Overview
Erosion control measures are essential for preventing land degradation. This article outlines seven authoritative strategies, including:
- Planting vegetation
- Mulching
- Silt fencing
- Reforestation
Research supports the effectiveness of these measures in stabilizing soil, enhancing water quality, and promoting sustainable land management practices. By addressing the pressing challenges posed by climate change and human activities, these strategies not only mitigate risks but also contribute to long-term environmental health.
Introduction
As environmental challenges intensify, effective erosion control has become a vital focus for land management and infrastructure development. Soil erosion threatens ecosystems and water quality, making it essential to understand the multifaceted strategies available to combat this issue.
From planting deep-rooted vegetation to utilizing innovative technologies such as erosion control blankets and energy dissipaters, the methods for mitigating soil loss are both diverse and impactful.
This article delves into the fundamental principles of erosion control, showcasing practical approaches and the latest advancements that not only safeguard soil integrity but also promote sustainable development in an era increasingly shaped by climate change.
Understanding Erosion Control: The Basics
Erosion control measures are essential for preventing or reducing land degradation caused by wind, water, or human actions. Understanding the primary causes of erosion—including rainfall, surface runoff, and land disturbances—is crucial for effective management. Recent forecasts indicate that climate change will significantly impact land degradation patterns, necessitating adaptive strategies in land management.
Efficient erosion control measures not only safeguard land integrity but also play a vital role in enhancing water quality by minimizing sedimentation in waterways. Research illustrates that human actions, particularly land-use changes, can exacerbate soil degradation rates, underscoring the need for targeted conservation methods. In 2025, statistics reveal that approximately 70% of land degradation in the U.S. is associated with agricultural practices, highlighting the urgent requirement for improved management systems.
Effective soil management strategies implemented in construction projects yield substantial benefits. For instance, erosion control measures such as vegetation buffers and sediment traps have proven effective in reducing runoff and stabilizing soil. Moreover, the latest research underscores the importance of employing erosion control techniques, including contour farming and terracing, to achieve sustainable outcomes.
Notably, the highest weight of the MCLM model in the BMA method is 0.46, serving as a benchmark for evaluating the effectiveness of various measures aimed at preventing soil degradation.
Expert opinions in 2025 stress that understanding the fundamental concepts of soil preservation is vital for professionals in land management and construction. These principles encompass maintaining vegetation cover, implementing appropriate drainage systems, and utilizing protective blankets to combat soil loss. As Jean-Philippe Jenny noted, 'Long before the more recent and sudden impacts of greenhouse gas emissions, human actions must have affected the global environment already 4,000 years ago,' emphasizing the necessity of adopting proactive measures to mitigate degradation.
Case studies on control practices reveal that effective land and water conservation measures are integral to achieving sustainable development goals. The research titled 'Driving Forces Affecting Land Degradation' explores the dual influence of natural and human factors on land degradation, highlighting that while natural elements such as rainfall and plant life remain relatively stable, human activities significantly impact degradation rates. By prioritizing these practices, professionals can ensure that infrastructure projects not only fulfill immediate needs but also contribute to long-term environmental health.
In conclusion, erosion control measures are critical for sustaining or reducing future land degradation rates within an ideal range.
Planting Vegetation: Harnessing Nature's Power
Planting greenery stands out as one of the most effective strategies for managing soil degradation. Deep-rooted plants—grasses, shrubs, and trees—play a vital role in stabilizing the ground, significantly reducing erosion risks. Native plants, in particular, provide distinct advantages due to their adaptation to local environmental conditions, resulting in lower maintenance requirements and higher survival rates.
The benefits of plant life extend beyond mere ground stabilization. Vegetation effectively absorbs rainfall, reducing surface runoff and enhancing water infiltration into the ground. This process not only aids in retaining moisture but also mitigates the risk of flooding in nearby areas.
A diverse mix of plant species can further bolster ground stability while offering essential habitats for wildlife, thus enhancing overall ecosystem resilience.
