Introduction
The acquisition of mineral rights is a complex yet vital aspect of resource management, particularly in the context of rapidly evolving energy projects, such as solar initiatives. As global investments surge, exemplified by substantial expenditures in mining, understanding the nuances of mineral rights becomes increasingly critical for stakeholders.
This article delves into the various types of mineral rights, the step-by-step process for acquiring them, and the legal and regulatory frameworks that govern these transactions. By exploring the importance of relationship-building with landowners and regulatory bodies, as well as assessing the value of mineral rights, readers will gain valuable insights into navigating this multifaceted landscape.
The discussion is further enriched by recent market trends and technological advancements that are reshaping the mineral rights acquisition process, making it essential for industry professionals to stay informed and strategically engaged.
Understanding Mineral Rights: Types and Initial Considerations
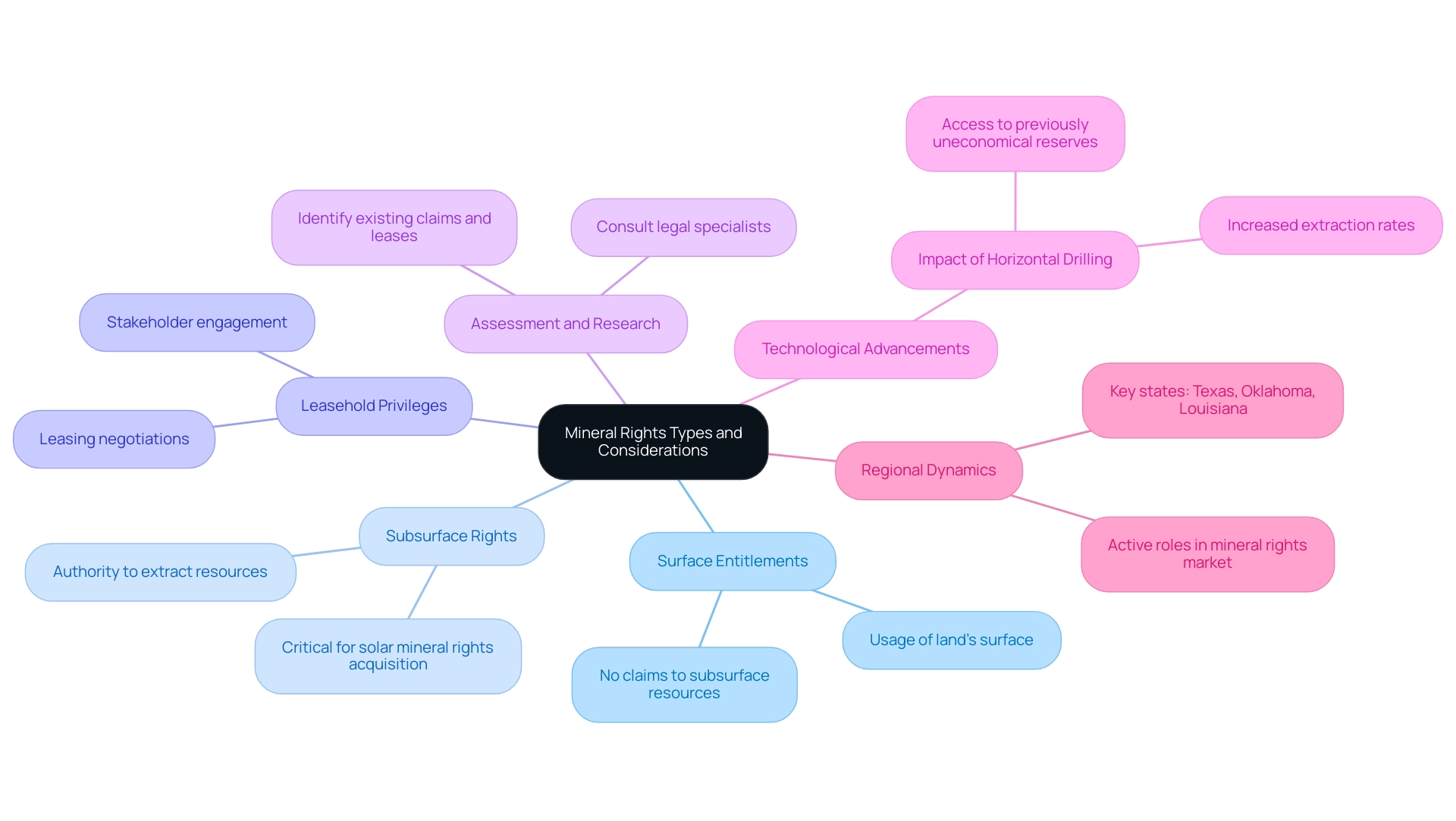
Subsurface extraction privileges, which encompass solar mineral rights acquisition, refer to the ownership entitlements to extract and use resources found beneath the surface of a property. Comprehending these entitlements is vital for effectively navigating the solar mineral rights acquisition process, especially in light of the rising investments in mining, as evidenced by China's unprecedented USD 10 billion expenditure on overseas mines in the first half of 2023. This statistic highlights the importance of solar mineral rights acquisition within the context of global investment trends.
