Overview
Underground mapping software is a specialized tool used for visualizing and managing subsurface utilities and structures, playing a critical role in sectors like construction and urban planning. The article highlights its importance in improving safety and efficiency by accurately identifying below-surface assets, while also addressing challenges such as data accuracy and regulatory compliance, thereby underscoring its essential role in modern infrastructure development.
Introduction
The realm of underground mapping software has emerged as a pivotal component in the management and visualization of subsurface utilities and structures, playing a crucial role across various sectors such as construction, civil engineering, and urban planning. As the demand for accurate identification of underground assets intensifies, these specialized tools harness advanced technologies like Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and 3D modeling to enhance the precision and efficiency of site assessments.
This article delves into the multifaceted benefits of underground mapping software, addressing its significance in ensuring safety, compliance, and operational efficiency in infrastructure projects. Additionally, it examines the challenges faced by professionals in the field, highlights recent technological innovations, and explores future trends and market opportunities that underscore the transformative potential of these solutions in an increasingly urbanized world.
Defining Underground Mapping Software: An Overview
Underground mapping software encompasses specialized tools that are essential for visualizing and managing subsurface utilities and structures. Underground mapping software plays a critical role across various sectors, including construction, civil engineering, and urban planning, by assisting professionals in accurately identifying the locations of below-surface assets such as pipes, cables, and other infrastructures. Leveraging advanced technologies such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and 3D modeling, underground mapping software solutions significantly enhance the accuracy and efficiency of site assessments, which is crucial for mitigating risks associated with excavation and construction activities.
For example, Rail Vikas Nigam Limited recently began the surveying of a 5.5km subterranean section of the Joka-Esplanade Metro in Kolkata, highlighting the significance of accurate surveying in urban development projects. However, the market faces challenges such as high initial costs for advanced surveying technologies and stringent regulatory standards across different regions, which can impact the adoption of these solutions. Furthermore, the integration of GIS technology not only ensures compliance with these regulatory requirements but also minimizes potential disruptions during construction projects.
