Overview
The article underscores the critical role of land use plans within biodiversity hotspots, emphasizing their necessity for effective conservation efforts. These plans are essential in managing resources and mitigating human impacts on fragile ecosystems. Supported by examples of successful community engagement and structured assessment processes, they significantly enhance biodiversity preservation.
By addressing the complexities of land acquisition and the associated legal and regulatory challenges, the article illustrates how these plans not only safeguard ecosystems but also empower communities to participate actively in conservation.
Ultimately, the call to action is clear: prioritize the development and implementation of comprehensive land use plans to ensure a sustainable future for our planet's biodiversity.
Introduction
Biodiversity hotspots stand as some of the planet's most vital ecological treasures, brimming with unique species yet confronting unprecedented threats from human activity. These regions, characterized by their rich endemic flora and significant habitat loss, are essential to global conservation efforts.
With 36 recognized hotspots worldwide, understanding their importance is critical—not only for the species that inhabit them but also for the ecosystem services that sustain human life. As climate change accelerates biodiversity loss, innovative conservation initiatives and community engagement emerge as pivotal strategies for preserving these fragile ecosystems.
This article explores the multifaceted approaches necessary to:
- Assess land suitability
- Navigate legal frameworks
- Engage stakeholders
- Implement effective land use plans that prioritize the protection of these invaluable hotspots.
Understand Biodiversity Hotspots and Their Importance
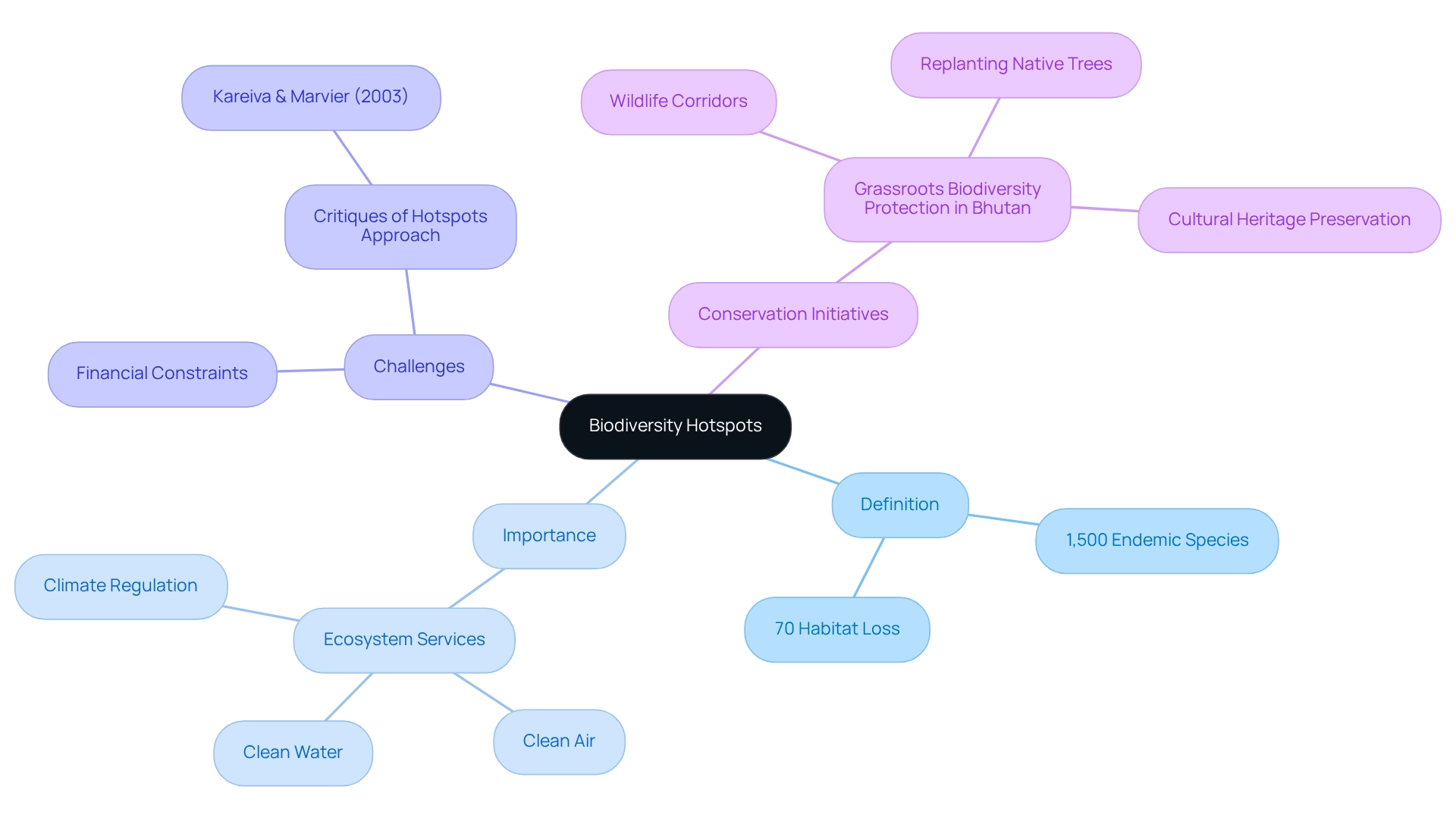
Biodiversity hotspots represent critical regions, distinguished by a high concentration of endemic species that are under significant threat from human activities. To qualify as a hotspot for biological diversity, a region must support at least 1,500 species of vascular plants as endemics and have lost no less than 70% of its original habitat. Currently, there are 36 recognized ecological hotspots worldwide, underscoring their vital role in global conservation efforts.
These areas are not only essential for preserving unique species but also for maintaining crucial ecosystem services that sustain human life, including clean air, water, and climate regulation. The decline in biological diversity within these hotspots can lead to severe ecological consequences. Notably, recent statistics indicate that climate change is the primary driver of species reduction in regions such as Western Asia and Oceania.
