Introduction
In the quest for sustainable energy solutions, solar energy has emerged as a frontrunner, necessitating effective land services to support its growth. These services encompass a wide array of critical activities ranging from land acquisition to compliance with regulatory requirements, all aimed at facilitating the successful deployment of solar projects.
As the global demand for solar energy surges, driven by technological advancements and a collective push towards cleaner energy sources, the importance of strategic land management becomes increasingly apparent. This article delves into the multifaceted role of land services in solar energy project development, the challenges faced by industry professionals, and the innovative tools and technologies that are reshaping the landscape.
By exploring these elements, it becomes clear that effective land services are not merely supportive functions; they are essential to the realization of ambitious renewable energy targets and the transition to a more sustainable future.
Defining Solar Energy Land Services: An Overview
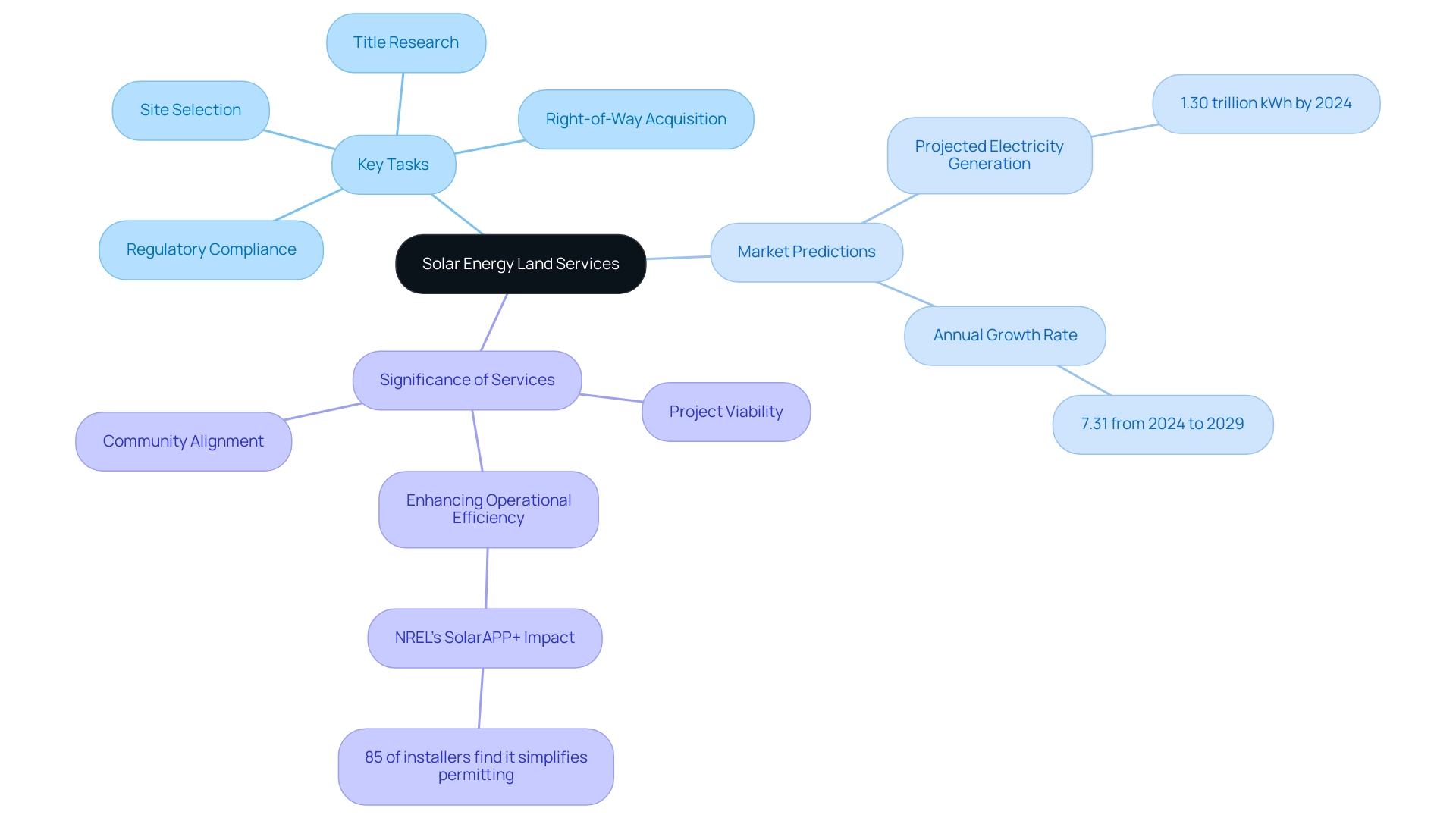
Renewable resource site offerings include a thorough range of tasks essential for the strategic acquisition, evaluation, and administration of areas intended for solar energy land services. These offerings are essential in recognizing and obtaining appropriate parcels, thus guaranteeing that the development process aligns with the particular requirements of project developers and stakeholders engaged in sustainable initiatives. Essential elements of renewable power site initiatives include:
- Meticulous site selection
- Right-of-way acquisition
- Thorough title research
- Strict adherence to local regulations
The significance of these solar energy land services cannot be exaggerated, as they enable access to terrain crucial for the effective execution of renewable energy projects. As indicated by recent market predictions, the worldwide renewable power sector is expected to produce roughly 1.30 trillion kWh of electricity by 2024, with a strong annual growth rate of 7.31% anticipated from 2024 to 2029. This expansion highlights the essential role that effective property acquisition plays in solar energy land services, especially as nations increasingly prioritize cleaner power solutions.
