Overview
This article presents a comprehensive overview of the essential steps required for conducting a wind energy feasibility analysis. It emphasizes:
- Project planning
- Resource assessment
- Technology selection
- Financial evaluation
- Stakeholder engagement
Each step is substantiated with evidence and relevant examples, underscoring the critical role of thorough research and community involvement in ensuring the success and sustainability of projects within the renewable energy sector.
Introduction
The transition to renewable energy sources is not merely a trend; it is an essential component of sustainable development. Among these sources, wind energy emerges as a particularly promising solution. However, the journey toward successful wind energy projects is laden with challenges. This article explores the critical steps involved in conducting a wind energy feasibility analysis, providing readers with the expertise needed to navigate the complexities of project planning.
How can stakeholders ensure their initiatives not only achieve energy objectives but also align with environmental and community expectations? The answers reside within a structured approach that harmonizes technical assessments with social engagement, paving the way for impactful renewable energy solutions.
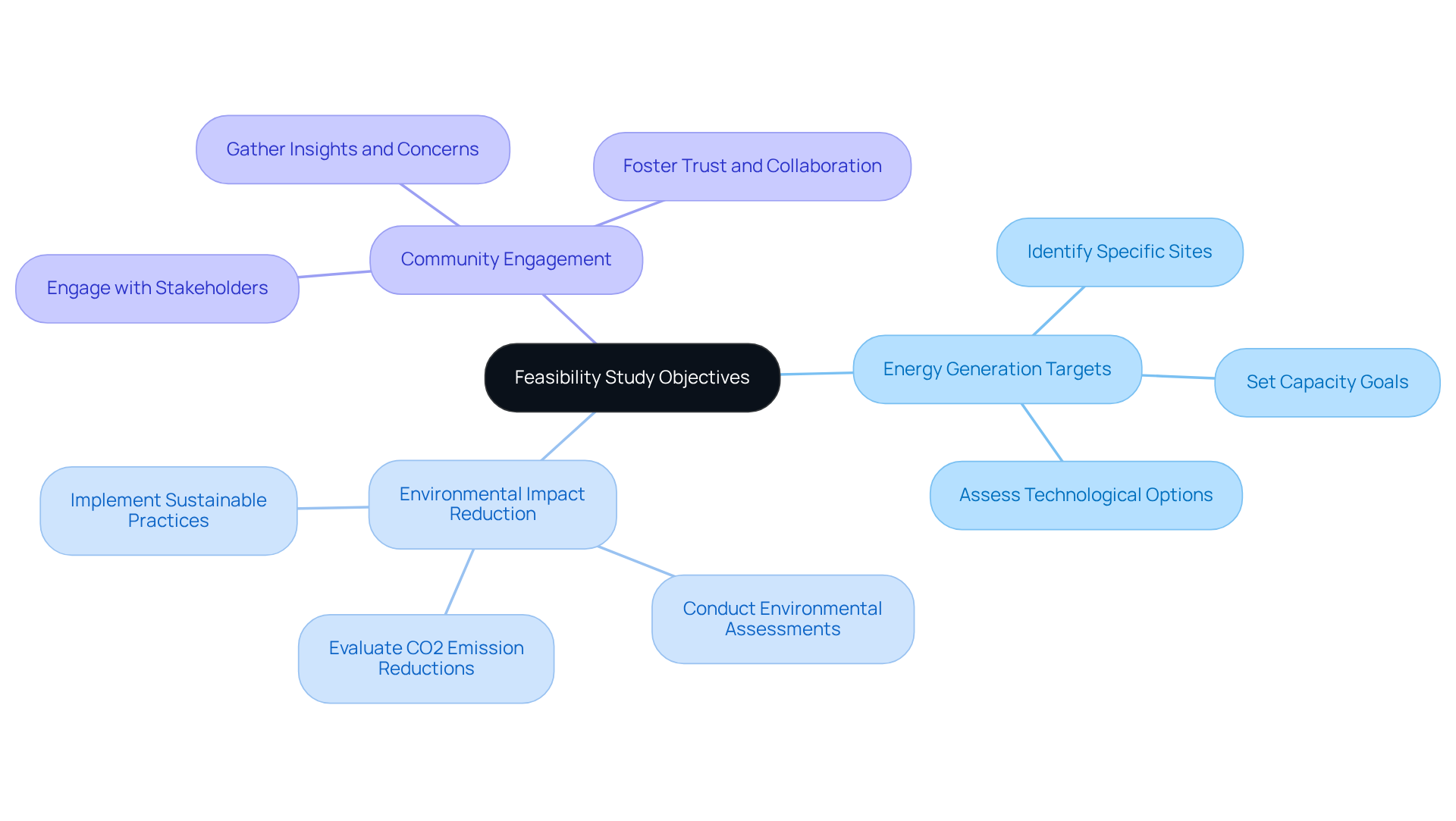
Define Objectives and Scope of the Feasibility Study
Establishing clear goals for the renewable energy initiative is paramount. Focus on critical elements such as energy generation targets, environmental impact reduction, and community engagement. Next, delineate the geographical boundaries of the wind energy feasibility analysis by identifying specific sites for potential wind farm developments. Furthermore, it is essential to actively engage stakeholders to gather their insights and concerns, ensuring that the initiative's objectives reflect a comprehensive understanding of its potential impacts. Effective stakeholder engagement is crucial; research indicates that initiatives with robust stakeholder participation are significantly more likely to succeed, fostering trust and collaboration among all involved parties.