Recent discourse in environmental literature has illuminated the limitations of the hotspots approach, particularly regarding financial constraints and phylogenetic diversity, as noted in the work of Kareiva & Marvier (2003). This critique underscores the need for a more nuanced understanding of conservation priorities.
Effective conservation initiatives, such as the grassroots ecological protection project in Bhutan, exemplify the potential for local communities to play a pivotal role in safeguarding these vital regions. By constructing wildlife corridors and replanting native trees, local villagers have not only protected endangered species but also preserved their cultural heritage and environment for future generations. This case study highlights the importance of local community engagement in conservation efforts.
Recognizing the significance of biodiversity hotspot land use plans is crucial for shaping resource management strategies aimed at mitigating human impact on these fragile ecosystems. As the Dalai Lama aptly stated, "It is our collective and individual responsibility to preserve and tend to the world in which we all live." This shared responsibility emphasizes the urgency of prioritizing conservation initiatives within biodiversity hotspot land use plans to ensure the survival of both unique species and the ecosystem services they provide. Moreover, tailored property acquisition strategies can be developed to support these conservation efforts, aligning with the needs of Directors of Property Acquisition.
Assess Land Suitability for Biodiversity Conservation
To effectively evaluate terrain appropriateness for ecological preservation, it is essential to follow these structured steps:
- Identify Key Biodiversity Areas (KBAs): Utilize existing biodiversity data to pinpoint regions crucial for the survival of various species. In the U.S., over 1,000 designated KBAs highlight areas of significant ecological importance. Recent research applied a methodology to data on ant diversity in eight land-use systems in Oumé, Côte d’Ivoire, which can inform similar assessments in the U.S.
- Conduct Habitat Assessments: Evaluate the current conditions of habitats within the identified KBAs, focusing on vegetation types, soil quality, and water availability. This assessment is vital for understanding the ecological health of these areas.
- Utilize GIS Tools: Employ Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to analyze spatial data, visualize usage patterns, and assess habitat fragmentation. Advanced GIS tools available in 2025 can enhance the accuracy of these analyses, providing insights into potential threats to biodiversity.
