Overview
This article presents a detailed, step-by-step guide for conducting a floodplain impact analysis, underscoring its critical role in regulatory compliance and environmental protection. It delineates essential steps, including:
- Risk assessment
- Stakeholder engagement
- The application of advanced tools
These components collectively contribute to effective flood management and bolster community resilience against flooding.
Introduction
In light of escalating climate challenges and urban development pressures, the significance of understanding floodplain impact analysis has reached a critical juncture. This systematic approach not only assesses how proposed projects influence flood-prone areas but also guarantees adherence to a complex array of regulations designed to protect communities and ecosystems.
By scrutinizing the multifaceted dimensions of floodplain management—from risk assessments and stakeholder engagement to contemporary regulatory frameworks—professionals can adeptly navigate the complexities of land use planning.
As the frequency and severity of flooding events continue to rise, the necessity for effective floodplain impact analysis becomes increasingly vital, underscoring the imperative for proactive strategies that cultivate resilience and sustainability in our dynamic landscapes.
Understanding Floodplain Impact Analysis: Importance and Relevance
The floodplain impact analysis is a critical framework for evaluating how proposed developments may influence floodplain regions. This systematic approach is vital not only for ensuring compliance with local, state, and federal regulations but also for mitigating environmental impacts. The analysis identifies potential flooding risks, informs stakeholders about necessary mitigation measures, and supports sustainable land use planning.
Its significance is particularly evident for professionals engaged in land acquisition and development, as it directly affects project feasibility and community safety.
Key aspects of impact analysis include:
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating the likelihood of flooding and its potential effects on infrastructure and communities is paramount. Historical data shows that flood events occurred on average every 2 to 5 years from 1950 to 2000, underscoring the necessity of proactive risk management.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to laws and guidelines governing flood management is essential. Recent revisions to HUD's Flood Management Regulations mandate that new constructions in flood zones must be built at least 2 feet above the base flood elevation. Compliance with these new standards is required by June 24, 2024, with specific amendments applicable to new constructions starting January 1, 2025. HUD has also indicated that development within the 1-percent-annual-chance area of potential flooding should not be prohibited, provided it undergoes a thorough evaluation through the 8-step decision-making process.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involving local communities and authorities in the decision-making process is crucial for addressing concerns and gathering input. For example, Charlotte-Mecklenburg, NC, has implemented mapping of flood-prone areas considering full watershed build-out conditions, revealing potential flood level increases of 2 to 9 feet in some regions at full development. This proactive engagement ensures that community needs and perspectives are integrated into planning procedures, directly influencing land acquisition and development.
