Overview
Community resilience planning serves as a strategic approach aimed at significantly enhancing a community's capacity to prepare for, respond to, and recover from adverse events. This concept underscores the vital importance of collective strength and active stakeholder engagement. Effective planning is characterized by the incorporation of:
- Risk assessments
- Resource allocation
- Inclusive strategies
These elements are essential for adapting to challenges such as climate change and socio-economic disparities. Ultimately, this approach fosters sustainable development and promotes social equity.
Introduction
In an era marked by escalating climate challenges, economic uncertainties, and public health crises, community resilience planning has emerged as a vital strategy for empowering local populations. This proactive approach not only prepares communities to face adverse events but also fosters a culture of preparedness and adaptability that enhances overall well-being.
By engaging diverse stakeholders and prioritizing inclusivity, community resilience planning:
- Identifies vulnerabilities
- Allocates resources effectively
- Implements sustainable solutions that ensure all voices are heard
As the world grapples with unprecedented challenges, understanding the core components and innovative strategies behind effective community resilience is essential for fostering sustainable development and social equity.
Defining Community Resilience Planning
Community resilience planning represents a strategic approach aimed at cultivating collective strength, empowering groups to prepare for, respond to, and recover from adverse events such as natural disasters, economic downturns, and public health crises. This multifaceted process necessitates a thorough assessment of vulnerabilities, active engagement of stakeholders, and the formulation of actionable plans that prioritize local needs. By nurturing a culture of community resilience planning, groups can bolster their capacity to endure shocks and stresses while sustaining essential services and infrastructure.
Key elements of effective community resilience planning encompass the integration of both direct and indirect risk assessments, which yield reliable evaluations at the tract level. For example, the Community Resilience Evaluation (CRE) merges direct survey estimates with indirect assessments to generate dependable risk evaluations, thereby informing decision-making processes. This methodology is vital for community resilience planning, as it aids in identifying vulnerable populations and ensures that disaster preparedness initiatives are inclusive and effective.
Importantly, the study omitted the variable of personal disaster experience from the model due to its high correlation with predicted variables, thereby ensuring the model adhered to fit criteria. A prominent case study is the 'Community-Based Disaster Risk Management Framework,' which underscores community resilience planning through a dual approach that combines bottom-up and top-down management strategies. This framework seeks to enhance governance by concentrating on vulnerable groups and fostering active resident participation. It emphasizes the critical role of community resilience planning in cultivating societal resources and facilitating effective communication for improved disaster management outcomes.
Statistics reveal that the PNFI for Model1 in urban settings is 0.511, indicating a robust link between local adaptation initiatives and enhanced disaster response capabilities. The COVID-19 pandemic has further underscored the necessity of strengthening local resilience metrics. As Bethany DeSalvo noted, there is a pressing need for advanced measurement tools for local organizers and disaster management professionals to bolster community resilience planning.
Looking ahead to 2025, effective frameworks for strengthening societal resilience will increasingly rely on data-driven insights and collaborative methodologies, ensuring that communities not only survive but thrive in the face of adversity.
The Importance of Community Resilience in Today's World
In today's society, characterized by climate change, rapid urban development, and escalating socio-economic inequalities, the significance of collective strength is increasingly clear. Communities face a multitude of challenges, including extreme weather events, public health crises, and economic disruptions. Effective community resilience planning for local adaptability empowers governments and organizations to anticipate these challenges, implement proactive strategies, and cultivate a culture of preparedness among residents.
Investing in adaptability not only diminishes vulnerability but also enhances recovery efforts, ultimately safeguarding the well-being of local members. Successful local recovery initiatives during public health crises exemplify how preparedness can mitigate the impacts of such emergencies. Furthermore, case studies on societal strength in the face of climate change illustrate that proactive measures can significantly improve outcomes for affected populations.
The impact of socio-economic inequalities on societal strength is critical. Communities with greater economic resources typically enjoy better access to information, infrastructure, and support systems, thereby bolstering their capacity to respond to crises. Conversely, individuals facing economic hardships may struggle to recover, underscoring the need for equitable recovery strategies.
Urbanization plays a pivotal role in shaping neighborhood strength. As cities grow, they encounter unique challenges, including heightened vulnerability to climate-related events. Consequently, community resilience planning is vital for integrating adaptive strategies into urban development, fostering sustainable growth.