Statistics underscore the efficacy of plants in preventing soil loss. Studies indicate that plant restoration can lead to notable decreases in ground degradation, with research demonstrating an average yearly degradation management index enhancement of 73.2% in regions where plant life was revived. Furthermore, contributions to soil degradation management vary by climate zones, with:
- 62% attributed to wind factors (WF)
- 25% to normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI)
- 13% to artificial intelligence (AI)
This underscores the critical role that well-planned planting strategies can serve as erosion control measures in sustainable infrastructure projects.
Recent findings from a distributed RWEQ model evaluating global wind degradation risk revealed an average loss of 312.5 Pg per year, highlighting the urgency of implementing erosion control measures for effective degradation management. Successful projects utilizing native plants for soil stabilization have yielded remarkable outcomes. For instance, initiatives on the Loess Plateau have shown that improved land use conditions, alongside plant restoration efforts, have led to a significant rise in soil preservation services since 1999.
Zhan Xie observed, "The approach applied in this research can be extended to other extensive basins with comparable climate and enhance the comprehension of shifts in soil preservation services under the impacts of vegetation restoration." Such case studies illustrate the tangible benefits of integrating native plant species into soil preservation strategies.
In summary, the incorporation of deeply established native flora not only inhibits ground degradation but also supports the broader objectives of sustainable land stewardship and ecosystem well-being. As the industry continues to evolve, leveraging these natural solutions will be essential for addressing the challenges posed by deterioration in infrastructure development.
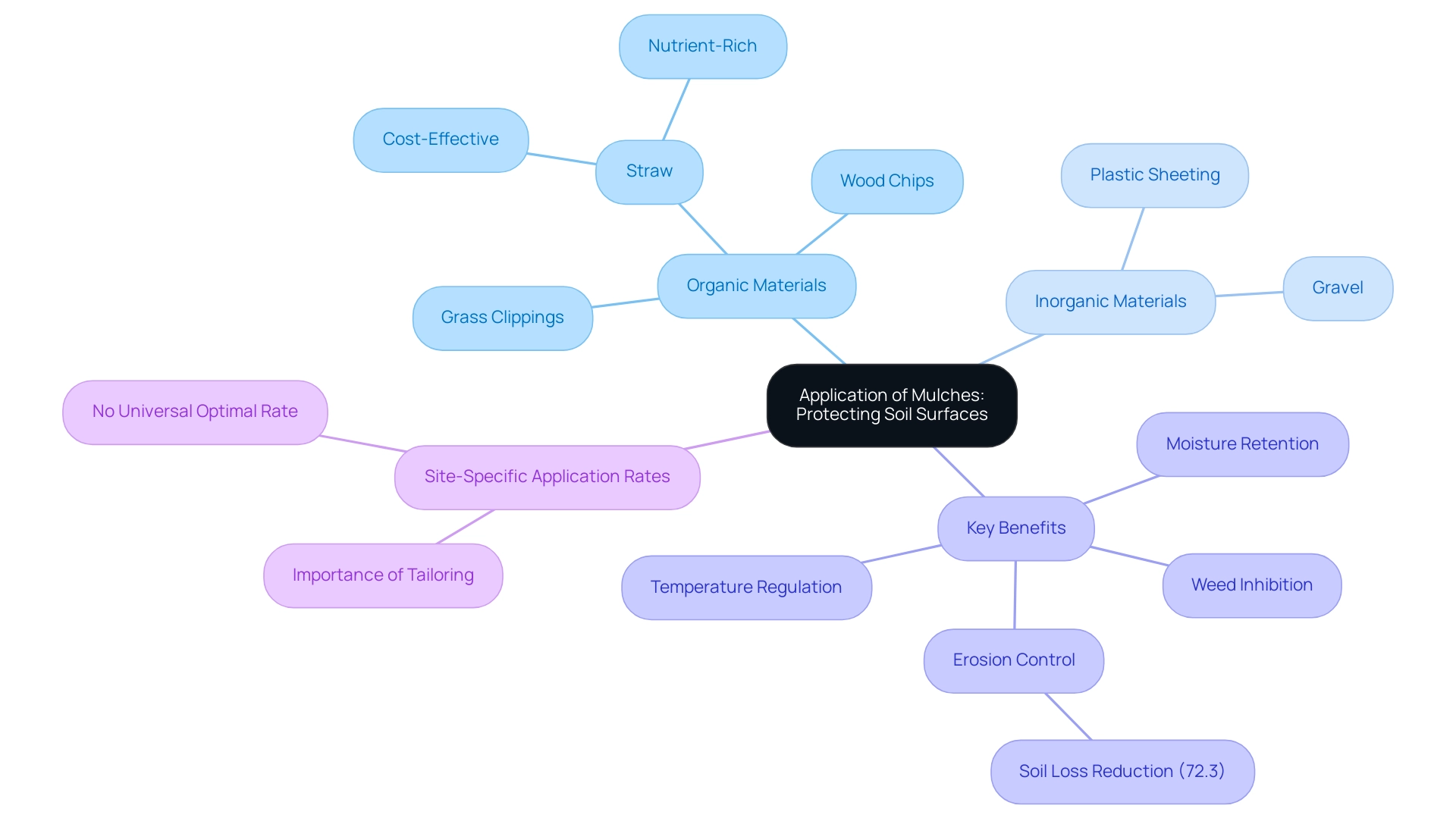
The Application of Mulches: Protecting Soil Surfaces
Mulches are an essential protective layer over ground surfaces, significantly minimizing degradation. They can be categorized into organic materials, such as straw, wood chips, and grass clippings, and inorganic materials, including gravel and plastic sheeting. The application of mulches not only aids in moisture retention but also inhibits weeds and regulates temperature, fostering a healthier environment for plant growth.
