Overview
Erosion control is crucial for sustainable projects, as it effectively prevents soil degradation. This degradation can lead to significant environmental decline, loss of fertile land, and increased water pollution. Effective erosion control measures, such as:
- Vegetative cover
- Adherence to regulations
not only safeguard natural resources but also enhance the longevity of infrastructure initiatives. These efforts align seamlessly with global sustainability goals, making them indispensable in today’s environmental landscape.
Introduction
In a world where environmental degradation presents significant challenges, erosion control stands as a cornerstone of sustainable development. This multifaceted approach not only tackles the pressing issue of soil erosion—driven by wind, water, and human activities—but also plays a critical role in preserving natural resources and enhancing the viability of infrastructure projects. Alarming statistics reveal the staggering economic costs associated with soil degradation, making the understanding and implementation of effective erosion control measures increasingly urgent.
Innovative techniques such as vegetative cover and hydroseeding, along with the importance of stakeholder collaboration, form a comprehensive roadmap for safeguarding ecosystems while promoting responsible development practices. As the stakes rise, the commitment to sustainable erosion control transcends mere environmental necessity; it is a pathway to a more resilient future.
Reflect on the challenges posed by soil erosion and consider the implications for your projects. By embracing effective erosion control strategies, we can not only mitigate these challenges but also foster sustainable growth and development. The time to act is now.
Understanding Erosion Control: The Foundation of Sustainable Development
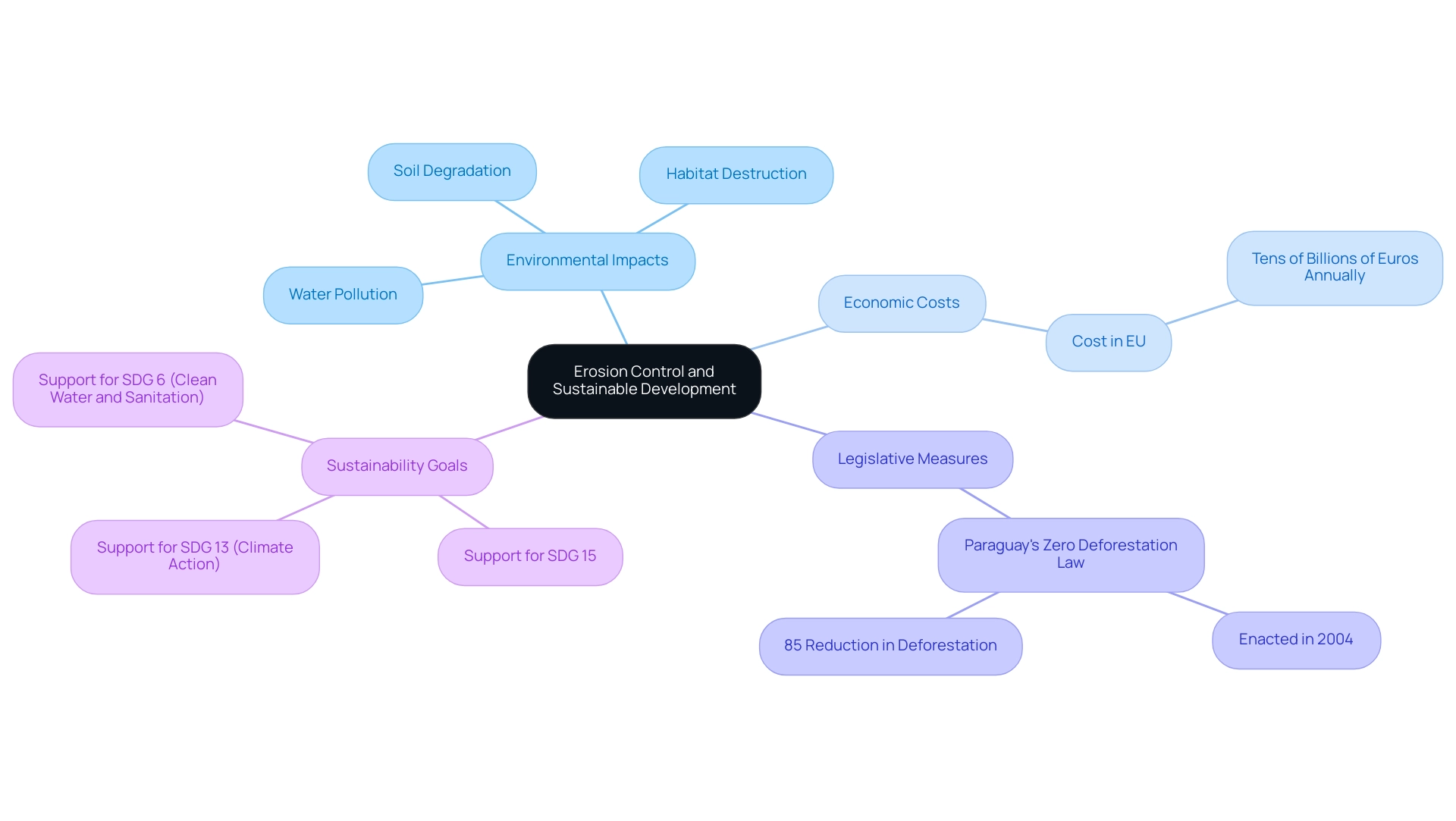
Erosion control for sustainable projects is critical in halting the degradation of earth caused by wind, water, and human actions. The unchecked degradation of soil can lead to severe environmental decline, including the loss of fertile land, increased water pollution, and destruction of habitats. Recent statistics reveal that the economic cost of soil degradation in the European Union reaches tens of billions of euros annually, underscoring the urgency for effective management of soil loss.
Implementing robust erosion control measures not only safeguards the environment but also enhances the longevity and effectiveness of infrastructure initiatives. Effective strategies in various regions demonstrate that managing soil degradation leads to improved outcomes. A notable example is Paraguay's Zero Deforestation Law, enacted in 2004, which resulted in an impressive 85% reduction in deforestation rates.
