Introduction
The realm of land management is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the integration of advanced technologies that enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of resource planning and utilization. Central to this evolution are Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing, tools that empower stakeholders to visualize and analyze spatial data critical for informed decision-making.
As urbanization escalates and environmental challenges mount, the imperative for sustainable land management practices becomes increasingly evident. This article delves into the multifaceted role of technology in land management, exploring key innovations, the obstacles to their implementation, and the future trends poised to reshape the landscape.
By examining these elements, a clearer understanding emerges of how technology can address the pressing issues of land use, ensuring that resources are managed responsibly in a rapidly changing world.
Defining Land Management Technology: An Overview
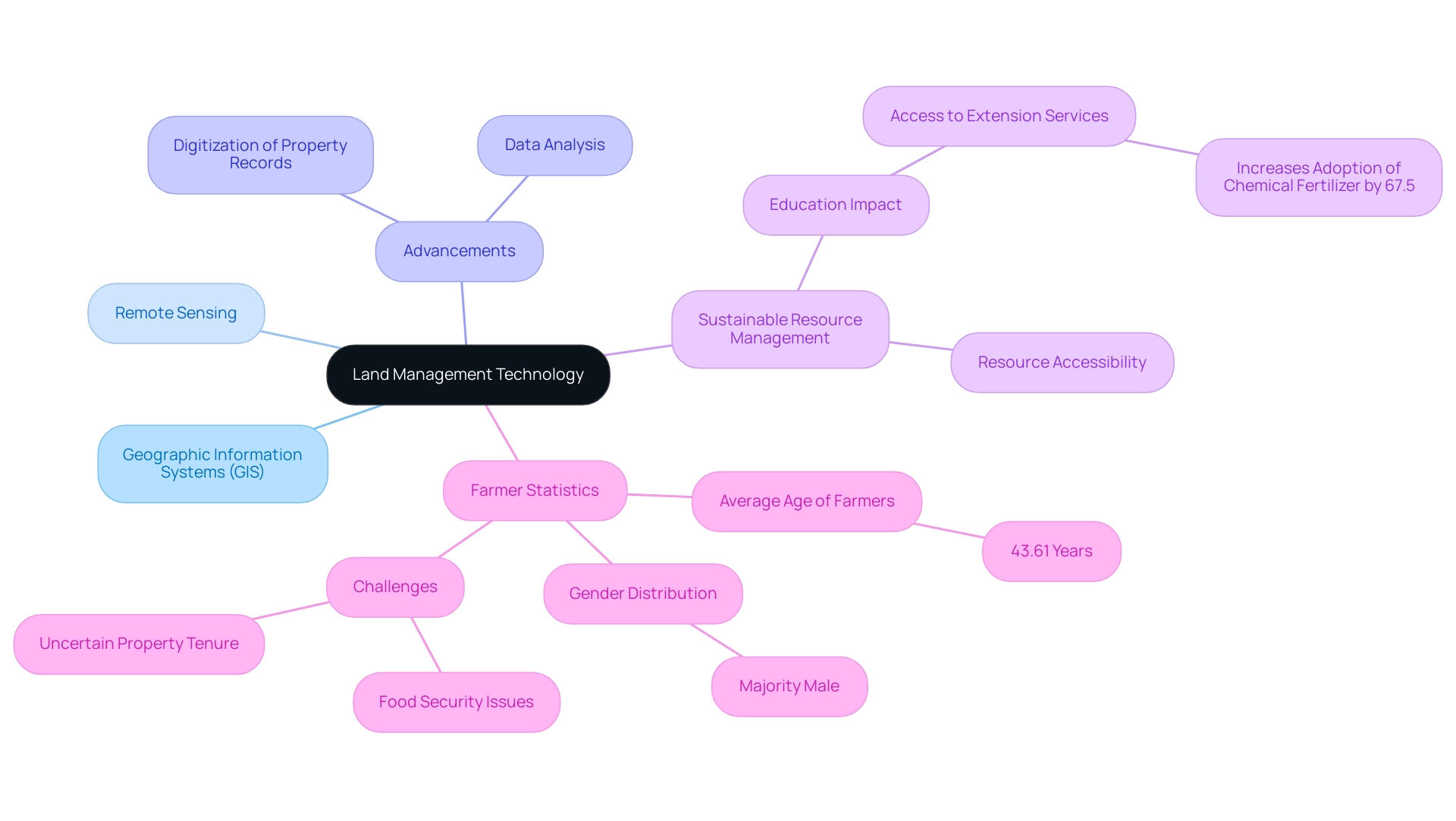
Resource administration systems include a varied range of instruments and frameworks that are crucial for the efficient planning and oversight of territory resources, particularly through the use of land management technology. At the forefront are Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing, which enable stakeholders to visualize, analyze, and interpret essential spatial data related to usage. Recent advancements in land management technology, especially approaching 2024, have transformed territory oversight methods by improving the digitization of property records and enabling data analysis.