The importance of flood risk assessment is further highlighted by its role in energy initiatives, where floodplain impact analysis can significantly affect site selection and project design. As communities increasingly confront the realities of climate change, the thorough assessment of flood areas becomes essential, ensuring that developments are resilient and sustainable. Additionally, new elevation standards applied to one-to-four-family residential structures insured by FHA enhance flood resilience, reinforcing the importance of regulatory compliance in land acquisition.
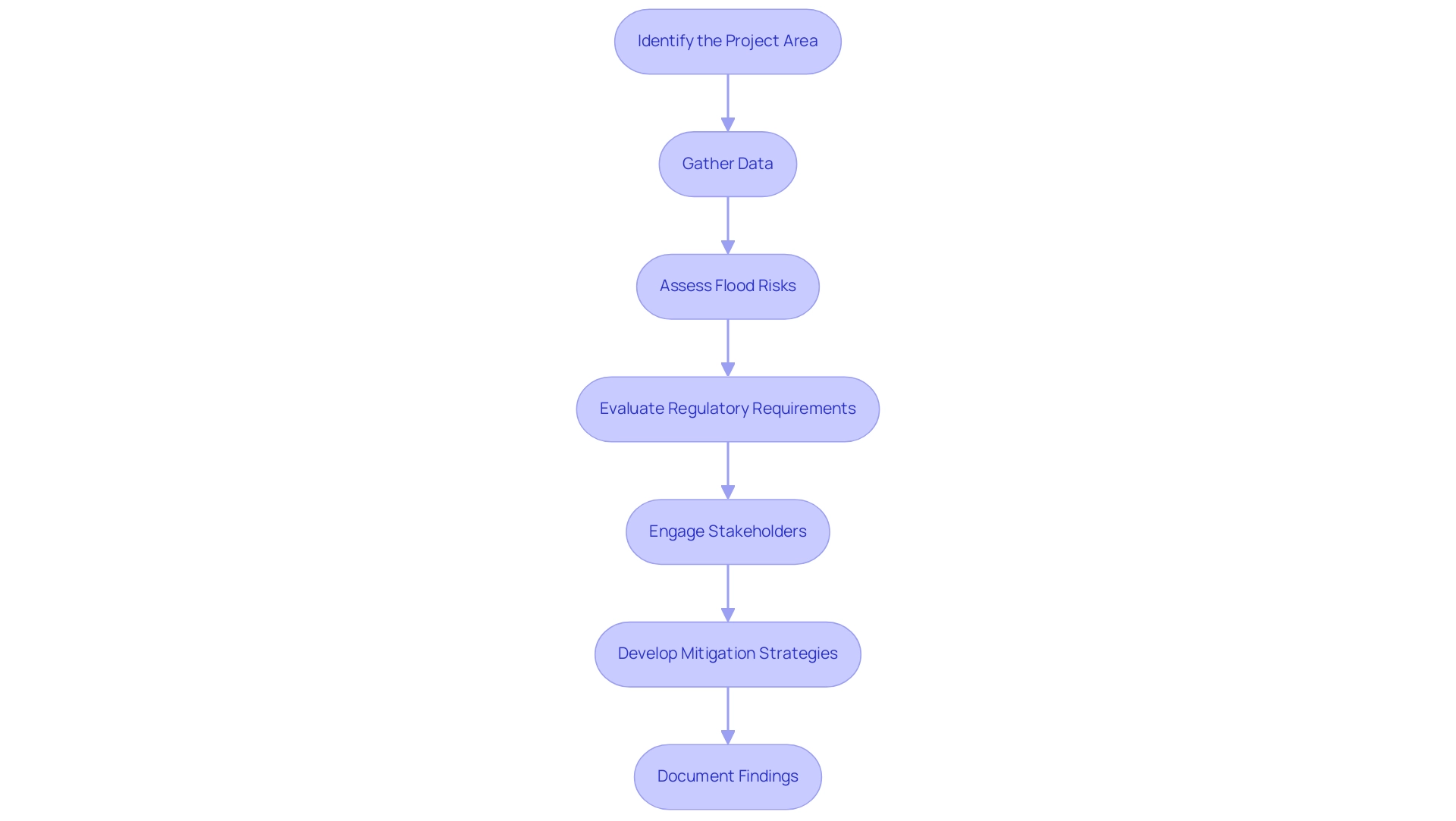
Key Steps in Conducting a Floodplain Impact Analysis
Conducting a floodplain impact analysis is a critical process that involves several essential steps to ensure effective flood risk management and compliance with regulatory standards.
- Identify the Project Area: Begin by clearly defining the boundaries of the proposed development. Evaluate its proximity to identified flood risk zones, utilizing current flood maps to comprehend potential hazards.
- Gather Data: Collect a wide range of relevant data, including hydrological, topographical, and environmental information. This should encompass flood maps, historical flood records, and current data on flood characteristics. In 2025, statistics indicate that effective project area identification relies heavily on accurate and comprehensive data collection techniques. Insurance providers can leverage observed floods from the database to better understand exposure for significant historic events and can access additional tools for higher resolution maps or live maps for ongoing events.
- Assess Flood Risks: Analyze the likelihood of flooding events based on historical data and predictive models. Evaluate the potential impacts these events could have on the project site and surrounding areas, considering factors such as storm intensity and land use changes.
- Evaluate Regulatory Requirements: Review local, state, and federal regulations related to flood management. This includes understanding the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) guidelines, which stipulate that new constructions in flood hazard areas must meet specific elevation requirements to qualify for mortgage insurance. The maximum available building coverage through the NFIP is $500,000 for multifamily structures with five or more housing units and commercial structures. Additionally, as stated by Kristin L. Fontenot, the lowest floor in newly constructed structures located within the 1-percent-annual-chance (100-year) floodplain must be built at least 2 feet above the base flood elevation (BFE) as determined by the best available information.
