Introduction
The growth of wind energy has emerged as a significant factor in the transition to renewable resources, with its capacity more than doubling over the past decade. However, this expansion is accompanied by a complex regulatory framework that governs the permitting process for wind energy projects. Understanding the intricacies of federal, state, and local regulations is crucial for developers, as it affects not only the feasibility of projects but also their alignment with safety and environmental standards.
From navigating the requirements set forth by agencies like the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management and the Federal Aviation Administration to engaging with various stakeholders, the path to obtaining necessary permits is fraught with challenges. This article delves into the multifaceted landscape of wind energy permitting, exploring the key laws, stakeholder dynamics, and best practices that can help streamline the process and ensure successful project outcomes.
Understanding the Regulatory Framework for Wind Energy Permitting
The regulatory environment overseeing turbine power permitting is complex, incorporating various federal, state, and local regulations that affect the development and operation of turbine power initiatives, often requiring wind energy permitting services. At the federal level, the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) oversees offshore projects, while the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is responsible for onshore energy developments. Both agencies are integral to ensuring compliance with safety and environmental standards.
Central to this regulatory framework are several key laws, notably:
- The National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA), which requires comprehensive environmental assessments.
- The Endangered Species Act (ESA), designed to protect threatened species that may be impacted by renewable initiatives.
Power generation from turbines has more than doubled from 2014 to 2023, emphasizing the growing importance of this renewable source and the need for effective regulatory oversight. The FAA has identified that without proper registration and marking of meteorological towers, additional collisions resulting in loss of life could occur, as noted by the NTSB, which emphasizes the importance of creating a publicly accessible national meteorological tower database.
Additionally, the recent Act requires the Secretary of the Interior to create regulations that enable prompt approval of renewable initiatives, while establishing ambitious national objectives for renewable production on Federal land. This evolving landscape is further complicated by state-specific regulations, leading to a patchwork of requirements that can challenge developers. The FAA's power to establish rules on aviation safety, as detailed in the case study about suggested changes to part 77, highlights the essential importance of adherence for renewable initiatives.
To effectively manage these complexities, a comprehensive grasp of the regulatory framework is crucial for obtaining required approvals and utilizing wind energy permitting services to promote renewable initiatives.
Navigating the Permitting Process: Requirements and Challenges
The authorization procedure for renewable resource initiatives, particularly wind energy permitting services, is complex, involving various essential stages such as:
- Pre-application discussions
- The filing of permit requests
- Specified public feedback intervals
Developers are required to compile comprehensive documentation, notably environmental impact assessments, which are essential for demonstrating compliance with an array of regulatory standards. A significant challenge within this framework is the necessity for coordination among various agencies, a factor that often results in delays and escalated costs.
Public opposition, driven by concerns regarding environmental effects, further complicates the approval landscape. To mitigate these challenges, developers must actively engage with a multitude of stakeholders, including local communities and environmental organizations, to address their concerns effectively. For example, effective stakeholder involvement has been crucial in renewable initiatives, promoting comprehension and backing that can result in a more efficient permitting procedure.
Moreover, it is essential for developers to grasp these requirements and challenges associated with wind energy permitting services, as this knowledge equips them to anticipate potential hurdles and devise strategic solutions. The recent statement from the US Department of Energy concerning up to US$1.2 billion for direct air capture demonstrations emphasizes the financial environment influencing renewable initiatives. Additionally, the investment in grid infrastructure is lagging, with significant capacity waiting for grid connection, as evidenced by the case study on investment in grid infrastructure.
This highlights the challenges that wind energy permitting services may face in securing necessary connections. Furthermore, the urgency for developers to navigate these authorization challenges is amplified by the need for dedicated policy support for renewable fuels to align with net-zero emissions goals by 2050. As Carolyn Amon, a research manager in power, utilities, and renewables, notes,
The storage boom is also reflected in the distributed segment, with residential solar attachment rates expected to rise from 14% in 2023 to a record 25% in 2024.
This projection highlights the urgent need for developers to align their authorization strategies with evolving market dynamics and public expectations, ensuring project viability and success.