When applied correctly, mulches are particularly effective in reducing erosion, especially on inclines and during intense rainfall events. Research indicates that earth loss can be reduced by as much as 72.3% for slope lengths greater than 20 meters when effective mulching practices are employed. This statistic underscores the necessity of selecting the appropriate type of mulch based on site-specific ground and environmental conditions, as there is no universal optimal application rate.
Emphasizing site-specific application rates is crucial, as it directly impacts the effectiveness of erosion control measures. Recent advancements in mulch application techniques in 2025 have further enhanced their efficacy. For instance, research has demonstrated that organic mulches, like straw, are not only economical but also beneficial for ground health. A case study evaluating the cost-effectiveness of various mulching materials revealed that straw mulch emerged as the most economical option, highlighting the importance of detailed cost analyses to guide decision-making for farmers and municipalities.
Moreover, mulching positively impacts moisture retention, which is critical for sustainable infrastructure projects. Expert insights emphasize that both organic and inorganic mulches offer unique benefits. Dr. Vijayalaxmi Kinhal notes that organic mulches frequently provide additional nutrients to the ground as they decompose, while inorganic mulches deliver enduring protection against wear.
As the field of soil degradation management continues to evolve, understanding the comparative effectiveness of these materials will be essential for implementing successful erosion control measures in infrastructure projects.
Reforestation: Restoring Natural Barriers
Reforestation stands as a pivotal strategy for combating land degradation and enhancing environmental resilience. By planting trees in deforested or degraded areas, we create natural barriers that effectively mitigate soil loss. The extensive root systems of trees play a crucial role in stabilizing soil, significantly curbing runoff and preventing further degradation.
In addition, the canopies of trees shield the soil from the impacts of heavy rainfall, which can exacerbate degradation.
The benefits of reforestation extend beyond mere soil preservation; it also fosters habitat restoration and boosts biodiversity. Successful reforestation initiatives have demonstrated a marked reduction in land degradation, underscoring the effectiveness of this approach. For example, projects that have strategically implemented tree planting not only stabilized the ground but also rejuvenated local ecosystems, contributing to a healthier environment.