These innovations allow for more knowledgeable decision-making and significantly enhance the efficiency of resource use methods. With urbanization and environmental issues growing, the role of GIS and remote sensing in sustainable resource oversight is becoming more essential. For example, a recent study suggests that enhancing farmers' education and increasing credit accessibility can promote the adoption of sustainable resource management methods, tackling the challenges encountered by numerous farmers, including inadequate education and uncertain property tenure.
Notably, access to extension services increases the probability of adopting chemical fertilizer by 67.5%, highlighting the importance of education and resources in these practices. As emphasized by M. Vieira from FAO, the project created a provisional list of change indicators aimed at evaluating project impact and sustainability. This thorough method highlights the necessity of incorporating land management technology in territory oversight to address the intricacies of resource use in a swiftly evolving environment.
Moreover, the typical age of farmers is 43.61 years, with most being male, which creates further challenges in food security and property oversight, as many farmers feel uncertain about their tenure despite possessing property certification.
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Land Management Practices
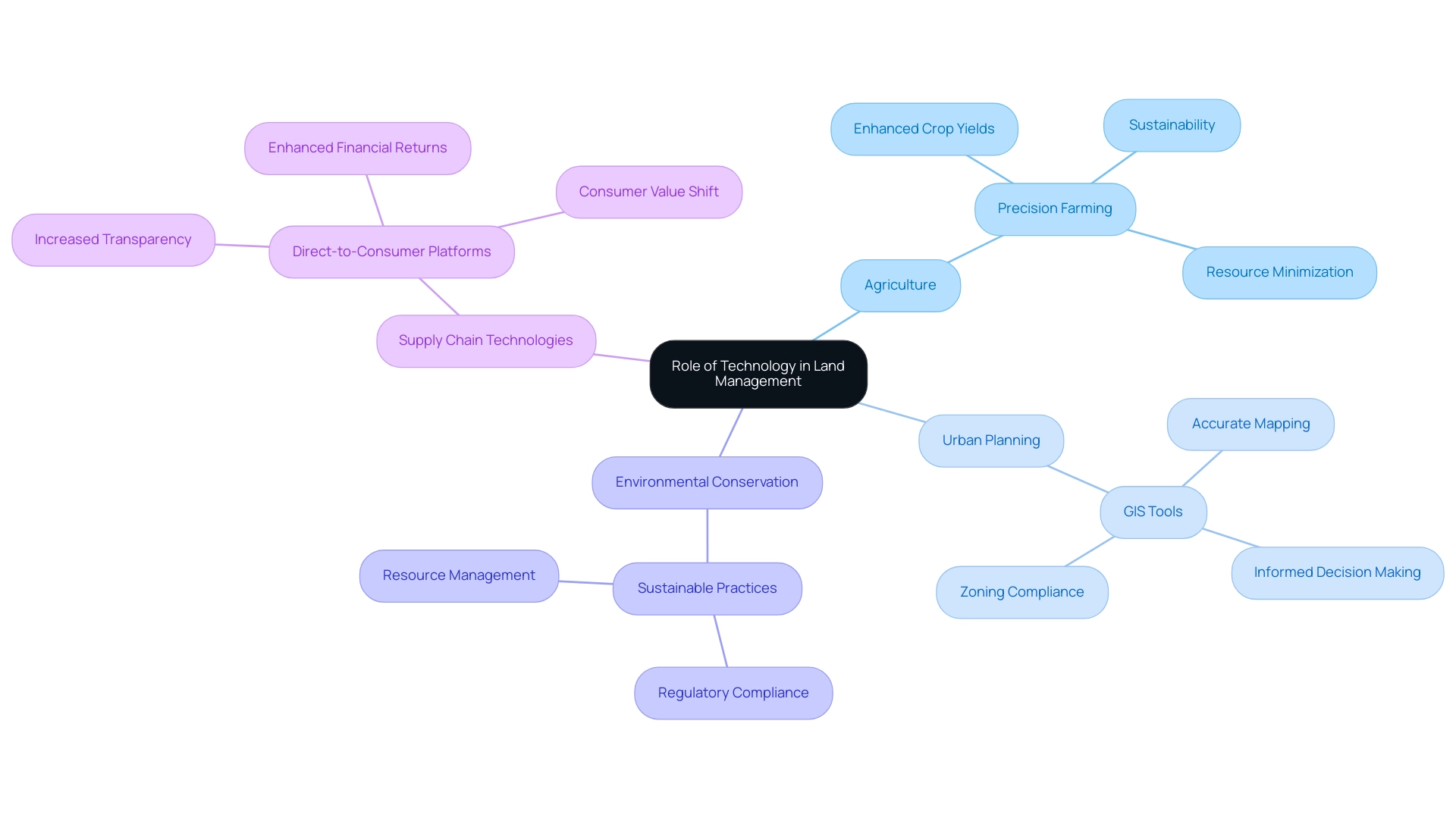
Land management technology is fundamentally transforming resource management methods across diverse sectors, notably agriculture, urban planning, and environmental conservation. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) tools are notable for their capacity to provide accurate mapping and analysis of property parcels, enabling planners to make informed choices about usage and zoning. In the agricultural realm, precision farming leverages data obtained from sensors and satellite imagery to enhance crop yields while minimizing the use of resources.
This approach not only maximizes productivity but also aligns with the growing demand for sustainable practices. Moreover, land management technology simplifies adherence to regulatory standards, enabling more efficient procedures for land acquisition and title research. As mentioned by Dave Muth, Managing Partner at Alternative Equity Advisors, "These innovations provide new and improved value creation opportunities for farmland owners and investors."
The digitization of supply chains and direct-to-consumer food platforms, which represent 40% of all 2020 agrifoodtech venture investment, has significantly influenced consumer preferences towards health, safety, and social impact. This shift offers farmland investors opportunities to seize increased product value and boost financial returns through improved transparency and operational methods. For instance, the case study titled 'Supply Chain Platforms' illustrates how the digitization of supply chains is reshaping consumer values and enhancing financial returns for investors.
Therefore, the incorporation of these innovations not only improves efficiency and precision but also promotes sustainable practices crucial in today’s swiftly changing environment.