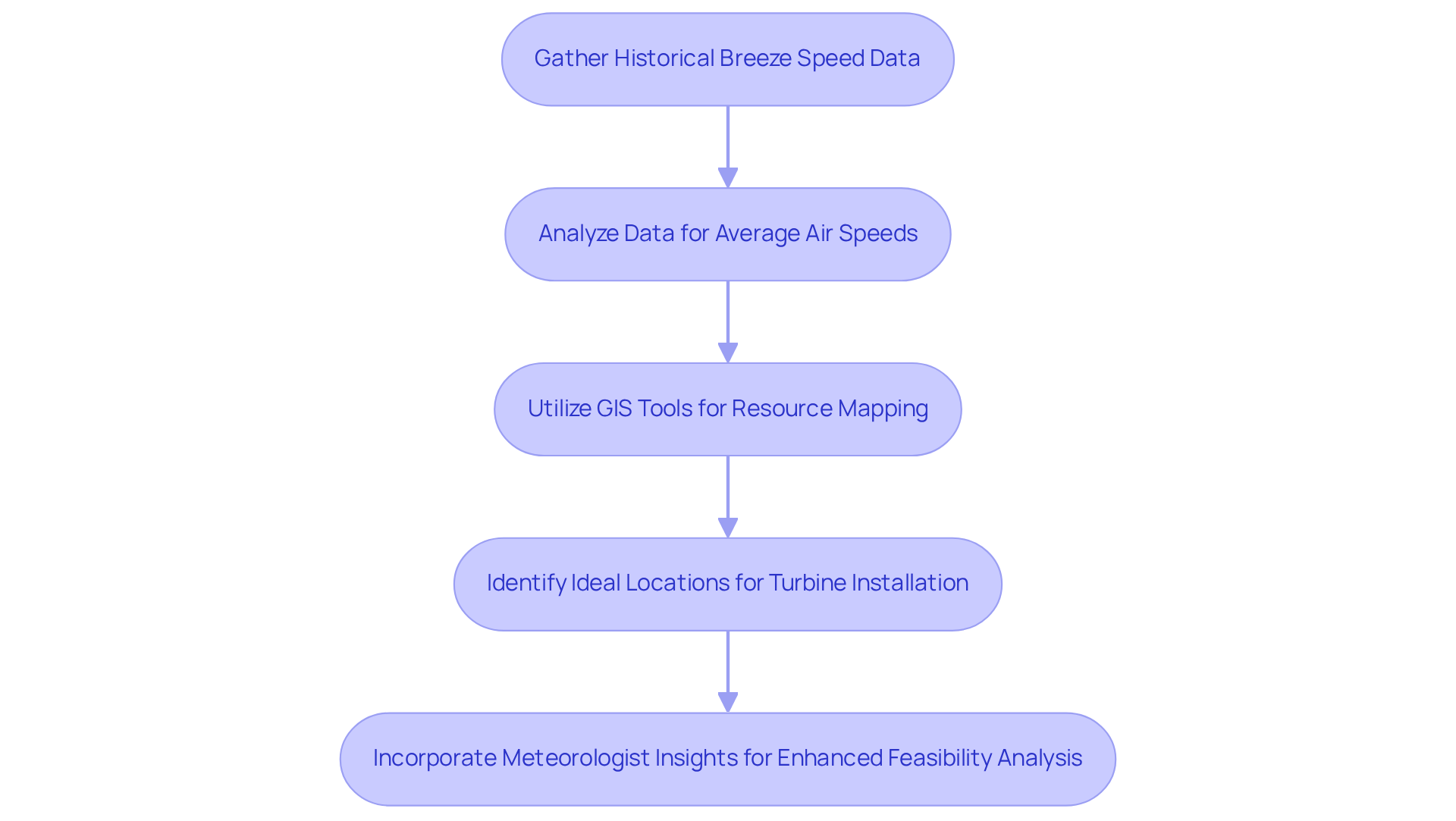
Assess Wind Resource Potential
To effectively evaluate air resource potential for energy projects, it is crucial to begin by gathering historical breeze speed data from meteorological stations or advanced remote sensing technologies. This foundational step is essential, as precise historical data informs wind energy feasibility analysis and aids in recognizing patterns in air movement. Meteorologists emphasize the significance of examining this data to ascertain average air speeds at different elevations, which is vital for enhancing turbine efficiency. Research has demonstrated that the optimal model can decrease RMSE for airspeed predictions by roughly 20%, underscoring the importance of accurate data gathering.
Next, GIS tools should be utilized to chart resource potential across the proposed locations. These tools can highlight areas with ideal atmospheric conditions for turbine installation, facilitating informed decision-making. Successful applications of GIS in resource mapping, such as the EARS4WindEnergy initiative, have shown significant improvements in planning and site selection, ensuring that initiatives are positioned for maximum efficiency and output. Incorporating insights from meteorologists can further enhance the wind energy feasibility analysis by providing expert viewpoints on the importance of historical air velocity data for power initiatives.
Select Technology and Design Parameters
-
Conducting thorough research on available wind turbine technologies is essential for a wind energy feasibility analysis, as it allows for the evaluation of key factors such as capacity, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. In 2025, advancements in turbine technology, including innovations in rotor design and materials, are anticipated to play a crucial role in optimizing power capture. These improvements are expected to enhance performance metrics significantly. As Marlene Motyka, US Renewable Energy Leader at Deloitte, notes, understanding these advancements is critical for effective project planning.
