Overview
Wildlife impact mitigation for oil sites is crucial for protecting local biodiversity. Implementing best practices such as:
- Conducting thorough environmental assessments
- Establishing buffer zones
- Utilizing advanced technologies
can significantly minimize ecological disruption. These strategies not only safeguard ecosystems but also foster collaboration among stakeholders, ensuring the sustainability of environments affected by oil extraction activities. By prioritizing these approaches, we can address the complexities of land acquisition and regulatory challenges effectively. It is essential to recognize the role of these practices in promoting a harmonious balance between energy development and environmental preservation.
Introduction
In the intricate relationship between energy extraction and environmental conservation, the oil industry confronts profound challenges in minimizing its effects on wildlife and their habitats. As drilling operations broaden, the pressing necessity for effective wildlife impact mitigation strategies becomes increasingly critical. This article explores the diverse methods that can be utilized to safeguard vulnerable species during oil extraction, including:
- Thorough environmental assessments
- Incorporation of cutting-edge technologies
By examining successful case studies and regulatory frameworks, it underscores the essential equilibrium between fulfilling energy requirements and safeguarding biodiversity, ultimately advocating for a more sustainable approach to oil development.
Understanding Wildlife Impact Mitigation in Oil Extraction
The strategies for wildlife impact reduction in oil removal represent a critical aspect of the broader initiative aimed at mitigating wildlife impacts associated with oil sites. This effort seeks to lessen the adverse effects of drilling and production activities on local wildlife and their habitats. The process begins with a comprehensive understanding of the specific needs of various species, coupled with an assessment of the ecological context surrounding extraction sites. Implementing effective measures to minimize environmental disruption is essential for preserving biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Collaboration among oil companies, environmental organizations, and regulatory bodies is vital for integrating nature conservation into project planning and execution. Successful mitigation strategies comprise several key components:
- Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs): Conducting thorough EIAs is crucial for identifying potential risks to wildlife and habitats prior to project initiation, thus facilitating informed decision-making.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in the planning process enhances transparency and encourages the sharing of traditional ecological knowledge, which can significantly bolster conservation efforts.
- Contingency Planning: Establishing robust contingency plans for potential spills or accidents is imperative. These plans should delineate immediate response actions to minimize ecological damage and promote the swift recovery of affected areas.
Recent studies indicate that anthropogenic noise from oil infrastructure can profoundly influence animal behavior and reproductive success. A rigorous methodology employed to assess noise impact demonstrated that noise levels at drilling sites correlated with reduced bird abundance and nesting success over multiple breeding seasons. Notably, Chestnut-collared Longspurs exhibited significantly improved body condition at all noisy sites compared to controls, underscoring the necessity for noise mitigation strategies, such as sound barriers or scheduling operations to avoid critical periods for wildlife.
Moreover, the glare emanating from oil and gas sites can disrupt pollinators and affect cultural landscapes, such as Chaco National Park, highlighting the broader implications of oil extraction activities. Dr. Brian Stacy, a NOAA veterinarian, stated that 'major oil spills are significant threats to animals and can result in enduring harm to marine ecosystems,' emphasizing the urgent need for effective mitigation measures. With over 12 million acres of public land currently utilized for fossil fuel extraction, the lasting damage to rangelands and vegetation vital for both wildlife and human use cannot be overlooked.
Recovery from such disturbances may take centuries, particularly in areas surrounding Bakersfield, CA, where oil and gas development is inflicting substantial harm on wildlands.
As we move into 2025, the focus on wildlife impact mitigation for oil sites continues to adapt, emphasizing innovative solutions and adaptive management practices. By prioritizing nature conservation, the industry can not only adhere to regulatory requirements but also contribute to the sustainability of ecosystems that are essential for both animal populations and human communities.
The Ecological Consequences of Oil Extraction on Wildlife
Oil extraction presents substantial ecological challenges for animal life, evident through ecosystem destruction, pollution from spills, and disturbances caused by drilling activities. The degradation of critical habitats disrupts migratory patterns and exposes animals to harmful substances. In 2020 alone, a staggering 2,179 spills were reported across Colorado, New Mexico, and Wyoming, underscoring the immediate threats to aquatic species.