Involving with photovoltaic resource services not only improves project viability but also corresponds with wider ecological objectives, ultimately propelling creativity and market expansion in the renewable sector. According to Ben Zientara, a policy analyst, "Effective property acquisition is crucial in ensuring that renewable energy initiatives not only meet regulatory requirements but also align with community interests." Moreover, the case study titled 'Worldwide Renewable Power Market Growth' illustrates how nations are transitioning to cleaner resources, leading to significant market expansion and technological advancements in related products.
Furthermore, with 85% of installers utilizing NREL’s SolarAPP+ permitting software indicating that it greatly simplifies the permitting process, the incorporation of such tools is crucial for enhancing operational efficiency.
The Role of Land Services in Solar Project Development
Territorial functions play a crucial role in the efficient advancement of renewable energy initiatives, tackling vital elements such as property leasing, site evaluations, and stakeholder discussions. Initially, professionals in property services conduct comprehensive feasibility studies to pinpoint suitable locations for solar energy land services installations. These studies consider various factors, including current usage of terrain—which can range from 0.5 percent to nearly 100 percent by county in the central Midwest—environmental impacts, and proximity to critical infrastructure.
Given that cultivated areas account for a significant portion of use in the central Midwest, careful analysis is crucial. Once viable sites are identified, services manage the complexities of leasing or acquisition, which encompasses negotiating terms with property owners and ensuring adherence to legal requirements. This process is further improved by conducting meticulous title research to validate ownership and address any potential disputes.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) mapping also plays a vital role, providing precise representations of terrain characteristics that aid in decision-making. Furthermore, findings from the case study named 'Future Space Needs for Renewable Power' emphasize that by 2050, renewable power installations could greatly affect the availability of agricultural space and ecosystem well-being. By efficiently organizing these processes, solar energy land services enable renewable developers to optimize project schedules, reduce risks linked to property acquisition, and ultimately assist in successfully achieving sustainable objectives.