According to a Global Consulting Firm, 'Our company has been working with [specific software provider] for some years now and we are very happy with the quality of the reports provided by the company.' This sentiment illustrates the increasing acknowledgment of underground mapping software as an essential tool for ensuring the successful implementation of construction and development projects. Additionally, key players in this competitive landscape, such as Leica Geosystems, Radiodetection, and Trimble Inc., are focusing on innovation and strategic partnerships to enhance their offerings.
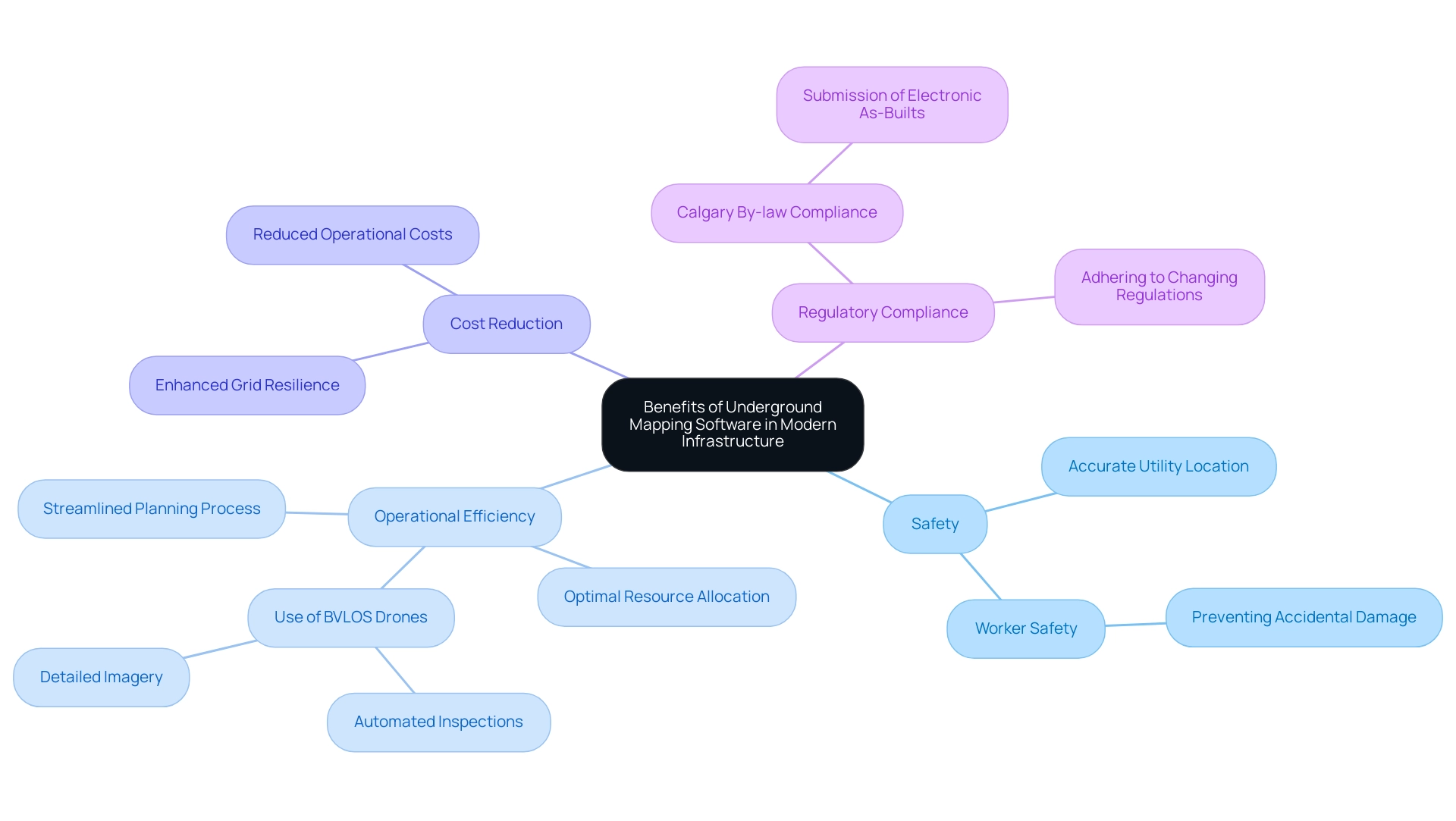
The Benefits of Underground Mapping Software in Modern Infrastructure
The incorporation of underground mapping software into contemporary infrastructure initiatives offers numerous benefits. Foremost among these is the substantial enhancement of safety; accurate identification of underground utilities is essential in preventing accidental damage during excavation, as emphasized by David J Eisenmann from Iowa State University, who stated,
The accurate identification and location of buried utilities is a critical step in ensuring worker safety and utility integrity.
Furthermore, GIS visualization can drive productivity and increase operational efficiency, reducing operational costs.
Underground mapping software significantly enhances operational efficiency by streamlining the planning process. Project teams gain the ability to visualize subsurface conditions prior to commencing work, which facilitates optimal resource allocation and minimizes potential delays. A pertinent example of technology enhancing safety and efficiency is the use of BVLOS drones for power line inspections.
This technology automates the inspection process, covering large distances while providing detailed imagery, ultimately reducing expenses and enhancing grid resilience—demonstrating the vital role of software in construction projects. Furthermore, this technology assists in adhering to changing legal and regulatory frameworks, such as the recent by-law enacted by the City of Calgary requiring network operators to submit electronic as-builts of newly installed subterranean systems. This compliance ensures that projects not only meet safety standards but also address environmental considerations.
As a result, underground mapping software leads to significant cost reductions and enhanced project success rates, emphasizing its crucial role in modern infrastructure development. Future research will integrate remote sensing data and evaluate the completeness of the hierarchical rules used, further enhancing the efficacy of these technologies.