- Engage Stakeholders: Actively communicate with local authorities, community members, and other stakeholders throughout the evaluation process. Gathering input and addressing concerns is vital for fostering community support and ensuring compliance with regulatory expectations.
- Develop Mitigation Strategies: Propose effective measures to minimize flood risks. This may include elevating structures above the base flood elevation (BFE) or implementing green infrastructure solutions, such as permeable pavements and rain gardens, which can enhance urban resilience against flooding. Feedback from the case study titled "Support for HUD's Proposed CISA Approach" highlights the importance of protecting communities from flooding, especially underserved ones, and emphasizes the need for a more dynamic and scientifically informed flood risk assessment.
- Document Findings: Prepare a comprehensive report that outlines the evaluation, findings, and recommendations. This documentation should be clear and accessible to stakeholders, ensuring that all parties understand the consequences of the area assessment and the suggested mitigation strategies. The case study titled "Requests for Clarification of Hazard Notice Requirement Regulations" underscores the importance of clear communication regarding hazard notifications related to flood areas.
By following these key steps, professionals can conduct a thorough floodplain impact analysis that not only complies with regulatory requirements but also contributes to the resilience of urban areas against flooding.
Navigating Regulatory Frameworks: Floodplain Management Requirements
Navigating the regulatory frameworks for flood zone oversight presents significant challenges that demand a comprehensive understanding of the laws and guidelines governing land use in flood-prone areas, particularly those related to floodplain impact analysis. Key regulations include:
- National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP): Administered by FEMA, this program establishes minimum standards for managing flood-prone areas, compelling communities to adopt management ordinances. As of 2025, compliance statistics indicate that approximately 90% of participating communities have adopted these standards, reflecting a commitment to reducing flood risks. FEMA considers the service life of the project in determining the FFRMS inundated areas using CISA, ensuring that flood protection measures are both effective and sustainable.
- Executive Order 11988: This order mandates federal agencies to avoid actions that adversely affect inundated areas and to explore alternatives that minimize impacts. It emphasizes the federal dedication to maintaining the integrity of flood areas while encouraging sustainable development practices. FEMA utilized its expert judgment to conclude that CISA is the optimal policy choice, as it guarantees that the level of extra flood protection for each project is founded on the most reliable, actionable hydrologic and hydraulic data and techniques.
- State and Local Regulations: Numerous states and municipalities enforce their own flood control regulations, often stricter than federal requirements. For instance, recent updates in 2025 have seen several states improve their flood management laws to tackle emerging climate challenges. Consulting local ordinances and zoning laws is crucial for compliance and effective project planning.
Professionals must remain vigilant about regulatory changes and ensure that their projects align with all applicable laws. This proactive approach not only mitigates risks but also supports floodplain impact analysis to enhance community resilience against flooding. Residents should follow emergency instructions during severe weather events and evacuations to ensure safety. Engaging with case studies, such as the advanced course on obtaining and developing Base Flood Elevations in Zone A areas, can provide valuable insights into navigating these complex regulations and improving technical skills in compliance with NFIP standards.
Tools and Methodologies for Effective Floodplain Impact Analysis
Effective floodplain impact analysis demands a suite of advanced tools and methodologies that enhance precision and decision-making capabilities. The complexities of land acquisition and the associated legal and regulatory challenges necessitate a robust approach. Key components include:
- Hydraulic Modeling Software: Essential tools such as HEC-RAS and MIKE FLOOD simulate water flow dynamics and evaluate the potential impacts of land use changes on flood behavior. These software solutions are increasingly recognized for their effectiveness, with the hydraulic evaluation software market projected to grow from USD 730.32 million in 2023 to USD 940.56 million by 2031, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.48% from 2024 to 2031. As noted by Deloitte, "We have been working with Mark Wide Research for a number of years now, and we have found their market research reports to be invaluable in helping us make strategic decisions for our business."
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS mapping plays a crucial role in flood management, enabling spatial examination of inundation boundaries, land use patterns, and infrastructure. This technology not only aids in visualizing flood risks but also supports informed decision-making processes. Expert insights underscore that GIS tools are indispensable for effective floodplain impact analysis, providing critical data that enhances planning and risk assessment.
- Flood Risk Assessment Tools: Comprehensive software solutions like FEMA's Risk MAP deliver vital flood risk data and mapping resources, crucial for supporting planning and development initiatives. These tools empower stakeholders to understand potential flood hazards and implement appropriate mitigation strategies.
