project viability. Incorporating the findings from the case study titled 'Investment Trends and Climate Goals' demonstrates the urgency for increased clean investments, particularly as current investment levels are not aligned with the necessary targets to limit global warming to 1.5°C.
Regular audits and thorough legal reviews of these contracts are vital strategies to preemptively identify any issues related to wind energy regulatory compliance that may arise. Moreover, Deloitte forecasts that data centers alone will create an estimated 44 GW of additional demand by 2030, emphasizing the necessity for strong financial frameworks as the power market continues to grow. With historical data indicating that market-driven growth fundamentals will endure, the interaction between declining interest rates and the financial environment for renewable resources will become progressively significant in shaping compliant and sustainable initiatives.
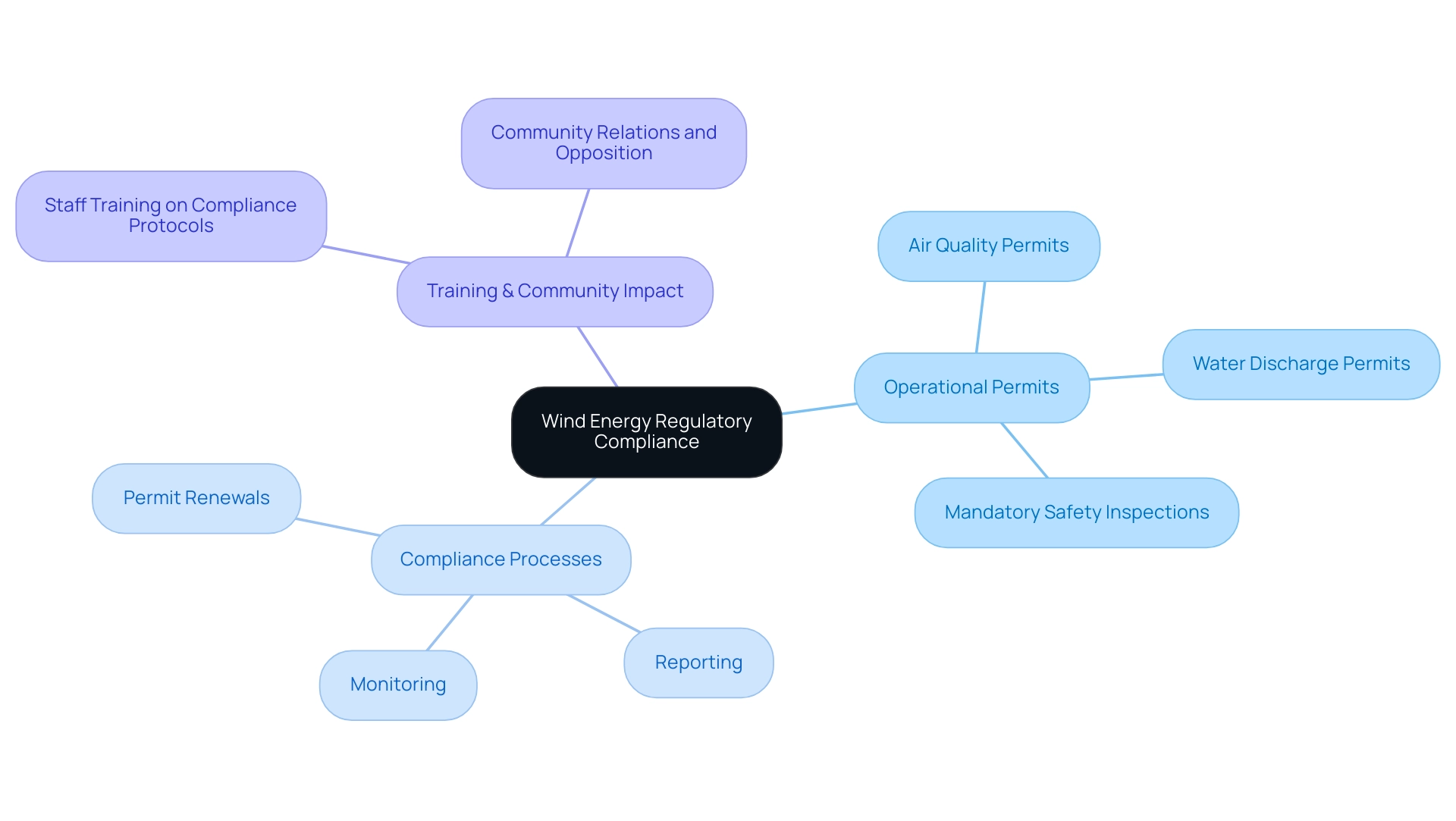
Operational Permits and Ongoing Compliance in Wind Energy
Upon the commencement of wind energy projects, it becomes essential to ensure wind energy regulatory compliance with all relevant permits and regulations. Among the essential operational permits are:
- Air quality permits
- Water discharge permits
- Mandatory safety inspections
Continuous monitoring and timely reporting are vital to ensuring adherence to wind energy regulatory compliance as well as operational standards.