-
It is imperative to set design criteria that optimize power capture, which is essential in a wind energy feasibility analysis and includes considerations such as turbine height, rotor diameter, and spacing between turbines. For instance, increasing rotor diameter can significantly enhance energy output, while optimal spacing minimizes turbulence and maximizes efficiency. The SunZia initiative exemplifies this approach, having successfully implemented design parameters that address both efficiency and environmental compliance.
-
Collaboration with manufacturers and engineers is vital to enhance specifications that correspond with project goals and site conditions. Richard Langford, Site Manager at Hitachi Energy, emphasizes the importance of partnerships, stating, 'You need partners who share your vision and can bring expertise to the table.' This collaborative approach not only addresses technical challenges but also fosters innovation in design and execution.

Estimate Costs and Financial Viability
- Begin by compiling a comprehensive inventory of all potential expenses associated with the initiative. This inventory should encompass land acquisition costs, equipment procurement, installation expenses, and ongoing maintenance fees. Notably, the offshore wind industry witnessed a landmark investment of $76.7 billion in 2023, underscoring the growing financial landscape for renewable initiatives.
- Subsequently, assess potential revenue streams, which may encompass power purchase agreements (PPAs), government incentives, and renewable resource credits. As Jigar Shah, Co-Founder of Generate Capital, aptly points out, climate change presents the most significant wealth generation opportunity of our time, making these revenue sources crucial for success.