- Data Gathering and Evaluation: Accurate data collection through remote sensing and field surveys is essential for a thorough study of flood areas. Gathering detailed information on topography, land use, and hydrology ensures that evaluations are based on reliable data, resulting in more precise outcomes.
By integrating these advanced instruments and techniques, experts can conduct a thorough and accurate floodplain impact analysis of flood-prone areas. This integration not only informs project planning but also enhances risk management strategies, ultimately contributing to more resilient urban environments. Furthermore, delivering prompt and precise services tailored to specific client needs is vital for effective assessment of flood risks, as highlighted by the anticipated growth in the hydraulic software market.
Challenges in Floodplain Impact Analysis: Stakeholder Negotiations and Conflicts
Navigating the intricate dynamics of stakeholders is essential in floodplain impact analysis, yet it presents several challenges:
- Conflicting Interests: Stakeholders frequently have differing priorities, such as the need to balance environmental protection with economic development. These conflicts must be addressed to ensure effective progress.
- Communication Barriers: Insufficient communication can obstruct collaboration, leading to resistance against proposed projects. Employing effective communication strategies is vital to mitigate these issues.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring that all stakeholders understand and comply with regulatory requirements can be complex, especially when local regulations diverge from federal guidelines. This complexity can result in confusion and potential non-compliance.
To effectively tackle these challenges, professionals should consider the following strategies:
- Foster Open Communication: Establishing transparent communication channels among stakeholders is crucial for building trust and understanding. Regular updates and inclusive discussions can help align interests and expectations.
- Articulate Project Benefits: Clearly conveying the advantages of the proposed project to all parties can help mitigate resistance. Highlighting how the project aligns with community goals and environmental standards fosters support.
- Engage in Collaborative Problem-Solving: Utilizing collaborative approaches to address stakeholder concerns can lead to mutually acceptable solutions. This may involve negotiating compromises that satisfy various interests while still achieving project objectives.
Recent statistics indicate a rise in stakeholder conflicts related to land use, particularly in urban areas. In 2025, it was estimated that over 30% of projects in flood-prone areas faced significant negotiation challenges. This underscores the importance of floodplain impact analysis, effective communication strategies, and stakeholder engagement. Additionally, FEMA's final rule is projected to increase costs for certain projects, with estimates suggesting that 13,476 structures will be affected in the first decade, resulting in substantial long-term financial implications.
Furthermore, the annual adjustment of $364,000 to reflect changes in the Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers highlights the economic context of these challenges. The involvement of HUD's wetlands subject matter experts, who review and suggest exemptions, emphasizes the importance of expert guidance in navigating these complexities.
Case studies have shown that enhancing public notice requirements can significantly improve community involvement and accessibility, ultimately leading to more successful project outcomes. By prioritizing these strategies, professionals can effectively manage the intricacies of floodplain impact analysis. Harbinger Land's expertise in land acquisition and GIS mapping positions the company as a valuable partner in addressing these challenges.
Best Practices for Conducting Floodplain Impact Analyses
To conduct effective floodplain impact analyses, professionals must adhere to best practices that ensure comprehensive evaluations and informed decision-making.
- Comprehensive Data Collection: Gathering a diverse array of data—including hydrological, topographical, and environmental information—is essential. This foundational step informs the analysis and guarantees that all relevant factors are considered, especially in light of evolving climate scenarios. Determining whether an action occurs in a flood-prone area is a crucial first step in HUD's regulatory process, underscoring the significance of thorough data gathering.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging stakeholders early in the process is vital. This approach facilitates the collection of valuable input and addresses concerns proactively, fostering collaboration and support. Statistics reveal that projects with robust stakeholder engagement strategies experience a 30% increase in community support and project success rates in 2025. Moreover, timely remediation of floodplain properties is essential, as highlighted by recent comments on the need for effective stakeholder engagement in these projects.
- Iterative Examination: Implementing multiple iterations of examination allows for the refinement of findings and adaptation to new information or stakeholder feedback. This iterative method is crucial for accurately evaluating flood risks and ensuring that assessments remain relevant as conditions evolve.
- Documentation and Reporting: Maintaining thorough documentation of the evaluation process, findings, and stakeholder interactions is imperative for transparency and accountability. This practice not only aids in regulatory compliance but also builds trust among stakeholders.