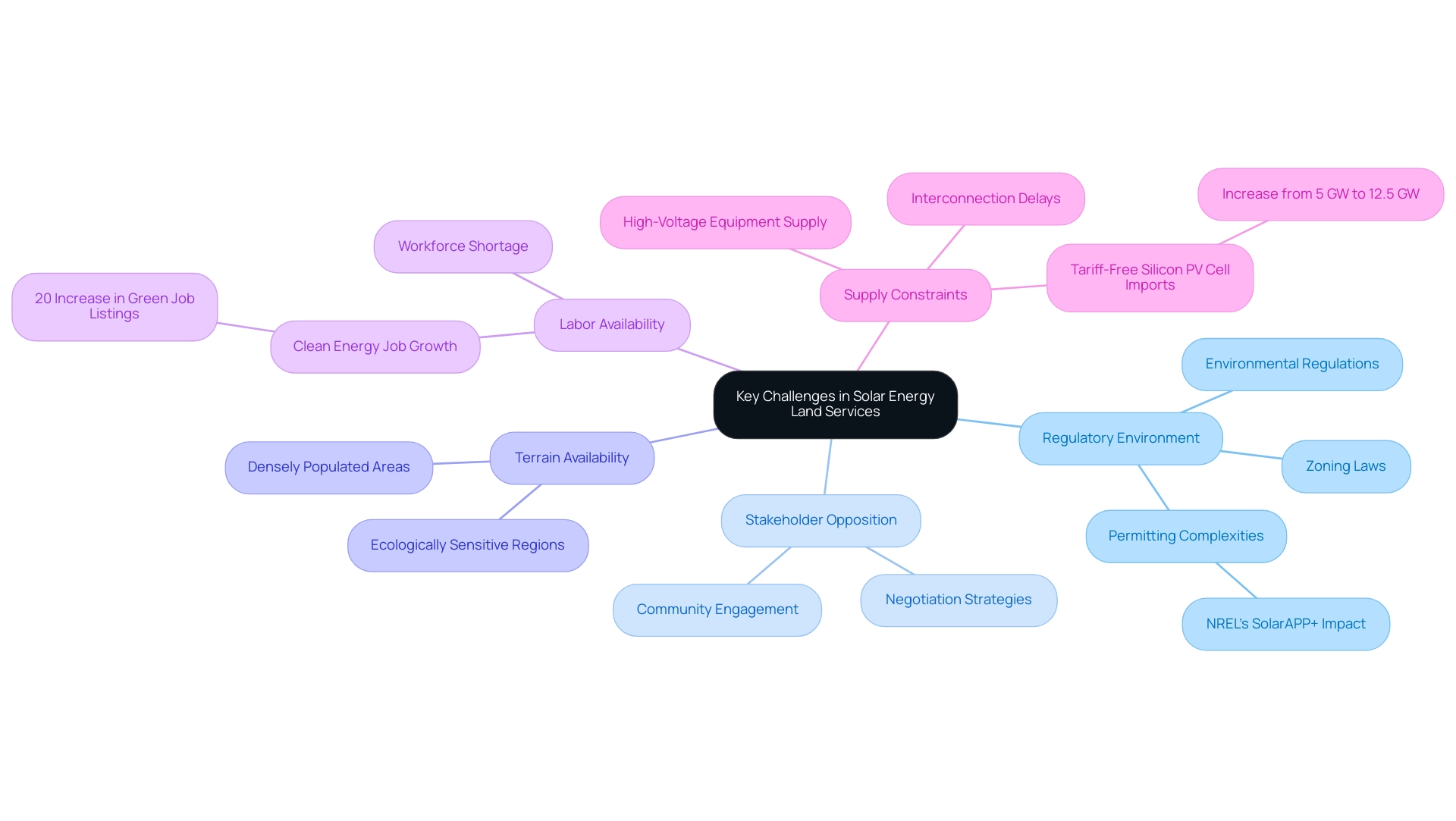
Key Challenges in Solar Energy Land Services
The terrain of renewable energy operations is filled with numerous obstacles that can greatly hinder project advancement. A primary hurdle is the regulatory environment, which varies considerably by jurisdiction and often includes intricate zoning laws and stringent environmental regulations. Navigating these legal frameworks necessitates specialized expertise and thorough knowledge; failure to do so can result in substantial delays.
In fact, 85% of installers who work with NREL’s SolarAPP+ permitting software report that it makes permitting significantly easier, highlighting the need for effective tools to navigate regulatory complexities. Moreover, stakeholder opposition, particularly from local communities and environmental organizations, presents a formidable obstacle. Engaging in effective communication and employing negotiation strategies are vital to addressing these concerns and securing necessary project support.
The availability of appropriate terrain is also a critical factor, especially in densely populated or ecologically sensitive regions. Moreover, utility-scale renewable energy expansion is restricted by labor availability, high-voltage equipment supply limitations, and interconnection delays, further complicating the environment for professionals in the field. To effectively tackle these challenges, professionals in solar energy land services are urged to adopt strategic planning, conduct comprehensive research, and proactively engage with stakeholders.