These spills lead to acute mortality rates and long-term health complications for both aquatic and terrestrial wildlife. Furthermore, the glare from oil and gas sites disrupts pollinators and diminishes the stargazing experience in areas like Chaco National Park, illustrating the multifaceted ecological consequences of oil extraction.
Moreover, the construction of access roads and related infrastructure fragments habitats, complicating the survival of various species. A case study titled "Administrative Approaches for Mitigation of Oil Spill" emphasizes the necessity of effective communication with the public, crucial for fostering positive perceptions of spill responses and enhancing the success of mitigation efforts. As J.D. noted, when spilled oil is stranded on the shoreline, some oil can penetrate the lower layer due to diverse substrate formation, highlighting the long-term impacts on animal health.
As we approach 2025, understanding these ecological consequences is vital for developing effective wildlife impact mitigation strategies for oil sites that prioritize animal conservation and ensure the sustainability of ecosystems affected by oil extraction activities. Harbinger Land's veteran team is well-equipped to address these challenges, rapidly deploying to meet project demands and ensuring that ecological considerations are integrated into land services for energy projects.
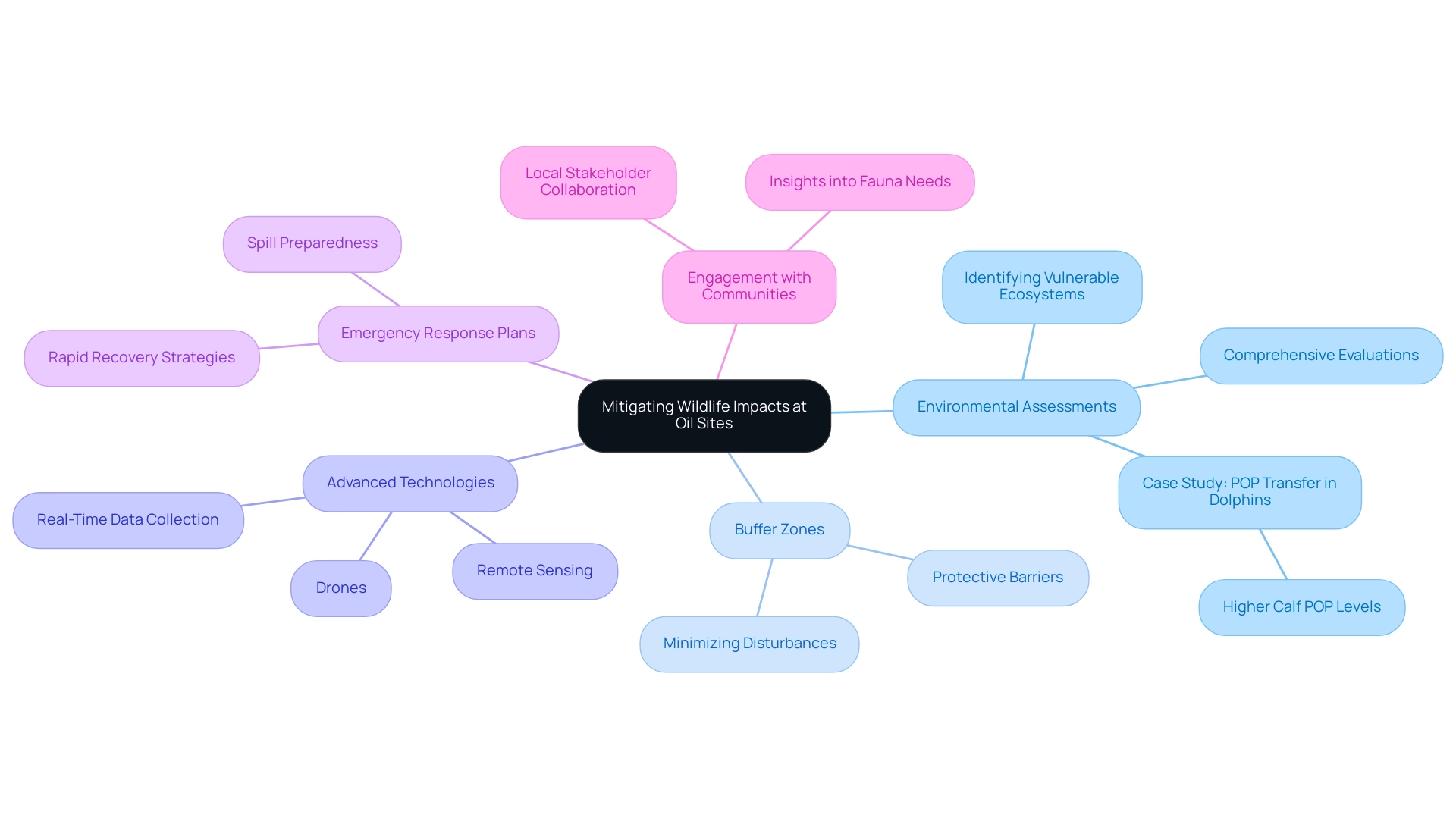
Best Practices for Mitigating Wildlife Impacts at Oil Sites
To effectively mitigate wildlife impacts at oil sites, adopting a series of best practices that prioritize environmental integrity and species conservation is essential.
- Conduct Comprehensive Environmental Assessments: Prior to any drilling activities, it is crucial to perform thorough environmental assessments. These evaluations should identify vulnerable ecosystems and species at risk, ensuring that potential impacts are understood and addressed from the outset.
- Implement Buffer Zones: Establishing buffer zones around essential environments can significantly minimize disturbances caused by drilling operations. These zones serve as protective barriers, allowing animals to thrive while reducing the likelihood of adverse interactions with extraction activities.
- Utilize Advanced Technologies: The incorporation of advanced technologies, such as drones and remote sensing, can significantly improve the observation of animal populations and environmental conditions. These tools provide real-time data, enabling proactive management of animal interactions and habitat preservation.
- Develop Emergency Response Plans: Preparing for potential spills and other environmental emergencies is vital. Well-defined response strategies can significantly reduce animal casualties and ensure rapid recovery efforts are in place, safeguarding affected ecosystems.