A well-organized system for wind energy regulatory compliance is critical; it serves to track reporting deadlines, facilitate permit renewals, and schedule inspections effectively. Furthermore, regular training sessions for staff on adherence protocols and updates regarding wind energy regulatory compliance are crucial to equip the team with the knowledge needed to meet these standards. Significantly, 73% of states enable local authorities to create siting standards, emphasizing the need for developers to be flexible and proactive in their wind energy regulatory compliance strategies.
The site will function as a virtual office for the Permitting Council, offering essential information and updates on regulatory requirements. A practical example of effective adherence management can be seen in the case study titled 'Environmental Studies and Review,' where developers conduct environmental studies to assess potential impacts and prepare mitigation strategies, ensuring wind energy regulatory compliance with federal, state, and local laws. By fostering a culture of compliance and staying abreast of the latest developments, organizations can mitigate the risk of community opposition, which often leads to legal challenges against government-issued permits, thereby complicating the permitting landscape for energy infrastructure projects.
Conclusion
Navigating the regulatory landscape of wind energy development is essential for ensuring project success and sustainability. This article has outlined the critical components of compliance, emphasizing the importance of understanding federal, state, and local regulations. Key frameworks such as the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) and the Clean Air Act serve as cornerstones in guiding developers through the complexities of environmental assessments, operational permits, and community engagement.
Moreover, the integration of robust financial structures and contracts is indispensable for managing compliance obligations while securing project viability. As the demand for renewable energy grows, the need for effective compliance management systems becomes increasingly evident. These systems not only facilitate adherence to regulatory requirements but also support ongoing operational excellence through continuous monitoring and training.
Ultimately, successful wind energy projects hinge on a comprehensive approach to regulatory compliance that encompasses:
- Environmental stewardship
- Community involvement
- Sound financial practices
By prioritizing these elements, developers can not only navigate the complexities of the regulatory environment but also contribute meaningfully to the global transition towards renewable energy. As the industry evolves, remaining vigilant and adaptive will be key to overcoming the challenges ahead and realizing the full potential of wind energy development.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is wind energy regulatory compliance?
Wind energy regulatory compliance involves adhering to a comprehensive set of laws and guidelines that govern the development and operation of wind energy projects, including federal, state, and local regulations.
What are some key regulations involved in wind energy compliance?
Key regulations include zoning laws, environmental protection standards, safety requirements, and specific laws such as the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) and the Clean Air Act.
Why is the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) important?
NEPA requires a rigorous assessment of environmental impacts, which significantly influences the timelines and processes for obtaining approvals for wind energy projects.
What role does the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) play in wind energy compliance?
FERC establishes the regulatory framework for wind energy compliance, outlining essential requirements for project approval, including detailed permit applications, public hearings, and environmental assessments.
How do state regulations affect wind energy compliance?
State public utility commissions impose additional requirements for wind energy compliance that can vary widely, necessitating developers to understand local ordinances.
What is the significance of engaging with local authorities during planning?
Engaging with local authorities early in the planning stages is vital for ensuring compliance and facilitating smoother execution of wind energy initiatives, leading to successful project approvals.
What recent developments have impacted wind energy regulatory compliance?
Recent publications have highlighted the changing regulatory environment, while case studies, such as that of Solar Star 3, LLC, provide practical examples of successfully navigating compliance frameworks.
What challenges do developers face in wind energy regulatory compliance?
Developers face challenges related to understanding and navigating a complex array of regulations that differ across jurisdictions, as well as overcoming barriers to market participation for demand response aggregators.
List of Sources
- Foundations of Wind Energy Regulatory Compliance
- Electricity – Renewables 2024 – Analysis - IEA (https://iea.org/reports/renewables-2024/electricity)
- energy.gov (https://energy.gov/eere/wind/articles/weto-2024-accomplishments-blowing-wind-energy-forward)
- atb.nrel.gov (https://atb.nrel.gov/electricity/2024/land-based_wind)
- Navigating Regulatory Frameworks for Wind Energy Projects
- 2024 Federal Register Index :: Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (https://federalregister.gov/index/2024/federal-energy-regulatory-commission)
- Summary of FERC Meeting Agenda for September 2024 | White & Case LLP (https://whitecase.com/insight-alert/summary-ferc-meeting-agenda-september-2024)
- Environmental Compliance and Community Engagement in Wind Energy
- aquaticbiosystems.biomedcentral.com (https://aquaticbiosystems.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/2046-9063-10-8)
- esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com (https://esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1890/ES14-00331.1)
- Financial Structures and Contracts in Wind Energy Compliance
- Distributed Wind Market Report (https://energy.gov/eere/wind/distributed-wind-market-report)
- 2025 Renewable Energy Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/renewable-energy/renewable-energy-industry-outlook.html)
- Overview and key findings – World Energy Investment 2024 – Analysis - IEA (https://iea.org/reports/world-energy-investment-2024/overview-and-key-findings)
- Operational Permits and Ongoing Compliance in Wind Energy
- energy.gov (https://energy.gov/eere/siting-large-scale-renewable-energy-projects)
- permits.performance.gov (https://permits.performance.gov/fpisc-content/empire-wind-latest-offshore-wind-project-complete-federal-permitting-review-fast-41)
- Eight facts about permitting and the clean energy transition - The Hamilton Project (https://hamiltonproject.org/publication/economic-fact/eight-facts-permitting-clean-energy-transition)