As noted by WWF, "Paraguay reduced the rate of deforestation in their country by 85% in the years just following enactment of its 2004 Zero Deforestation Law," illustrating how legislative measures can combat environmental degradation effectively.
Experts emphasize that understanding erosion control is essential for managers. By adopting best practices, they can implement strategies focused on erosion control, reducing erosion and fostering ecological balance. This approach ensures that development projects are not only economically viable but also environmentally responsible, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Moreover, recent findings highlight the complex relationships between climate change and human actions on soil preservation in China, laying the groundwork for future studies and targeted approaches in managing soil degradation.
In summary, the importance of soil preservation in erosion control cannot be overstated. It plays a vital role in protecting natural resources, enhancing viability, and contributing to broader environmental goals, such as those outlined in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) related to climate action and clean water. Over 50% of participants recognize that sustainable land management supports SDG 15, SDG 13 (Climate Action), and SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation), further emphasizing the necessity for effective measures to manage soil degradation.
Key Techniques and Strategies for Effective Erosion Control
Effective erosion control is essential for sustainable infrastructure projects, and various techniques have proven successful in mitigating soil erosion:
- Vegetative Cover: Establishing a diverse range of plants, including grasses, shrubs, and trees, stands out as one of the most effective methods for stabilizing earth. The root systems of these plants not only secure the soil but also enhance its structure, significantly reducing soil degradation. Research indicates that when plant coverage exceeds 60%, the effectiveness of measures for preventing soil displacement, such as Root Reinforcement Benefits (RRB) and Soil Reinforcement Benefits (SRB), can reach approximately 60% and 85%, respectively. As Zhan Xie noted, "The approach applied in this research can be extended to other extensive basins with comparable climate and enhance the comprehension of changes in control services under the impacts of vegetation restoration."