- Assess Land Use Disputes: Recognize current uses of terrain that may clash with preservation goals, such as agriculture, urban development, or industrial activities. Future preservation efforts should concentrate on restricting the growth of urban regions and farmland to safeguard ecological diversity. Grasping these conflicts is crucial for creating effective preservation strategies.
- Focus on Areas for Protection: Based on the evaluations, emphasize regions with significant ecological importance and low human interference for protective measures. This prioritization is crucial for maximizing the impact of preservation initiatives. Studies show that preservation easements are a useful method for safeguarding ecological variety on private properties, especially in regions encountering development challenges. The effectiveness of these easements as a strategy for mitigating usage threats has been well documented.
In nations, particularly developing ones, where customary tenure systems are practiced, landscape composition is largely dependent on the usage preferences of individuals, as noted by Kwame Oppong Hackman. By applying these measures, property acquisition specialists can play a crucial role in ecological preservation and carbon capture initiatives.
Navigate Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Navigating the complex landscape of legal and regulatory requirements for biodiversity conservation demands a strategic approach. Understanding these regulations is not merely advisable; it is essential for effective planning and compliance. The Amazon rainforest, home to nearly 30 million people, underscores the urgent need for biodiversity protection.
- Research Local and National Regulations: Begin by thoroughly researching the laws governing resource use, environmental safeguarding, and ecological preservation at both local and national levels. This foundational knowledge is crucial for aligning your initiatives with legal standards.
- Acquire Required Permits: Identify and apply for all necessary permits related to property use modifications or preservation activities. This may encompass environmental impact assessments and specific land use permits, both vital for ensuring projects meet legal requirements.
- Engage with Regulatory Bodies: Proactively communicate with relevant regulatory agencies. As Richard Rogers aptly stated, "The only way forward, if we are going to improve the quality of the environment, is to get everybody involved." This engagement not only secures compliance but also provides access to invaluable guidance on best practices for environmental planning.