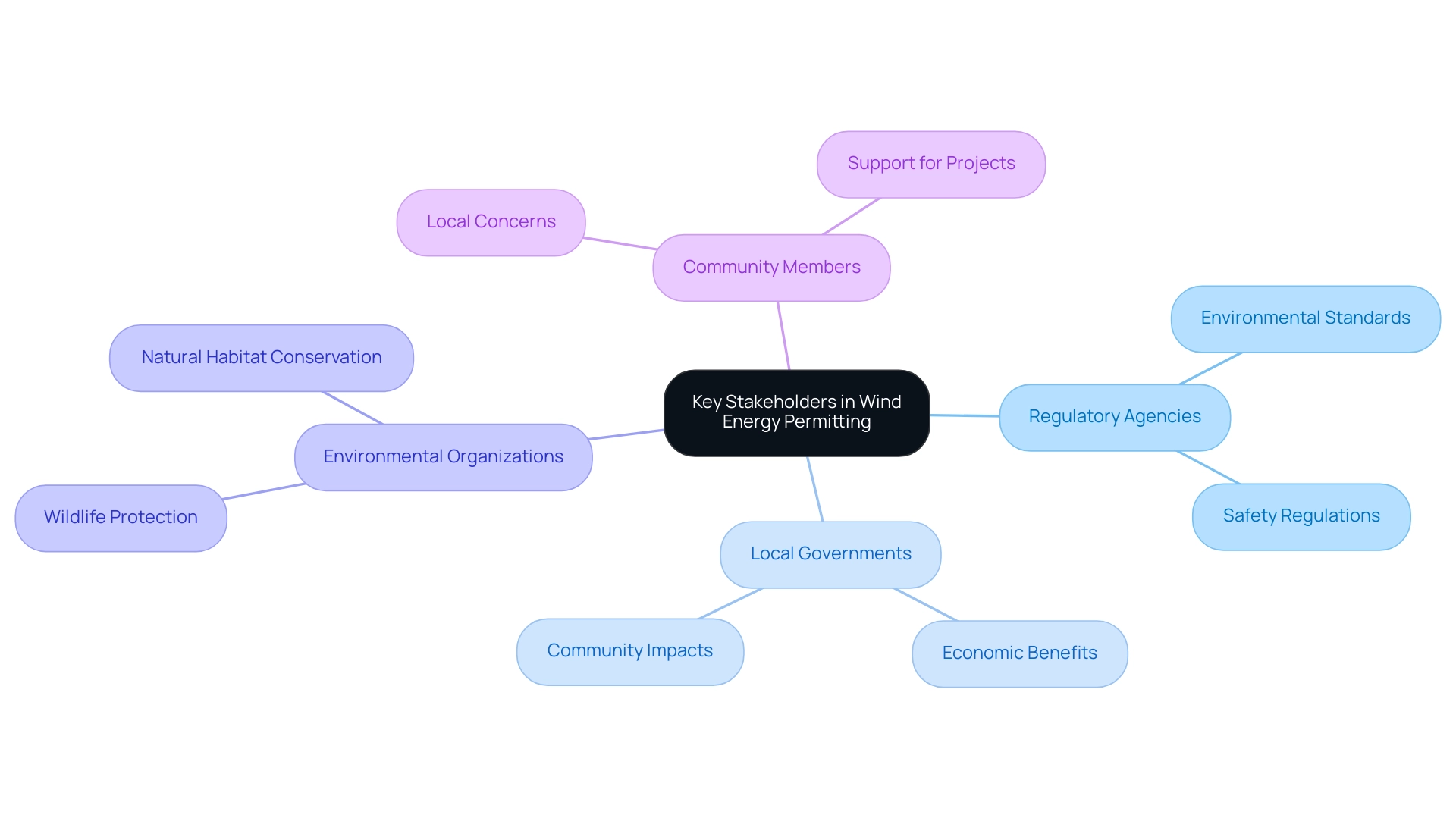
Key Stakeholders in Wind Energy Permitting
The energy development approval process involves a diverse group of key stakeholders, including:
- federal and state regulatory agencies
- local governments
- environmental organizations
- community members
Each group brings unique perspectives and concerns that significantly influence the regulatory landscape. For instance, regulatory agencies prioritize adherence to environmental and safety standards, while local governments often focus on the economic benefits and community impacts of wind initiatives.