Key Technologies in Land Management
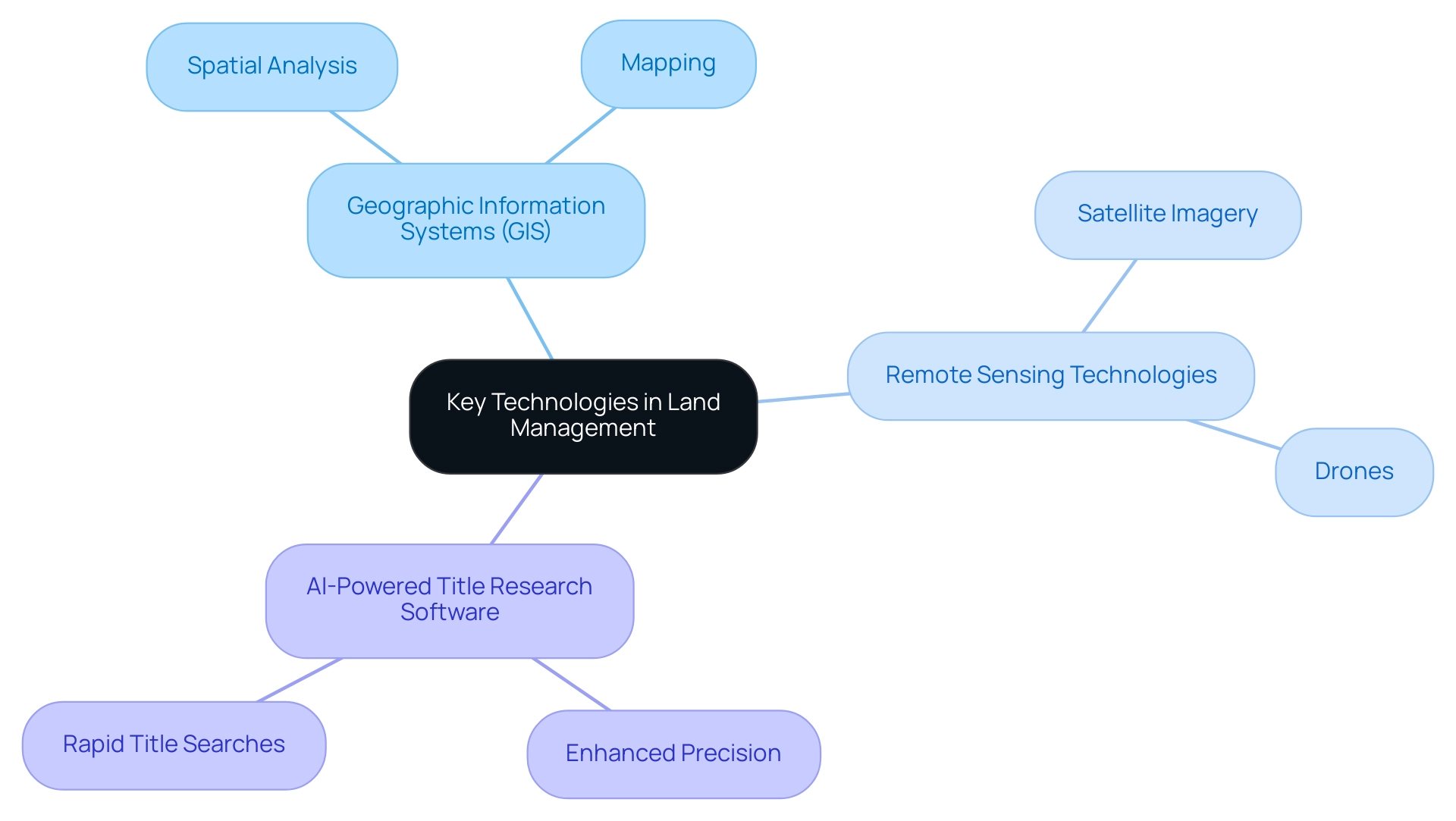
Efficient resource management depends on various crucial innovations, including land management technology, that improve decision-making and operational effectiveness, similar to how 66% of customer service teams use knowledge bases to enhance service delivery. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) play a crucial role in land management technology by facilitating spatial analysis and mapping, which allows stakeholders to visualize complex usage patterns with clarity. Remote sensing technologies, especially satellite imagery and drones, are becoming increasingly essential for land management technology due to their capability to provide real-time information on terrain conditions.
These tools are essential for monitoring environmental changes, utilizing land management technology to enable proactive responses to issues such as deforestation, urban sprawl, and natural disasters. Significantly, in 2024, advancements in remote sensing are anticipated to improve data accuracy and accessibility, further transforming land management technology practices. As Bain and Company noted, 'A customer is four times more likely to switch to a competitor if the problem they're having is service-based,' highlighting the importance of service quality in acquisition processes.