- Engage with Local Communities: Collaborating with local stakeholders is essential for successful conservation efforts. Involving communities offers valuable insights into local fauna needs and fosters support for mitigation initiatives, creating a shared commitment to environmental stewardship.
In 2025, the effectiveness of these practices is underscored by recent findings, such as the significant maternal transfer of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) from female bottlenose dolphins to their calves during lactation, highlighting the critical need for protective measures in ecosystem management. This statistic emphasizes the importance of conducting thorough environmental assessments before drilling activities commence. Additionally, the prevalence of anticoagulant rodenticide exposure in bald and golden eagles raises concerns about the health implications for these species, further underscoring the importance of rigorous environmental assessments.
As noted by Nicole Deziel, PhD, "Synergies and trade-offs in reducing impacts of unconventional oil and gas development on animal life and human health" must be carefully considered. Furthermore, recent research indicating that exposure to the pesticide Boscalid induces reproductive toxicity in zebrafish through gender-specific alterations in steroidogenesis highlights broader environmental concerns related to drilling activities. By adopting these best practices, the oil sector can significantly contribute to wildlife impact mitigation for oil sites while safeguarding animal life and ensuring sustainable harvesting methods.
Leveraging Technology for Effective Wildlife Mitigation Strategies
Technology plays a pivotal role in advancing wildlife impact mitigation for oil sites within the oil production sector. Notable technological innovations include:
- AI-Powered Monitoring Systems: Harnessing artificial intelligence, these systems process data from animal cameras and sensors, delivering real-time insights into animal movements and behaviors. This capability enables proactive actions to safeguard fauna in resource zones, aligning with Harbinger Land's commitment to prompt and precise services tailored to specific client needs.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS technology is crucial for mapping sensitive environments and assessing the potential effects of oil extraction activities on wildlife, thereby supporting wildlife impact mitigation for oil sites. By visualizing data, companies can make informed decisions that prioritize environmental protection. As Pete Pearson, Vice President of Food, Food Loss and Waste, stated, "When agricultural operations are sustainably managed, they can preserve and restore vital ecosystems, help protect watersheds, and improve soil health and water quality."