Environmental organizations play a crucial role as advocates for the protection of wildlife and natural habitats, which can intensify the scrutiny during the permitting phase. Effective engagement with these stakeholders is paramount for developers involved in wind energy permitting services, as it fosters trust, addresses potential concerns, and can ultimately lead to more efficient approvals. In 2022, turbine farms accounted for 30% of all renewable capacity contracted in corporate power purchase agreements, highlighting the industry's growth and relevance.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) highlights the significance of joint initiatives in this context, stating that:
"the IEA Wind Systems Technology Collaboration Program offers an information platform for participating governments and industry leaders on co-operative R&D efforts to lower the cost of renewable technologies, enhance transmission and power system flexibility, and improve social acceptance of related endeavors."
As the sector advances toward ambitious goals—such as attaining an annual electricity generation of roughly 7,400 TWh by 2030—addressing these stakeholder dynamics becomes increasingly essential for successful outcomes. A pertinent illustration is the University of Maine’s New England Aqua Ventus I, a demonstration initiative in state waters that tests new technologies and engages various stakeholders, contributing to the advancement of offshore renewable technology.
Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) in Wind Energy Permitting
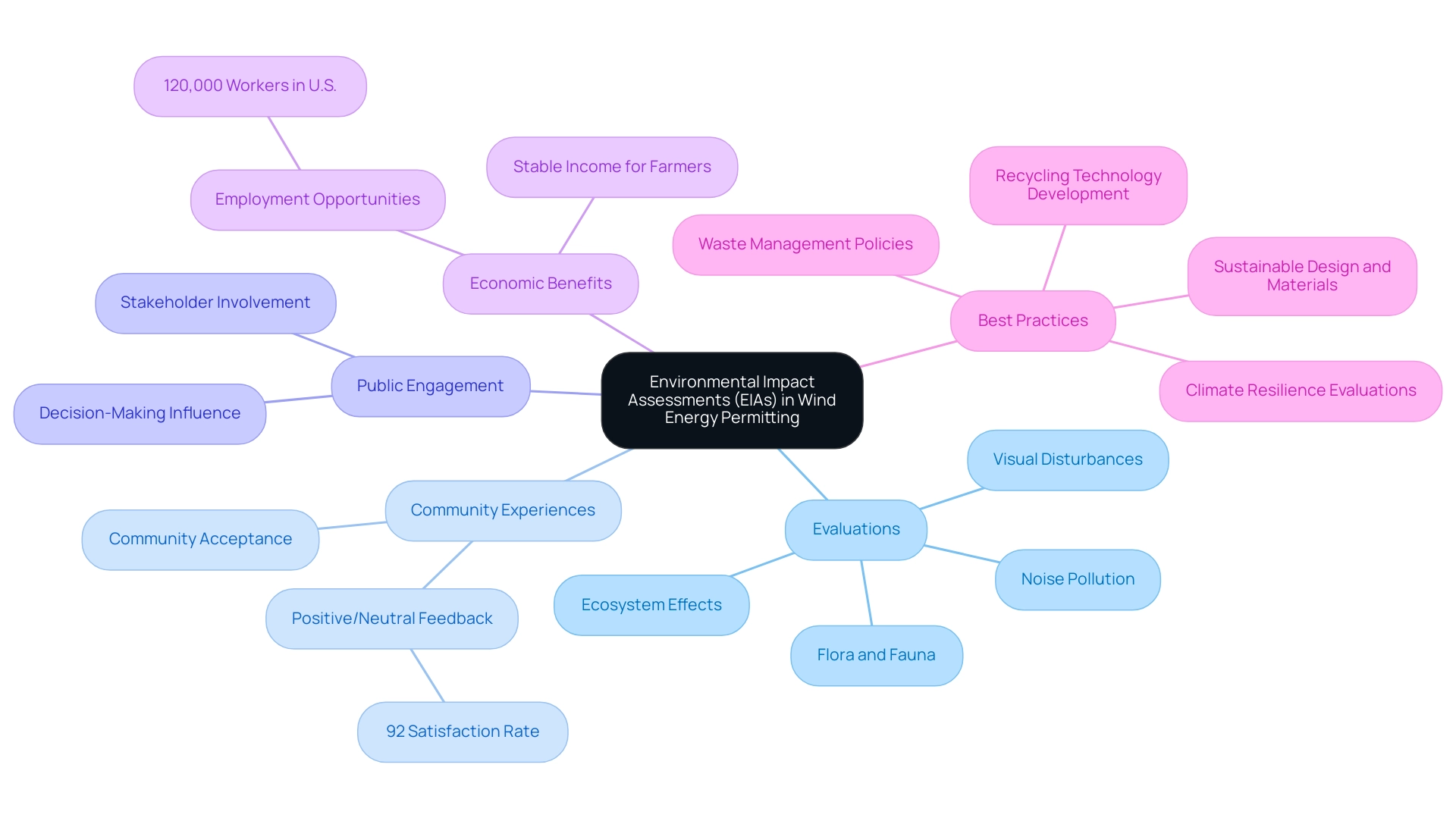
Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) are essential in the renewable energy sector, acting as a thorough instrument for recognizing and managing possible environmental effects linked to initiatives. Typically, EIAs encompass evaluations of local flora and fauna, noise pollution, visual disturbances, and broader effects on ecosystems. According to the Center for Sustainable Systems at the University of Michigan, the findings from an EIA significantly influence design and operational strategies to mitigate adverse effects.