Additionally, AI-powered title research software is transforming the landscape of title searches. By greatly enhancing both precision and rapidity, these innovations reduce legal risks during property acquisition processes. Just as the customer service sector gains from emphasizing employee contentment to lower turnover expenses, organizations in resource stewardship can likewise improve operational effectiveness and employee satisfaction by utilizing these advancements.
Collectively, these innovations create a comprehensive toolkit that empowers organizations to manage resources efficiently and responsibly, utilizing land management technology to ensure sustainable practices are at the forefront of acquisition strategies.
Challenges in Implementing Land Management Technology
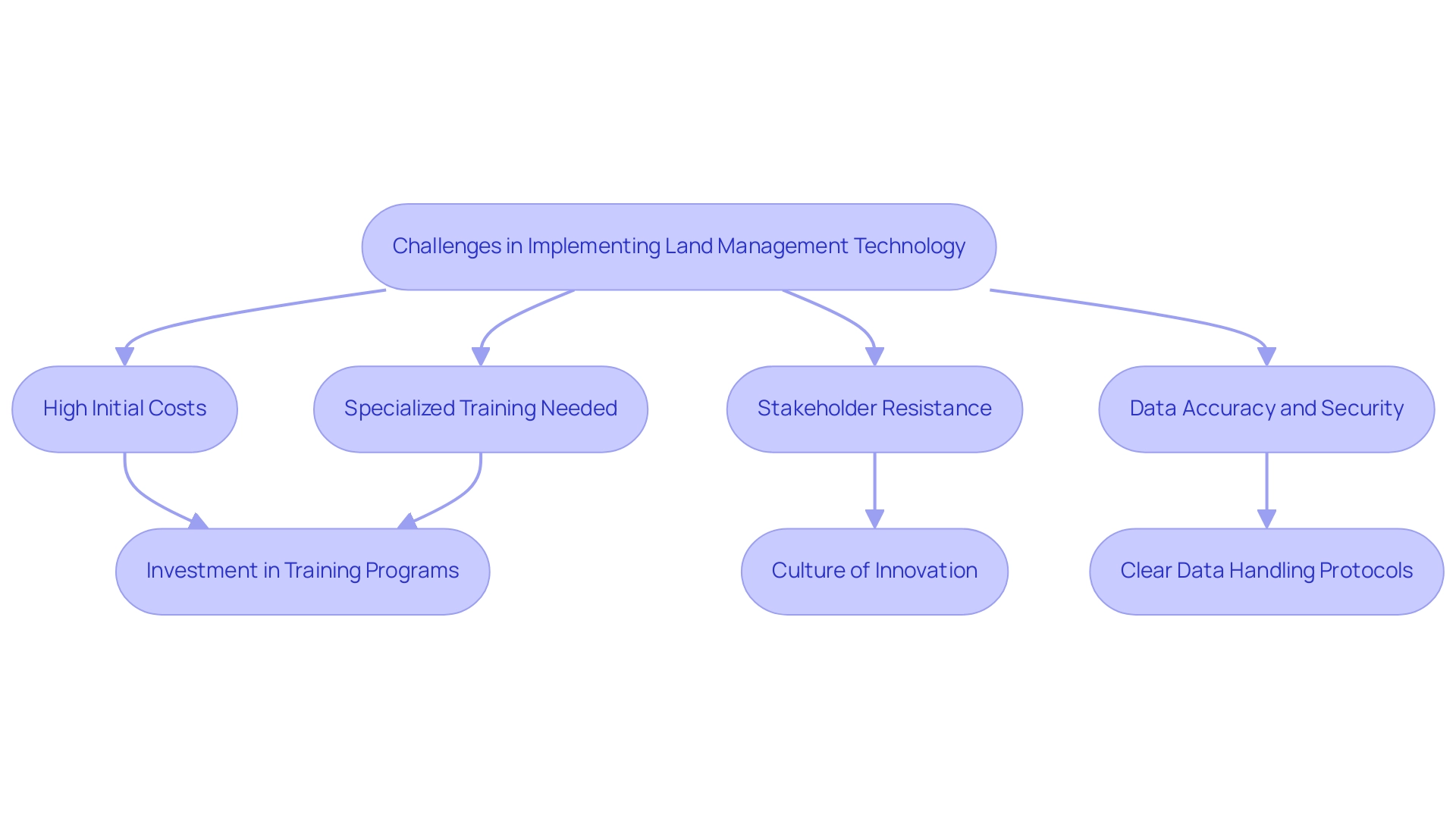
The execution of resource management tools, despite their numerous benefits, presents several substantial obstacles that organizations must address. High initial costs often deter adoption, combined with the necessity for specialized training to ensure effective usage of these tools. Stakeholder resistance to shifting from traditional methods further complicates matters, as many individuals may be hesitant to embrace new technologies.