For instance, the recent increase in the U.S. quota for tariff-free silicon photovoltaic cell imports—rising from 5 GW to 12.5 GW—signals a strategic pivot towards enhancing domestic manufacturing capacity. This shift reflects a broader effort to alleviate supply constraints that could hinder utility-scale energy development. Moreover, the construction industry encounters an anticipated half-a-million workforce deficit, which could impede progress in clean employment opportunities, despite a significant 20% increase in green job listings throughout 2022.
Such dynamics highlight the significance of navigating the regulatory landscape skillfully while nurturing strong relationships with community stakeholders to ensure successful outcomes in project development. Furthermore, as the renewable natural gas (RNG) utilization could possibly increase tenfold by 2050, this statistic demonstrates wider patterns in renewable resources that affect terrain management.
The Importance of GIS Mapping in Solar Land Services
Geographic Information System (GIS) mapping acts as an essential resource in renewable energy site operations, allowing thorough examination and representation of terrain features. This technology equips land service professionals with the ability to assess critical factors, including:
- Topography
- Land use
- Proximity to existing infrastructure
- Environmental constraints
By leveraging GIS mapping, experts can produce detailed visualizations that pinpoint optimal sites for solar energy land services development, thus facilitating more informed decision-making processes.
Moreover, GIS technology streamlines site selection while ensuring compliance with regulatory mandates by delivering precise data for environmental assessments. As the energy sector shifts from traditional sources such as oil and gas to renewable options, the significance of solar energy land services becomes even more evident. Tools like those provided by PVcase help developers comprehend the importance of site selection with capacity information, demonstrating the practical uses of GIS technology in the present market.
Additionally, the use of Locational Marginal Pricing (LMP) data is essential for developers to forecast profitability and minimize financial risks associated with site selection. By leveraging LMP data, developers can optimize their site selection process within solar energy land services, enhancing financial viability and reducing risks in solar project development. As the resource landscape continues to evolve, GIS is set to become increasingly central to the development and management of sustainable resources.
This change not only fosters innovation but also promotes a more sustainable future, emphasizing the significance of data-driven strategies in optimizing resource use and enhancing project efficiency.
Future Trends in Solar Energy Land Services
The future of renewable energy services, particularly solar energy land services, is on the verge of major change, largely driven by technological advancements and the shifting environment of regulatory frameworks. A notable trend is the increasing adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning within property assessment and acquisition processes. These technologies promise to streamline operations by enhancing efficiency in title research and data processing, leading to quicker and more precise decision-making.
However, despite the anticipated average annual buildout of 31 GW over the next five years, the renewable energy sector faces challenges such as:
- A half-a-million workforce shortage in the construction sector
- Equipment constraints, which could significantly impede this progress
Moreover, the community solar sector, which experienced an installation of 291 MW in Q3 2024, shows varied performance across states, emphasizing the need for flexibility in operations. States such as Maine and Illinois have demonstrated growth, whereas New York's overall momentum is decelerating, suggesting that professionals in the field must stay adaptable in reaction to regional dynamics.
As renewable resources policies evolve, these professionals must also remain vigilant regarding legislative changes that could affect property use and acquisition methodologies. The growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental stewardship is set to further shape the industry, with an increasing focus on minimizing ecological impacts during project development. As the need for sunlight-derived power grows, the role of solar energy land services will become progressively essential in ensuring that initiatives are carried out responsibly and efficiently.
As Rahul B. aptly states, 'The integration of AI in solar energy land services will redefine our approach to solar energy projects, making them more efficient and environmentally conscious.
Conclusion
The exploration of solar energy land services highlights their critical role in the successful development of solar projects, addressing essential activities such as:
- Land acquisition
- Site assessments
- Regulatory compliance
As the demand for solar energy grows, the effective management of land resources becomes paramount. The integration of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) mapping and innovative technologies, such as artificial intelligence, underscores the importance of data-driven decision-making in optimizing land use and enhancing project feasibility.
Despite the promising growth projections for the solar industry, various challenges persist, including:
- Navigating complex regulatory environments
- Addressing stakeholder concerns
These hurdles necessitate strategic planning and robust community engagement to ensure project success. The ability to adapt to evolving legislative frameworks and regional dynamics will be crucial for land service professionals as they strive to meet the increasing demand for renewable energy solutions.