Expert opinions underscore the importance of societal strength in addressing climate change. Prof. Petteri Taalas, WMO Secretary-General, highlights the gravity of the climate crisis, stating, "Greenhouse gas levels are record high. Global temperatures are record high. Sea level rise is record high. Antarctic sea ice is record low. It’s a deafening cacophony of broken records."
As we approach 2025, the urgency for effective adaptive strategies becomes increasingly evident, particularly given data indicating that climate change is already impacting populations worldwide. The Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI) has assessed the climate action efforts of 59 nations since 2005, revealing insufficient measures to curb global temperature rise, further emphasizing the necessity for robust local adaptation initiatives.
Additionally, a report by the UN stresses the urgent need for developed nations to mobilize at least $100 billion annually to support developing countries in climate change mitigation and adaptation, highlighting the critical importance of planning for resilience.
Ultimately, community resilience planning that prioritizes collective strength not only mitigates risks but also promotes sustainable growth and social equity, ensuring that all community members can thrive in the face of adversity. The case study 'Greening the Blue 2020' exemplifies effective environmental management and a commitment to minimizing ecological footprints, serving as a model for local sustainability initiatives.
Core Components of Community Resilience Planning
Community resilience planning is fundamentally anchored in essential elements such as risk assessment, stakeholder involvement, resource distribution, and ongoing monitoring and evaluation. Risk assessment stands out as a critical first step, as it involves identifying potential hazards and vulnerabilities that a community may encounter. Understanding these specific risks is crucial for addressing them effectively within community resilience planning, thereby enhancing overall resilience.
Stakeholder engagement is equally vital, ensuring that a diverse range of voices contributes to the development process. Effective engagement fosters collaboration among community members, local governments, and organizations, which is essential for creating plans that reflect the area’s needs and priorities. Such involvement not only enhances the outcomes of community resilience planning but also builds trust and promotes collective ownership of initiatives.
Resource allocation emerges as another critical aspect, directing funding and support towards essential areas like infrastructure improvements and emergency services. By prioritizing resources effectively, groups can significantly enhance their capacity for community resilience planning, improving their response to and recovery from disasters.
Ongoing monitoring and assessment are indispensable for community resilience planning, allowing for adjustments to preparedness plans based on evolving conditions and insights from past incidents. This iterative process ensures that groups remain responsive to new challenges and can refine their strategies over time.
Together, these components establish a comprehensive framework for community resilience planning and adaptability. The NIST Community Recovery Strategy Guide exemplifies this approach, offering a structured six-step process that aids groups in integrating sustainability objectives into their local development activities. As Therese P. McAllister notes, "Utilizing the Guide can assist areas in incorporating uniform durability objectives into their comprehensive, economic development, zoning, mitigation, and other local strategies that influence structures, public utilities, and additional infrastructure systems."
By aligning social and economic needs with performance objectives, groups can enhance community resilience planning to create robust systems capable of withstanding various hazards, ultimately fostering sustainable development. Moreover, insights from the University of South Carolina's Hazards and Vulnerability Research Institute (HVRI) underscore the importance of adaptability data in local development, ensuring that strategies are informed by the latest insights and statistics, including those updated on April 5, 2022.