- Continuous Learning: Professionals should stay informed of the latest tools, methodologies, and regulatory changes. Engaging in continuous education and training enhances the efficiency of upcoming evaluations and ensures preparedness to address new challenges in waterway oversight. As Kristin L. Fontenot, Director of the Office of Environment and Energy at HUD, stated, "Through this final rule, HUD is prioritizing using CISA in defining the area prone to flooding because it provides a forward-looking assessment of flood risk based on likely or potential climate change scenarios."
Incorporating these best practices not only enhances the quality of floodplain impact analysis but also aligns with expert recommendations for effective oversight. For example, case studies have demonstrated that projects adhering to these principles—such as the amendment of Minimum Property Standards for FHA-insured properties to require higher elevation standards in flood hazard areas—significantly reduce flood damage potential and enhance community resilience in flood-prone areas.
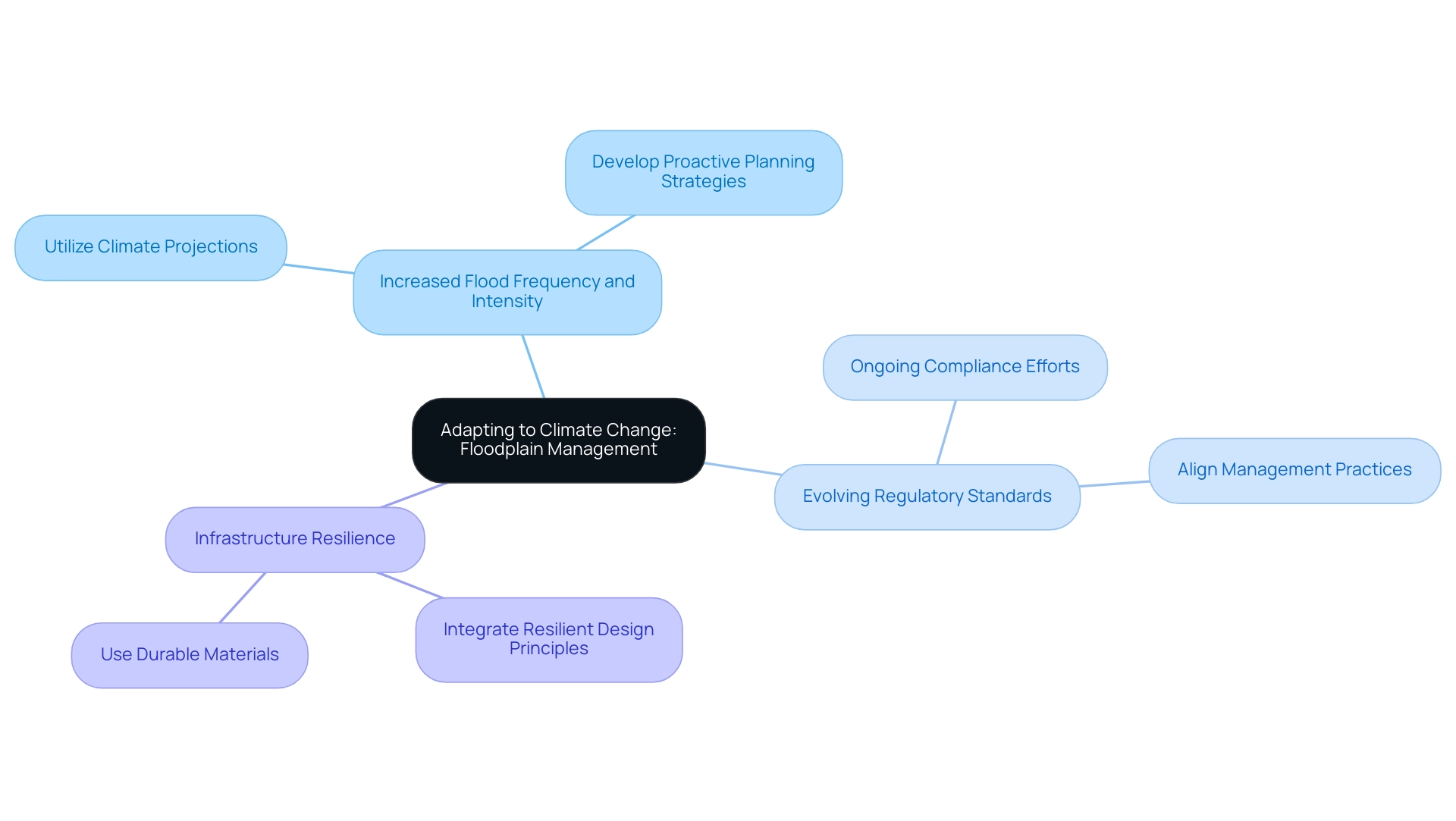
Adapting to Climate Change: Implications for Floodplain Management
Climate change presents formidable challenges to flood area oversight, necessitating the adoption of adaptive strategies to effectively mitigate associated risks. The implications of these changes are profound:
- Increased Flood Frequency and Intensity: Projections indicate that climate change will lead to a significant rise in both the frequency and severity of flooding events. Recent data underscores that the western United States is currently experiencing its most intense drought in over 1,200 years, highlighting the urgent need for revised practices that can adapt to these shifting patterns.