- Erosion Control Blankets: These blankets, made from natural or synthetic materials, serve a dual purpose: they protect the ground from degradation while fostering vegetation growth. Their successful application in various construction projects has demonstrated their effectiveness in maintaining ground integrity during critical growth periods.
- Silt Fences: Commonly used during construction activities, silt fences act as barriers that trap sediment and prevent it from contaminating nearby waterways. Their strategic placement can significantly reduce sediment transport, thereby safeguarding aquatic ecosystems.
- Mulching: The application of organic materials, such as straw or wood chips, on bare ground surfaces aids in moisture retention and suppresses weed growth, which can otherwise exacerbate degradation. This technique not only protects the ground but also enhances its fertility over time.
- Terracing: By creating stepped levels on inclined landscapes, terracing reduces water runoff and minimizes ground degradation. This method is particularly effective in hilly regions where water flow can lead to substantial erosion.
- Riprap: The strategic placement of large stones along shorelines or slopes offers a robust defense against water damage. This technique is especially beneficial in areas susceptible to heavy rainfall or wave action, as it absorbs and dissipates energy from flowing water.
- Hydroseeding: This innovative method involves spraying a mixture of seeds, mulch, and water onto the soil surface, promoting rapid vegetation growth. Hydroseeding is particularly effective in regions where conventional planting techniques may be challenging, ensuring swift establishment of plant cover to counteract soil degradation.
Integrating these methods into project planning not only enhances erosion control for sustainable projects but also aligns with best practices in soil management. Ongoing studies indicate that the annual degradation rate continues to exceed allowable limits, underscoring the necessity for effective strategies. For instance, areas with soil degradation rates surpassing 8000 t/km·a accounted for 10.7%, 9.7%, 7.1%, and 13.2% of the total area in 1982, 2000, 2008, and 2016, respectively, highlighting the urgency of implementing robust control measures.
Furthermore, the case study on the Lhasa River aids in understanding historical hydrological patterns, emphasizing the importance of these techniques in effectively managing land degradation. By leveraging these methods, project managers can significantly mitigate risks of soil degradation and promote long-term environmental sustainability.
Navigating Regulations: Compliance and Best Practices in Erosion Control
Erosion control for sustainable projects is governed by a complex framework of federal, state, and local guidelines aimed at protecting water quality and reducing land degradation. Among the most critical regulations are:
- National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES): This program mandates that construction sites manage stormwater discharges effectively, necessitating the implementation of robust erosion and sediment control measures. Recent statistics indicate that compliance rates for NPDES regulations among construction sites have improved; however, challenges remain, particularly in areas with steep slopes or significant bare soil exposure. Notably, development projects in these areas may need to submit an engineered sediment management plan as part of the development review process.
- Stormwater Pollution Prevention Plans (SWPPPs): These comprehensive plans outline the sediment management practices that will be utilized on construction sites to reduce sediment runoff. Successful implementations of SWPPPs have demonstrated significant reductions in sediment discharge, underscoring their importance in erosion control for sustainable projects.
- Best Management Practices (BMPs): BMPs offer a collection of recommendations that detail effective strategies for erosion control for sustainable projects, particularly in managing soil degradation and sedimentation. Regulatory agencies often require compliance with these practices to ensure environmental protection.
In 2025, it is essential for managers overseeing initiatives to remain updated on existing guidelines concerning erosion control for sustainable projects in construction. Development initiatives involving cuts and fills surpassing fifteen feet in height are especially prone to necessitate an engineered sediment management plan as part of the development review process. Moreover, construction projects that disturb soils must implement erosion control for sustainable projects to prevent negative environmental effects.
Routine evaluations and comprehensive records of soil management practices are essential for ensuring adherence to NPDES regulations. A benchmark inspection level is suggested for standard soil stabilization activities, encompassing both temporary and permanent measures. This level of inspection, as emphasized in the case study titled "Erosion Control for Sustainable Projects," ensures that soil preservation strategies are applied correctly and effectively throughout the project lifecycle, ultimately contributing to the sustainability of infrastructure development.