Inclusive Planning: Engaging Communities for Resilience
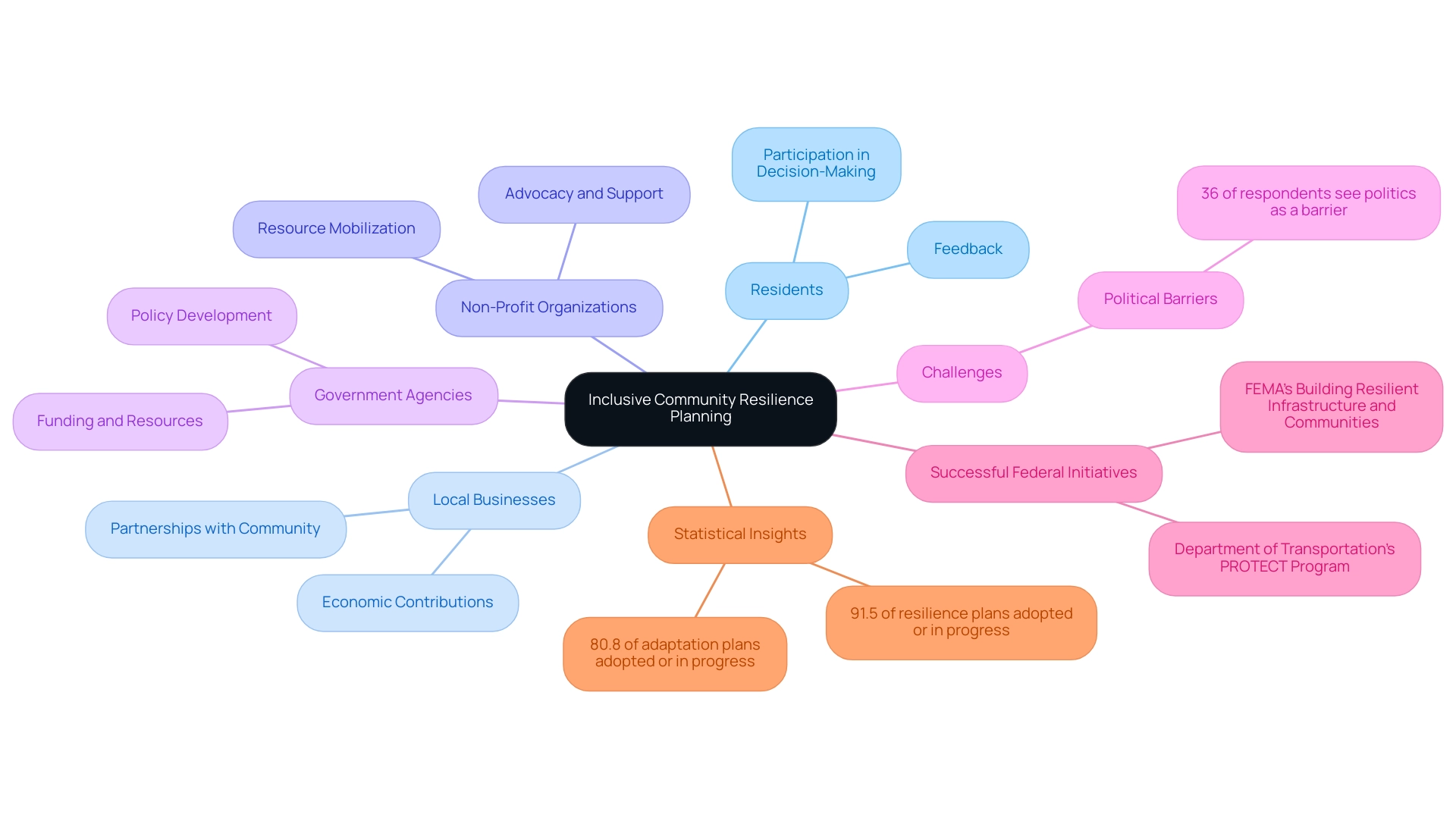
Inclusive strategies serve as a crucial foundation for effective community resilience planning. By involving a diverse group of stakeholders—including residents, local businesses, non-profit organizations, and government agencies—the planning process becomes representative of the area's unique needs and perspectives. This participatory method cultivates trust and develops social capital, significantly enhancing the overall effectiveness of adaptive plans.
The active involvement of community members in decision-making is essential in community resilience planning. It enables planners to identify local strengths and address specific vulnerabilities, resulting in tailored solutions that align with the community's values and priorities. Planners must evaluate the vulnerabilities of structures and infrastructure systems to enhance robustness, ensuring that strategies are comprehensive and effective. Notably, statistics reveal that 36% of participants perceive political barriers as a significant challenge to adaptability strategies, underscoring the necessity for inclusive dialogue to tackle these hurdles.
Successful examples of inclusive strategies illustrate that collaborative efforts are vital for effective community resilience planning, yielding more robust and sustainable recovery plans. Recent federal initiatives, such as the Department of Transportation’s PROTECT program and FEMA’s Building Resilient Infrastructure and Communities, have allocated historic funding levels to support adaptation and sustainability initiatives. These programs highlight the importance of community resilience planning in recovery strategies, aiming to strengthen local capabilities and promote inclusive decision-making processes.
Furthermore, McNemar's tests indicate that recovery plans are significantly more likely to be adopted or in progress (91.5%) compared to adaptation plans (80.8%), further emphasizing the effectiveness of community-driven approaches. As Jennifer Helgeson noted, '[insert quote here],' reinforcing the value of inclusive strategies. By emphasizing these approaches, groups can enhance their durability and ensure that their methods are fair and representative of the diverse perspectives within them.
