Overview
The article presents four essential strategies for emissions monitoring at gas sites:
- Understanding regulatory requirements
- Selecting advanced monitoring technologies
- Implementing effective data management practices
- Engaging stakeholders
These strategies are reinforced by examples and practices that underscore the significance of:
- Compliance
- Technological advancements
- Robust data handling
- Community involvement
in achieving effective emissions tracking and management.
Introduction
In the pursuit of environmental sustainability, organizations face increasing complexities in emissions monitoring and compliance. As regulatory frameworks evolve—particularly under the Clean Air Act—companies must remain vigilant in understanding their obligations to avoid substantial fines and promote public health. This article explores the essential components of an effective emissions monitoring strategy. It covers the selection of advanced technologies that enhance detection capabilities and the implementation of robust data management practices. Additionally, it underscores the significance of engaging stakeholders to foster transparency and accountability in emissions reduction efforts. By navigating these multifaceted challenges, organizations can not only ensure compliance but also contribute to a healthier planet.
Understand Regulatory Requirements for Emissions Monitoring
Organizations must thoroughly comprehend the regulatory framework overseeing environmental assessments, which encompasses federal, state, and local regulations. Central to this framework is the Clean Air Act, along with specific EPA guidelines that detail practices for greenhouse gases (GHGs) and other pollutants. For instance, the EPA's Continuous Monitoring Systems (CEMS) require that facilities continuously assess pollutants to ensure compliance. Starting in 2025, it is essential for businesses to remain informed about these regulations, as the EPA has released new guidelines that further enhance tracking requirements.
A pertinent case study is the exploitation of Clean Air Act loopholes, where the Trump administration's EPA allowed certain facilities to bypass hazardous air pollution limits by self-declaring exemptions. This initiative has raised concerns about public health and safety, highlighting the importance of adhering to established regulations. Regularly reviewing updates from the EPA and other regulatory bodies not only helps avoid potential fines but also supports the development of a robust emissions monitoring for gas sites strategy that aligns with legal standards.
Statistics show that companies can seek a renewable two-year exemption from clean air standards by merely sending an email, which highlights the necessity for vigilance in adherence efforts. Furthermore, conducting regular training sessions for staff on these regulatory updates can greatly improve adherence efforts, ensuring that all team members are informed and ready to meet evolving requirements.
Understanding the implications of the Clean Air Act is vital, as it directly impacts operational practices and public health considerations. As Richard K. Lattanzio notes, "The ability to self-declare exemptions without public input undermines clean air protections and public trust." This reinforces the importance of proactive compliance strategies in navigating the complex regulatory landscape.
Select Advanced Emission Monitoring Technologies
Organizations must prioritize investment in advanced pollution tracking technologies that significantly enhance detection capabilities and information accuracy. Technologies such as AI-enabled Optical Gas Imaging (AI-OGI) and laser-based systems are essential for emissions monitoring for gas sites, enabling real-time monitoring and swift identification of leaks.
Moreover, emissions monitoring for gas sites involves continuous monitoring systems (CMS) that can automate data collection, thereby reducing the potential for human error. For example, deploying drones equipped with gas sensors allows for emissions monitoring for gas sites, enabling rapid coverage of large areas and effectively identifying pollution hotspots that require immediate attention.
When selecting technologies, it is essential to evaluate factors such as:
- Compatibility with existing systems
- Reporting functionalities
- Compliance with regulatory standards
Conducting pilot tests on various technologies can further assist in identifying the optimal solution tailored to specific operational requirements.