The Environmental Impact of Erosion: Why Sustainable Practices Matter
Erosion presents significant environmental challenges that can lead to extensive repercussions, including:
- Land Degradation: The loss of topsoil diminishes fertility, which is crucial for agricultural productivity and the health of natural ecosystems. Soil degradation affects the well-being of at least 3.2 billion individuals globally, underscoring the urgency of addressing this issue. The Food and Agricultural Organization's Afrisoils program aims to enhance land productivity in 47 African nations by 30% and reduce land degradation by 25% over the next decade, highlighting global initiatives to confront this pressing challenge.
- Water Quality Issues: Sediment runoff from land degradation can severely pollute waterways, adversely affecting aquatic life and degrading overall water quality. Data indicates that water-driven wear and soil compaction are prevalent concerns, impacting 24% and 22% of agricultural fields, respectively. This emphasizes the necessity for targeted interventions to mitigate sediment-related water quality challenges, as evidenced by recent case studies.
- Increased Flooding Risks: Erosion can compromise natural barriers, leading to heightened flooding risks in adjacent areas. The alteration of landscapes due to soil degradation not only increases vulnerability to flooding but also disrupts the natural flow of water, exacerbating the issue.
- Habitat Destruction: The physical changes induced by soil degradation can result in the loss of habitats for various species, threatening biodiversity. As ecosystems are modified, the delicate balance that sustains wildlife is disturbed, leading to long-term ecological consequences. To mitigate these impacts, implementing effective erosion control for sustainable projects is essential. Successful strategies for erosion control include the use of cover crops, contour farming, and the establishment of buffer zones, which have proven effective in reducing erosion effects. The Afrisoils program's objective to improve soil productivity aligns with these sustainable practices, particularly through erosion control initiatives, emphasizing the importance of environmental stewardship. By prioritizing these strategies, project managers can significantly contribute to ecosystem health and implement erosion control measures to enhance the sustainability of their infrastructure. This proactive approach not only addresses immediate concerns but also fosters long-term resilience against the adverse effects of deterioration, ensuring that services are tailored to meet client needs.
Collaboration and Stakeholder Engagement: Keys to Successful Erosion Control
Effective management of soil degradation hinges on the collaboration of diverse stakeholders, each playing a vital role in the success of initiatives. Key participants include:
- Project Managers: Charged with implementing erosion control measures and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, their role is essential for both adherence and effectiveness.
- Environmental Consultants: These specialists offer critical insights into best practices and regulatory requirements, guiding initiatives toward sustainable solutions.
- Local Authorities: They enforce regulations and provide invaluable advice on soil management techniques, aligning local policies with overarching objectives.
- Community Members: Their involvement is crucial; local perspectives can highlight specific issues and foster acceptance of conservation strategies, ultimately leading to more successful outcomes.
Engaging stakeholders from the beginning of the planning process is vital for promoting collaboration and ensuring that erosion control for sustainable projects is both effective and broadly supported. Regular communication and feedback mechanisms not only improve results but also cultivate trust among all parties involved.
Statistics reveal that effective stakeholder engagement can significantly boost success rates. A recent initiative illustrated this, with over 1,500 practitioners attending open field days, underscoring the importance of collaborative efforts in environmental activities. This level of engagement not only showcases the advantages of stakeholder involvement but also reinforces the necessity for ongoing collaboration.
Moreover, as Kevin Z. Mganga, Associate Editor of Ecological Solutions and Evidence, remarked, "This scoping project demonstrated that combining pasture management, improved agricultural practices, and rainwater harvesting and retention has great potential to support sustainable livestock production in the arid and semi-arid drylands." This statement underscores the significance of integrating diverse methods and knowledge systems to achieve effective soil preservation.
Additionally, case studies, such as 'Incorporating Traditional Knowledge in Agricultural Research,' exemplify the practical application of blending traditional knowledge with strategies for addressing soil degradation. By sharing insights on native pastures and traditional agricultural practices, initiatives can formulate comprehensive approaches that effectively tackle specific ecological challenges.