Mineral entitlements can be classified into several key categories:
- Surface Entitlements: These privileges allow the owner to use the land’s surface for various activities, but they do not include any claims to the resources found beneath.
- Subsurface Rights: This category grants the owner the authority to extract resources from beneath the surface, a critical consideration for projects involving solar mineral rights acquisition, as the interaction between land use and resource extraction is significant.
- Leasehold Privileges: These privileges involve the leasing of resource entitlements from the owner, often requiring negotiations with various stakeholders, which can complicate the procurement process.
Before starting any procurement efforts, it is essential to conduct a thorough assessment of the specific resource entitlements tied to the land in question, including those related to solar mineral rights acquisition. This involves comprehensive research related to solar mineral rights acquisition to identify any existing claims, leases, or encumbrances that could affect your capacity to obtain and use these privileges. Interacting with legal specialists or land advisors can offer essential perspectives and direction on these preliminary factors, ensuring that you are sufficiently prepared to manage the intricacies involved in the resource ownership process.
Recent advancements in technology, such as horizontal drilling, have transformed the ability to access previously uneconomical reserves, making it imperative to stay informed about ownership trends and regulations as they evolve. Importantly, states such as Texas, Oklahoma, and Louisiana are key participants in the resource ownership market, further highlighting the necessity of grasping regional dynamics in the solar mineral rights acquisition process.
Step-by-Step Process for Acquiring Solar Mineral Rights
Acquiring solar mineral rights necessitates a systematic approach that encompasses several critical steps:
- Identify Potential Sellers: Start by investigating landowners who have the resource entitlements pertinent to your project. Utilize local land records, GIS mapping tools, and industry networking to identify potential sellers. An informed approach in this initial stage can streamline the acquisition process.
- Estimate Asset Value: Before entering into discussions, perform a thorough assessment of the resource ownership. Consider current market trends, the quality of the resources involved, and potential extraction costs. Significantly, in early 2024, the purchase of Cuprous Capital by MMG for US$3.6 billion highlights the substantial magnitude of resource transactions. Consulting a land appraiser or leveraging high-level valuation software can yield precise estimates that bolster your negotiation position.
- Negotiate Conditions: After identifying possible sellers and evaluating the worth of the resources, begin discussions. Be prepared to discuss various terms, including purchase price, payment structures, and any applicable contingencies. A clear understanding of your objectives and boundaries will facilitate a more effective negotiation process.
- Conduct Due Diligence: Before completing the purchase, engage in thorough due diligence. This involves reviewing title documents, evaluating any legal restrictions, and comprehending environmental regulations that may influence the resource utilization. Experts assert that due diligence is vital in mitigating risks related to the acquisition of solar mineral rights. As noted by OIG, "The BLM should conduct and support bond adequacy reviews and bond increases periodically and do so before problems arise," highlighting the importance of regulatory compliance.