Data from 2025 indicate that reforestation initiatives significantly impact land degradation management, with well-designed projects yielding notable improvements in ground stability. Furthermore, expert opinions highlight the critical role of reforestation as an effective erosion control measure, emphasizing its dual function in environmental restoration and climate change mitigation. As Edzo Veldkamp aptly states, "We stress the significance of land knowledge not only in cross-disciplinary research on deforestation and reforestation but also in creating effective incentives and policies to lessen deforestation."
Recent reforestation initiatives have brought to light the necessity of strategic planning to circumvent challenges such as monocultures and the introduction of invasive species, which can jeopardize indigenous flora and fauna. The Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020 notes that over 20 billion hectares of forest have management plans; however, impulsive reforestation can yield adverse outcomes, including diminished biodiversity and land degradation. It is also essential to consider the broader implications of land use; for instance, beef production accounts for 41% of global deforestation, highlighting the urgent need for reforestation efforts.
Moreover, the challenges encountered by reforestation initiatives, as illustrated in various case studies, underscore the importance of strategic planning to optimize benefits and mitigate negative effects. The reference to UNESCO world heritage forests transforming into carbon sources over the past 20 years serves as a stark reminder of the repercussions of inadequate management practices.
In summary, reforestation emerges as a vital method for land management and conservation, offering a sustainable solution to the pressing challenges of land degradation and climate change.
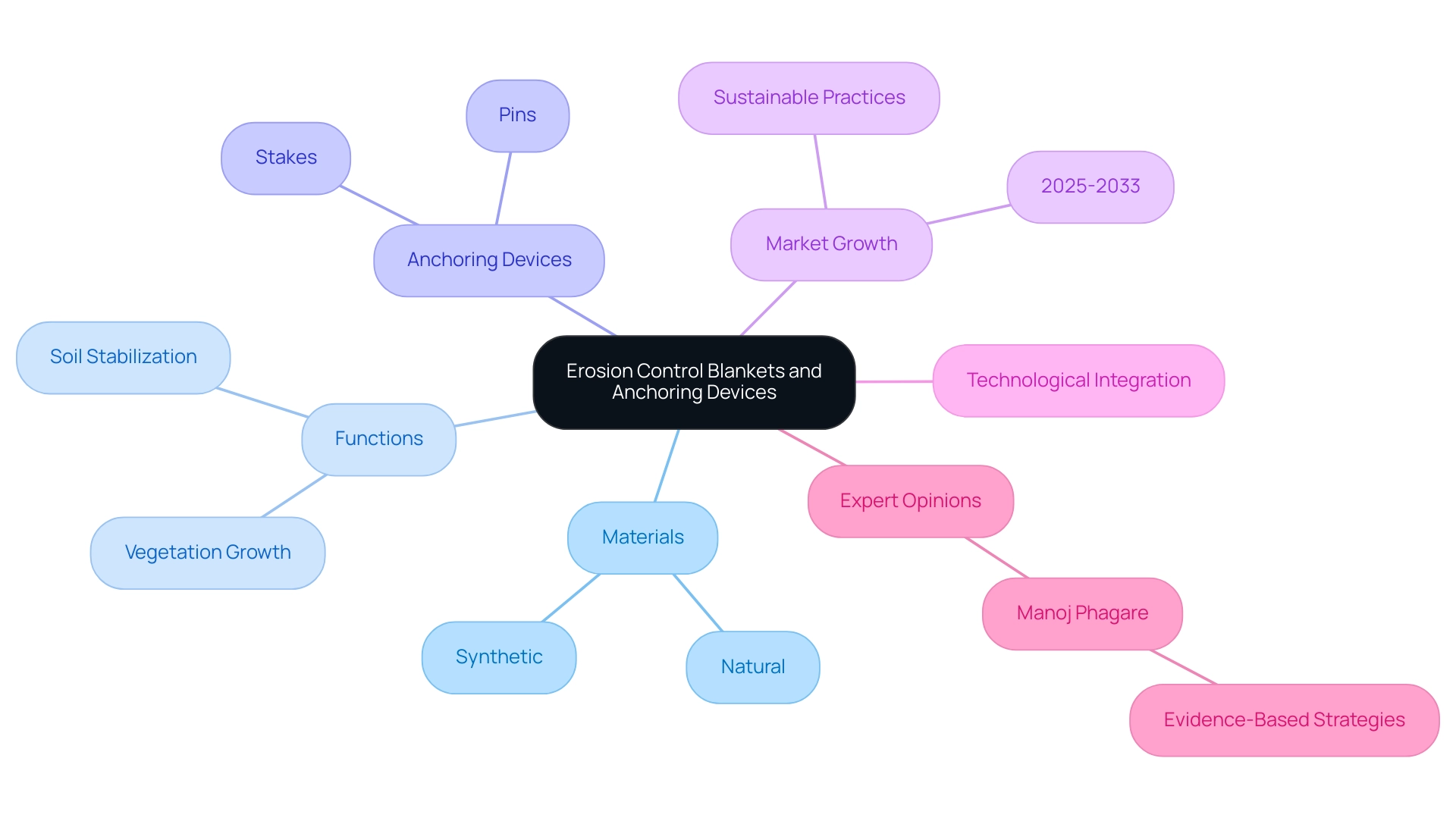
Erosion Control Blankets and Anchoring Devices: Stabilizing Soil
Erosion prevention blankets, constructed from either natural or synthetic materials, serve as a vital tool for the prompt coverage and protection of land, particularly in areas susceptible to degradation, such as steep slopes. These blankets not only stabilize the soil but also foster an optimal environment for vegetation growth, facilitating seed germination and promoting ecological restoration. Their effectiveness is significantly bolstered by the use of anchoring devices, including stakes and pins, which secure them firmly in place.
This becomes especially crucial during adverse weather conditions—like heavy rains or high winds—where the risk of displacement increases.