In conclusion, the importance of teamwork in soil management cannot be overstated. By recognizing and harnessing the unique contributions of each stakeholder, initiatives can realize sustainable outcomes through erosion control for projects that benefit both the environment and the communities they serve.
Case Studies: Successful Erosion Control in Action
The Green Roof Project represents a significant advancement in urban sustainability. A city has successfully launched a green roof initiative across public buildings, aimed at reducing runoff and soil degradation. By adding greenery on rooftops, this initiative not only minimizes soil degradation but also improves air quality and lowers urban heat. This dual benefit underscores the effectiveness of green roofs as a sustainable solution in urban environments, contributing to both ecological balance and improved living conditions. Notably, the GASEMT database includes 3,030 individual modeling records from 126 countries, providing a broader context for the effectiveness of erosion control for sustainable projects.
Streambank Restoration is another commendable initiative, driven by community efforts focused on restoring eroded stream banks through the use of native vegetation and bioengineering techniques. This initiative effectively stabilizes the banks, leading to improved water quality and the enhancement of local wildlife habitats. The integration of natural elements into the restoration process exemplifies a holistic approach to environmental management, showcasing the potential for community involvement in sustainable practices. The findings from this initiative provide a basis for integrated soil and water management efforts, environmental protection, and spatial planning.
In the realm of Construction Site Management, a construction firm has implemented rigorous erosion control measures, including silt fences and sediment basins, during a significant infrastructure undertaking. These proactive strategies minimize sediment runoff and ensure adherence to environmental regulations, culminating in a successful completion without incurring fines. This case illustrates the critical role of effective site management in maintaining environmental integrity while achieving objectives. Moreover, as verified by Jules Rutebuka, the introduction of bench terraces can greatly minimize earth loss, as shown in the Rwamagana district where earth loss decreased from 23.5 to 1.7 tons per hectare.