Notably, in recent evaluations, 92% of individuals residing within five miles of wind turbines reported either positive or neutral experiences, underscoring the importance of thorough assessments in fostering community acceptance.
Moreover, effective EIAs are instrumental in enhancing public engagement by providing stakeholders with opportunities to express their concerns and influence the decision-making process. This proactive approach not only assists in obtaining necessary permits through wind energy permitting services but also contributes to the long-term sustainability of initiatives. As the industry evolves, the integration of best practices in conducting EIAs becomes increasingly crucial.
For instance, recent studies have emphasized the need for EIAs to evaluate the resilience of renewable energy initiatives to climate impacts, ensuring their longevity and operational efficiency amidst changing environmental conditions. This aligns with findings from a case study that highlights how EIAs can assess projects' resilience to extreme weather events, ultimately supporting sustainable and socially responsible development.
Additionally, with over 120,000 full-time workers in the U.S. renewable energy industry, the economic benefits of these projects further underscore the importance of comprehensive EIAs. Furthermore, as the current cost of landfilling turbine blades remains relatively low, it is essential to develop better design, materials, recycling technology, and waste management policies to enhance end-of-life performance. Thus, robust EIAs are not merely regulatory requirements; they are vital components that enhance the environmental and social responsibility of turbine initiatives.
Best Practices for Successful Wind Energy Permitting
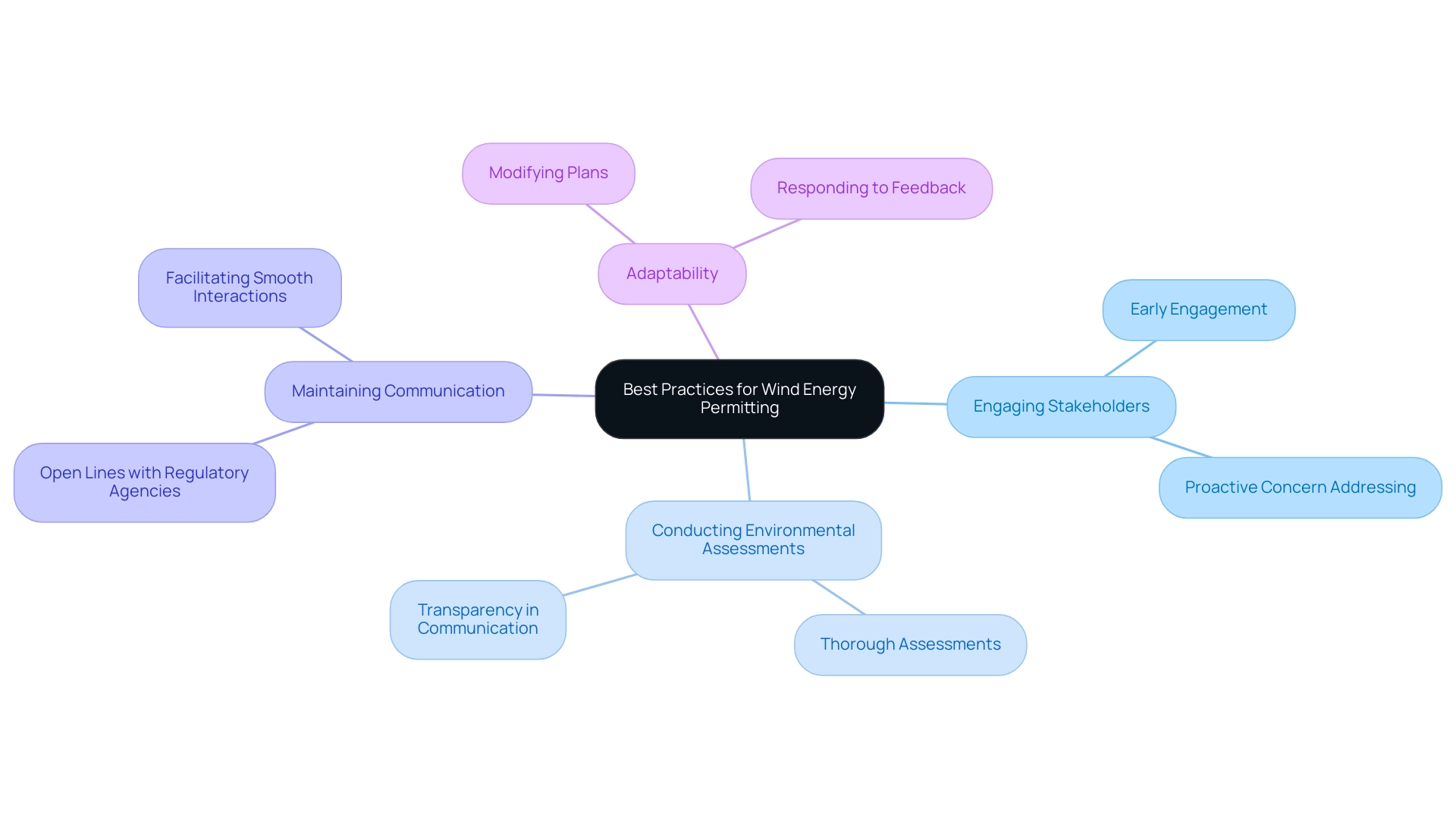
To significantly enhance the chances of successful wind energy permitting services, developers should implement a series of best practices. Engaging stakeholders early in the process is paramount, as it fosters collaboration and allows for proactive addressing of concerns. This approach is reflected in the recent trend of small wind turbine retrofits, which accounted for 68% of small wind capacity additions in 2020 and 42% in 2021.
This trend indicates a growing preference for installing new turbines on existing towers and foundations, illustrating how stakeholder input can shape project feasibility. Additionally, conducting thorough environmental assessments and transparently communicating potential impacts not only demonstrates a commitment to responsible development but also builds trust among stakeholders. As noted by The Hamilton Project and Energy Policy Institute at the University of Chicago,