- Execute a comprehensive financial analysis, which includes a wind energy feasibility analysis to determine key metrics such as Net Present Value (NPV), Internal Rate of Return (IRR), and Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE). These metrics are vital for the wind energy feasibility analysis, evaluating the initiative's financial viability and ensuring it meets the necessary economic criteria for success in the competitive renewable sector. Additionally, consider the impact of rising expenses and interest rates on the initiative's feasibility, as these factors can significantly influence financial outcomes.

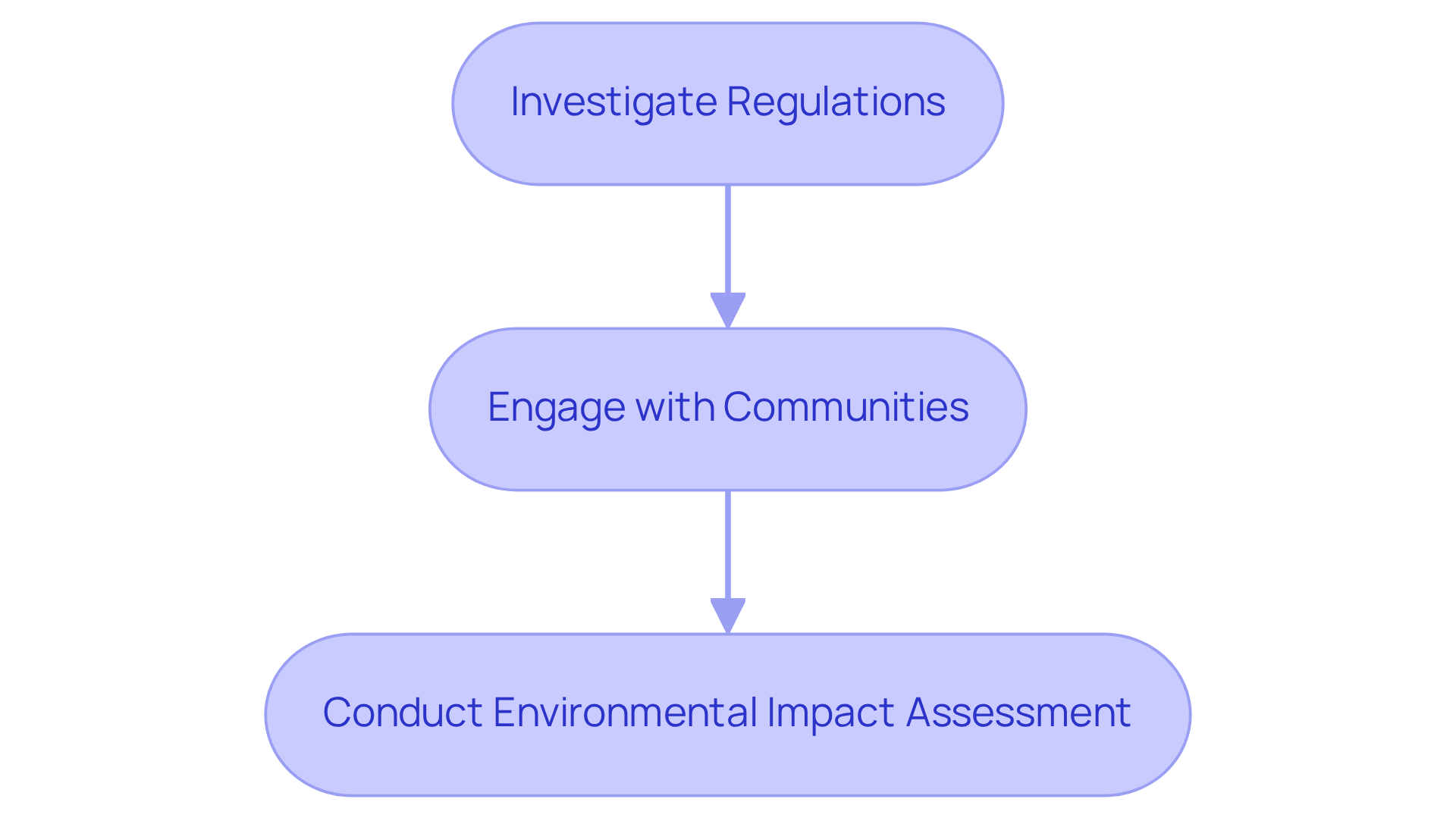
Evaluate Legal, Social, and Environmental Considerations
Investigate the local, state, and federal regulations pertinent to wind energy initiatives, with a focus on the wind energy feasibility analysis, permitting, and environmental evaluations. Understanding these regulations is crucial for successful project implementation.