Together, these case studies emphasize the importance of strong measures, such as erosion control for sustainable projects, against deterioration and their positive effects on both the environment and the success of infrastructure projects. Moreover, the effective restoration of 2,970 hectares for natural forest regeneration and the building of infrastructure to manage flooding further highlight the wider influence of soil preservation efforts on environmental management. By adopting innovative practices such as green roofs and community-led restoration efforts, stakeholders can contribute to sustainable development while addressing pressing environmental challenges.
The application of the Erosion Potential Model (EPM) in various regions also provides a scientific basis for understanding soil degradation rates and spatial distribution, enhancing the credibility of the discussion on effective management.
Future Trends in Erosion Control: Preparing for Tomorrow's Challenges
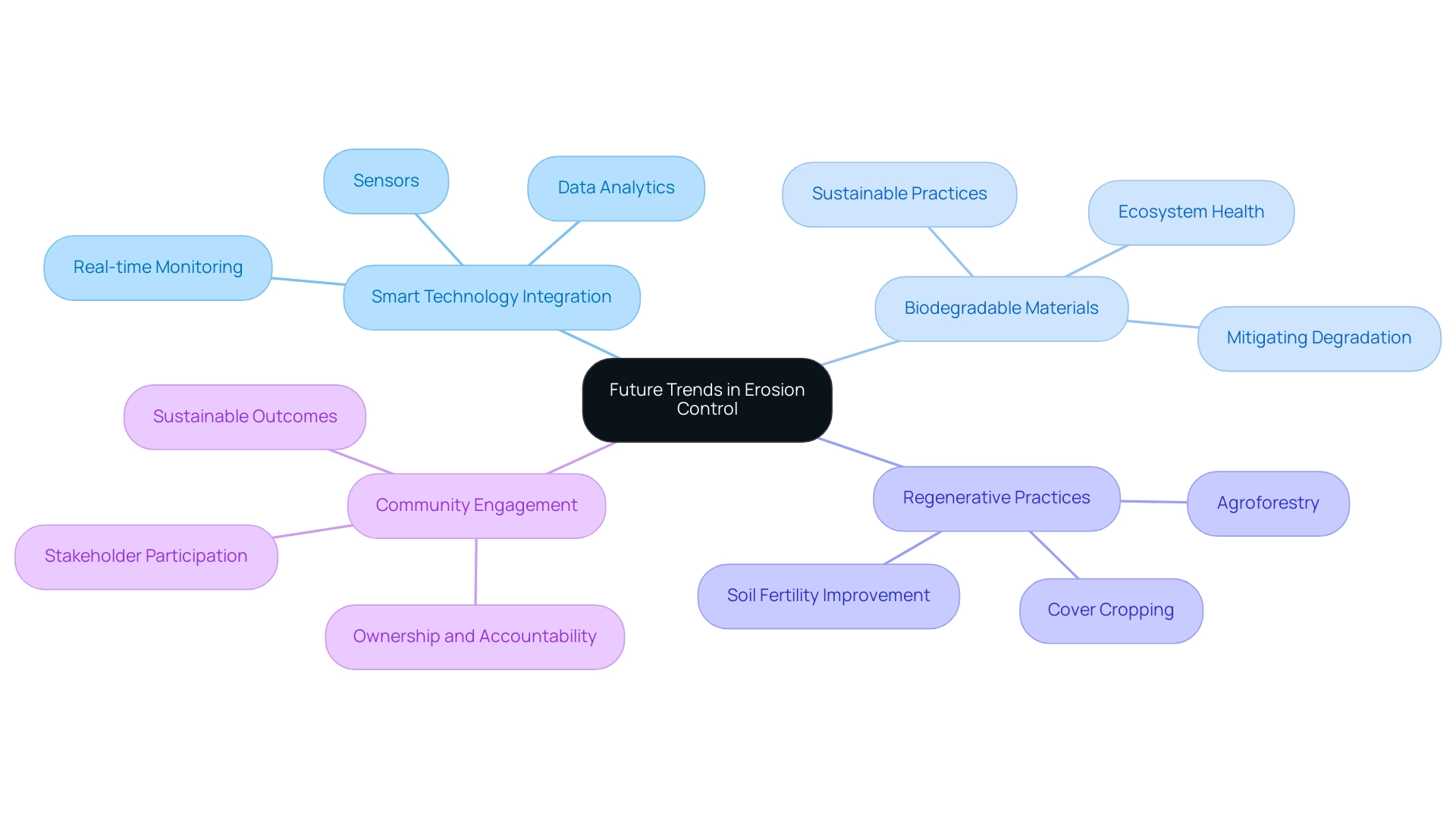
The landscape of soil management is undergoing rapid transformation, driven by several pivotal trends that will shape its future:
- Smart Technology Integration: The adoption of sensors and data analytics for real-time monitoring of soil degradation and sediment management is on the rise. This technology enables precise observation of degradation patterns, allowing for timely interventions that bolster the sustainability of initiatives. As highlighted by Akash Anand, Head of Business Development & Strategy, the integration of smart technology is vital for enhancing the efficiency of soil preservation strategies.
- Biodegradable Materials: Increasing attention is being directed towards sustainable, biodegradable materials in soil preservation practices. These materials not only reduce environmental impact but also foster healthier ecosystems by blending seamlessly into the natural landscape. Successful initiatives employing biodegradable materials have demonstrated their effectiveness in mitigating degradation while enhancing biodiversity.
- Regenerative Practices: Techniques aimed at revitalizing and improving land health, such as cover cropping and agroforestry, are gaining traction. These regenerative practices address soil degradation while simultaneously boosting soil fertility and biodiversity, thereby contributing to long-term sustainability.
- Community Engagement: There is a growing trend of incorporating community input and participation in degradation management planning and implementation. This approach fosters a sense of ownership and accountability among stakeholders, leading to more effective and sustainable outcomes.