- Finalize the Agreement: Upon reaching an agreement on all terms, draft a formal purchase agreement that specifies the details of the transaction. It is prudent to have legal counsel review this agreement to ensure adherence to both state and federal regulations.
- Secure Financing: If required, investigate various financing options to support the acquisition. This could include traditional loans, private investors, or grants that are customized for energy development initiatives.
By following these steps and taking into account the complexities demonstrated by the BLM's proposed clarification of lease suspensions, you will be well-positioned to successfully obtain renewable resource privileges, thereby advancing your energy project efficiently.
Navigating Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Meticulous compliance with various legal and regulatory standards is required for solar mineral rights acquisition. Consider the following key factors:
- Understand zoning laws: It is crucial to familiarize yourself with local zoning regulations prior to solar mineral rights acquisition. These regulations dictate permitted activities and impose restrictions on resource extraction, which can significantly impact your project.
- Obtain Necessary Permits: Depending on your jurisdiction, acquiring the appropriate permits for resource extraction or solar development is essential. Conduct thorough research to identify the specific permits required and the associated application processes.
- Environmental Regulations: Adherence to environmental laws regulating land use and resource extraction is essential. This includes adherence to the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) and state-specific regulations that may mandate environmental assessments or impact studies.
- Consult Legal Experts: Engaging legal professionals specializing in land use and resource management is highly beneficial. Their expertise can provide valuable insights into navigating the regulatory landscape, ensuring compliance with all legal requirements, and mitigating risks associated with non-compliance.
- Consider Regulatory Context: The Bureau of Land Management (BLM) is currently reducing nationwide bonds from 243 to approximately 143 statewide bonds, which reflects a shift in regulatory oversight. Understanding these changes is vital for effective planning and compliance.
- Importance of Compliance: As noted in Report No. OI-OG-12-0085-I, the OIG emphasizes that "The BLM should conduct and support bond adequacy reviews and bond increases periodically and do so before problems arise." This underscores the necessity of staying updated with compliance requirements.
- Real-World Application: Leases can be consolidated upon written request, identifying each lease and justifying the consolidation, with a processing fee required. This case study demonstrates the practical measures involved in managing legal obligations for resource ownership.
By diligently understanding and navigating these legal and regulatory frameworks, you can facilitate a smoother procurement process and effectively avert potential setbacks during the solar mineral rights acquisition for your project.
Assessing the Value of Mineral Rights
Evaluating the worth of resource entitlements requires a multifaceted approach, considering various essential factors:
-
Staying informed about current market trends in solar mineral rights acquisition is essential. Recent sales data and the demand for particular resources can serve as a valuable baseline for valuation. For instance, the Australian government's emphasis on 'digital certification' highlights a growing global demand for resources, which simplifies processes and lowers costs, thereby impacting market dynamics significantly. Furthermore, with Arizona Public Service (APS) serving approximately 1.4 million customers, the demand for resources in the region is likely impacted by the energy requirements of such a significant customer base.
- Quality of Resources: The intrinsic quality and quantity of the resources in question are paramount. Generally, higher-quality and more abundant resources tend to command greater prices in the market.
-
Potential for Development: Evaluate the development potential, which includes factors such as proximity to infrastructure, accessibility, and existing environmental conditions. These elements can greatly influence the overall value of resource rights.
-
Valuation Methods: Various established methods can be employed to accurately value mineral rights, including:
- Comparable Sales: Examining recent transactions of similar mineral rights within the region provides a useful reference point.
- Income Approach: This method involves estimating the potential income generated from mineral extraction, providing insight into future earnings.
- Cost Approach: This involves calculating the costs associated with extraction and development, which can help determine a fair market price.
Utilizing these assessment techniques enables you to derive a fair value for mineral rights, equipping you to negotiate effectively during the acquisition process. As the mining industry encounters financial difficulties, indicated by a reported drop in 2023 revenues to US$845 billion and net earnings at US$90 billion amid increasing expenses and decreasing commodity prices, grasping these dynamics is essential for making informed choices in resource ownership. Furthermore, leveraging advanced geospatial tools can assist in finding and filtering RFPs, optimizing project siting and enhancing the acquisition strategy.