The market for protective blankets is poised for substantial expansion from 2025 to 2033, driven by a heightened awareness of sustainable practices in infrastructure development. Regular monitoring and maintenance of these blankets are essential to ensure their long-term effectiveness. Furthermore, the integration of new technologies in the design and application of sediment management blankets is revolutionizing the industry, leading to improved performance and durability.
Expert opinions underscore the critical role of anchoring devices in ground stabilization. Manoj Phagare, Senior Research Analyst at Cognitive Market Research, asserts that "the effectiveness of measures to prevent degradation is significantly enhanced by reliable anchoring solutions, which are essential for maintaining ground integrity under environmental stresses." Successful applications of anchoring devices have been documented, demonstrating their capacity to withstand environmental challenges while preserving soil integrity.
Leading companies in the degradation and sediment management sector, such as Commercial Metals Company and Contech Engineered Solutions LLC, are at the forefront of developing innovative solutions to address these issues. As the sector evolves, the combination of cutting-edge erosion control measures and reliable anchoring solutions will be indispensable in overcoming the challenges posed by soil degradation in sustainable infrastructure projects.
Using Silt Fencing: Managing Sediment Runoff
Silt fencing is an essential temporary erosion control measure on construction sites, designed to significantly reduce sediment runoff. Made from porous fabric, these fences are strategically positioned around the perimeter of disturbed areas, capturing sediment-laden water before it can contaminate nearby streams or rivers. The necessity of proper installation is paramount; the bottom of the fence must be buried to prevent water from flowing underneath, thereby ensuring maximum effectiveness.
In 2021, more than 100,000 construction sites across the United States adhered to EPA regulations regarding sediment management, underscoring the critical need for effective erosion control measures like silt fencing. These fences are not only efficient but also cost-effective, representing a budget-friendly best management practice (BMP) compared to the potential costs associated with unchecked soil loss, environmental degradation, and penalties for non-compliance with sediment regulations. Recent studies indicate that, when installed correctly, silt fences can achieve an impressive average of 83% sediment capture, as evidenced by a case study involving modifications to the Nebraska Department of Transportation's standard silt fence.