In the broader context of construction trends, the annual building production rate in the European Union saw a modest increase of 0.1% in 2023 compared to 2022. This underscores the importance of adapting soil management practices to align with evolving industry demands. Staying informed about these trends is essential for professionals seeking to navigate future challenges in erosion control for sustainable projects. By leveraging smart technology and sustainable materials, they can enhance the effectiveness of their strategies and promote erosion control in the development of resilient infrastructure.
Conclusion
Erosion control is not merely beneficial; it is essential for sustainable development, with profound implications for both the environment and society. Effective strategies—such as vegetative cover, erosion control blankets, and hydroseeding—are crucial for mitigating soil erosion, enhancing infrastructure durability, and safeguarding ecosystems for future generations.
Compliance with regulatory frameworks, like the National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System, is imperative for successful erosion control. By adhering to these regulations, project managers fulfill legal obligations and contribute to broader environmental protection goals.
Collaboration among stakeholders—including project managers, environmental consultants, local governments, and community members—is vital for fostering innovative solutions. Engaging diverse perspectives not only enhances commitment to sustainable practices but also leads to more effective outcomes.
As the field evolves, embracing trends such as smart technology and biodegradable materials will be critical in addressing future challenges. These advancements can significantly enhance the effectiveness of erosion control measures, contributing to resilient infrastructure and healthier ecosystems.
In conclusion, the urgent need to address soil erosion through sustainable practices is unmistakable. By prioritizing effective erosion control strategies, stakeholders can combat environmental degradation and promote a resilient future for all. The time to act is now; collective efforts toward responsible development will yield lasting benefits for both people and the planet.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is erosion control important for sustainable projects?
Erosion control is critical in preventing soil degradation caused by wind, water, and human actions, which can lead to environmental decline, loss of fertile land, increased water pollution, and destruction of habitats.
What are the economic implications of soil degradation?
The economic cost of soil degradation in the European Union is estimated to reach tens of billions of euros annually, highlighting the urgent need for effective soil management.
How can erosion control measures benefit infrastructure projects?
Implementing robust erosion control measures not only protects the environment but also enhances the longevity and effectiveness of infrastructure initiatives.
Can you provide an example of effective erosion control through legislation?
Paraguay's Zero Deforestation Law, enacted in 2004, led to an 85% reduction in deforestation rates, demonstrating how legislative measures can effectively combat environmental degradation.
What role do managers play in erosion control?
Managers must understand erosion control to adopt best practices that reduce erosion and promote ecological balance, ensuring development projects are both economically viable and environmentally responsible.
How does climate change relate to soil preservation efforts?
Recent findings indicate complex relationships between climate change and human actions on soil preservation, particularly in China, which informs future studies and targeted approaches to managing soil degradation.
What are some effective techniques for erosion control?
Effective techniques include: 1. Vegetative Cover: Utilizing diverse plants to stabilize soil and enhance its structure. 2. Erosion Control Blankets: Protecting the ground while promoting vegetation growth. 3. Silt Fences: Trapping sediment to prevent waterway contamination. 4. Mulching: Retaining moisture and suppressing weed growth. 5. Terracing: Reducing water runoff on inclined landscapes. 6. Riprap: Using large stones to protect shorelines from water damage. 7. Hydroseeding: Spraying a mixture of seeds, mulch, and water for rapid vegetation growth.
Why is it necessary to integrate erosion control methods into project planning?
Integrating these methods enhances erosion control, aligns with best practices in soil management, and addresses the ongoing issue of soil degradation, which continues to exceed allowable limits.
What historical case study emphasizes the importance of erosion control techniques?
The case study on the Lhasa River helps understand historical hydrological patterns and underscores the effectiveness of erosion control techniques in managing land degradation.