In conclusion, the future of solar energy land services is poised for transformation, driven by technological advancements and a growing emphasis on sustainability. By harnessing innovative tools and fostering strong relationships with stakeholders, the solar industry can effectively navigate challenges and capitalize on opportunities. Ultimately, the role of land services will be instrumental in achieving ambitious renewable energy targets, paving the way for a cleaner, more sustainable energy landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are renewable resource site offerings?
Renewable resource site offerings include a comprehensive range of tasks necessary for the strategic acquisition, evaluation, and management of land intended for solar energy services, ensuring alignment with the needs of project developers and stakeholders.
What essential elements are involved in renewable power site initiatives?
Essential elements include meticulous site selection, right-of-way acquisition, thorough title research, and strict adherence to local regulations.
Why are solar energy land services significant?
Solar energy land services are crucial for accessing land necessary for the successful execution of renewable energy projects, especially as the global renewable power sector is expected to grow significantly in the coming years.
What are the expected growth predictions for the renewable power sector?
The renewable power sector is anticipated to produce approximately 1.30 trillion kWh of electricity by 2024, with an expected annual growth rate of 7.31% from 2024 to 2029.
How does effective property acquisition impact renewable energy initiatives?
Effective property acquisition ensures that renewable energy initiatives meet regulatory requirements while aligning with community interests, thus enhancing project viability and supporting broader ecological goals.
What tools enhance the operational efficiency of solar energy projects?
Tools like NREL’s SolarAPP+ permitting software are utilized by 85% of installers to simplify the permitting process, significantly enhancing operational efficiency.
What role do territorial functions play in renewable energy initiatives?
Territorial functions are vital for the efficient advancement of renewable energy initiatives, addressing aspects such as property leasing, site evaluations, and stakeholder discussions.
How do professionals conduct feasibility studies for solar energy land services?
Professionals perform comprehensive feasibility studies to identify suitable locations for installations, considering factors like current land usage, environmental impacts, and proximity to critical infrastructure.
What is the importance of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) mapping in solar energy land services?
GIS mapping provides precise representations of terrain characteristics, aiding in decision-making and optimizing project schedules while reducing risks associated with property acquisition.
What findings were highlighted in the case study 'Future Space Needs for Renewable Power'?
The study emphasizes that by 2050, renewable power installations could significantly affect the availability of agricultural space and ecosystem well-being.
List of Sources
- Defining Solar Energy Land Services: An Overview
- 2025 Solar Energy Statistics: Latest Industry Survey Data (https://solarreviews.com/blog/solarreviews-solar-industry-survey-key-statistics)
- statista.com (https://statista.com/outlook/io/energy/renewable-energy/solar-energy/worldwide)
- Solar Market Insight Report – SEIA (https://seia.org/research-resources/us-solar-market-insight)
- The Role of Land Services in Solar Project Development
- The potential land requirements and related land use change emissions of solar energy - Scientific Reports (https://nature.com/articles/s41598-021-82042-5)
- The True Land Footprint of Solar Energy (https://betterenergy.org/blog/the-true-land-footprint-of-solar-energy)
- pnas.org (https://pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.1517656112)
- Key Challenges in Solar Energy Land Services
- 2025 Renewable Energy Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/renewable-energy/renewable-energy-industry-outlook.html)
- Quarterly Solar Industry Update (https://energy.gov/eere/solar/quarterly-solar-industry-update)
- Solar Market Insight Report Q3 2024 – SEIA (https://seia.org/research-resources/solar-market-insight-report-q3-2024)
- 2025 Solar Energy Statistics: Latest Industry Survey Data (https://solarreviews.com/blog/solarreviews-solar-industry-survey-key-statistics)
- The Importance of GIS Mapping in Solar Land Services
- landgate.com (https://landgate.com/news/the-changing-role-of-gis-in-the-new-energy-landscape)
- The importance of quality GIS data for solar site selection | PVcase (https://pvcase.com/blog/the-importance-of-quality-gis-data-for-solar-site-selection)
- GIS-based decision support for solar energy planning in urban environments (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0198971500000326)
- Future Trends in Solar Energy Land Services
- Solar Market Insight Report – SEIA (https://seia.org/research-resources/us-solar-market-insight)
- Solar Market Insight Report Q3 2024 – SEIA (https://seia.org/research-resources/solar-market-insight-report-q3-2024)
- 2025 Renewable Energy Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/renewable-energy/renewable-energy-industry-outlook.html)