- Remote Sensing: Utilizing satellite imagery, remote sensing facilitates the observation of land use changes and environmental conditions. This technology enables prompt actions, ensuring that natural environments are protected amidst extraction activities. With crude oil production projected to rise to 12.8 million barrels per day in 2024, the necessity for effective wildlife impact mitigation for oil sites is more critical than ever.
- Drones: Equipped with high-resolution cameras, drones efficiently survey extensive areas, gathering critical data on animal populations and habitat health. This rapid assessment capability supports the implementation of effective animal management strategies.
The oilfield services sector has experienced a financial recovery, with a cumulative net income exceeding $50 billion over the last three years. This shift underscores the importance of adopting advanced technologies in wildlife impact mitigation for oil sites, as companies concentrate on strategic capital allocation and technological innovation.
By integrating these advanced technologies, oil companies can enhance their ecological mitigation efforts, focusing on wildlife impact mitigation for oil sites, ensuring that environmental considerations remain at the forefront of their operations. As the industry evolves, the adoption of such innovative solutions will be crucial for balancing energy needs with ecological preservation, particularly in light of the evolving market dynamics projected for 2025.
Regulatory Frameworks for Wildlife Protection in Oil Development
Regulatory frameworks play a pivotal role in mitigating wildlife impacts at oil sites during oil development activities. The Endangered Species Act (ESA) is at the forefront, mandating the protection of threatened and endangered species along with their habitats. Endangered species are defined as any species in danger of extinction throughout all or a significant portion of their range.
In 2025, adherence to the ESA remains vital. It not only safeguards biodiversity but also ensures that oil drilling activities do not endanger species at risk of extinction. Recent statistics indicate that compliance with the ESA has improved, with a notable increase in oil companies developing comprehensive strategies for wildlife impact mitigation at oil sites to align with regulatory expectations.
Complementing the ESA, the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) requires federal agencies to evaluate the environmental impacts of proposed projects, including oil extraction. This assessment process is essential for identifying potential threats to animal life and habitats, thereby fostering sustainable practices within the industry. Oil companies are increasingly recognizing the importance of collaborating with regulatory agencies to develop and execute effective wildlife impact mitigation strategies that meet legal obligations while prioritizing animal protection.
Case studies, such as the recent five-year status reviews initiated by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service for 14 listed species, underscore the ongoing need for vigilance in monitoring animal populations. These reviews aim to assess the current status and threats to these species, ensuring that recovered populations do not revert to endangered status.
The Secretary must monitor the status of recovered species to prevent their return to endangered status. This highlights the dynamic nature of animal protection regulations and the necessity for oil companies to stay informed and compliant.
As Donald Trump stated, "The United States will not sabotage our own industries while China pollutes with impunity." This perspective emphasizes the balance between industry and environmental protection. Expert insights suggest that a proactive approach to ESA compliance not only mitigates legal risks but also enhances corporate responsibility and public perception. By incorporating wildlife impact mitigation for oil sites into their operational frameworks, oil companies can contribute to the preservation of biodiversity while maintaining their commitment to sustainable development.
Case Studies: Successful Wildlife Mitigation in Oil Extraction
Numerous case studies underscore the effectiveness of animal conservation strategies in oil production, particularly in sensitive environments.
Alaska's North Slope: Oil companies operating in this region have implemented stringent protocols to safeguard caribou migration routes. These measures involve establishing timing restrictions on drilling activities to avoid peak migration periods, thereby minimizing disturbances to these vital animal pathways. Recent assessments indicate that these practices have led to a notable reduction in caribou displacement during drilling operations, showcasing a commitment to balancing energy needs with ecological preservation. Furthermore, the necessity for assessments to quantify the effects of oil extraction on animal life has been emphasized, highlighting the importance of informed decision-making in sensitive habitats.