List of Sources
- Understanding Erosion Control: The Foundation of Sustainable Development
- What is Erosion? Effects of Soil Erosion and Land Degradation (https://worldwildlife.org/threats/soil-erosion-and-degradation)
- Soil conservation service underpins sustainable development goals (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2351989421005242)
- Key messages | Global Symposium on Soil Erosion | Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (https://fao.org/about/meetings/soil-erosion-symposium/key-messages/en)
- Monitoring soil erosion in support of achieving SDGs: A special focus on rainfall variation and farming systems vulnerability (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0341816223006288)
- Key Techniques and Strategies for Effective Erosion Control
- Trade‐off between vegetation type, soil erosion control and surface water in global semi‐arid regions: A meta‐analysis (https://besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/1365-2664.13597)
- Assessment of vegetation restoration impacts on soil erosion control services based on a biogeochemical model and RUSLE (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2214581824001782)
- Navigating Regulations: Compliance and Best Practices in Erosion Control
- Chapter 17.20 REGULATIONS FOR EROSION CONTROL (https://codepublishing.com/CA/Lakeport/html/Lakeport17/Lakeport1720.html)
- Chapter 4: Construction Details, Section 21: Erosion Control | Caltrans (https://dot.ca.gov/programs/construction/construction-manual/section-4-21-erosion-control)
- The Environmental Impact of Erosion: Why Sustainable Practices Matter
- Key messages | Global Symposium on Soil Erosion | Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (https://fao.org/about/meetings/soil-erosion-symposium/key-messages/en)
- Farmers Report Soil-Related Resource Concerns on About Half of Soybean, Wheat, Cotton, and Oat Fields | Economic Research Service (https://ers.usda.gov/amber-waves/2022/may/farmers-report-soil-related-resource-concerns-on-about-half-of-soybean-wheat-cotton-and-oat-fields)
- Soil Degradation (https://undrr.org/understanding-disaster-risk/terminology/hips/en0005)
- 95% of the Earth’s Land Set to Be Degraded by 2050 | Earth.Org (https://earth.org/95-of-the-earths-soil-on-course-to-be-degraded-by-2050)
- Collaboration and Stakeholder Engagement: Keys to Successful Erosion Control
- Multi‐stakeholder participation for successful implementation of applied research projects in Africa (https://besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/2688-8319.12252)
- Case Studies: Successful Erosion Control in Action
- Soil erosion modelling: A global review and statistical analysis (https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S004896972101562X)
- Erosion Control Success Stories and Challenges in the Context of Sustainable Landscape Management, Rwanda Experience (https://intechopen.com/chapters/75436)
- (PDF) Effects of Erosion Control Works: Case Study-Grdelica Gorge, the South Morava River (Serbia) (https://researchgate.net/publication/327075028_Effects_of_Erosion_Control_Works_Case_Study-Grdelica_Gorge_the_South_Morava_River_Serbia)
- Effects of Erosion Control Works: Case Study—Grdelica Gorge, the South Morava River (Serbia) (https://mdpi.com/2073-4441/10/8/1094)
- Future Trends in Erosion Control: Preparing for Tomorrow's Challenges
- Erosion & Sediment Control Market Report 2025, Trends & Insights (https://thebusinessresearchcompany.com/market-insights/erosion-and-sediment-control-market-overview-2025)
- Sustainable Erosion Control and Sediment Management Market Report (https://bccresearch.com/market-research/membrane-and-separation-technology/sustainable-erosion-control-sediment-management-market-report.html?srsltid=AfmBOoo_1Vuvalt1jhabzOcJpSgBYH1SugDLsCYVKNEuhHzdtx_UBr0U)
- Erosion and Sediment Control Market Projected to Reach USD 5.9 Billion by 2032 | Rising Infrastructure Development and Environmental Regulations Drive Market Growth (https://globenewswire.com/news-release/2025/01/13/3008479/0/en/Erosion-and-Sediment-Control-Market-Projected-to-Reach-USD-5-9-Billion-by-2032-Rising-Infrastructure-Development-and-Environmental-Regulations-Drive-Market-Growth.html)
- coreerosioncontrol.com (https://coreerosioncontrol.com/the-future-of-sediment-control-upcoming-trends-and-advancements)