- Evolving Regulatory Standards: As the landscape of climate risks continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks are likely to undergo substantial changes. This necessitates ongoing compliance efforts to ensure that management practices align with the latest standards and best practices.
- Infrastructure Resilience: It is imperative that infrastructure projects are designed with resilience in mind, capable of withstanding the unpredictable nature of future flood conditions. This includes the integration of resilient design principles and materials that can endure extreme weather events.
To effectively adapt to these challenges, professionals in the field should:
- Incorporate Climate Projections: Utilize climate projections in floodplain impact analyses to better anticipate future risks and inform decision-making processes.
- Engage in Proactive Planning: Develop proactive planning strategies that leverage floodplain impact analysis to consider the long-term effects of climate change on floodplain areas, ensuring that communities are prepared for potential flooding scenarios.
- Collaborate with Experts: Work closely with climate scientists and local authorities to formulate comprehensive adaptation strategies that address the unique challenges posed by climate change.
As Emily K. Laidlaw observed, 'As extreme events and other climate hazards intensify, detrimental effects on individuals throughout the United States are rising.' This underscores the urgency of addressing these challenges. The Human Climate Horizons platform exemplifies the importance of localized data in this context, providing detailed projections of sea-level rise and its effects under various emissions scenarios.
Such information empowers both citizens and policymakers to comprehend and respond effectively to the anticipated impacts of climate change, emphasizing the urgent necessity for prompt action in managing flood areas. Furthermore, accelerating adaptation efforts is essential to address current climate risks and prepare for future consequences, particularly as regions such as Alaska and the Midwest experience significant temperature increases due to climate change.
Resources and Support for Floodplain Management and Impact Analysis
Experts engaged in flood risk assessment and floodplain impact analysis possess access to a vast array of resources designed to amplify their effectiveness and expertise in the field. These resources are vital for navigating the complexities of flood management and ensuring community resilience. Key resources include:
- FEMA Resources: The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) provides comprehensive guidelines, tools, and training materials that are essential for effective oversight of flood-prone areas and risk evaluation. Understanding the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) minimum standards established in 1973 is crucial, as these standards continue to influence flood policy today, setting the baseline for practices nationwide.
- Professional Organizations: Membership in organizations such as the Association of State Floodplain Managers (ASFPM) offers invaluable networking opportunities, training sessions, and access to best practices in the field. These organizations significantly shape flood area statistics and practices, particularly as they adapt to evolving challenges anticipated in 2025. Notably, Virginia, Florida, and South Carolina have consistently ranked highest in building regulations from 2012 to 2024, reflecting regional differences in flood management practices.
- Online Training and Webinars: A multitude of organizations provide online courses and webinars focused on various aspects of flood area oversight. These flexible learning options enable professionals to stay informed about the latest techniques and regulatory changes, ensuring they are well-prepared to tackle contemporary challenges.
- Research Publications: Engaging with scholarly journals and publications centered on waterway oversight can provide insights into advanced research and innovative techniques. Staying updated on the latest studies is imperative for implementing effective strategies in flood-prone areas.
- Local Government Resources: Numerous local authorities offer resources and support for flood zone oversight, including technical assistance and funding opportunities. These local initiatives are crucial for addressing specific community needs and enhancing resilience against flooding. It is important to note that the Immediate Needs Funding guidance will be removed on October 1, 2024, potentially impacting the availability of resources for flood area oversight.