Building Relationships with Stakeholders
Establishing connections with stakeholders is crucial for the solar mineral rights acquisition. Here are key strategies to consider:
- Engage with Landowners: Initiating open and honest communication with landowners is vital for understanding their concerns and objectives. Building trust fosters a more favorable negotiation environment, which is crucial for successful agreements.
- Collaborate with Regulatory Bodies: Establishing connections with local regulatory agencies ensures you remain informed about the latest requirements and regulatory changes. This collaboration can facilitate smoother permitting processes and demonstrate your commitment to compliance.
- Involve the Community: Engaging with the local community is critical to addressing concerns regarding resource extraction and its potential impacts. Transparency and receptiveness to feedback can significantly bolster community support for your project. Initiatives such as Mineral-X at Stanford University are pioneering efforts to create resilient resource supply chains, highlighting the importance of community involvement in clean energy transitions.
- Network within the Industry: Attending industry events and joining professional organizations can help you expand your network. Establishing connections with other experts in the energy and infrastructure field can result in valuable collaborations and insights that improve your procurement efforts.
It's important to note that researchers have identified 22 barriers to smooth ROW procurement, emphasizing the need for effective communication strategies. Prioritizing relationship-building not only helps in navigating the complexities of solar mineral rights acquisition but also cultivates a supportive environment that contributes to the overall success of your solar projects. As Professor Eila Järvenpää from Aalto University has noted, "the expertise Professor Eila Järvenpää from Aalto University has been crucial along the research," highlighting that collaboration and expertise are crucial in overcoming barriers to effective communication and operational success.
Additionally, the case study on Responsible Sourcing illustrates how suppliers must comply with relevant laws and industry regulations, aligning with the company's business code of ethics, which can serve as a model for stakeholder engagement in your projects.
Conclusion
Acquiring mineral rights is a multifaceted endeavor that requires a deep understanding of various types of rights, a systematic acquisition process, and a thorough grasp of the legal and regulatory landscape. The classification of mineral rights into surface, subsurface, and leasehold rights emphasizes the importance of a clear strategy tailored to specific projects, particularly in the context of renewable energy initiatives like solar power.
The step-by-step process for acquiring solar mineral rights highlights the necessity of:
- Identifying potential sellers
- Estimating asset values
- Negotiating favorable terms
- Conducting due diligence
Each of these stages is critical in ensuring a successful acquisition that aligns with both market demands and regulatory requirements. Furthermore, compliance with zoning laws, obtaining necessary permits, and understanding environmental regulations are paramount to avoiding potential setbacks during project development.
Assessing the value of mineral rights involves:
- Analyzing market trends
- Evaluating the quality of minerals
- Considering development potential
Utilizing established valuation methods to inform decision-making is essential. Building strong relationships with stakeholders, including landowners, regulatory agencies, and the local community, fosters trust and collaboration, which are essential for navigating the complexities associated with mineral rights acquisition.
In conclusion, staying informed about evolving market dynamics and regulatory changes, while prioritizing relationship-building and strategic planning, will empower stakeholders to effectively navigate the mineral rights landscape. As global investments in energy projects continue to surge, a comprehensive understanding of mineral rights will be indispensable for success in this competitive field.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are subsurface extraction privileges?
Subsurface extraction privileges refer to the ownership entitlements to extract and use resources found beneath the surface of a property, which are essential for navigating the solar mineral rights acquisition process.
Why is understanding mineral entitlements important?
Understanding mineral entitlements is vital due to the increasing investments in mining, such as China's significant expenditure on overseas mines, which underscores the importance of solar mineral rights acquisition in the context of global investment trends.
What are the key categories of mineral entitlements?