- 'Given the immense threat that climate change represents, it is crucial that policymakers implement efficient solutions that minimize climate damages from our use of energy.'
Maintaining open lines of communication with regulatory agencies is essential for navigating the complexities of approval requirements, facilitating smoother interactions, and ensuring compliance with evolving regulations. Furthermore, adaptability is crucial; being prepared to modify plans in response to stakeholder feedback can lead to more favorable outcomes. By adhering to these best practices, developers can streamline the wind energy permitting services process, significantly contribute to the successful implementation of wind energy projects, and support the substantial economic impact reflected in over $2 billion in state and local tax payments and land-lease payments last year.
Conclusion
The permitting landscape for wind energy projects is complex, shaped by federal, state, and local regulations. It is crucial for developers to understand the roles of agencies such as the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management and the Federal Aviation Administration to ensure compliance with safety and environmental standards. Key laws, including the National Environmental Policy Act and the Endangered Species Act, provide essential guidelines for environmental assessments as wind energy capacity continues to expand.
Navigating the permitting process involves challenges such as extensive documentation and public consultations. Engaging local communities and environmental organizations is vital for addressing concerns and fostering support, leading to more efficient project approvals. Recent funding announcements from the US Department of Energy underscore the importance of aligning permitting strategies with market dynamics and public expectations.
The diverse stakeholders involved in the permitting process—from regulatory agencies to local governments—play a significant role. Effective engagement with these groups builds trust and facilitates smoother interactions, enabling developers to anticipate challenges and implement strategic solutions. Furthermore, comprehensive Environmental Impact Assessments are essential for meeting regulatory requirements and enhancing community acceptance.
By adopting best practices such as early stakeholder engagement and transparent communication, developers can streamline the permitting process and bolster the growth of the wind energy sector. This commitment to responsible development will maximize the benefits of wind energy while minimizing its environmental impact, paving the way for a more sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the regulatory environment for turbine power permitting?