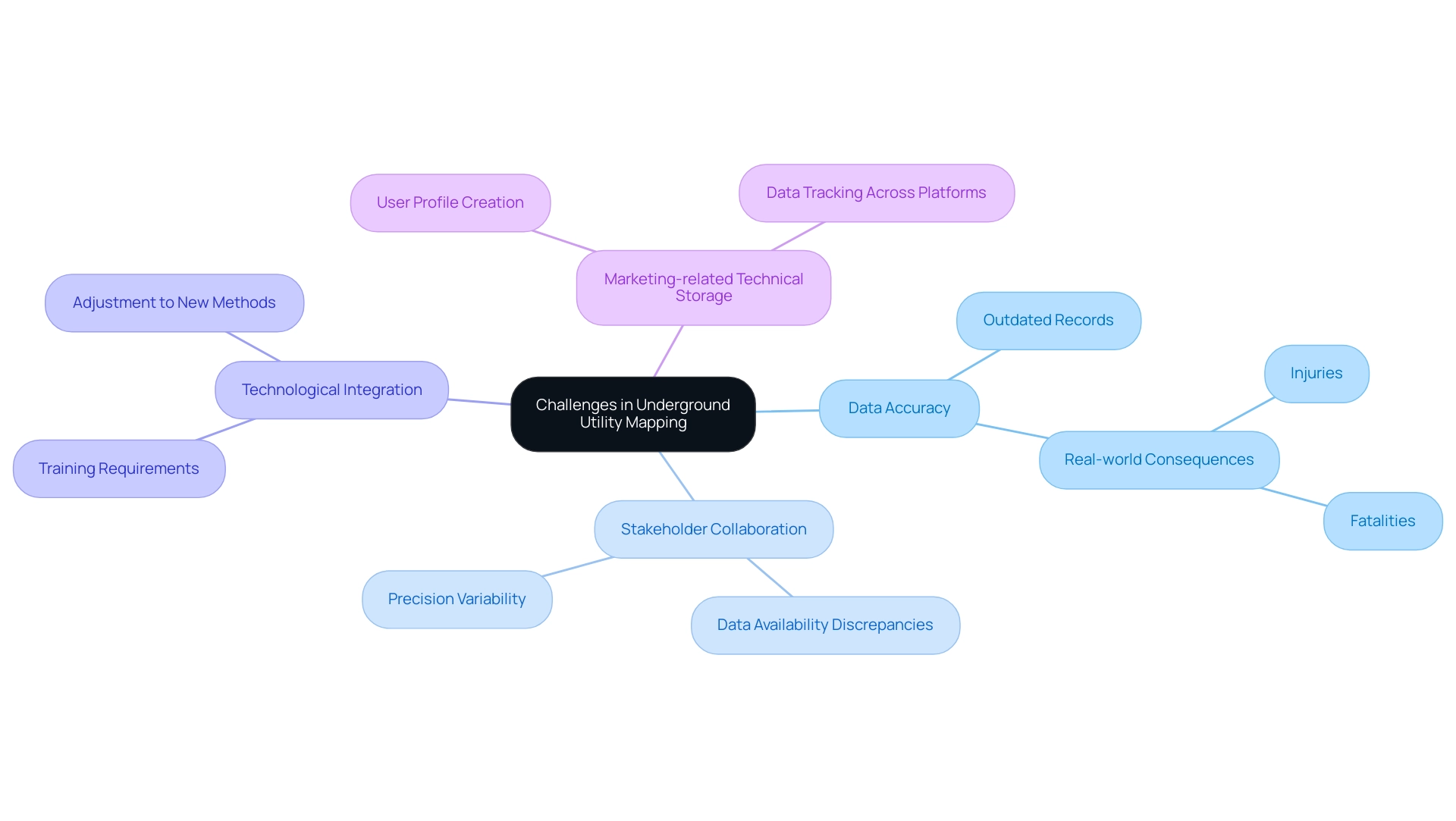
Challenges in Underground Utility Mapping: Navigating the Complexities
Subterranean service location, although beneficial, presents several notable obstacles that experts must tackle to guarantee efficiency. A primary concern is ensuring data accuracy; outdated or incomplete records can lead to serious misinterpretations of subsurface conditions, which have real-world consequences—over 1,500 injuries and nearly 400 fatalities related to underground service issues have been reported in the past two decades. Moreover, the collaboration among various stakeholders, including service providers and local authorities, complicates the charting process, as differing levels of data availability and precision can result in discrepancies.
For instance, in a recent historical investigation of a nearly 175-year-old stone church, GPRS utilized advanced techniques to uncover buried artifacts, demonstrating how accurate surveying methods can significantly enhance our understanding of subsurface conditions. This case underscores the importance of accurate data in heritage sites, where misinterpretations can lead to both cultural loss and safety hazards. The integration of new technologies into existing workflows also presents hurdles, necessitating substantial training and adjustment for teams accustomed to traditional methods.
Furthermore, marketing-related technical storage plays a vital role in this context; it facilitates the creation of user profiles and the tracking of data across various platforms, ultimately enhancing data management and accuracy in utility representation. As GPRS articulates,
Data Control = Damage Control™
emphasizing that addressing these challenges is not only crucial for the successful implementation of underground mapping software but also vital for safeguarding lives and preserving infrastructure.