This study demonstrated that enhancements, such as a dewatering board with an overflow weir and a 15.2 cm offset trench, significantly improved structural performance and sediment retention during storm events. As noted by B.G.R., this research was funded by the Nebraska Department of Transportation, further establishing its credibility.
To maintain the ongoing effectiveness of silt fences, regular inspections and maintenance are crucial throughout the construction process. Best practices for installation include ensuring that the fabric is taut and securely anchored, as well as positioning the fence at the correct angle to optimize sediment capture.
As we approach 2025, it is vital to stay informed about the latest advancements in silt fencing technology and installation techniques for compliance and environmental protection. By adhering to these guidelines, construction projects can effectively implement erosion control measures that minimize their environmental impact while fulfilling regulatory requirements.
The Application of Seeding: Quick Vegetation Establishment
Seeding is pivotal in the rapid establishment of plant life on disturbed ground, a fundamental aspect of effective erosion control measures. As we look to 2025, land managers are increasingly prioritizing the selection of seed mixes that feature fast-germinating species, facilitating swift soil stabilization. Temporary seeding acts as an interim solution, providing essential cover until permanent vegetation can take root.
Current techniques, such as hydroseeding and drill seeding, are gaining traction due to their efficacy in enhancing seed-to-soil contact, which significantly boosts germination rates. Recent research reveals that hydroseeding can result in a 30% increase in vegetation establishment compared to traditional methods, establishing it as a preferred choice for numerous projects.
Regular monitoring and maintenance are crucial for ensuring the successful establishment of seeded areas. This proactive approach not only supports long-term soil preservation but also integrates erosion control measures that align with the latest trends in sustainable land management. Experts emphasize that selecting the right seed mixture is vital; employing a combination tailored to specific environmental conditions can further enhance the effectiveness of erosion control strategies and soil preservation efforts.
Case studies illustrate successful applications of hydroseeding across various land management projects, highlighting its effectiveness in fostering rapid vegetation establishment. The landscaping sector is witnessing substantial growth, with companies like TruGreen reporting $1.5 billion in revenue in 2023, underscoring the profitability potential within this field. Furthermore, with 42% of landscape professionals experiencing revenue declines in 2024, the urgency for innovation in soil management techniques has never been greater.
The case study titled 'Future Gardening Projects' showcases successful applications of creative gardening and landscaping methods, paralleling the effectiveness of seeding strategies in combating soil degradation. As the landscaping sector evolves, the significance of innovative seeding techniques remains paramount. By embracing these practices, land managers can ensure the resilience and sustainability of infrastructure projects amidst environmental challenges.
As noted by [specialist Jelaine Lim Gan, insights from experts in the field are essential for selecting the appropriate seed mixes that facilitate effective soil preservation.
Installing Energy Dissipaters: Controlling Water Flow
Energy dissipaters play a crucial role in reducing the speed and force of moving water, effectively preventing degradation across various environments. Common types include riprap, stilling basins, and plunge pools, each designed to manage water flow effectively. Strategically positioned at the outlets of pipes or channels, these devices absorb the energy of fast-moving water, significantly mitigating its erosive potential.
Recent advancements in energy dissipator design have concentrated on optimizing efficiency. For instance, studies reveal that the configuration of type-A Piano Key Weirs can greatly enhance energy dissipation, surpassing standard weirs. This is particularly relevant, as energy loss decreases with increasing magnification and relative width ratios, while energy dissipation improves with the number of key cycles.
Amin Mahmoudi noted, "The present work investigated the changes in the water surface profile upstream and downstream of the culvert for different culvert slopes, bed levels and apron widths," underscoring the importance of tailored designs in maximizing the effectiveness of these structures.