- Document Compliance Efforts: Maintain meticulous records of all compliance activities, including permits obtained, assessments conducted, and communications with regulatory bodies. Proper documentation is essential for demonstrating adherence to legal requirements and facilitating smoother project execution.
- Stay Informed on Policy Changes: Regularly monitor changes in laws and regulations that may impact biodiversity conservation efforts. Staying abreast of developments, such as the evolving environmental protection laws in 2025, is critical for ongoing compliance and adapting strategies as necessary. Gaylord Nelson's vision for environmentalism reminds us of our moral obligation to protect the environment for future generations.
By following these essential steps, organizations can adeptly navigate the legal framework surrounding biodiversity hotspot land use plans for ecological preservation. This ensures that their usage plans contribute positively to environmental sustainability and compliance.
Engage Stakeholders in the Planning Process
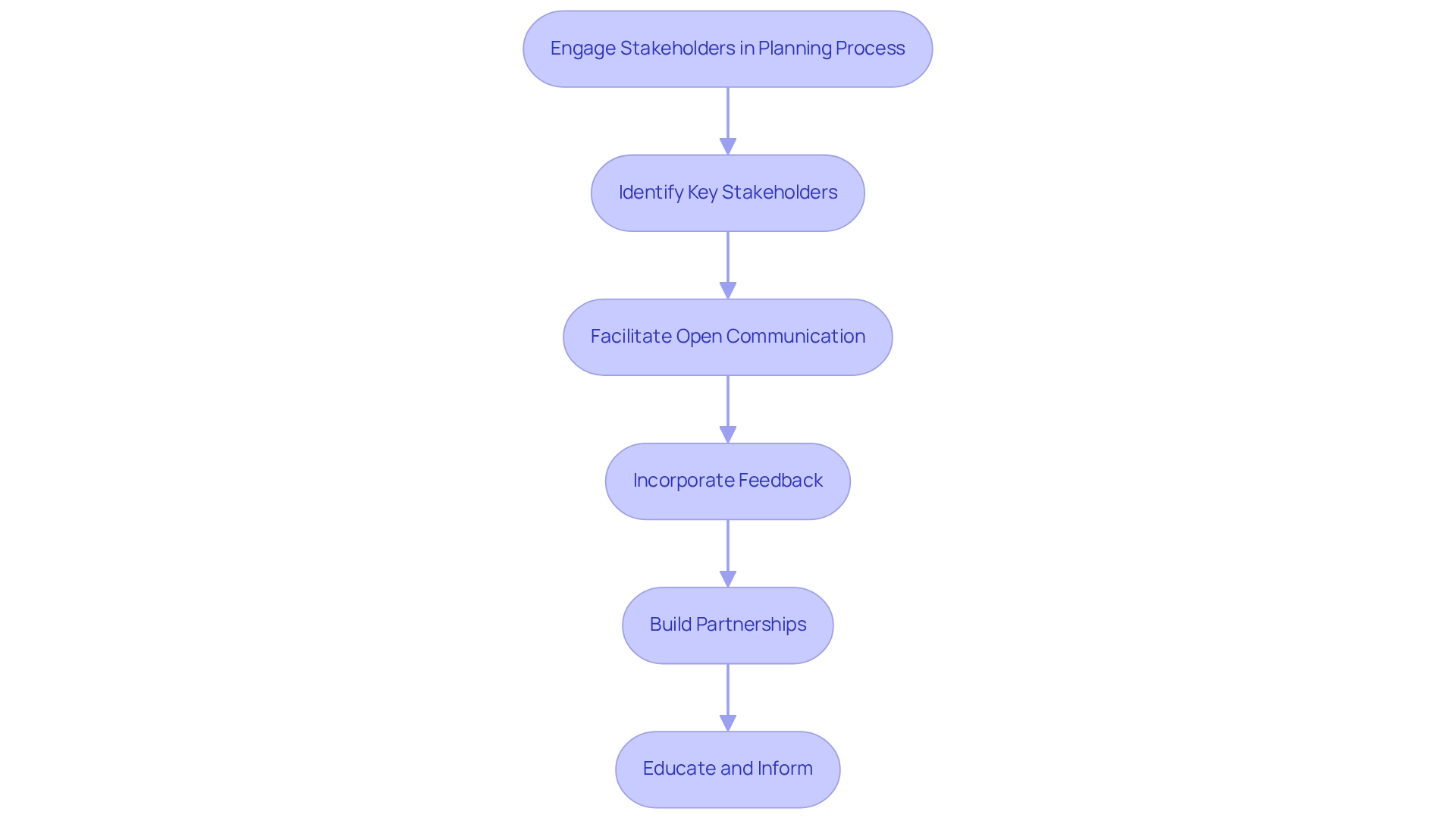
Involving stakeholders in the biodiversity hotspot land use plans is essential for effective biodiversity preservation. To ensure effective participation, consider the following key steps:
- Identify Key Stakeholders: Recognize individuals and groups impacted by land use decisions, including local communities, government entities, NGOs, and private sector stakeholders. Understanding the demographics of these stakeholders, as highlighted in the case study "Demographic Insights of Participating Farmers," reveals that many may have limited education, underscoring the need for targeted educational initiatives.
- Facilitate Open Communication: Establish platforms that encourage dialogue, allowing stakeholders to voice concerns, share insights, and contribute innovative ideas. YNB acknowledges assistance from the Audemars-Watkins Foundation for the CBCR’s protected area monitoring initiatives, highlighting the significance of joint efforts in environmental protection.
- Incorporate Feedback: Actively solicit and integrate stakeholder feedback into the planning process, ensuring their perspectives and needs are reflected in the final plans. Monitoring should be regarded as a commitment to the future of ecological preservation, emphasizing the importance of stakeholder contributions.
- Build Partnerships: Develop collaborative relationships with stakeholders to foster trust and commitment toward shared environmental objectives. Donors and investors must ensure monitoring budgets are funded and hold project managers accountable, which can enhance trust among stakeholders.