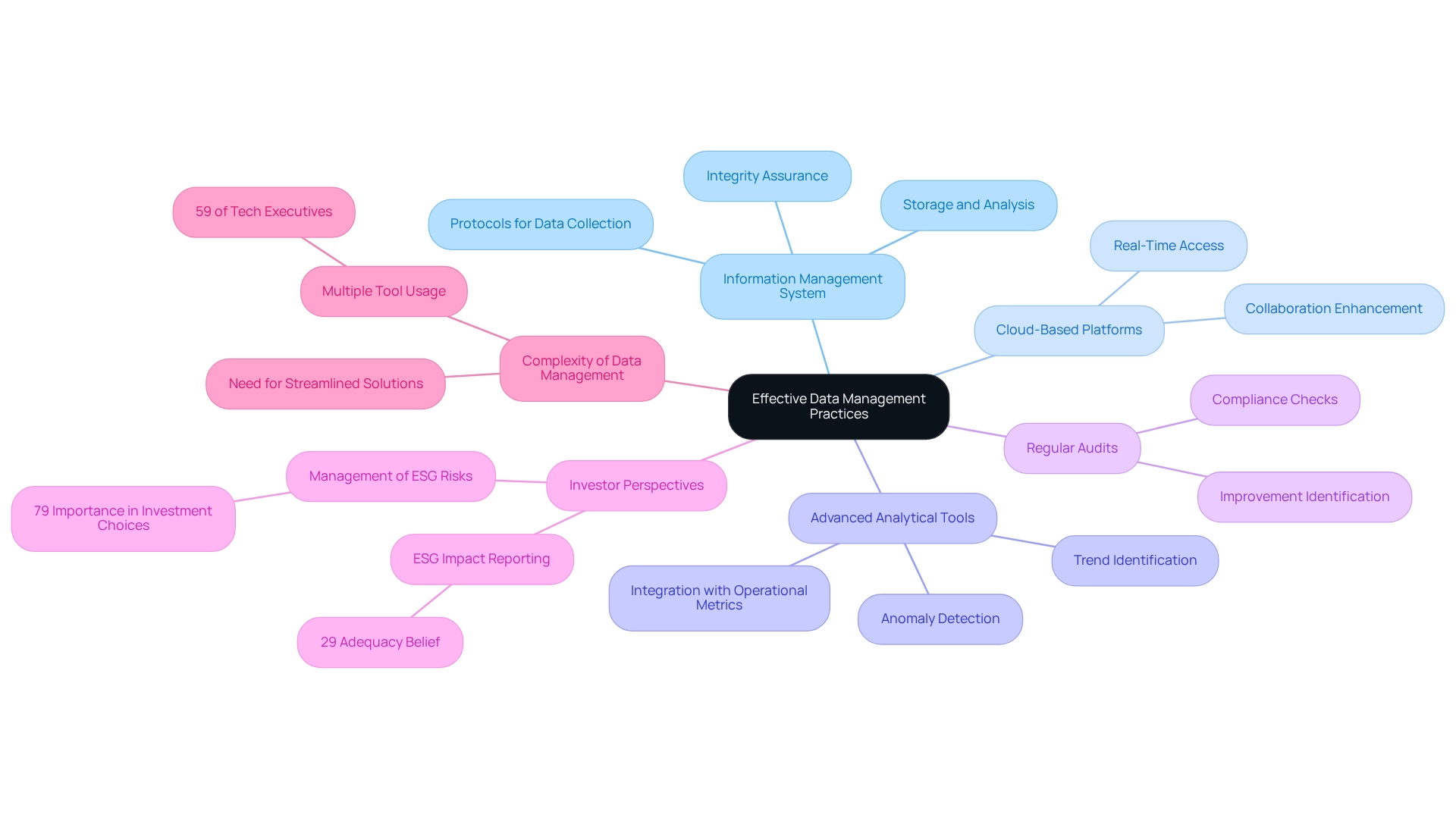
Implement Effective Data Management and Analysis Practices
Establishing a robust information management system is essential for emissions monitoring for gas sites and accurately tracking emissions records. Organizations must implement clear protocols for information collection, storage, and analysis to ensure integrity. The use of cloud-based platforms facilitates real-time access to information and fosters collaboration among teams, which is vital for timely decision-making.
Furthermore, employing advanced analytical tools allows organizations to identify trends and anomalies in emissions data, which is crucial for emissions monitoring for gas sites and supports proactive management of pollution sources. For example, integrating pollution data with operational metrics can illustrate how production processes influence pollution levels.
Regular audits of information management practices are crucial, as they help pinpoint areas for improvement and ensure compliance with evolving reporting requirements. Notably, only 29% of investors believe that current company disclosures adequately reflect the impact of ESG on business performance, underscoring the necessity for accurate reporting in emissions monitoring for gas sites.
Additionally, 79% of investors consider a company's management of ESG risks and opportunities essential in their investment choices, highlighting the importance of effective management systems. The complexity of managing output-related data is further evidenced by the fact that 59% of tech executives use multiple tools to oversee cloud expenses, emphasizing the need for efficient solutions.
As the landscape of pollution tracking continues to evolve, adopting these best practices will be critical for effective management and compliance.