- Case Studies: Real-world examples, such as the Hurricane Wind Risk Assessment, underscore the importance of risk management in evaluating flood areas. This case study assesses wind risk levels associated with hurricanes, categorizing them from extreme to moderate, detailing the number of homes impacted and estimating reconstruction costs. Such assessments highlight the significant threat posed by hurricanes and the necessity for effective floodplain management strategies. By leveraging these resources, professionals can significantly enhance their floodplain impact analysis capabilities, ultimately contributing to more resilient urban environments.
Conclusion
Floodplain impact analysis is a crucial instrument for navigating the complexities of urban development amidst the pressing challenges of climate change and flooding. This systematic approach not only ensures compliance with numerous regulations but also advocates for sustainable land use practices that protect communities and ecosystems. Essential components such as risk assessments, stakeholder engagement, and adherence to evolving regulatory frameworks are vital in mitigating flood risks and enhancing community resilience.
As the frequency and intensity of flooding events rise, the significance of thorough floodplain impact analysis becomes increasingly evident. By utilizing advanced tools and methodologies, professionals can accurately assess flood risks and devise effective mitigation strategies that safeguard both infrastructure and the environment. Moreover, fostering open communication among stakeholders and embracing best practices will yield more successful project outcomes, ultimately benefiting the communities most vulnerable to flooding.
In conclusion, the proactive implementation of floodplain impact analysis transcends mere regulatory obligation; it is a vital strategy for building resilience in the face of climate change. As communities adapt to these challenges, integrating innovative practices and collaborative approaches will ensure that future developments are sustainable, safe, and aligned with the needs of the environment and its inhabitants. The time for decisive action is now; effective floodplain management is crucial for cultivating a sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of a floodplain impact analysis?
A floodplain impact analysis evaluates how proposed developments may influence floodplain regions, ensuring compliance with regulations and mitigating environmental impacts. It identifies potential flooding risks, informs stakeholders about necessary mitigation measures, and supports sustainable land use planning.
Why is floodplain impact analysis important for land acquisition and development?
It is crucial for professionals in land acquisition and development as it directly affects project feasibility and community safety by assessing flood risks and ensuring compliance with regulations.
What are the key aspects of floodplain impact analysis?
The key aspects include risk assessment, regulatory compliance, and stakeholder engagement. These aspects help evaluate flooding risks, adhere to legal standards, and involve local communities in the decision-making process.
How often did flood events occur historically, according to the article?
Historical data indicates that flood events occurred on average every 2 to 5 years from 1950 to 2000, highlighting the need for proactive risk management.
What are the new regulatory requirements for constructions in flood zones?
New constructions in flood zones must be built at least 2 feet above the base flood elevation, with compliance required by June 24, 2024. Specific amendments apply to new constructions starting January 1, 2025.
What role does stakeholder engagement play in floodplain impact analysis?
Engaging local communities and authorities is essential for addressing concerns and gathering input, ensuring that community needs are integrated into planning procedures.
What are the steps involved in conducting a floodplain impact analysis?
The steps include: identifying the project area, gathering data, assessing flood risks, evaluating regulatory requirements, engaging stakeholders, developing mitigation strategies, and documenting findings.
What types of data are collected during the floodplain impact analysis?
Relevant data includes hydrological, topographical, and environmental information, such as flood maps, historical flood records, and current flood characteristics.
What strategies can be developed to mitigate flood risks?
Mitigation strategies may include elevating structures above the base flood elevation, implementing green infrastructure solutions like permeable pavements and rain gardens, and other measures to enhance urban resilience against flooding.
What is the significance of documenting findings in a floodplain impact analysis?
Documenting findings ensures that the evaluation, results, and recommended mitigation strategies are clear and accessible to stakeholders, facilitating understanding and compliance with flood management regulations.