Tools and Strategies for Effective Resilience Planning
Effective community resilience planning is crucial, relying on a diverse array of tools and strategies designed to enhance a group's ability to withstand and recover from adverse events. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) play a pivotal role in this process, mapping vulnerabilities and assessing risks. This capability allows planners to visualize essential data about their regions. For instance, GIS can analyze demographic and socioeconomic characteristics, which is vital for justifying blight remediation plans and fostering the development of more resilient neighborhoods. This ability is significant as it aids in developing targeted interventions that meet specific societal needs.
Data analytics further enhances the decision-making process by providing insights that direct strategic development. By utilizing advanced analytics, groups can recognize trends and patterns that guide their preparedness plans, ensuring that interventions are both timely and effective. Engagement platforms are essential as they promote communication and collaboration among stakeholders, ensuring that a wide range of viewpoints is considered in the development process.
Scenario forecasting and modeling techniques enable groups to envision potential future challenges, allowing them to create adaptive strategies responsive to evolving conditions. A notable example is the City of Auburn, Alabama, which implemented a green infrastructure master plan aimed at addressing urban challenges and promoting sustainability. This initiative not only strengthened local adaptability but also boosted environmental health, showcasing the concrete advantages of merging adaptability strategies into urban development.
Integrating these tools into the development process significantly enhances a locality's community resilience planning to respond to and recover from adverse events, ultimately promoting a more robust future. With tract shape files averaging around 50 MB, the effective use of GIS and data analytics in community sustainability efforts is essential for sustainable development. Harbinger Land's dedication to providing prompt and precise services tailored to client requirements underscores the significance of these tools in achieving successful outcomes in recovery strategies.
Challenges in Community Resilience Planning
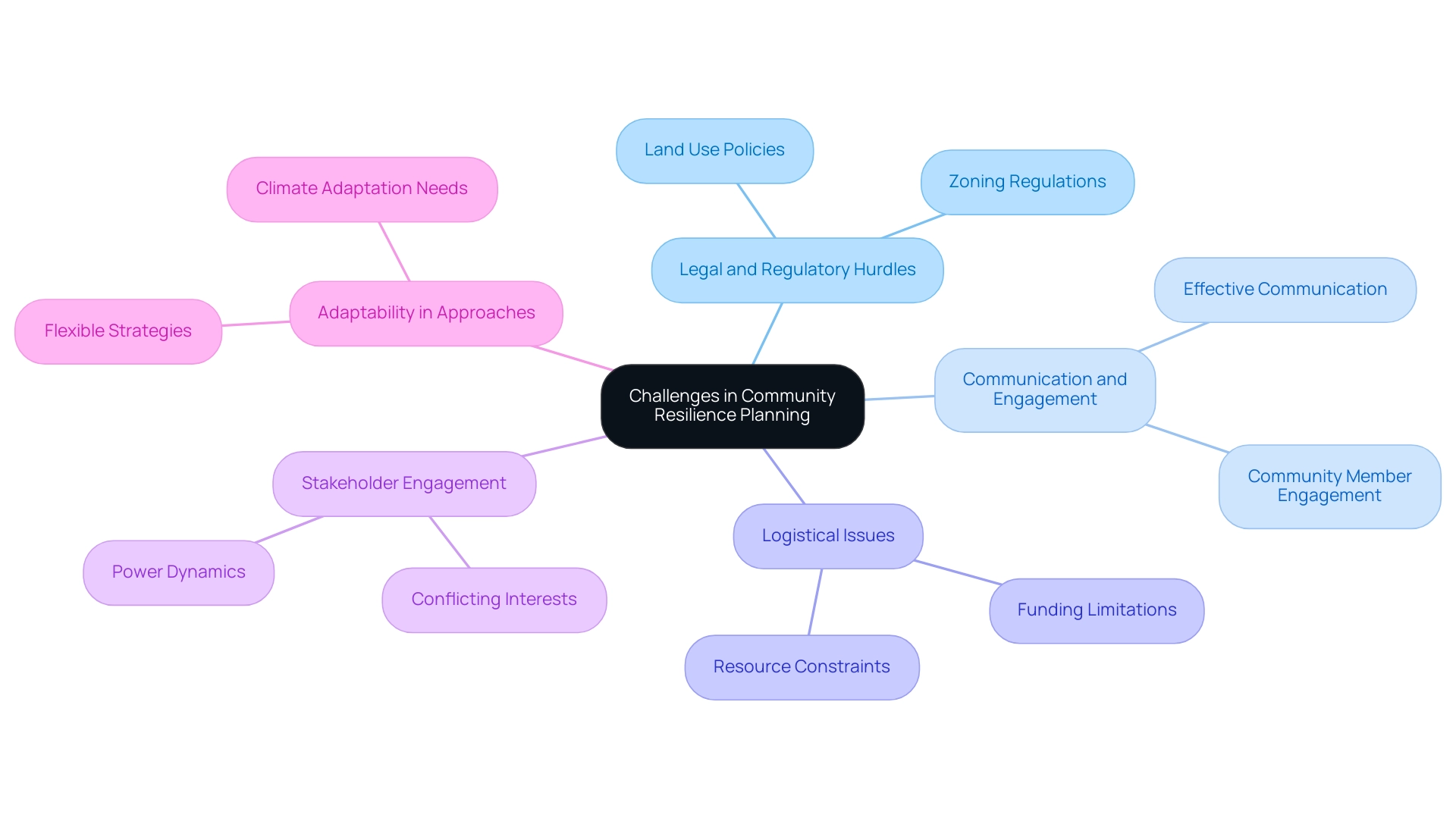
Community resilience planning faces significant challenges that can impede progress. Legal and regulatory hurdles frequently emerge, particularly concerning land use policies and zoning regulations, complicating the implementation of essential strategies. Notably, 26% of practitioners identify effective communication and engagement with local members as the most critical action needed to navigate these complexities.
This underscores the importance of fostering dialogue to overcome obstacles in support initiatives. Logistical issues, such as limited funding and resources, further amplify the difficulties in executing these initiatives. Engaging a diverse range of stakeholders introduces its own challenges, often complicated by conflicting interests and power dynamics. This situation necessitates a collaborative approach, prioritizing open communication and actively pursuing consensus among stakeholders.