Next, engage with local communities to grasp their concerns and gather support for the project. Community involvement not only fosters goodwill but also enhances project viability.
Finally, conduct a wind energy feasibility analysis to evaluate potential effects on wildlife, land use, and local ecosystems as part of the environmental impact assessment (EIA). This assessment is essential for developing necessary mitigation strategies, ensuring that the project aligns with environmental standards and community expectations.
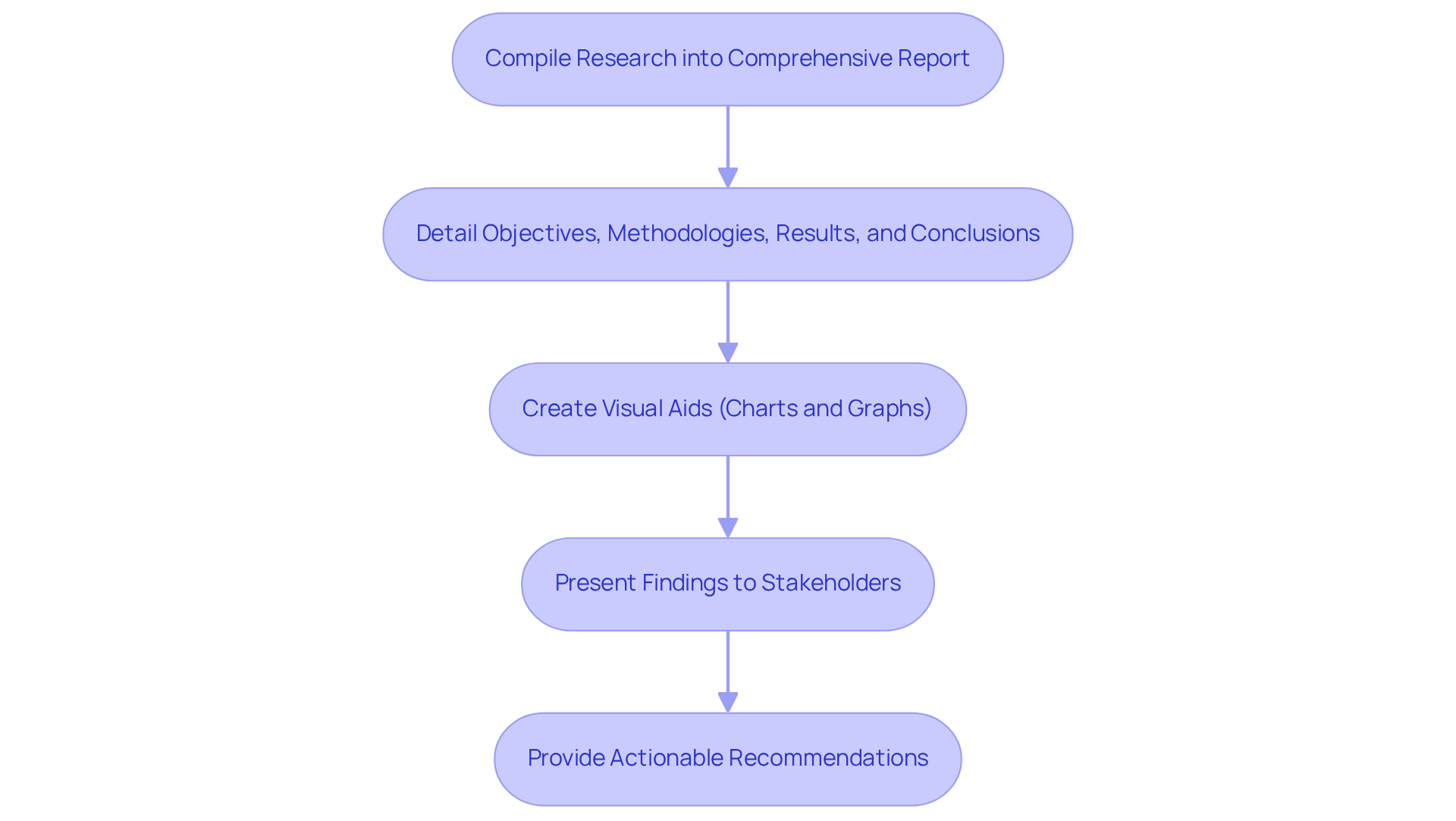
Present Findings and Recommendations
To effectively present findings from a wind energy feasibility analysis, compile all research into a comprehensive report that details the analysis's objectives, methodologies, results, and conclusions. This structured approach ensures clarity and facilitates understanding among diverse stakeholders. According to Deloitte’s 2024 power and utilities survey, 97% of utilities emphasize clean sources, underscoring the significance of wind initiatives in the current environment.