Moreover, recent findings suggest further investigation into the influence of energy dissipaters within the culvert pathway on water level variations, highlighting the need for ongoing research in this area. Statistics indicate that the minimum water level upstream can increase by as much as 83.1% under varying slope conditions, emphasizing the critical role of energy dissipaters in effectively managing water flow. Furthermore, the XGBoost model has shown superior accuracy in predicting downstream energy loss, reinforcing the necessity for advanced modeling techniques in the design process of energy dissipators.
Maintenance is another critical aspect that ensures the longevity and effectiveness of energy dissipators. Experts emphasize that regular inspections are essential to address sediment buildup and structural integrity, which can significantly impact performance. Successful projects utilizing erosion control measures such as riprap and stilling basins demonstrate that proactive maintenance strategies lead to improved soil preservation results.
In summary, energy dissipaters are essential for sustainable infrastructure projects, and erosion control measures in their design and maintenance must evolve to meet the challenges posed by changing environmental conditions. By implementing innovative designs and adhering to best maintenance practices, stakeholders can ensure these structures effectively serve as erosion control measures.
Conclusion
Erosion control stands as a critical pillar of sustainable land management, especially as climate change impacts intensify. This article has examined various strategies to mitigate soil erosion, underscoring the necessity of grasping its root causes and implementing effective practices. From planting deep-rooted vegetation to utilizing mulches, and employing erosion control blankets and energy dissipaters, each method plays a vital role in safeguarding soil integrity and enhancing environmental resilience.
The effectiveness of these approaches is highlighted by numerous studies and case examples, demonstrating that a multifaceted strategy often yields the most success. Reforestation, for example, not only combats erosion but also restores habitats and fosters biodiversity. Similarly, the application of silt fencing and innovative seeding techniques illustrates how targeted interventions can significantly curtail erosion risks, particularly in construction and disturbed areas.
As the landscape of land management evolves, adopting a holistic approach that integrates these diverse erosion control methods is imperative. By prioritizing sustainable practices and harnessing the latest advancements in technology and research, stakeholders can protect vital soil resources and contribute to long-term environmental health. The collective efforts to implement these strategies will be crucial in building resilience against the challenges posed by soil erosion and climate change, emphasizing the need for immediate and sustained action in the field of erosion control.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are erosion control measures and why are they important?
Erosion control measures are practices designed to prevent or reduce land degradation caused by wind, water, or human actions. They are essential for safeguarding land integrity and enhancing water quality by minimizing sedimentation in waterways.
What are the primary causes of erosion?
The primary causes of erosion include rainfall, surface runoff, and land disturbances, which can be exacerbated by human actions, particularly land-use changes.
How does climate change affect land degradation?
Climate change is expected to significantly impact land degradation patterns, necessitating adaptive strategies in land management to address these changes.
What percentage of land degradation in the U.S. is associated with agricultural practices?
In 2025, approximately 70% of land degradation in the U.S. is attributed to agricultural practices.
What are some effective erosion control techniques?
Effective erosion control techniques include vegetation buffers, sediment traps, contour farming, and terracing, which help reduce runoff and stabilize soil.
Why is understanding soil preservation important for land management professionals?
Understanding soil preservation is vital for professionals in land management and construction as it encompasses key principles such as maintaining vegetation cover, implementing appropriate drainage systems, and using protective blankets to combat soil loss.
What role do native plants play in managing soil degradation?
Native plants, particularly deep-rooted species like grasses, shrubs, and trees, stabilize the ground, reduce erosion risks, and absorb rainfall, which mitigates surface runoff and flooding.
How does plant restoration impact soil degradation management?
Plant restoration has been shown to significantly decrease ground degradation, with studies indicating an average yearly degradation management index enhancement of 73.2% in areas where plant life was revived.
What are the contributing factors to soil degradation management in different climate zones?
The contributing factors to soil degradation management vary by climate zones, with 62% attributed to wind factors, 25% to the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), and 13% to artificial intelligence (AI).
What are the benefits of integrating native plant species into soil preservation strategies?
Integrating native plant species into soil preservation strategies enhances ground stability, supports wildlife habitats, and contributes to sustainable land stewardship and ecosystem well-being.