Technological Innovations in Underground Mapping: Tools and Techniques
Recent technological advancements in underground mapping software have significantly improved subterranean surveying practices, resulting in greater efficiency and accuracy. Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) stands out as a leading technology, serving as underground mapping software that offers non-invasive subsurface imaging to enable professionals to detect and map services without excavation. This capability is crucial for minimizing disruption and optimizing project timelines.
Simultaneously, Electromagnetic Induction (EMI) methods are employed to identify conductive materials hidden below the surface, offering crucial information for efficient utility layout. These advancements are complemented by the latest developments in Geographic Information Systems (GIS), particularly through underground mapping software, which have dramatically improved the visualization and analysis of spatial data. According to Laura Wood, Senior Press Manager at ResearchAndMarkets.com, "ResearchAndMarkets.com is the world's leading source for international market research reports and market data," underscoring the importance of market insights in understanding these technological advancements.
A notable case study is that of multiVIEW Locates, which expanded its CCTV sewer inspection services to include NASSCO-certified inspections, thereby supporting asset management and minimizing construction risks associated with aging systems in Ontario. Moreover, researchers have observed that the sodium battery has the capability to offer four times more storage than lithium batteries, emphasizing the significance of innovative technologies in improving efficiency across different areas, including subterranean exploration. Such enhancements facilitate informed decision-making during project planning, making underground mapping software essential for contemporary development initiatives.
Their incorporation into service layout not only assists in maneuvering the intricacies of subsurface environments but also enhances strategic asset management and risk reduction.
Future Trends and Market Opportunities in Underground Mapping Software
The sector for underground mapping software is on the verge of significant expansion, driven by a rising demand for accurate service location in different infrastructure initiatives. As urbanization accelerates, efficient land use and utility management emerge as vital necessities. Technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are poised to transform the capabilities of underground mapping software, enabling advanced predictive analytics and seamless data integration.
Additionally, the emergence of smart city initiatives offers new market prospects, as municipalities increasingly aim to enhance management of facilities. An illustrative case is Exodigo's Subsurface Mapping Initiative, which, under the GOPHURRS program by the U.S. Department of Energy’s ARPA-E, aims to produce accurate subsurface maps for better undergrounding of power lines. This initiative emphasizes the vital significance of dependable resource representation in improving the durability and safety of power systems.
IoT sensors embedded in utility systems enable continuous data monitoring, significantly reducing unexpected failures. As Snehal Singh, Assistant Manager - Research, observes, "High acumen in analyzing complex macro & micro markets is essential for navigating the evolving landscape of underground navigation solutions." Stakeholders in the energy and infrastructure sectors must stay attuned to these evolving trends and consider investing in underground mapping software to leverage future growth opportunities.
Conclusion
The exploration of underground mapping software reveals its indispensable role in modern infrastructure management. By enhancing the visualization and management of subsurface utilities, these advanced tools significantly improve safety, compliance, and operational efficiency across various sectors, including construction and urban planning. The integration of technologies such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) has empowered professionals to accurately identify and map underground assets, thereby mitigating risks associated with excavation activities and ensuring the integrity of essential services.
However, the implementation of underground mapping software is not without challenges. Issues such as data accuracy, stakeholder coordination, and the need for substantial training in new technologies can complicate the mapping process. Addressing these challenges is crucial for ensuring the successful deployment of these tools, as they directly impact safety and the preservation of infrastructure. As technological innovations continue to emerge, the landscape of underground mapping is evolving, offering new methodologies that enhance the precision and efficiency of subsurface assessments.
Looking ahead, the future of underground mapping software is promising, driven by an increasing demand for accurate utility mapping in response to urbanization and the rise of smart city initiatives. With the advent of artificial intelligence and machine learning, the capabilities of these tools are set to expand, enabling advanced predictive analytics and more seamless data integration. Stakeholders in the energy and infrastructure sectors must remain vigilant and proactive in adopting these cutting-edge technologies to capitalize on the market opportunities that lie ahead. The transformative potential of underground mapping software is clear, making it a critical component in the development of resilient and efficient urban environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is underground mapping software?
Underground mapping software encompasses specialized tools designed for visualizing and managing subsurface utilities and structures, assisting professionals in accurately identifying the locations of below-surface assets like pipes and cables.
In which sectors is underground mapping software used?
This software plays a critical role in various sectors, including construction, civil engineering, and urban planning.
How does underground mapping software enhance site assessments?
It leverages advanced technologies such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and 3D modeling to significantly improve the accuracy and efficiency of site assessments, which is essential for mitigating risks during excavation and construction activities.