Enhance communication further by creating visual aids such as charts and graphs, which succinctly convey key data points and trends, making complex information more accessible. As Gihan Samaraweera noted, innovative technology plays a crucial role in effective communication.
Finally, present these findings to stakeholders—including investors, regulatory bodies, and community members—while providing clear, actionable recommendations for the project's next steps. This method not only fosters transparency but also builds trust and engagement among all parties involved.
The successful communication strategies employed in Thermax's sustainable energy solutions at Hudson Yards illustrate the importance of clear presentations in stakeholder engagement.
Conclusion
Establishing a successful wind energy project necessitates a meticulous feasibility analysis that encompasses various critical steps.
- Clearly defining objectives and engaging stakeholders
- Assessing wind resource potential
- Selecting appropriate technology
- Estimating costs
- Evaluating legal and environmental considerations
These are essential for project planners to lay a solid foundation for their initiatives. Each phase contributes to a comprehensive understanding of the project's viability and impact, ensuring that all aspects are thoroughly considered.
The importance of gathering accurate data and utilizing advanced tools to assess wind resources effectively cannot be overstated. Collaboration with experts and stakeholders fosters innovation and enhances project outcomes. Furthermore, understanding financial implications and legal requirements is crucial for navigating the complexities of renewable energy projects. Transparent communication of findings builds trust and support among all parties involved.
Ultimately, the journey toward successful wind energy initiatives hinges on careful planning and execution. By following these outlined steps and prioritizing stakeholder engagement, project planners can achieve their energy generation goals while contributing positively to the environment and local communities. Embracing the potential of wind energy aligns with global sustainability efforts and paves the way for a cleaner, more resilient future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main objectives of a feasibility study for a renewable energy initiative?
The main objectives include establishing clear goals for energy generation targets, reducing environmental impact, and engaging the community effectively.
How should the geographical scope of the wind energy feasibility study be defined?
The geographical scope should be delineated by identifying specific sites for potential wind farm developments.
Why is stakeholder engagement important in a feasibility study?
Stakeholder engagement is crucial as it helps gather insights and concerns, ensuring that the initiative's objectives reflect a comprehensive understanding of its potential impacts. Initiatives with robust stakeholder participation are significantly more likely to succeed.
What is the first step in assessing wind resource potential for energy projects?
The first step is to gather historical breeze speed data from meteorological stations or advanced remote sensing technologies.
Why is historical data important in wind energy feasibility analysis?
Historical data is essential as it informs the feasibility analysis and helps recognize patterns in air movement, which is vital for enhancing turbine efficiency.
How can GIS tools be utilized in evaluating wind resource potential?
GIS tools can be used to chart resource potential across proposed locations, highlighting areas with ideal atmospheric conditions for turbine installation.
What benefits have been observed from using GIS in resource mapping for wind energy?
Successful applications of GIS, such as the EARS4WindEnergy initiative, have shown significant improvements in planning and site selection, ensuring initiatives are positioned for maximum efficiency and output.
How can insights from meteorologists enhance wind energy feasibility analysis?
Insights from meteorologists can provide expert viewpoints on the importance of historical air velocity data, further enhancing the analysis for power initiatives.