The importance of adaptability in application is highlighted by experts, including Matthew Malecha from Johns Hopkins University, who points out the shared recognition among professionals of the need for flexible approaches in climate adaptation and sustainability planning. Additionally, recent findings indicate that while substantial research has focused on societal recovery following seismic events, there is an urgent need for studies concentrating on climate-related disasters. This gap emphasizes the necessity for a comprehensive national database of practitioners to enhance understanding and refine approaches in community resilience planning for societal durability.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has underscored the importance of critical facilities in societal robustness during disruptive events. They note that adherence to building codes does not guarantee hazard-proof structures, adding another layer of complexity to planning for stability.
To effectively tackle these challenges, localities must proactively identify potential obstacles and develop targeted strategies within community resilience planning to overcome them. Successful case studies illustrate that by fostering cooperation and leveraging diverse perspectives, communities can significantly enhance their preparedness efforts, ultimately leading to more sustainable outcomes. The challenges related to sampling and representativeness, as discussed in the case study titled 'Survey Limitations and Future Research,' further highlight the need for a comprehensive approach to developing societal strength.
Case Studies: Successful Community Resilience Initiatives
Across the United States, numerous groups have successfully implemented planning initiatives that serve as exemplary models. New Orleans, for instance, has made significant strides in enhancing its recovery capabilities following Hurricane Katrina. The city has prioritized infrastructure improvements and fostered public involvement, ensuring that recovery efforts are both inclusive and effective.
This approach not only addresses immediate needs but also builds lasting capacity for future challenges. It underscores the importance of shared resources and collective needs among communities in resilience planning, ultimately enhancing recovery capabilities. Similarly, Miami has developed a comprehensive adaptability plan that tackles the impacts of climate change through innovative land use strategies and robust stakeholder collaboration. This strategy highlights the critical nature of integrating diverse perspectives and resources, which are essential for effective capacity building.
These case studies underscore the necessity for tailored approaches that consider local contexts and engage a wide range of stakeholders. Research indicates that successful local recovery initiatives often hinge on shared resources and collective needs, thereby enhancing recovery capabilities across diverse demographics. For example, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) outlines a six-step process for strengthening collective resilience, which helps prioritize improvements in physical infrastructure performance during and after hazard events.