The key categories of mineral entitlements include: 1. Surface Entitlements: Allow the owner to use the land’s surface but do not include claims to subsurface resources. 2. Subsurface Rights: Grant the authority to extract resources from beneath the surface, relevant for solar mineral rights acquisition. 3. Leasehold Privileges: Involve leasing resource entitlements from the owner, often requiring negotiations.
What should be done before starting procurement efforts for solar mineral rights?
It is essential to conduct a thorough assessment of the specific resource entitlements tied to the land, including researching existing claims, leases, or encumbrances that could affect the acquisition process.
How can legal specialists assist in the solar mineral rights acquisition process?
Interacting with legal specialists or land advisors can provide essential insights and direction on the complexities involved in the resource ownership process, ensuring preparedness for management of these intricacies.
What recent advancements have impacted access to mineral resources?
Recent advancements in technology, such as horizontal drilling, have improved access to previously uneconomical reserves, making it crucial to stay informed about ownership trends and regulations.
Which states are key participants in the resource ownership market?
Texas, Oklahoma, and Louisiana are highlighted as key participants in the resource ownership market, emphasizing the need to understand regional dynamics in the solar mineral rights acquisition process.
What are the critical steps to acquiring solar mineral rights?
The critical steps to acquiring solar mineral rights include: 1. Identify Potential Sellers 2. Estimate Asset Value 3. Negotiate Conditions 4. Conduct Due Diligence 5. Finalize the Agreement 6. Secure Financing.
Why is due diligence important in the acquisition process?
Due diligence is vital for mitigating risks related to the acquisition of solar mineral rights, as it involves reviewing title documents, legal restrictions, and environmental regulations that may influence resource utilization.
What should be done after reaching an agreement on terms?
After reaching an agreement, a formal purchase agreement should be drafted, specifying transaction details, and it is advisable to have legal counsel review it to ensure compliance with state and federal regulations.
List of Sources
- Understanding Mineral Rights: Types and Initial Considerations
- Executive summary – Global Critical Minerals Outlook 2024 – Analysis - IEA (https://iea.org/reports/global-critical-minerals-outlook-2024/executive-summary)
- Unearthing Value: The States Dominating in Mineral Rights | DW Energy Group (https://dwenergygroup.com/unearthing-value-the-states-dominating-in-mineral-rights)
- Step-by-Step Process for Acquiring Solar Mineral Rights
- Mine 2024: Preparing for impact (https://pwc.com/gx/en/industries/energy-utilities-resources/publications/mine.html)
- Fluid Mineral Leases and Leasing Process (https://federalregister.gov/documents/2024/04/23/2024-08138/fluid-mineral-leases-and-leasing-process)
- Navigating Legal and Regulatory Requirements
- Fluid Mineral Leases and Leasing Process (https://federalregister.gov/documents/2024/04/23/2024-08138/fluid-mineral-leases-and-leasing-process)
- Assessing the Value of Mineral Rights
- Mineral and Royalty Outlook: 2024 and Beyond | Enverus (https://enverus.com/blog/mineral-and-royalty-outlook-2024-and-beyond)
- Mineral Market Report 2024 - Mineral Industry Size And Analysis (https://thebusinessresearchcompany.com/report/mineral-global-market-report)
- Mine 2024: Preparing for impact (https://pwc.com/gx/en/industries/energy-utilities-resources/publications/mine.html)
- Building Relationships with Stakeholders
- blog.harbingerland.com (https://blog.harbingerland.com/how-to-navigate-oil-and-gas-right-of-way-acquisition-a-step-by-step-guide)
- (PDF) Stakeholder engagement of mineral exploration companies in Finland (https://researchgate.net/publication/287199881_Stakeholder_engagement_of_mineral_exploration_companies_in_Finland)
- Key Strategies in Oil and Gas Land Acquisition: An In-depth Analysis (https://blog.harbingerland.com/key-strategies-in-oil-and-gas-land-acquisition-an-in-depth-analysis)
- Integrated stakeholder engagement - 2022 | AngloGold Ashanti (https://reports.anglogoldashanti.com/22/ir/world-in-which-we-operate/integrated-stakeholder-engagement)