- Educate and Inform: Provide stakeholders with an understanding of the importance of biodiversity preservation and the specific objectives of usage plans, thereby encouraging their support and active participation. For example, data indicate that crop diversity improved food security for farmers during the COVID-19 pandemic, demonstrating the concrete advantages of community participation in biodiversity hotspot land use plans.
By prioritizing these strategies and incorporating insights from external sources, planners of biodiversity hotspot land use plans can enhance stakeholder involvement, leading to more effective preservation outcomes and sustainable resource management.
Develop and Implement Effective Land Use Plans
To create and execute efficient usage strategies for ecological preservation, it is essential to follow these steps:
- Set Clear Objectives: Establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives tailored to the biodiversity hotspot land use plans aimed at preservation goals. This approach ensures clarity and focus in achieving conservation outcomes.
- Integrate Data and Assessments: Utilize information from site suitability evaluations and stakeholder input to guide the planning process. This integration is crucial, as freshwater habitats alone support one-third of all described vertebrates and nearly 10% of all known animal species. The importance of informed decision-making cannot be overstated.
- Design Actionable Strategies: Formulate detailed strategies that encompass specific actions, such as habitat restoration, land acquisition, or sustainable land management practices. These strategies should align with the concept of Biodiversity Net Gain (BNG), which mandates that development projects enhance ecological variety to counterbalance negative impacts. This approach not only addresses the imperative for biodiversity enhancement but also preserves essential ecosystem services, as evidenced in case studies on ecosystem services provided by biodiversity.
- Establish a Monitoring Framework: Create metrics and indicators to assess the effectiveness of the use plan. This framework enables continuous evaluation and necessary modifications, ensuring that the plan remains adaptable to evolving circumstances and preservation needs.
- Implement the Plan: Execute the usage plan by coordinating with stakeholders, securing funding, and mobilizing resources to carry out the outlined strategies. Engaging stakeholders is critical for successful implementation, as their insights and support can significantly enhance the effectiveness of the plan. Successful implementation is essential for achieving the desired environmental outcomes.
- Review and Adapt: Conduct regular reviews of the plan's effectiveness and adapt it based on monitoring results and evolving environmental conditions. This iterative process is vital for sustaining biodiversity and ensuring the long-term success of conservation efforts.
By following these steps, land acquisition professionals can develop biodiversity hotspot land use plans that protect biodiversity while also enhancing ecosystem services essential for sustaining life.
Conclusion
Recognizing the significance of biodiversity hotspots is imperative for global conservation efforts. These unique regions, rich in endemic species, face threats from human activities, making their preservation essential not only for the species themselves but also for the ecosystem services they provide, such as clean air and water. Innovative conservation initiatives, like community-led projects in Bhutan, demonstrate the potential for local involvement to make a meaningful impact in safeguarding these vital ecosystems.
To effectively protect biodiversity hotspots, a structured approach to land suitability assessment, legal navigation, stakeholder engagement, and land use planning is crucial. Identifying key biodiversity areas, conducting thorough habitat assessments, and utilizing advanced tools like GIS enable conservationists to develop informed strategies that prioritize the most critical regions. Engaging stakeholders throughout the planning process fosters collaboration and ensures diverse perspectives are incorporated, enhancing the overall effectiveness of conservation efforts.
Ultimately, the fight against biodiversity loss requires a collective commitment to responsible land management and conservation practices. As climate change continues to pose challenges, adapting land use plans and fostering community participation will be key to preserving these ecological treasures for future generations. The responsibility to protect our planet's biodiversity lies with everyone, and proactive steps taken today can lead to a sustainable and thriving environment tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are biodiversity hotspots?
Biodiversity hotspots are critical regions characterized by a high concentration of endemic species that face significant threats from human activities. To qualify as a hotspot, a region must have at least 1,500 species of vascular plants as endemics and must have lost at least 70% of its original habitat.
How many biodiversity hotspots are currently recognized worldwide?
There are currently 36 recognized biodiversity hotspots worldwide.
Why are biodiversity hotspots important?
Biodiversity hotspots are essential for preserving unique species and maintaining crucial ecosystem services that support human life, including clean air, water, and climate regulation.