List of Sources
- Understanding Floodplain Impact Analysis: Importance and Relevance
- Analysis of 220 Years of Floodplain Population Dynamics in the US at Different Spatial Scales (https://mdpi.com/2073-4441/13/2/141)
- Floodplain Management and Protection of Wetlands; Minimum Property Standards for Flood Hazard Exposure; Building to the Federal Flood Risk Management Standard (https://federalregister.gov/documents/2024/04/23/2024-06246/floodplain-management-and-protection-of-wetlands-minimum-property-standards-for-flood-hazard)
- Moving Beyond the Essentials - Page 2 of 5 - Flood Science Center (https://floodsciencecenter.org/products/elected-officials-flood-risk-guide/moving-beyond-the-essentials/2)
- Key Steps in Conducting a Floodplain Impact Analysis
- Floodplain Management and Protection of Wetlands; Minimum Property Standards for Flood Hazard Exposure; Building to the Federal Flood Risk Management Standard (https://federalregister.gov/documents/2024/04/23/2024-06246/floodplain-management-and-protection-of-wetlands-minimum-property-standards-for-flood-hazard)
- Global Flood Database (https://global-flood-database.cloudtostreet.ai)
- Navigating Regulatory Frameworks: Floodplain Management Requirements
- Updates to Floodplain Management and Protection of Wetlands Regulations To Implement the Federal Flood Risk Management Standard (https://federalregister.gov/documents/2024/07/11/2024-15169/updates-to-floodplain-management-and-protection-of-wetlands-regulations-to-implement-the-federal)
- Floodplain / Flood Management | Building Inspection Services (https://charlestoncounty.org/departments/building-inspection-services/flood-plain.php)
- National Flood Insurance Program (https://water.ca.gov/Programs/Flood-Management/National-Flood-Insurance-Program)
- Tools and Methodologies for Effective Floodplain Impact Analysis
- Hydraulic Analysis Software Market Size, Analysis And Forecast (https://verifiedmarketresearch.com/product/hydraulic-analysis-software-market)
- Hydraulic Modeling Software Market 2025-2034 | Size,Share, Growth (https://markwideresearch.com/hydraulic-modeling-software-market)
- Hydraulic Modeling Software Market Comprehensive Insights: Growth Trends, Key Players, and Industry Forecasts to 2032 (https://whatech.com/og/markets-research/it/926679-hydraulic-modeling-software-market-comprehensive-insights-growth-trends-key-players-and-industry-forecasts-to-2032.html)
- Challenges in Floodplain Impact Analysis: Stakeholder Negotiations and Conflicts
- Updates to Floodplain Management and Protection of Wetlands Regulations To Implement the Federal Flood Risk Management Standard (https://federalregister.gov/documents/2024/07/11/2024-15169/updates-to-floodplain-management-and-protection-of-wetlands-regulations-to-implement-the-federal)
- Floodplain Management and Protection of Wetlands; Minimum Property Standards for Flood Hazard Exposure; Building to the Federal Flood Risk Management Standard (https://federalregister.gov/documents/2024/04/23/2024-06246/floodplain-management-and-protection-of-wetlands-minimum-property-standards-for-flood-hazard)
- A Nationwide Analysis of Community‐Level Floodplain Development Outcomes and Key Influences (https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2024EF004585)
- Flood Planning and Studies (https://water.ca.gov/Programs/Flood-Management/Flood-Planning-and-Studies)
- Best Practices for Conducting Floodplain Impact Analyses
- Floodplain Management and Protection of Wetlands; Minimum Property Standards for Flood Hazard Exposure; Building to the Federal Flood Risk Management Standard (https://federalregister.gov/documents/2024/04/23/2024-06246/floodplain-management-and-protection-of-wetlands-minimum-property-standards-for-flood-hazard)
- Elevation Data for Floodplain Mapping (https://nap.nationalacademies.org/catalog/11829/elevation-data-for-floodplain-mapping)
- Adapting to Climate Change: Implications for Floodplain Management
- Fifth National Climate Assessment (https://nca2023.globalchange.gov)
- Climate change’s impact on coastal flooding to increase five times over this century | Human Development Reports (https://hdr.undp.org/content/climate-changes-impact-coastal-flooding-increase-five-times-over-century)
- Resources and Support for Floodplain Management and Impact Analysis
- Association of State Floodplain Managers (https://floods.org)
- Facts + Statistics: Flood insurance | III (https://iii.org/fact-statistic/facts-statistics-flood-insurance)
- Disaster Relief Fund: Monthly Reports (https://fema.gov/about/reports-and-data/disaster-relief-fund-monthly-reports)