Engage Stakeholders for Successful Emissions Monitoring
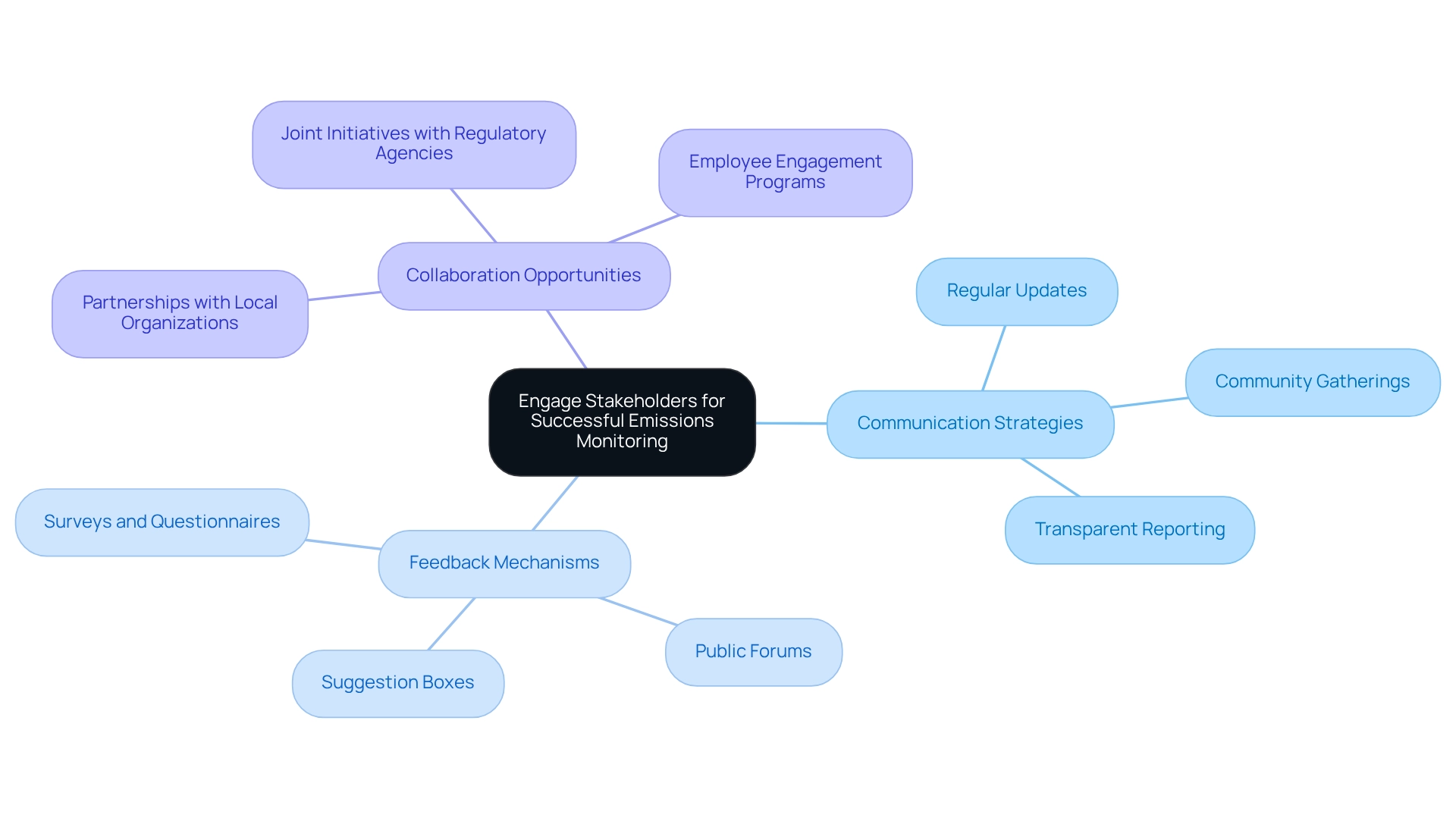
Involving stakeholders—regulatory agencies, local communities, and internal groups—is crucial for effectively tracking air pollutants. Organizations must develop a stakeholder engagement plan that clearly outlines:
- Communication strategies
- Feedback mechanisms
- Collaboration opportunities
By consistently sharing pollution data and results with stakeholders, organizations promote transparency and cultivate trust. For example, organizing community gatherings to discuss pollution tracking initiatives can effectively address concerns and gather valuable feedback. Additionally, engaging employees in oversight initiatives enhances accountability and fosters a culture of environmental responsibility. By actively engaging stakeholders, organizations can create a supportive environment for emissions monitoring for gas sites and drive collective efforts toward emissions reduction.