What is the primary driver of species reduction in biodiversity hotspots?
Climate change is identified as the primary driver of species reduction in regions such as Western Asia and Oceania.
What are some challenges associated with the biodiversity hotspots approach?
Recent discussions highlight limitations in the hotspots approach, particularly regarding financial constraints and the need for a more nuanced understanding of conservation priorities, as noted by Kareiva & Marvier (2003).
How can local communities contribute to conservation efforts in biodiversity hotspots?
Local communities can play a pivotal role in conservation efforts, as demonstrated by grassroots ecological protection projects, such as those in Bhutan, where villagers construct wildlife corridors and replant native trees to protect endangered species and preserve their cultural heritage.
What role do biodiversity hotspot land use plans play in conservation?
Biodiversity hotspot land use plans are crucial for shaping resource management strategies to mitigate human impact on fragile ecosystems, emphasizing the collective responsibility to preserve these areas.
What steps are involved in evaluating terrain for ecological preservation?
The steps include identifying Key Biodiversity Areas (KBAs), conducting habitat assessments, utilizing GIS tools, assessing land use disputes, and focusing on areas for protection.
What are Key Biodiversity Areas (KBAs)?
Key Biodiversity Areas (KBAs) are regions identified as crucial for the survival of various species, with over 1,000 designated KBAs in the U.S. that highlight areas of significant ecological importance.
How can GIS tools aid in ecological preservation?
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) can analyze spatial data, visualize usage patterns, and assess habitat fragmentation, enhancing the accuracy of biodiversity threat assessments.
What is the significance of preservation easements?
Preservation easements are a useful method for safeguarding ecological variety on private properties, particularly in areas facing development challenges, and have been documented as effective in mitigating usage threats.
List of Sources
- Understand Biodiversity Hotspots and Their Importance
- Scientists warn of dangerous decline in Asia-Pacific’s biodiversity (https://unep.org/news-and-stories/story/scientists-warn-dangerous-decline-asia-pacifics-biodiversity)
- 20 Environmental Sustainability Quotes: Expert Guide with Insights and Inspiration | What is Green Living? (https://whatisgreenliving.com/environmental-sustainability-quotes)
- Biodiversity hotspot - Wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biodiversity_hotspot)
- Assess Land Suitability for Biodiversity Conservation
- A method for assessing land-use impacts on biodiversity in a landscape (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2351989414000651)
- Key areas for conserving United States' biodiversity likely threatened by future land use change (https://esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1890/ES12-00376.1)
- Navigate Legal and Regulatory Requirements
- 20 Environmental Quotes That Inspire Action - Environment Co (https://environment.co/environmental-quotes-that-inspire-action)
- 20 Environmental Sustainability Quotes: Expert Guide with Insights and Inspiration | What is Green Living? (https://whatisgreenliving.com/environmental-sustainability-quotes)
- Climate and Environmental Law | Martindale-Avvo (https://martindale-avvo.com/blog/environmental-and-climate-law-changes-in-2025)
- 15 Inspirational Quotes On The Environment | EcoMENA (https://ecomena.org/inspirational-quotes-environment)
- Engage Stakeholders in the Planning Process
- Measuring the Impact of Conservation: The Growing Importance of Monitoring Fauna, Flora and Funga (https://mdpi.com/1424-2818/14/10/824)
- Multi-stakeholder Approach to Conserving Agricultural Biodiversity and Enhancing Food Security and Community Health During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Kampong Cham, Cambodia(SITR7-11) - The International Partnership for the Satoyama Initiative (IPSI) (https://satoyamainitiative.org/case_studies/multi-stakeholder-approach-to-conserving-agricultural-biodiversity-and-enhancing-food-security-and-community-health-during-the-covid-19-pandemic-in-kampong-cham-cambodiasitr7-11)
- Develop and Implement Effective Land Use Plans
- 19 Key Biodiversity Facts & Statistics (https://gaiacompany.io/biodiversity-facts-statistics)
- earth.org (https://earth.org/endangered-species-quotes)