The regulatory environment for turbine power permitting is complex and involves various federal, state, and local regulations that impact the development and operation of turbine power initiatives. This often necessitates wind energy permitting services.
Which federal agencies oversee turbine power projects?
The Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) oversees offshore projects, while the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is responsible for onshore energy developments. Both agencies ensure compliance with safety and environmental standards.
What key laws govern turbine power initiatives?
Key laws include the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA), which mandates comprehensive environmental assessments, and the Endangered Species Act (ESA), which protects threatened species that may be affected by renewable initiatives.
How has power generation from turbines changed from 2014 to 2023?
Power generation from turbines has more than doubled from 2014 to 2023, highlighting the growing importance of this renewable energy source and the need for effective regulatory oversight.
What role does the FAA play in turbine power safety?
The FAA emphasizes the importance of proper registration and marking of meteorological towers to prevent collisions that could lead to loss of life, as noted by the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB).
What recent regulatory changes have been made to facilitate renewable initiatives?
Recent regulations require the Secretary of the Interior to create processes for prompt approval of renewable initiatives and establish ambitious national objectives for renewable production on Federal land.
What challenges do developers face in the permitting process?
Developers face challenges such as the need for coordination among various agencies, public opposition regarding environmental impacts, and the complexity of state-specific regulations, which can lead to delays and increased costs.
What are the essential stages in the authorization procedure for renewable resource initiatives?
The essential stages include pre-application discussions, filing of permit requests, and specified public feedback intervals, along with the requirement to compile comprehensive documentation like environmental impact assessments.
How can developers effectively manage public opposition during the permitting process?
Developers can mitigate public opposition by actively engaging with stakeholders, including local communities and environmental organizations, to address concerns and promote understanding and support for their initiatives.
What financial considerations are influencing renewable initiatives?
The financial environment is influenced by significant funding opportunities, such as the US Department of Energy's commitment of up to US$1.2 billion for direct air capture demonstrations, alongside challenges in grid infrastructure investment and capacity.
Why is it important for developers to understand the regulatory framework?
A comprehensive understanding of the regulatory framework is crucial for developers to obtain necessary approvals, anticipate potential hurdles, and devise strategic solutions to navigate the complexities of wind energy permitting services.
List of Sources
- Understanding the Regulatory Framework for Wind Energy Permitting
- State and Local Permitting Restrictions on Wind Energy Development - R Street Institute (https://rstreet.org/commentary/state-and-local-permitting-restrictions-on-wind-energy-development)
- Requirements To File Notice for Meteorological Towers and Other Wind Energy Systems (https://federalregister.gov/documents/2024/11/18/2024-26741/requirements-to-file-notice-for-meteorological-towers-and-other-wind-energy-systems)
- Text - S.4753 - 118th Congress (2023-2024): Energy Permitting Reform Act of 2024 (https://congress.gov/bill/118th-congress/senate-bill/4753/text)
- Navigating the Permitting Process: Requirements and Challenges
- 2025 Renewable Energy Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/renewable-energy/renewable-energy-industry-outlook.html)
- Executive summary – Renewables 2024 – Analysis - IEA (https://iea.org/reports/renewables-2024/executive-summary)
- Key Stakeholders in Wind Energy Permitting
- Wind - IEA (https://iea.org/energy-system/renewables/wind)
- WINDExchange: Offshore Wind Energy Guide (https://windexchange.energy.gov/offshore-wind-energy-guide)
- Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) in Wind Energy Permitting
- Wind Energy Factsheet (https://css.umich.edu/publications/factsheets/energy/wind-energy-factsheet)
- Wind Power Facts and Statistics | ACP (https://cleanpower.org/facts/wind-power)
- inogenalliance.com (https://inogenalliance.com/blog-post/harnessing-renewable-energy-responsibly-role-environmental-impact-assessments)
- Best Practices for Successful Wind Energy Permitting
- Wind Power Facts and Statistics | ACP (https://cleanpower.org/facts/wind-power)
- energy.gov (https://energy.gov/eere/wind/wind-market-reports-2022-edition)
- Eight facts about permitting and the clean energy transition - The Hamilton Project (https://hamiltonproject.org/publication/economic-fact/eight-facts-permitting-clean-energy-transition)
- Wind - IEA (https://iea.org/energy-system/renewables/wind)