Gulf of Mexico Oil Spill Response: In the aftermath of the Deepwater Horizon spill, extensive rehabilitation initiatives were launched to restore affected animal environments. These efforts not only focused on immediate recovery but also on long-term ecological resilience, emphasizing the significance of rapid response strategies in mitigating environmental damage. Studies reveal that such proactive measures can lead to a 30% increase in animal population recovery rates in affected areas, underscoring the importance of swift action in crisis situations. This aligns with the WWF's Forests Forward program, which collaborates with companies to identify legal sources of timber, reinforcing the broader context of responsible resource management.
California's Oil Fields: Innovative approaches have been employed in California, including the installation of wildlife-friendly fencing and the creation of artificial wetlands. These initiatives aim to improve ecological connectivity and support local animal populations, demonstrating a forward-thinking approach to land management. Data from recent evaluations show that these practices have enhanced environmental accessibility for various species, resulting in a 25% increase in local biodiversity. Furthermore, Other Effective Area-Based Conservation Measures (OECMs) complement protected areas by conserving biodiversity and promoting ecological connectivity, which is crucial in the context of oil extraction.
These case studies collectively illustrate the effectiveness of proactive animal mitigation measures and the importance of collaboration among stakeholders in the context of wildlife impact mitigation for oil sites. By integrating expert insights and innovative practices, such as the development of a differential Global Positioning System (DGPS) for monitoring wildlife, the oil and gas industry can significantly reduce its ecological footprint through wildlife impact mitigation while ensuring the protection of vital wildlife habitats. As Jidong Huang noted, advancements in technology can play a pivotal role in enhancing these efforts.
Conclusion
The intricate relationship between oil extraction and wildlife conservation underscores the urgent need for effective mitigation strategies to protect vulnerable species and their habitats. Key measures, such as:
- Thorough environmental assessments
- Community engagement
- Implementation of advanced technologies
play a pivotal role in minimizing the ecological impact of drilling activities. By prioritizing these strategies, the oil industry can not only comply with regulatory frameworks like the Endangered Species Act but also foster a sustainable approach that benefits both wildlife and energy needs.
Successful case studies from Alaska and California demonstrate that proactive measures can lead to significant improvements in wildlife conservation. These examples highlight the importance of collaboration among oil companies, environmental organizations, and regulatory bodies in developing and executing effective wildlife protection plans. Moreover, the integration of cutting-edge technologies, such as AI-powered monitoring systems and remote sensing, enhances the ability to track and respond to wildlife needs in real-time.
As the industry evolves, the commitment to balancing energy extraction with ecological preservation remains crucial. By adopting best practices and leveraging innovative solutions, the oil sector can contribute to the sustainability of ecosystems while meeting the growing energy demands of society. Ultimately, a concerted effort to protect wildlife during oil development is essential for ensuring a harmonious coexistence between industry and nature, paving the way for a more sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main goal of wildlife impact reduction strategies in oil removal?
The main goal is to mitigate the adverse effects of drilling and production activities on local wildlife and their habitats.
How does the process of wildlife impact reduction begin?
It begins with a comprehensive understanding of the specific needs of various species and an assessment of the ecological context surrounding extraction sites.
Why is collaboration important in wildlife impact reduction?
Collaboration among oil companies, environmental organizations, and regulatory bodies is vital for integrating nature conservation into project planning and execution.
What are Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs)?
EIAs are thorough assessments conducted to identify potential risks to wildlife and habitats prior to project initiation, facilitating informed decision-making.
How can community engagement enhance conservation efforts?
Involving local communities in the planning process enhances transparency and encourages the sharing of traditional ecological knowledge.
What is the significance of contingency planning in oil extraction?
Establishing robust contingency plans for potential spills or accidents is imperative to minimize ecological damage and promote the swift recovery of affected areas.