Jennifer Helgeson, a research economist at NIST, noted that businesses owned by minorities, women, and veterans—known as historically underrepresented group operated (HUGO) businesses—encountered significantly greater challenges due to the pandemic compared to other enterprises. This highlights the crucial role of recovery planning in supporting various community stakeholders.
The experiences of New Orleans and Miami illustrate that community resilience planning for recovery extends beyond infrastructure; it also involves fostering a culture of preparedness and adaptability within communities. The intricacies of transportation robustness, as examined in studies like Murray-Tuite (2006), further emphasize the need for models that consider interactions with other infrastructure systems. By learning from these successful initiatives, other regions can formulate their own plans to enhance adaptability and ensure sustainable development in the face of climate challenges.
Future Trends in Community Resilience Planning
The terrain of societal adaptability planning is undergoing significant transformation, driven by several key trends. The integration of advanced technologies, particularly artificial intelligence and big data analytics, is revolutionizing how communities assess risks and formulate plans. For instance, AI tools are utilized to analyze extensive datasets, enabling more precise risk evaluations and tailored strategies that address specific local needs.
Furthermore, an increasing focus on equity and social justice is redefining community resilience planning. Recent studies reveal that 26% of local members assert that effective communication and engagement are vital for prioritizing vulnerable populations in decision-making processes. This emphasis ensures that the perspectives of those most impacted by climate change and other disruptions are acknowledged and integrated.
Collaborative governance models are rising in prominence within community resilience planning, as they promote the engagement of various stakeholders, including local authorities, organizations, and residents. This inclusive framework cultivates a sense of ownership and accountability, resulting in more adaptive and responsive strategies.
Looking ahead to 2025, these trends will continue to shape societal adaptation strategies. The frameworks established by U.S. Presidential Policy Directives, such as PPD-21, highlight the necessity of preparing for and adapting to evolving conditions. As noted in PPD-21, "the ability to prepare for and adapt to changing conditions and withstand and recover rapidly from disruptions" is crucial for effective planning for resilience.
By leveraging these insights and incorporating AI into community resilience planning and recovery initiatives, groups can enhance their capacity to withstand and recover from disruptions, ultimately promoting sustainable development and long-term stability. Additionally, case studies on PPD-8 and PPD-21 illustrate how federal frameworks guide recovery strategies, ensuring that communities are equipped with the essential tools and metrics to bolster their resilience. It is also imperative to uphold data privacy, as mandated by U.S. Census Bureau disclosure procedures, when utilizing data in community resilience strategies.
Conclusion
Community resilience planning is an essential strategy that empowers local populations to effectively navigate and recover from a range of challenges, including climate change, economic uncertainties, and public health crises. By concentrating on core components such as:
- Risk assessment
- Stakeholder engagement
- Resource allocation
- Continuous monitoring
communities can significantly enhance their capacity to withstand shocks and stresses. The integration of advanced tools such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and data analytics enriches the planning process, facilitating informed decision-making that reflects the unique needs of each community.
The significance of inclusivity in resilience planning cannot be overstated. Engaging a diverse array of stakeholders ensures that the voices of all community members are heard, fostering trust and collaboration. Successful case studies from cities like New Orleans and Miami illustrate how tailored, community-driven approaches lead to sustainable outcomes. These examples highlight that resilience transcends infrastructure; it encompasses cultivating a culture of preparedness and adaptability among residents.
As the world confronts unprecedented challenges, the urgency for effective community resilience strategies becomes increasingly critical. The future of resilience planning will likely be shaped by technological advancements, an emphasis on equity, and collaborative governance models. By prioritizing these elements, communities can not only mitigate risks but also promote social equity and sustainable development. Ultimately, fostering community resilience is vital for ensuring that all members can thrive in the face of adversity, paving the way for a more sustainable and equitable future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is community resilience planning?
Community resilience planning is a strategic approach aimed at building collective strength, enabling groups to prepare for, respond to, and recover from adverse events such as natural disasters, economic downturns, and public health crises.
What are the key elements of effective community resilience planning?
Key elements include thorough assessments of vulnerabilities, active stakeholder engagement, and the creation of actionable plans that prioritize local needs. It also involves integrating direct and indirect risk assessments to inform decision-making.
How does the Community Resilience Evaluation (CRE) contribute to resilience planning?
The CRE merges direct survey estimates with indirect assessments to produce reliable risk evaluations at the tract level, helping to identify vulnerable populations and ensure inclusive disaster preparedness initiatives.
Why was personal disaster experience omitted from the resilience planning model?