Furthermore, ensuring data accuracy and security is essential; inaccuracies in property records can result in significant legal and financial consequences. For example, in 2008, sand dunes encompassed 25,208 hectares of territory, an 80 percent reduction from the 1950s, demonstrating the urgent ecological challenges that require efficient resource oversight. Additionally, Ewers et al. (2006) offer significant insights into the historical and forthcoming trends of forest loss in New Zealand, further highlighting the urgency of adopting resource stewardship technologies.
Recognizing these challenges, organizations should prioritize:
- Investment in comprehensive training programs related to land management technology
- Establishment of clear data handling protocols
- Cultivation of a culture of innovation that welcomes technological advancements
As highlighted by the PCE, the deterioration in the health of our ecosystems not only influences environmental integrity but also affects cultural customs and community welfare, stressing the necessity of effective resource stewardship strategies.
Moreover, the case study titled 'The many-headed beast of wildfire risks in Aotearoa-New Zealand' demonstrates the necessity for comprehensive risk control strategies that are vital not only for addressing wildfire threats but also for promoting sustainable resource practices through the use of land management technology in the future. By linking these discoveries to the difficulties of implementing resource stewardship advancements, organizations can gain a clearer insight into the significance of incorporating creative solutions to tackle these urgent concerns.
Future Trends in Land Management Technology
The terrain of resource oversight is on the verge of significant change, primarily driven by advancements such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and blockchain. These innovations in land management technology are poised to transform how terrain is observed and administered. For instance, AI and machine learning enable advanced data analysis, which improves forecasting and decision-making abilities, ultimately resulting in more effective management strategies.
A notable statistic indicates that diverse forests, including woodlands and urban forests, collectively cover 187.8 million acres in the U.S., underscoring the necessity for innovative monitoring techniques. The Forest Inventory and Analysis Program (FIA), in operation since 1930, has been vital in supplying data on forest health and productivity, establishing a foundational context for the adoption of these new advancements. Furthermore, blockchain innovations promise to enhance transparency and security in property transactions, reducing fraud and accelerating processes.
The incorporation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices further enhances these advancements by allowing ongoing observation of terrain conditions, thereby aiding proactive oversight strategies. The discussions from the 2016 American Indian and Alaska Native Data Workshop emphasize the critical need for enhanced data development and cooperation, uncovering substantial gaps that innovation can help bridge. For instance, AI can facilitate better data collection methods that address these gaps, fostering partnerships among stakeholders.
As these technologies evolve, they are set to play an increasingly crucial role in fostering sustainable land use and tackling the intricate challenges faced in land management technology.
Conclusion
The integration of advanced technologies in land management represents a pivotal shift towards more efficient and sustainable resource utilization. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing have emerged as key tools, enabling stakeholders to visualize and analyze spatial data effectively. These innovations not only enhance decision-making processes but also address the complexities associated with urbanization and environmental challenges, thereby reinforcing the necessity for sustainable land management practices.
Despite the significant benefits offered by these technologies, challenges remain in their implementation. High initial costs, the need for specialized training, and resistance to change can hinder adoption. Moreover, ensuring data accuracy and security is paramount, as inaccuracies can lead to serious legal and financial consequences. Organizations must prioritize investment in training programs and foster a culture of innovation to overcome these obstacles and facilitate the integration of technology in land management.