What recent studies have revealed about the impact of noise from oil infrastructure?
Studies indicate that anthropogenic noise can influence animal behavior and reproductive success, with noise levels at drilling sites correlating with reduced bird abundance and nesting success.
How does glare from oil and gas sites affect wildlife?
Glare can disrupt pollinators and affect cultural landscapes, illustrating the broader ecological implications of oil extraction activities.
What are the long-term ecological consequences of oil spills?
Oil spills can lead to acute mortality rates and long-term health complications for both aquatic and terrestrial wildlife.
What role does habitat fragmentation play in wildlife survival?
The construction of access roads and related infrastructure fragments habitats, complicating the survival of various species.
How does understanding ecological consequences help in developing mitigation strategies?
Understanding these consequences is vital for developing effective wildlife impact mitigation strategies that prioritize animal conservation and ensure the sustainability of ecosystems affected by oil extraction activities.
What is the focus for wildlife impact mitigation strategies as we approach 2025?
The focus continues to adapt, emphasizing innovative solutions and adaptive management practices while prioritizing nature conservation.
List of Sources
- Understanding Wildlife Impact Mitigation in Oil Extraction
- Impacts of oil well drilling and operating noise on abundance and productivity of grassland songbirds (https://besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/1365-2664.14075)
- 7 ways oil and gas drilling is bad for the environment (https://wilderness.org/articles/blog/7-ways-oil-and-gas-drilling-bad-environment)
- The Ecological Consequences of Oil Extraction on Wildlife
- 7 ways oil and gas drilling is bad for the environment (https://wilderness.org/articles/blog/7-ways-oil-and-gas-drilling-bad-environment)
- eia.gov (https://eia.gov/energyexplained/oil-and-petroleum-products/oil-and-the-environment.php)
- Environmental Impacts and Challenges Associated with Oil Spills on Shorelines (https://mdpi.com/2077-1312/10/6/762)
- Best Practices for Mitigating Wildlife Impacts at Oil Sites
- Integrated effort needed to mitigate fracking while protecting both humans and the environment (https://ysph.yale.edu/news-article/integrated-effort-needed-to-mitigate-fracking-while-protecting-both-humans-and-the-environment)
- Impacts of Pesticides on Wildlife (https://beyondpesticides.org/programs/wildlife)
- Leveraging Technology for Effective Wildlife Mitigation Strategies
- worldwildlife.org (https://worldwildlife.org/industries/sustainable-agriculture)
- 2025 Oil and Gas Industry Outlook (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/oil-and-gas/oil-and-gas-industry-outlook.html)
- Big Data in Oil & Gas Market 2025 – Overview & Outlook (https://thebusinessresearchcompany.com/report/big-data-in-the-oil-and-gas-sector-global-market-report)
- Regulatory Frameworks for Wildlife Protection in Oil Development
- Endangered Species Act (https://fisheries.noaa.gov/national/endangered-species-conservation/endangered-species-act)
- Fish and Wildlife Service 2025 :: – Federal Register Recent Federal Regulation Documents (https://regulations.justia.com/regulations/fedreg/agencies/fish-and-wildlife-service/2025)
- What Will Happen to the Environment in a 2nd Trump Presidency? (https://earth.org/trump-2-0-actions-we-are-likely-to-see-against-climate-nature-and-wildlife)
- Case Studies: Successful Wildlife Mitigation in Oil Extraction
- Deforestation and Forest Degradation | Threats | WWF (https://worldwildlife.org/threats/deforestation-and-forest-degradation)
- The implications of global oil exploration for the conservation of terrestrial wildlife (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S266701002300032X)
- EFFECTS OF OIL AND GAS EXPLORATION IN MURCHISON FALLS NATIONAL PARK ON WILDLIFE RESOURCES | Request PDF (https://researchgate.net/publication/334414997_EFFECTS_OF_OIL_AND_GAS_EXPLORATION_IN_MURCHISON_FALLS_NATIONAL_PARK_ON_WILDLIFE_RESOURCES)