Personal disaster experience was omitted due to its high correlation with predicted variables, ensuring that the model adhered to fit criteria.
What is the Community-Based Disaster Risk Management Framework?
This framework emphasizes community resilience planning through a dual approach that combines bottom-up and top-down management strategies, focusing on governance, vulnerable groups, and active resident participation.
What statistics indicate the effectiveness of local adaptation initiatives?
The PNFI for Model1 in urban settings is 0.511, which shows a strong link between local adaptation initiatives and improved disaster response capabilities.
How has the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the need for community resilience planning?
The pandemic has underscored the necessity for advanced measurement tools for local organizers and disaster management professionals to enhance community resilience planning.
What challenges do communities face that make resilience planning important?
Communities confront challenges such as climate change, rapid urban development, extreme weather events, public health crises, and economic disruptions, making resilience planning essential for preparedness and recovery.
How does socio-economic inequality affect community resilience?
Communities with greater economic resources often have better access to information, infrastructure, and support systems, enhancing their crisis response capacity. Conversely, economically disadvantaged individuals may struggle to recover, highlighting the need for equitable recovery strategies.
What role does urbanization play in community resilience?
Urbanization introduces unique challenges, including increased vulnerability to climate-related events, making it crucial for community resilience planning to integrate adaptive strategies into urban development for sustainable growth.
What is the significance of expert opinions on climate change in relation to community resilience?
Experts, like Prof. Petteri Taalas, emphasize the severity of the climate crisis and the urgent need for effective adaptive strategies, reinforcing the importance of community resilience planning in addressing these challenges.
What is the future outlook for community resilience planning by 2025?
By 2025, effective frameworks for strengthening societal resilience will increasingly rely on data-driven insights and collaborative methodologies, ensuring communities can not only survive but thrive in the face of adversity.
List of Sources
- Defining Community Resilience Planning
- The community resilience measurement throughout the COVID-19 pandemic and beyond -an empirical study based on data from Shanghai, Wuhan and Chengdu - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8612460)
- A Research Note on Community Resilience Estimates: New U.S. Census Bureau Data With an Application to Excess Deaths From COVID-19 | Demography | Duke University Press (https://read.dukeupress.edu/demography/article/61/3/627/387672/A-Research-Note-on-Community-Resilience-Estimates)
- The Importance of Community Resilience in Today's World
- Climate Reports | United Nations (https://un.org/en/climatechange/reports)
- Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI) (https://ccpi.org)
- Core Components of Community Resilience Planning
- Community Resilience Planning Guide (https://nist.gov/community-resilience/planning-guide)
- Community Resilience | National Risk Index (https://hazards.fema.gov/nri/community-resilience)
- Inclusive Planning: Engaging Communities for Resilience
- How well are US communities planning for resilience, climate adaptation, and sustainability—and what’s missing? Results of a national survey of local staff and officials (https://tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/09640568.2024.2314172)
- Community Resilience | U.S. Climate Resilience Toolkit (https://toolkit.climate.gov/community-resilience)
- Tools and Strategies for Effective Resilience Planning
- Community Resilience Planning with GIS (https://esri.com/en-us/industries/urban-community-planning/initiatives/resilience-planning)
- Community Resilience Estimates Datasets (https://census.gov/programs-surveys/community-resilience-estimates/data/datasets.html)
- Challenges in Community Resilience Planning
- State of the research in community resilience: progress and challenges - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6508589)
- Community resilience (https://nist.gov/community-resilience)
- How well are US communities planning for resilience, climate adaptation, and sustainability—and what’s missing? Results of a national survey of local staff and officials (https://tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/09640568.2024.2314172)
- Case Studies: Successful Community Resilience Initiatives
- State of the research in community resilience: progress and challenges - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6508589)
- Community resilience (https://nist.gov/community-resilience)
- Future Trends in Community Resilience Planning
- A Research Note on Community Resilience Estimates: New U.S. Census Bureau Data With an Application to Excess Deaths From COVID-19 | Demography | Duke University Press (https://read.dukeupress.edu/demography/article/61/3/627/387672/A-Research-Note-on-Community-Resilience-Estimates)
- State of the research in community resilience: progress and challenges - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6508589)
- How well are US communities planning for resilience, climate adaptation, and sustainability—and what’s missing? Results of a national survey of local staff and officials (https://tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/09640568.2024.2314172)