Can you provide an example of underground mapping software in use?
Rail Vikas Nigam Limited recently conducted a survey of a 5.5km subterranean section of the Joka-Esplanade Metro in Kolkata, demonstrating the importance of accurate surveying in urban development projects.
What challenges does the underground mapping software market face?
The market faces challenges such as high initial costs for advanced surveying technologies and stringent regulatory standards across different regions, which can impact the adoption of these solutions.
How does GIS technology contribute to underground mapping software?
The integration of GIS technology ensures compliance with regulatory requirements and minimizes potential disruptions during construction projects.
What benefits does underground mapping software provide in terms of safety?
It enhances safety by accurately identifying underground utilities, which is crucial in preventing accidental damage during excavation.
How does underground mapping software improve operational efficiency?
It streamlines the planning process by allowing project teams to visualize subsurface conditions before commencing work, facilitating optimal resource allocation and minimizing delays.
What role do drones play in relation to underground mapping software?
BVLOS drones automate the inspection process for power lines, covering large distances and providing detailed imagery, which reduces expenses and enhances grid resilience.
How does underground mapping software help with compliance?
It assists in adhering to legal and regulatory frameworks, such as the requirement for network operators to submit electronic as-builts of newly installed subterranean systems, ensuring safety standards and environmental considerations are met.
What is the impact of underground mapping software on project success rates?
It leads to significant cost reductions and enhanced project success rates, emphasizing its crucial role in modern infrastructure development.
List of Sources
- Defining Underground Mapping Software: An Overview
- Underground Utility Mapping Market Size, Industry Share | Forecast [2025-2032] (https://fortunebusinessinsights.com/underground-utility-mapping-market-105689)
- Underground Utility Mapping Market Research Report 2032 (https://dataintelo.com/report/global-underground-utility-mapping-market)
- The Benefits of Underground Mapping Software in Modern Infrastructure
- 5 Reasons to Utilize GIS with Utility Mapping - UtiliSource (https://utilisource.us/gis-utility-mapping)
- Probabilistic Method to Fuse Artificial Intelligence-Generated Underground Utility Mapping - PMC (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11175323)
- The role of surveyors in locating and mapping underground utilities (https://geospatial.blogs.com/geospatial/2020/04/opportunities-for-surveyors-in-underground-locating-and-mapping.html)
- Challenges in Underground Utility Mapping: Navigating the Complexities
- Underground Utility Mapping Market Trends (https://mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/underground-utility-mapping-market/market-trends)
- Challenges of an underground utility survey - Landform Surveys (https://luciongroup.com/news/what-are-the-challenges-of-an-underground-utility-survey)
- Common Ground Alliance's 2022 Report Highlights Cost of Inaccurate Utility Mapping | GPRS (https://gp-radar.com/article/new-report-highlights-the-cost-of-inaccurate-utility-data-in-the-construction-industry)
- Technological Innovations in Underground Mapping: Tools and Techniques
- Underground Utility Mapping Global Strategic Research Report 2024-2030: Expanding Use in Oil & Gas Pipelines Sustains Market Growth (https://globenewswire.com/news-release/2025/01/31/3018595/28124/en/Underground-Utility-Mapping-Global-Strategic-Research-Report-2024-2030-Expanding-Use-in-Oil-Gas-Pipelines-Sustains-Market-Growth.html)
- Underground Utility Mapping Market by Services - 2024 | MarketsandMarkets (https://marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/underground-utility-mapping-market-178657041.html)
- Top Tech Trends for Utilities in 2024 (https://theutilityexpo.com/news/top-tech-trends-for-utilities-in-2024)
- Future Trends and Market Opportunities in Underground Mapping Software
- Underground Utility Mapping Market Size, Growth, Report 2034 (https://marketresearchfuture.com/reports/underground-utility-mapping-market-24647)
- Key Trends and Insights into the Underground Utility Mapping Market: Growth Rate and Opportunities to 2034 - Latest Global Market Insights (https://blog.tbrc.info/2025/02/global-underground-utility-mapping-market)
- Underground Utility Mapping Market Size | Mordor Intelligence (https://mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/underground-utility-mapping-market)
- Underground Utility Locating: Future Trends and Advancements (https://util-locate.com/future-trends-in-underground-utility-locating)
- thebusinessresearchcompany.com (https://thebusinessresearchcompany.com/report/underground-utility-mapping-global-market-report)