Looking to the future, the landscape of land management technology is poised for transformation through advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain. These innovations promise to enhance monitoring and management capabilities, fostering transparency and improving decision-making. As the pressures on land resources intensify, the proactive adoption of these technologies will be critical in ensuring sustainable land use and addressing the pressing challenges of our time. The path forward is clear: embracing technological advancements is essential for effective land management in a rapidly evolving world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are resource administration systems?
Resource administration systems are tools and frameworks essential for the efficient planning and oversight of territory resources, particularly through land management technology.
What technologies are at the forefront of resource administration?
The primary technologies include Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing, which help stakeholders visualize, analyze, and interpret spatial data related to land use.
How have recent advancements in land management technology impacted resource oversight?
Recent advancements have improved the digitization of property records and enabled better data analysis, leading to more informed decision-making and enhanced efficiency in resource use.
Why is GIS and remote sensing important for sustainable resource oversight?
GIS and remote sensing are crucial for sustainable resource oversight as they help monitor environmental changes and support proactive responses to challenges like urban sprawl and deforestation.
What challenges do farmers face regarding resource management?
Many farmers face challenges such as inadequate education, uncertain property tenure, and a lack of access to credit and extension services, impacting their ability to adopt sustainable practices.
What impact does access to extension services have on farmers?
Access to extension services significantly increases the likelihood of farmers adopting chemical fertilizers, highlighting the importance of education and resources in sustainable practices.
How does land management technology assist in agriculture?
Land management technology, particularly GIS tools, enhances precision farming by utilizing data from sensors and satellite imagery to improve crop yields while minimizing resource use.
What role does digitization play in the agricultural sector?
The digitization of supply chains and direct-to-consumer food platforms has influenced consumer preferences and provided farmland investors with opportunities to enhance product value and financial returns.
What obstacles do organizations face in implementing resource management tools?
Organizations face high initial costs, the need for specialized training, stakeholder resistance to new technologies, and the necessity for accurate and secure data management.
How are AI and machine learning transforming land management?
AI and machine learning improve data analysis, forecasting, and decision-making, leading to more effective management strategies in land oversight.
What potential does blockchain technology have in resource management?
Blockchain technology can enhance transparency and security in property transactions, reducing fraud and expediting processes in land management.
What is the significance of the Internet of Things (IoT) in land management?
IoT devices allow for continuous monitoring of terrain conditions, aiding proactive oversight strategies and improving resource management practices.
List of Sources
- Defining Land Management Technology: An Overview
- Land condition change indicators for sustainable land resource management (https://fao.org/4/w4745e/w4745e09.htm)
- Determinants of farmers’ adoption of land management practices in Gelana sub-watershed of Northern highlands of Ethiopia - Ecological Processes (https://ecologicalprocesses.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s13717-017-0085-5)
- The Role of Technology in Enhancing Land Management Practices
- Five Emerging Technologies Impacting Farmland Investing (https://peoplescompany.com/blog/five-emerging-technologies-impacting-farmland-investing)
- Statistics, services and land management - Grupo TYPSA (https://typsa.com/en/statistics-services-and-land-management)
- Key Technologies in Land Management
- 107 Customer Service Statistics and Facts You Shouldn't Ignore - Help Scout (https://helpscout.com/75-customer-service-facts-quotes-statistics)
- Precision Technology | New Holland (https://agriculture.newholland.com/en-us/nar/products/plm)
- Challenges in Implementing Land Management Technology
- Our land 2024 (https://environment.govt.nz/publications/our-land-2024)
- Barriers for energy and sustainability professionals when implementing initiatives | Statista (https://statista.com/statistics/808900/challenges-for-energy-and-sustainability-professionals-when-implementing-initiatives)
- Future Trends in Land Management Technology
- Forest Ownership Statistics - National Association of State Foresters (https://stateforesters.org/timber-assurance/legality/forest-ownership-statistics)
- Economic Analysis | U.S. Department of the Interior (https://doi.gov/ppa/what-we-make/reports-and-statistics)