Conclusion
Effectively managing emissions monitoring and compliance is not just essential; it is a critical imperative for organizations committed to environmental sustainability. A thorough understanding of the regulatory framework, particularly the Clean Air Act and updated EPA guidelines, is crucial for ensuring compliance and safeguarding public health. Regular training and staying informed about regulatory changes empower organizations to mitigate risks associated with non-compliance.
Investing in advanced monitoring technologies, such as AI-enabled Optical Gas Imaging and automated continuous monitoring systems, significantly enhances detection capabilities and data accuracy. These tools facilitate real-time leak identification, thereby streamlining compliance efforts and aligning operational practices with regulations.
Equally important are robust data management practices for accurate emissions tracking. Utilizing cloud-based platforms and advanced analytics allows organizations to analyze emissions trends effectively, supporting proactive management and improving transparency—an increasingly vital aspect for investors focused on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors.
Engaging stakeholders, including regulatory bodies, local communities, and internal teams, is key to successful emissions monitoring. Open communication builds trust and enhances accountability, fostering collaborative efforts toward emissions reduction.
In conclusion, organizations that implement a comprehensive emissions monitoring strategy—rooted in regulatory understanding, advanced technology, effective data management, and stakeholder engagement—are not only well-equipped to ensure compliance but also positioned to contribute positively to a healthier planet.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the regulatory framework for environmental assessments?
The regulatory framework for environmental assessments includes federal, state, and local regulations, with the Clean Air Act being central to this framework, along with specific EPA guidelines for greenhouse gases and other pollutants.
What are Continuous Monitoring Systems (CEMS)?
Continuous Monitoring Systems (CEMS) are required by the EPA for facilities to continuously assess pollutants to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
Why is it important for businesses to stay informed about EPA regulations starting in 2025?
Starting in 2025, businesses must stay informed about new EPA guidelines that enhance tracking requirements for pollutants, which is essential for compliance and avoiding potential fines.
What concerns arose from the exploitation of Clean Air Act loopholes during the Trump administration?
The exploitation of Clean Air Act loopholes allowed certain facilities to bypass hazardous air pollution limits by self-declaring exemptions, raising concerns about public health and safety.
How can companies avoid fines related to environmental regulations?
Companies can avoid fines by regularly reviewing updates from the EPA and other regulatory bodies, which supports the development of robust emissions monitoring strategies that align with legal standards.
What is the significance of the statistic regarding renewable exemptions from clean air standards?
Companies can obtain a renewable two-year exemption from clean air standards by simply sending an email, highlighting the need for vigilance in adherence to environmental regulations.
How can training sessions improve adherence to environmental regulations?
Conducting regular training sessions for staff on regulatory updates can improve adherence efforts by ensuring that all team members are informed and prepared to meet evolving requirements.
Why is understanding the implications of the Clean Air Act important?
Understanding the implications of the Clean Air Act is vital as it impacts operational practices and public health considerations, emphasizing the need for proactive compliance strategies.
List of Sources
- Understand Regulatory Requirements for Emissions Monitoring
- Trump’s EPA Attempts to Hand Polluters Free Pass to Pollute Communities with Toxic Chemicals - Center for International Environmental Law (https://ciel.org/news/trumps-epa-attempts-to-hand-polluters-free-pass-to-pollute-communities-with-toxic-chemicals)
- Clean Air Act: A Summary of the Act and Its Major Requirements (https://crsreports.congress.gov/product/pdf/rl/rl30853)
- Implement Effective Data Management and Analysis Practices
- 50 Sustainability Statistics: Must Know In 2025 | KEY ESG (https://keyesg.com/article/50-esg-statistics-you-need-to-know-in-2024)
- AT&T - Corporate Responsibility - Efficiency & Emissions (https://sustainability.att.com/priority-topics/climate-change-ghg)
- 90+ Cloud Computing Statistics: A 2025 Market Snapshot (https://cloudzero.com/blog/cloud-computing-statistics)




